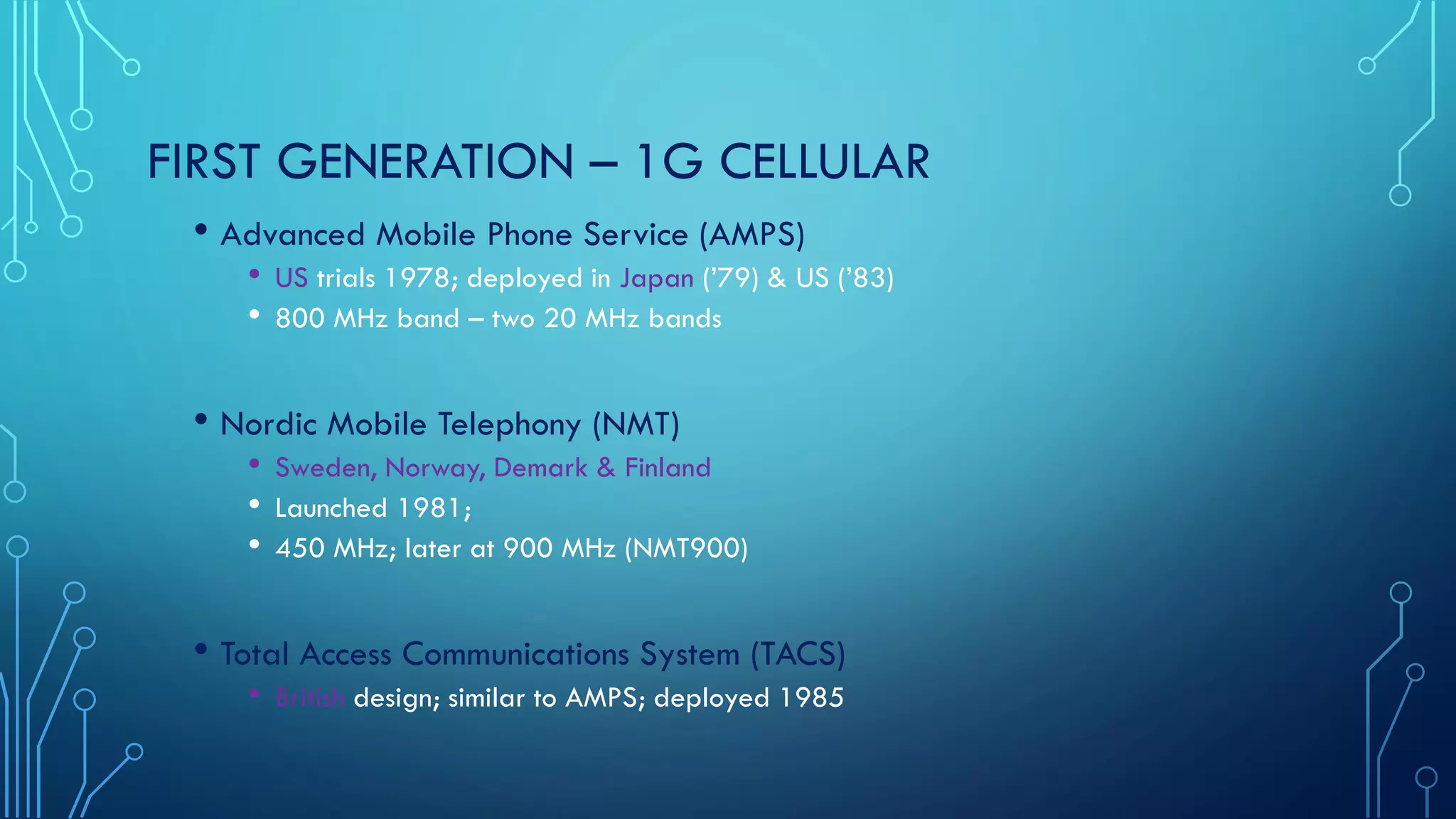
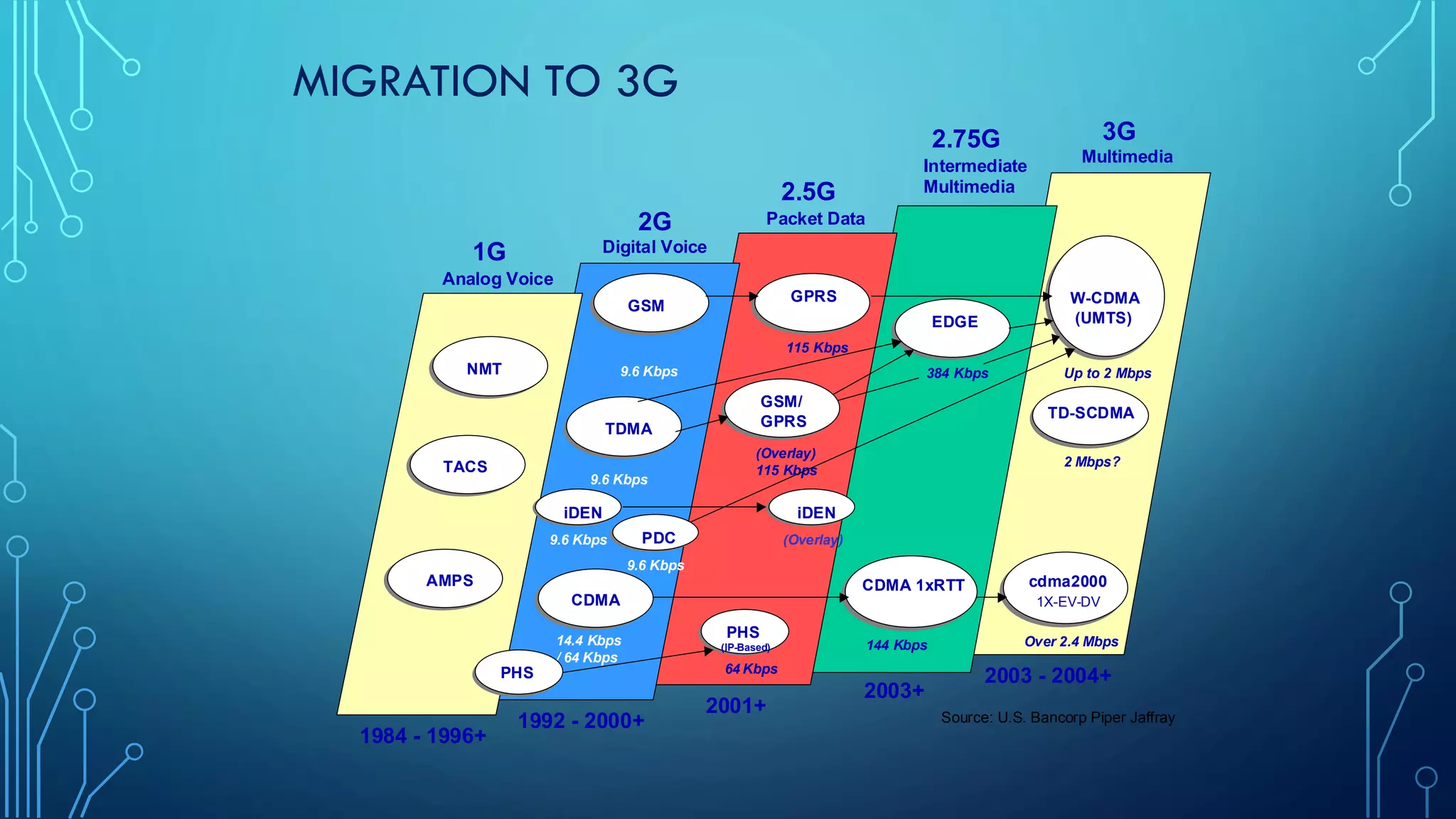
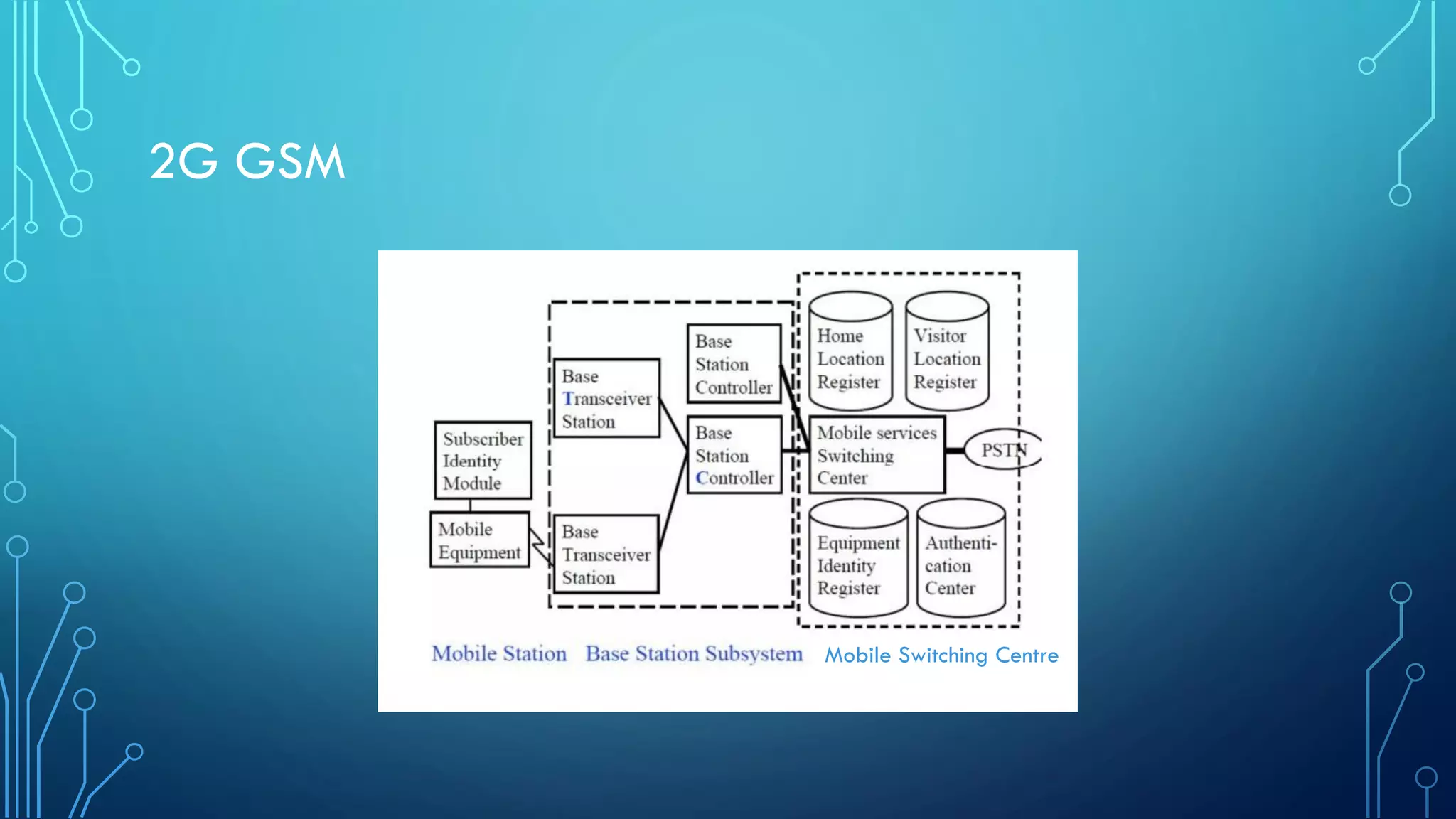
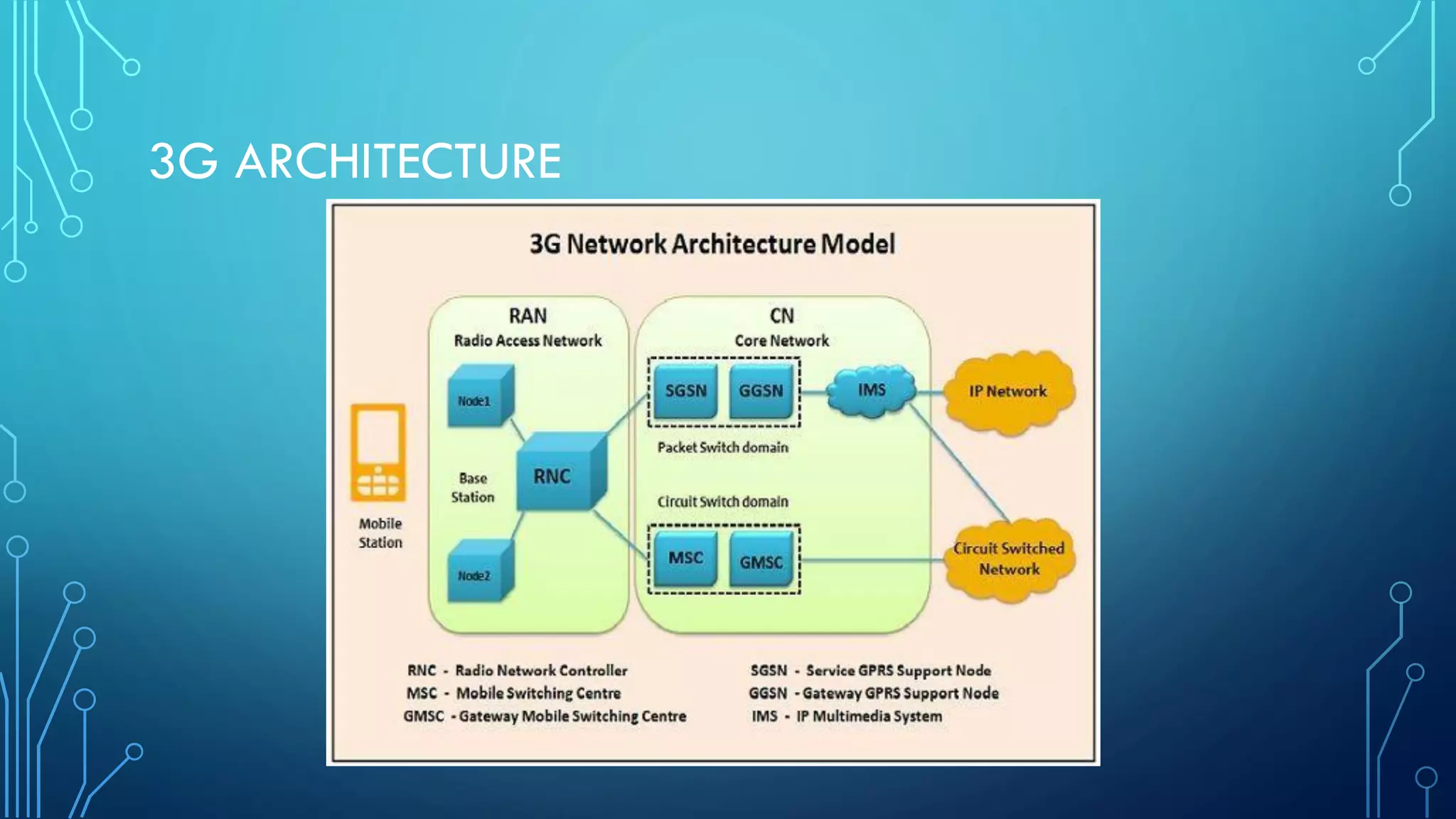
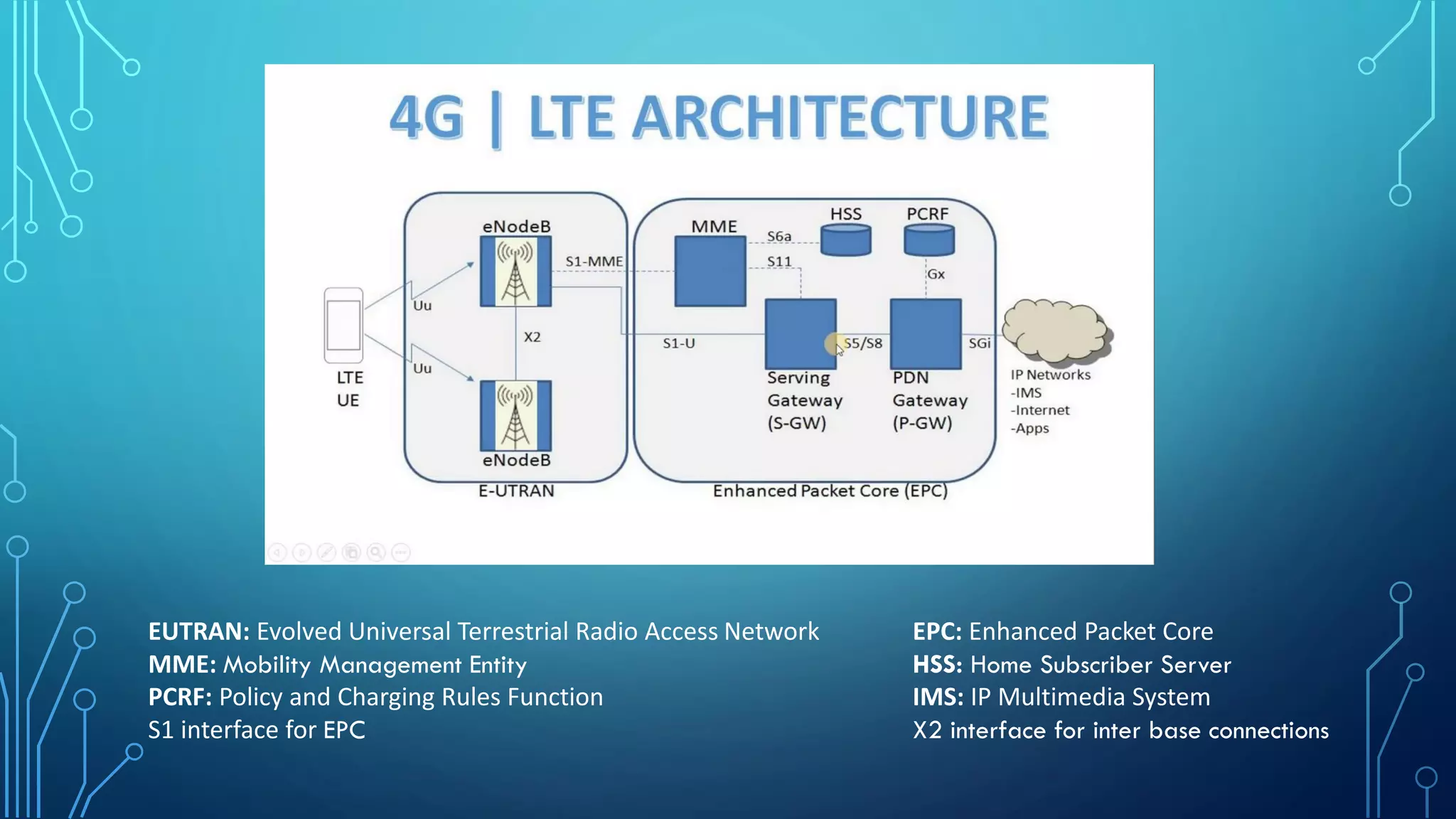
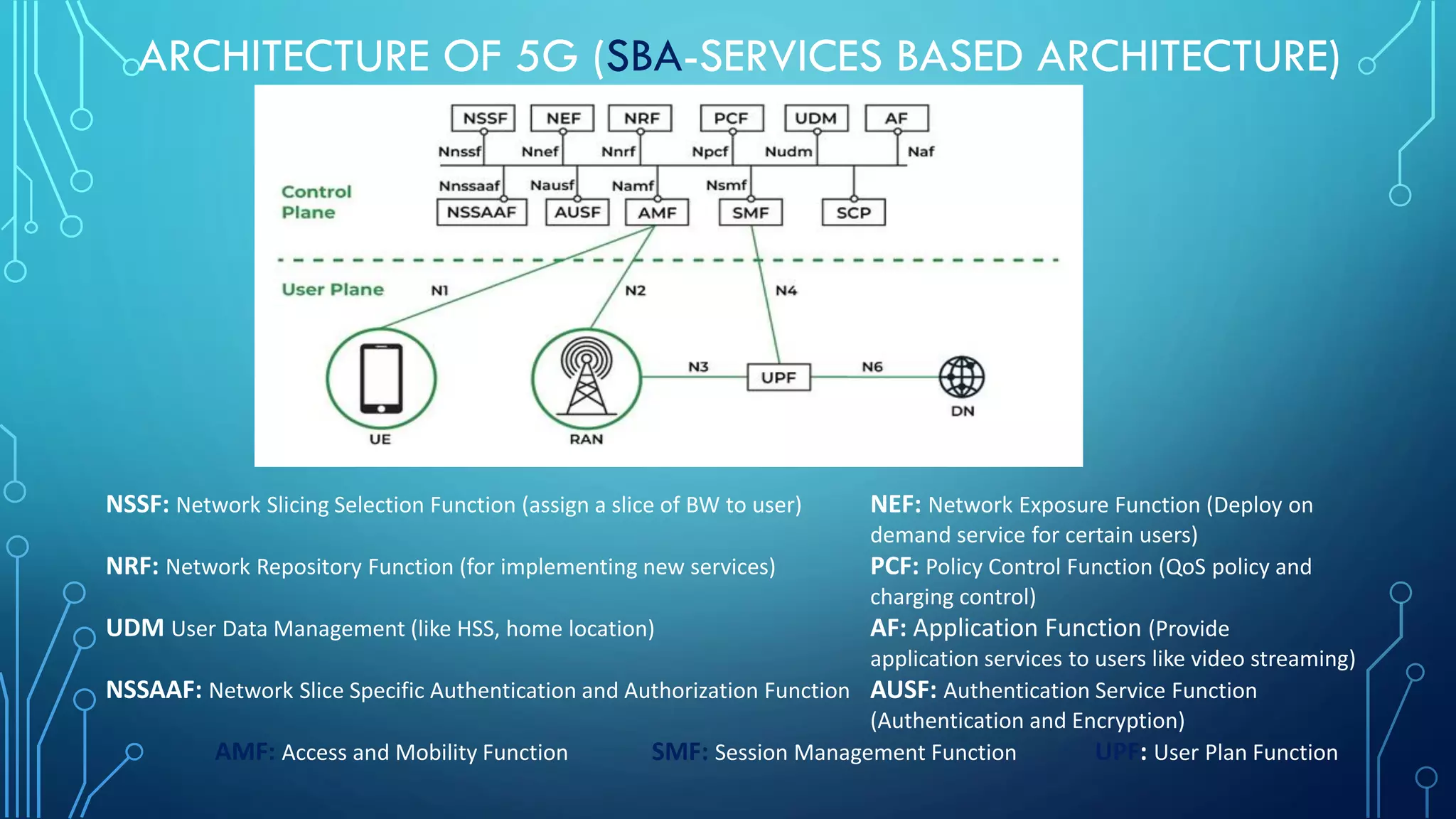
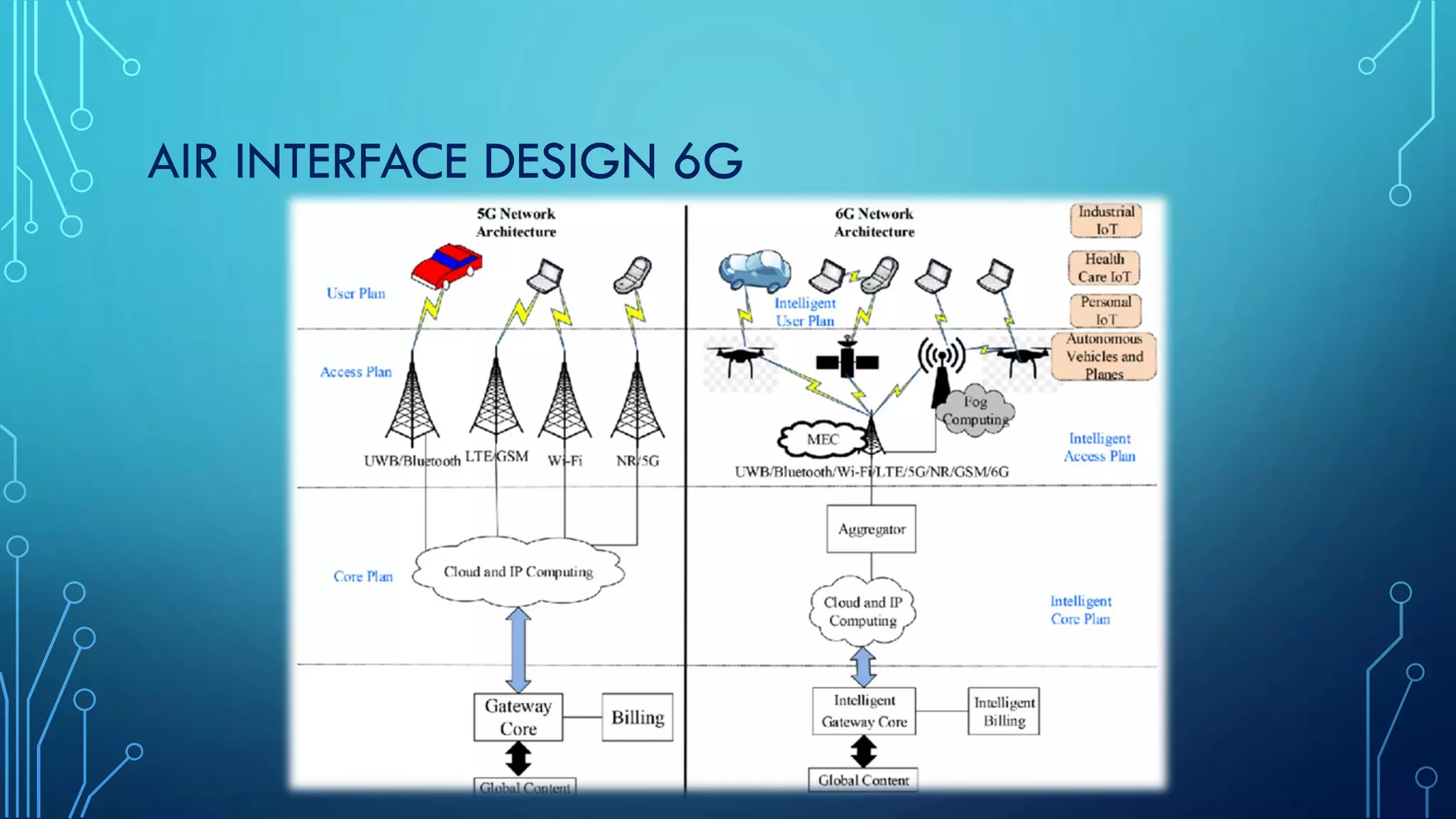
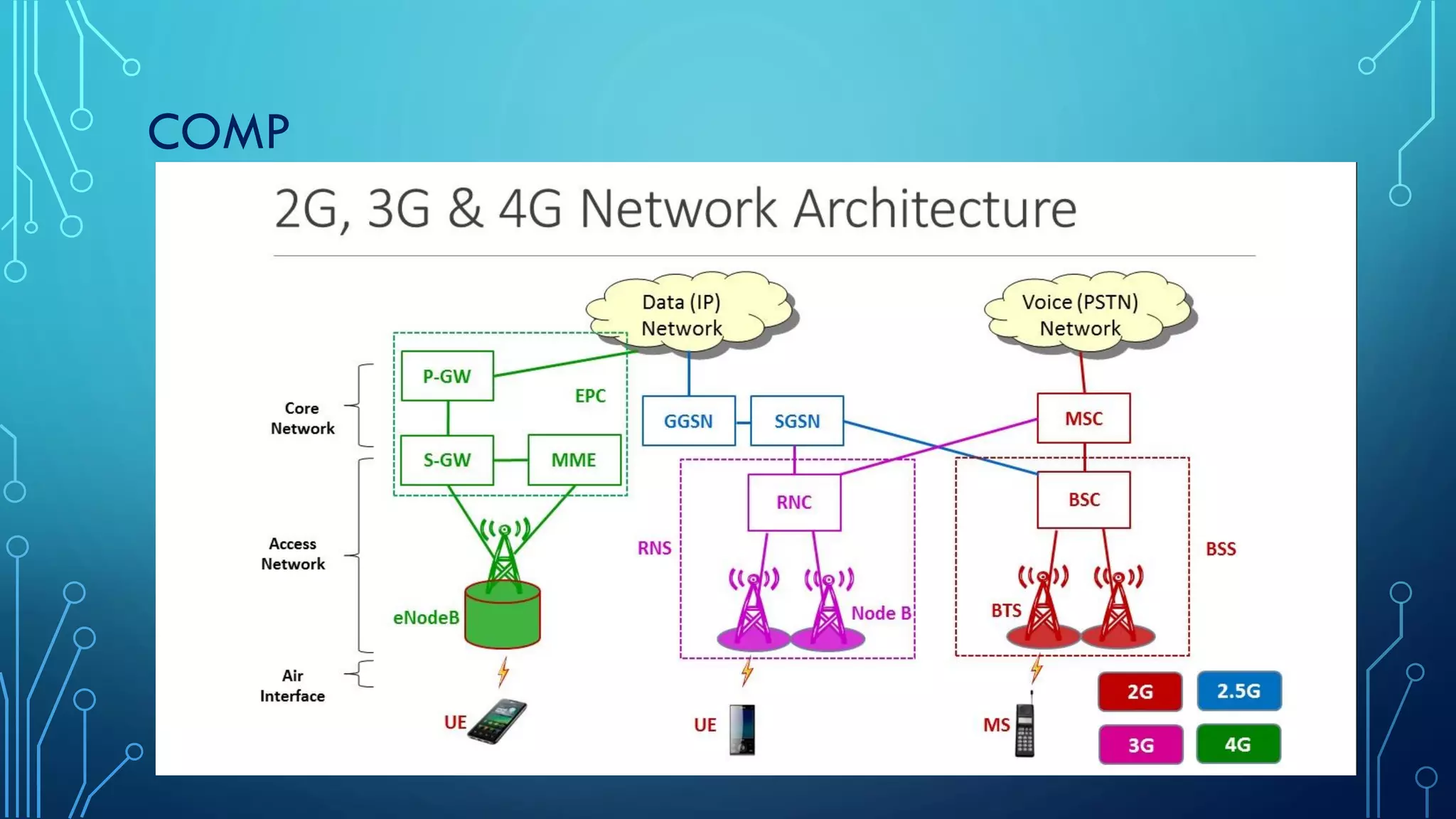
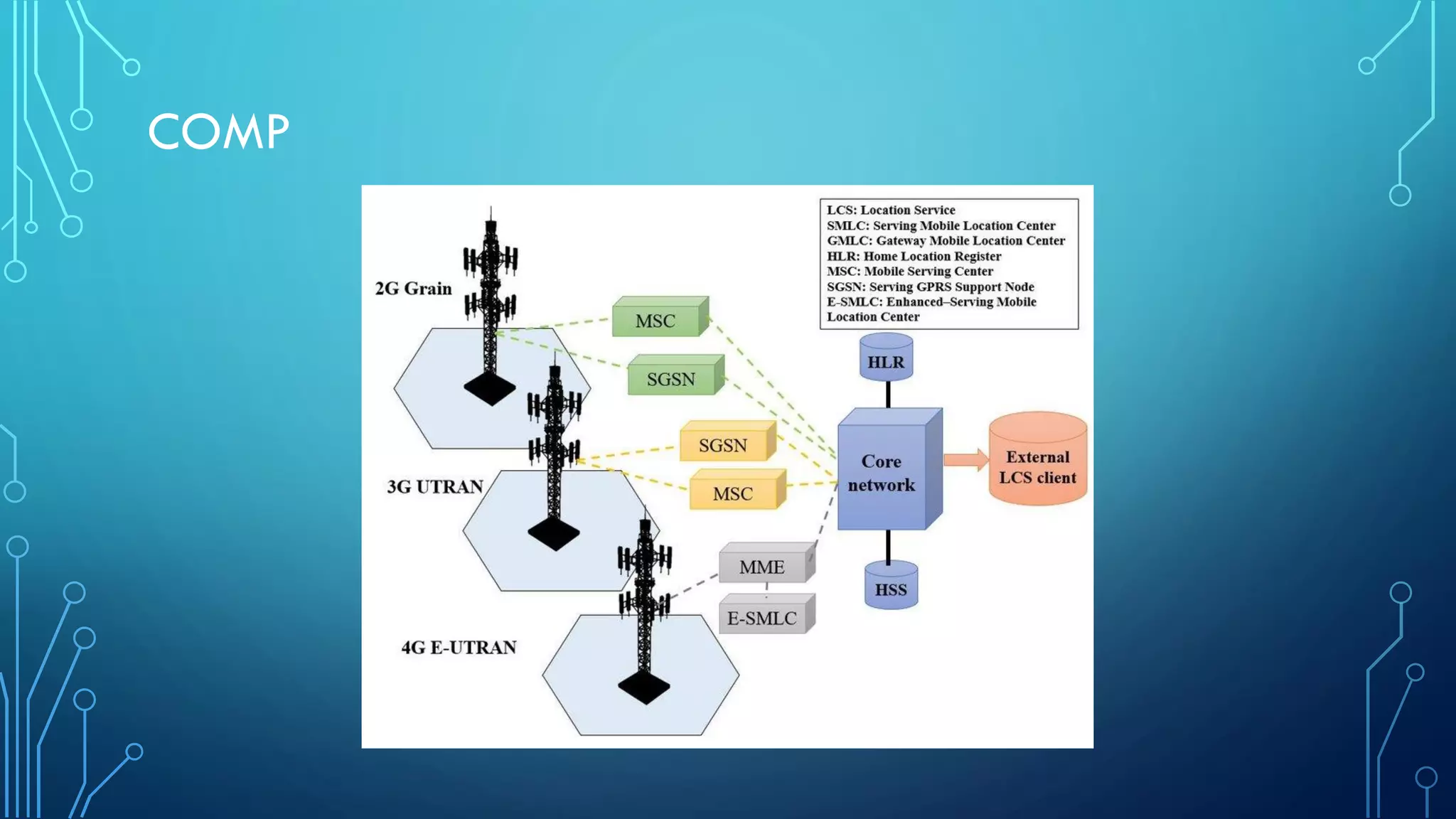
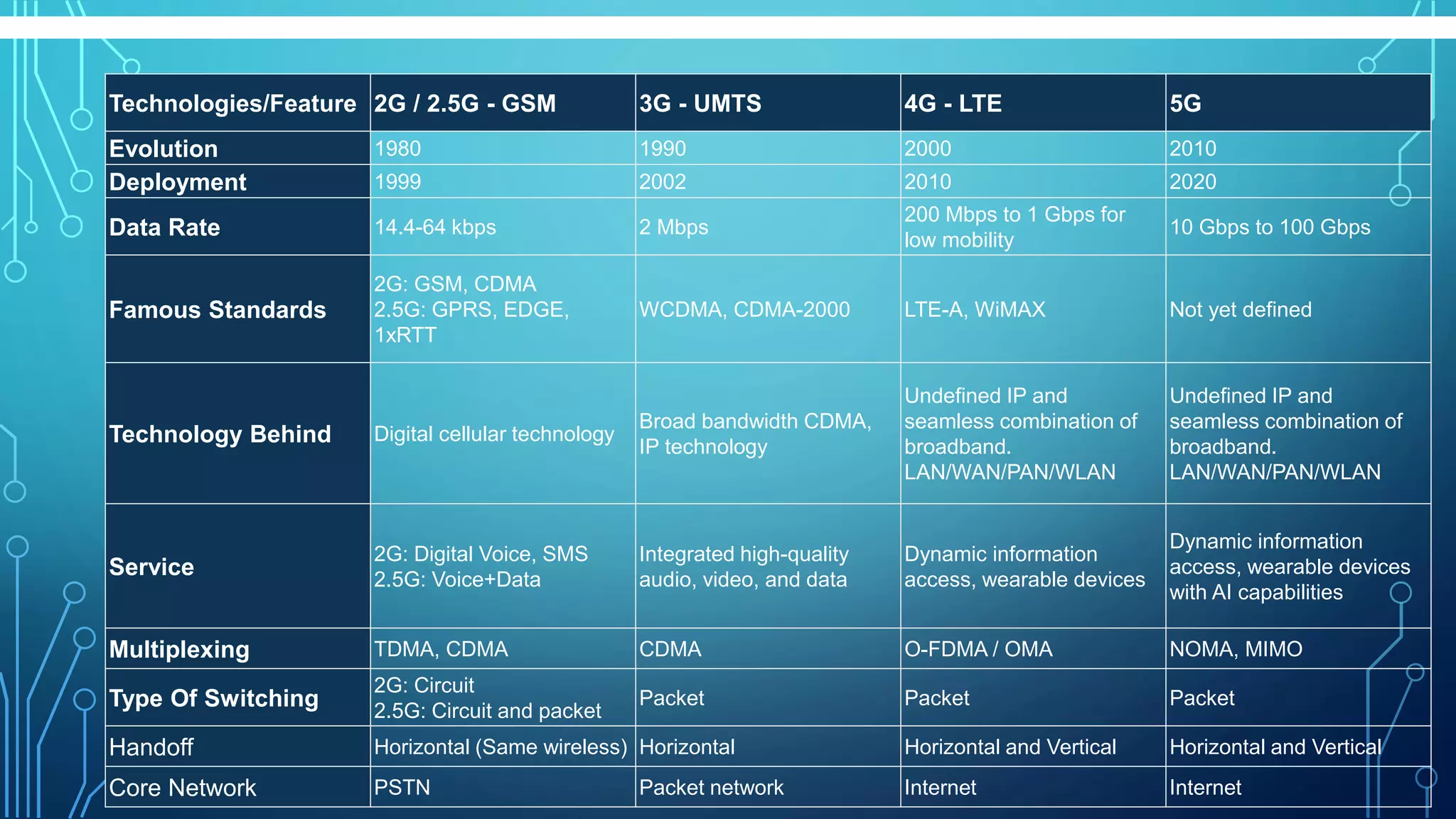
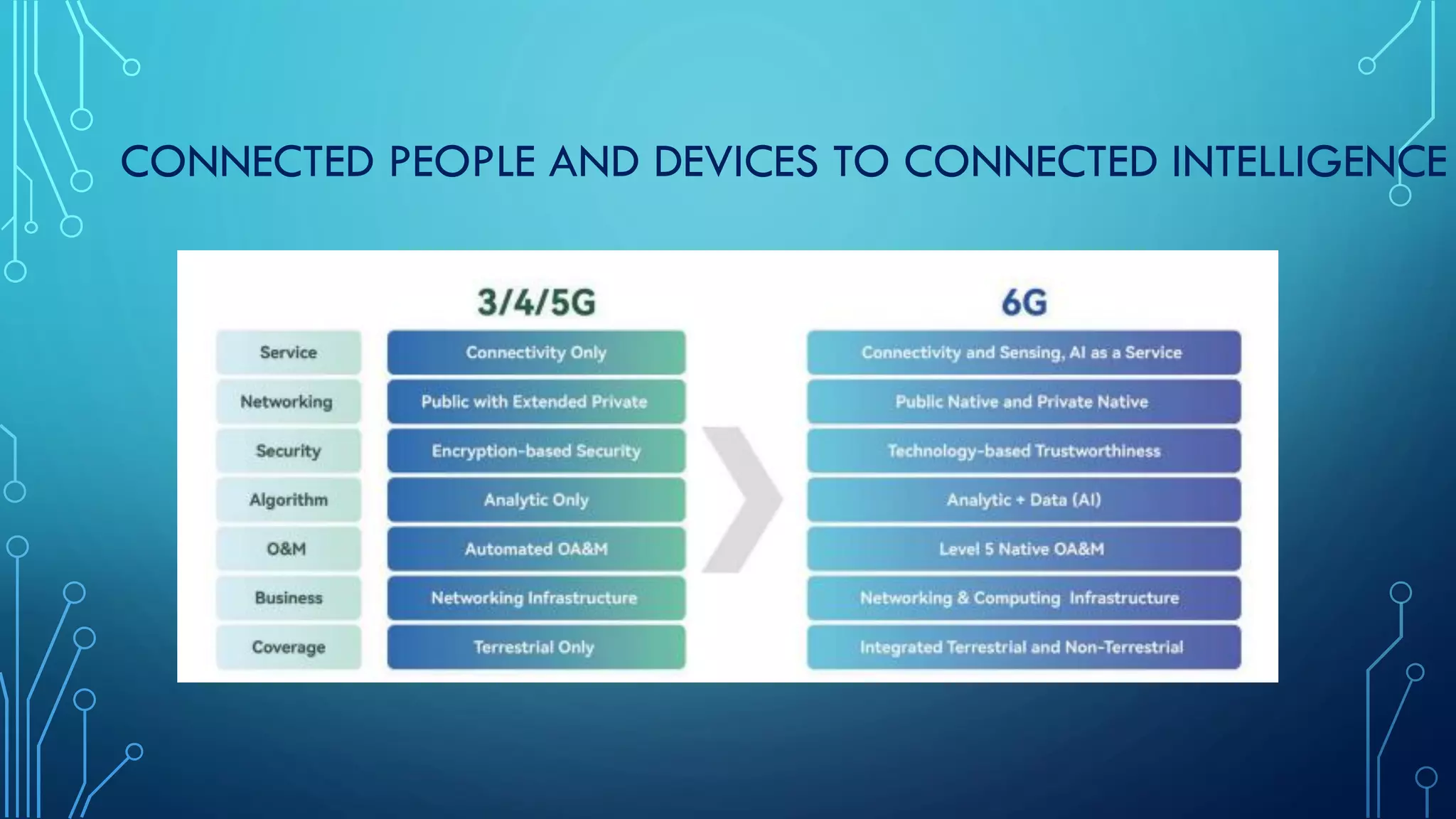
This document summarizes the evolution of mobile generations from 1G to 5G networks. It discusses the key technologies and standards for each generation including AMPS for 1G, GSM for 2G, UMTS for 3G, and LTE for 4G. For 5G, it mentions technologies like NOMA and MIMO but notes the standards are not yet defined. It also provides high-level diagrams of network architectures for 3G, 4G, and 5G, highlighting the transition to an all-IP infrastructure and the introduction of network slicing in 5G.