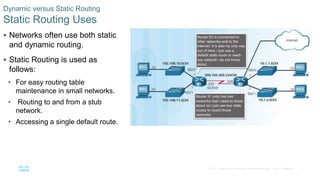
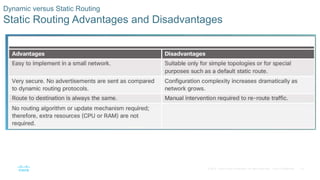
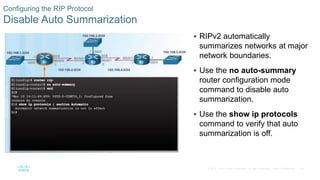
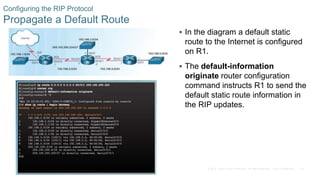
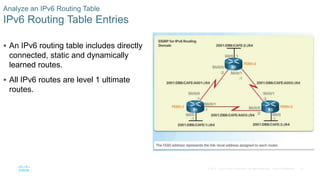
This document provides an overview of dynamic routing protocols and configuration of RIPv2. It discusses the purpose of dynamic routing protocols in discovering remote networks, maintaining up-to-date routing information, and choosing the best path. RIPv2 configuration topics include enabling RIP, advertising networks, verifying RIP operation, and propagating a default route. The document also examines the components of routing table entries, such as route source, metric, and next hop. It describes the hierarchy of dynamically learned routes including ultimate, level 1, parent and child routes.