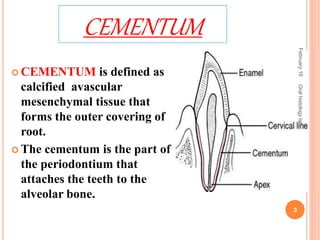
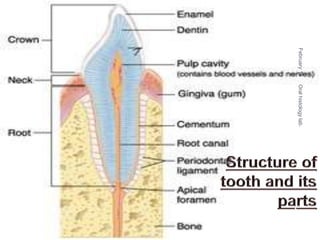
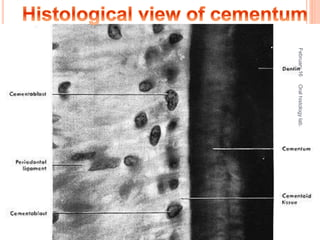
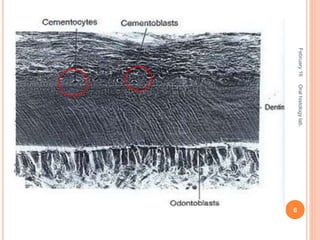
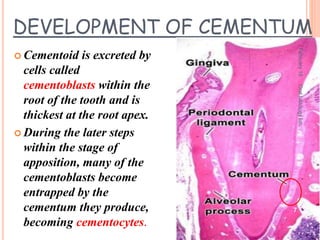
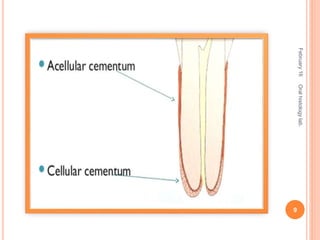
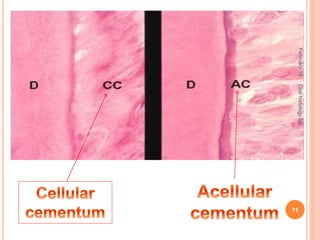
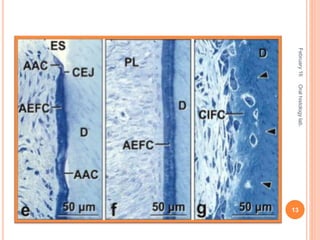
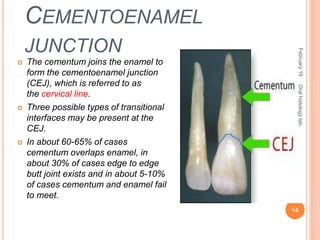
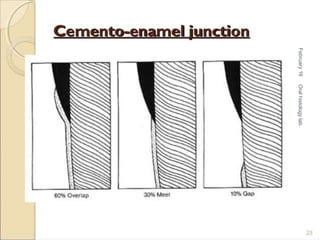
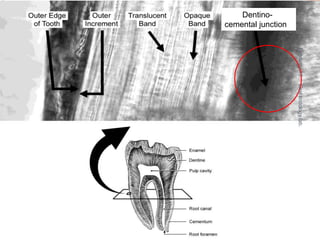
Cementum is the calcified avascular tissue that forms the outer covering of the root and attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone. There are two types of cementum - acellular/primary cementum which is the first formed and does not contain cells, covering the cervical third of the root. Cellular/secondary cementum forms after the tooth reaches occlusion, is more irregular and contains cells. Cementum develops through the excretion of cementoid by cementoblasts and the entrapment of some cementoblasts which become cementocytes. It joins enamel at the cementoenamel junction in various forms and dentin at the dentinocemental junction.