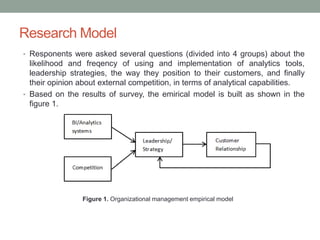
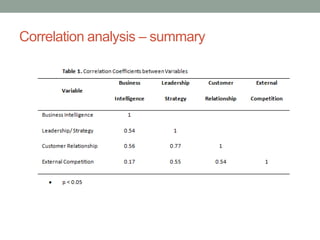
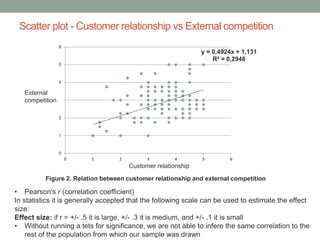
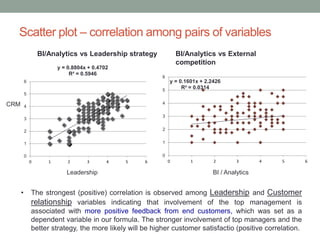
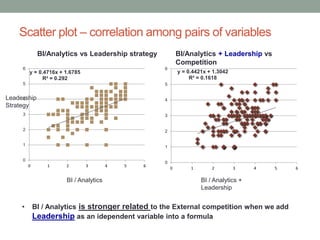
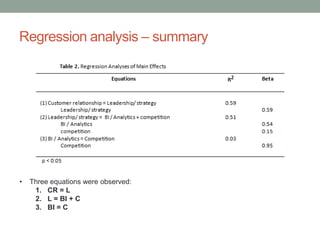
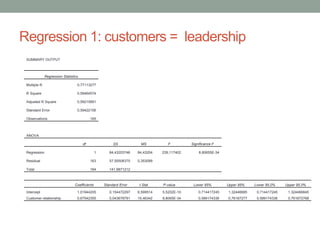
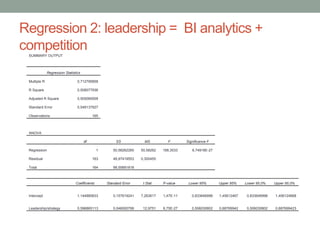
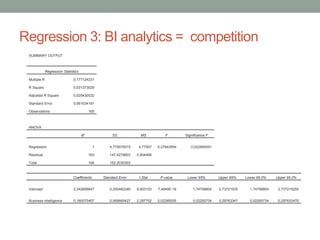
The document analyzes data from a survey of 165 managers in Bosnian organizations to identify relationships between variables related to business intelligence/analytics, leadership strategies, customer relationships, and external competition. Correlation analysis found the strongest relationship was between leadership strategies and customer satisfaction. Regression analysis showed customer satisfaction can be predicted by leadership, leadership can be predicted by business intelligence and competition, and business intelligence is weakly related to competition alone but more strongly related when including leadership. The findings indicate leadership and customer relationships are most closely linked, and leadership plays an important role in relationships between other variables.