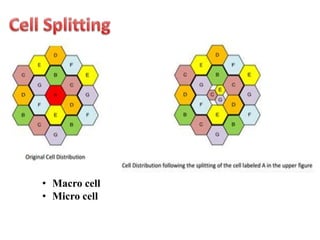
This document discusses key concepts in cellular communication including cells and cell splitting, frequency bands and reuse, roaming and handoff. It provides a qualitative comparison of GSM and CDMA systems, explaining their operating frequencies, phone call security, encoding, roaming capabilities, signal quality, handoff processes, and power consumption. Diagrams illustrate a cellular network architecture and frequency reuse pattern using a cluster of 7 cells. Concepts like ARFCN, IMEI, SIM cards, and their functions are also defined.