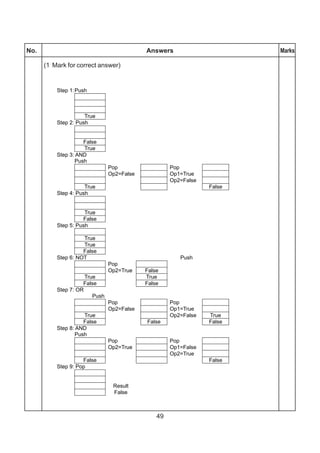
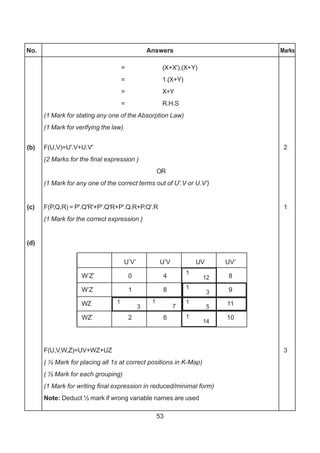
The document contains a computer science question paper with 7 questions covering topics like C++, data structures, SQL, computer networks and Boolean algebra. Some of the questions ask to write C++ code for classes, functions and algorithms. Others involve writing SQL queries on sample tables and analyzing network topologies to suggest appropriate designs. The overall document tests knowledge of key concepts in these domains through descriptive and coding questions.
![264
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language : C++
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) Nametheheaderfiletowhichthefollowingbelong 1
(i) abs( ) (ii) isupper( )
(b) Illustrate the use of #define in C++ to define a macro. 2
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerror(s),if
any.Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{ struct STUDENT
{ charstu_name[20];
charstu_sex;
intstu_age=17;
} student;
gets(stu_name);
gets(stu_sex);
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
class state
{ char*state_name;
intsize;
public:
state( ); { size=0; state_name=new char[size+1]; }
state(char *s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/75/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-1-2048.jpg)
![265
{ size = strlen(s) ; state_name = new char[size+1];
strcpy(state_name,s);
}
voiddisplay(){cout<<state_name<<endl;}
void Replace (state & a, state & b)
{ size = a.size + b.size;
deletestate_name;
state_name=newchar[size+l];
strcpy(state_name,a.state_name);
strcat(state_name,b.state_name);
}
};
voidmain()
{ char*temp=“Delhi”;
state state1 (temp), state2(“Mumbai”), state3(“Nagpur”), S1, S2;
S1.Replace(state1, state2);
S2. Replace(S1, state3);
S1.display();
S2.display();
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{ long NUM= 1234543;
int F=0, S=0;
do
{ int Rem = NUM% 10 ;
if (Rem % 2 !=0)
F+=R;
else
S+=R;
NUM /=10;
}while(NUM>0);
cout<<F-S;
}
(f) What are Nested Structures ? Give an example. 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-2-320.jpg)
![266
2. (a) DefineMultilevelandMultipleinheritanceincontextofObjectOrientedProgramming.
Givesuitableexampletoillustratethesame. 2
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingclass:
classInterview
{ intmonth;
public:
Interview(inty) {month=y;} //Constructor 1
Interview(Interview&t); //Constructor 2
};
(i) Create an object, such that it invokes Constructor 1 1
(ii) WritecompletedefinitionforConstructor2 1
(c) DefineaclassnamedADMISSIONinC++withthefollowingdescriptions: 4
Privatemembers:
AD_NO integer (Ranges 10 - 2000)
NAME Arrayofcharacters(String)
CLASS Character
FEES Float
PublicMembers:
• Function Read_Data( ) to read an object ofADMISSION type
• Function Display( ) to display the details of an object
• Function Draw-Nos( ) to choose 2 students randomly.
Anddisplaythedetails.Userandomfunctiontogenerateadmission
nos. to match withAD_NO.
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iii) based on the following code :
classstationary
{
charType;
charManufacturer[10];
public:
stationary();
void Read_sta_details( );
voidDisp_sta_details();
};
classoffice:publicstationary
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-3-320.jpg)
![267
intno_of_types;
floatcost_of_sta;
public:
voidRead_off_details();
voidDisp_off_details();
};
classprinter:privateoffice
{
intno_of_users;
char delivery _date [10];
public:
voidRead_pri_details();
voidDisp_pri_details();
};
voidmain()
{ printer MyPrinter; }
(i) Mention the member names which are accessible by MyPrinter declared in
main()function 1
(ii) What is the size of MyPrinter in bytes ? 1
(iii) Mention the names of functions accessible from the member function
Read_pri_details( ) of class printer. 2
3. (a) Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as
arguments/parameters and assign the elements into a two dimensional array of
integersinthefollowingformat
If the array is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 If the array is 1, 2, 3 3
Theresultant2Darrayisgiven The resultant2Darrayisgiven
below below
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3
1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 0
1 2 3 4 0 0 1 0 0
1 2 3 0 0 0
1 2 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-4-320.jpg)
![268
(b) An array MAT[30][10] is stored in the memory column wise with each
element occupying 8 bytes of memory. Find out the base address and the
address of element MAT[20][5], if the location of MAT[5][7] is stored at
the address 1000. 4
(c) classqueue 4
{ intdata[10];
intfront,rear;
public:
queue( ) {front = -1; rear=-1;}
voidadd(); // to add an element into the queue
voidremove(); // to remove an element from the queue
voidDelete(intITEM); //To deleteallelementswhichareequal
// to ITEM
};
CompletetheclasswithallfunctiondefinitionsforacirculararrayQueue.Use
another queue to transfer data temporarily
(d) WriteafunctioninC++toperformPushoperationonadynamicallyallocated
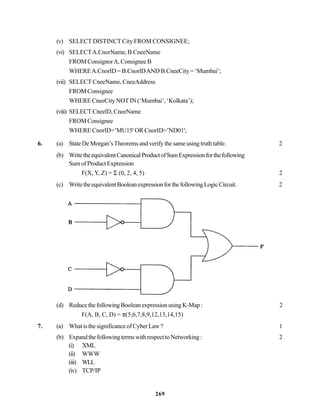
stackcontainingrealnumber. 3
(e) Writetheequivalentinfixexpressionfor
a, b, AND, a, c, AND, OR 2
4. (a) voidmain()
{ char ch='A';
fstreamfileout(“data.dat”,ios::out);
fileout<<ch;
intp=fileout.tellg();
cout<<p;
Whatistheoutputifthefilecontentbeforetheexecutionoftheprogramisthe
string “ABC” (Note that “ ” are not part of the file)
(b) Write a function to count the number of words present in a text file
named “PARA.TXT”. Assume that each word is separated by a single
blank/space character and no blanks/spaces in the beginning and end of
thefile. 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-5-320.jpg)
![269
(c) Following is the structure of each record in a data file named
“COLONY.DAT”. 3
struct COLONY
{ char Colony_Code[10];
charColony_Name[10];
intNo_of_People;
};
WriteafunctioninC++toupdatethefilewithanewvalueofNo_of_People.Thevalue
of Colony_Code and No_of_People are read during the execution of the program.
5. (a) What is anAlternate Key ? 2
(b) Study the following tables DOCTOR and SALARY and write SQL commands
for the questions (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (vi): 6
TABLE : DOCTOR
ID NAME DEPT SEX EXPERIENCE
101 John ENT M 12
104 Smith ORTHOPEDIC M 5
107 George CARDIOLOGY M 10
114 Lara SKIN F 3
109 K George MEDICINE F 9
105 Johnson ORTHOPEDIC M 10
117 Lucy ENT F 3
111 Bill MEDICINE F 12
130 Morphy ORTHOPEDIC M 15
TABLE : SALARY
ID BASIC ALLOWANCE CONSULTATION
101 12000 1000 300
104 23000 2300 500
107 32000 4000 500
114 12000 5200 100
109 42000 1700 200
105 18900 1690 300
130 21700 2600 300](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-6-320.jpg)
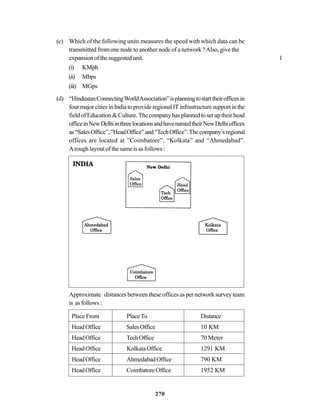
![271
Distancebetweenvariouswingsaregivenbelow
Wing A to Wing S 100 m
Wing A to Wing J 200 m
Wing A to Wing H 400 m
Wing S to Wing J 300 m
Wing S to Wing H 100 m
Wing J to Wing H 450 m
Number of Computers
Wing A 150
Wirig S 10
Wing J 5
Wing H 50
(i) SuggestasuitableTopologyfornetworkingthecomputerofallwings 1
(ii) Name the wing where the Server to be installed. Justify your answer, 1
(iii) SuggesttheplacementofHub/Switchinthenetwork. 1
(iv) Mention an economic technology to provide internet accessibility to all
wings. 1
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
1. (a) Nametheheaderfiletowhichthefollowingbelong: 1
(i) pow()
(ii) random()
(b) IllustratetheuseofinlinefunctioninC++withthehelpofanexample. 2
(c) Rewrite the followingprogram afterremovingthe syntactical error(s), ifany.
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include<idstream.h>
voidmain()
{ structmovie
{ charmovie_name[20];
charmovie_type;
int ticket_cost = 100;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-8-320.jpg)
![272
}MOVIE;
gets(movie_name);
gets(movie_type);
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
classstudent
{ char*name;
intl;
public:
student() { 1=0; name=new char[1+1]; }
student(char*s)
{ 1=strlen(s);name=newchar[1+1];
strcpy(name,s);
}
voiddisplay(){cout<<name<<endl;}
void manipulate(student & a, student & b)
{ 1=a.1 + b.1;
deletename;
name=newchar[l+l];
strcpy(name,a.name);
strcat(name,b.name);
}
};
voidmain()
{ char * temp =''Jack'';
student name1(temp), name2('' Jill''), name3('' John'' ),S1,S2;
S1.manipulate(name1,name2);
S2.manipulate(S1,name3);
S1.display();
S2.display();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-9-320.jpg)

![274
PublicMembers
• Function Read_Data() to read an object of HOUSING type
• FunctionDisplay()todisplaythedetailsofanobject
• Function Draw_Nos()to choose and display the details of 2 houses
selected randomly from an array of 10 objects of type HOUSING. Use
randomfunctiontogeneratetheregistrationnos.tomatchwithREG_NO
fromthearray.
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iii) based on the following code :
classfurniture
{
charType;
char Model[10];
public:
furniture();
voidRead_fur_details();
voidDisp_fur_details();
};
classsofa:publicfurniture
{
intno_of_seats;
floatcost_of_sofa;
public:
voidRead_sofa_details();
voidDisp_sofa_details();
};
classoffice:privatesofa
{
intno_of_pieces;
chardelivery_date[10];
public:
voidRead_office_details();
voidDisp_office_details();
};
voidmain()
{ officeMyFumiture; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-11-320.jpg)
![275
(i) MentionthemembernameswhichareaccessiblebyMyFumituredeclaredin
main()function. 1
(ii) WhatisthesizeofMyFumiture inbytes? 1
(iii) Mention the names of functions accessible from the member function
Read_office_details()ofclassoffice. 2
3. (a) Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/
parameters and assign the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the
followingformat: 3
If the array is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 If the array is 1, 2, 3
The resultant 2 D array is given below The resultant 2 D array is given below
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 2 0 0 0 0 1 2 0
1 2 3 0 0 0 1 2 3
1 2 3 4 0 0
1 2 3 4 5 0
1 2 3 4 5 6
(b) An array MAT[20][10] is stored in the memory along the row with each element
occupying 4 bytes of memory. Find out the base address and the address of element
MAT[10][5], if the location of MAT[3][7] is stored at the address 1000. 4
(c) Introduction class stack
{ int data[10];
int top;
public:
stack() {top=-l)
void push(); // to push an element into the stack
void pop(); // to pop an element from the stack
void Delete(int ITEM); // To delete all elements which are equal to ITEM
};
Complete the class with all function definitions. Use another stack to transfer data
temporarily. 4
(d) WriteafunctioninC++toperformInsertoperationindynamicallyallocatedQueue
containingnamesofstudents. 3
(e) Writetheequivalentinfixexpressionfor 2
10, 3, *, 7, 1, -, *, 23, +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-12-320.jpg)
![276
4. (a) voidmain()
{ char ch='A';
fstreamfileout(“data.dat”,ios::app);
fileout<<ch;
intp=fileout.tellg();
cout<<p;
}
Whatistheoutputifthefilecontentbeforetheexecutionoftheprogramisthestring?
“ABC” (Note that “”are not part of the file) 1
(b) Write a function to count the number of blanks present in a text file named
“PARA.TXT. 2
(c) Following is the structure of each record in a data file named PRODUCT.DAT”.
struct PRODUCT
{ char Product_Code[10];
charProduct_Description[10];
intStock;
};
Write a function in C++ to update the file with a new value of Stock. The Stock and
the Product_Code, whose Stock to be updated, are read during the execution of the
program. 3
5. (a) What are DDL and DML ? 2
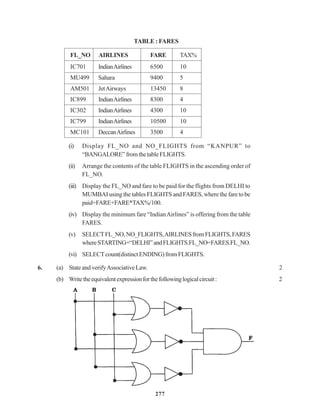
(b) Study the following tables FLIGHTS and FARES and write SQLcommands for the
questions (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (vi).
TABLE : FLIGHTS
FL_NO STARTING ENDING NO_FLIGHTS NO_STOPS
IC301 MUMBAI DELHI 8 0
IC799 BANGALORE DELHI 2 1
MC101 INDORE MUMBAI 3 0
IC302 DELHI MUMBAI 8 0
AM812 KANPUR BANGALORE 3 1
IC899 MUMBAI KOCHI 1 4
AM501 DELHI TRIVANDRUM 1 5
MU499 MUMBAI MADRAS 3 3
IC701 DELHI AHMEDABAD 4 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-13-320.jpg)

![279
Marking Scheme --- Computer Science
General Instruction :
1. Theanswersgiveninthemarkingschemearemerelysuggestive;
Examiners are requested to consider all alternative correct answers conveying the
similarmeaning.
2. Allprogrammingquestions-havetobeansweredwithrespecttoC++languageonly.
3. In SQL related questions - both ways text i.e. character entries should be acceptable.
(Forexample:‘Amar’or“Amar”)
4. InSQLrelatedquestions-ignoresemicolon / terminationforqueries.
5. In SQLrelated questions - ignore case sensitivity.
6. InC++questions—Ignorecasesensitivityforfunctionnamesandvariablenames.
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
EXPECTEDANSWERS/VALUEPOINTS
1. (a) (i) math.h (ii) ctype.h
( ½ Marks for each correct Header File)
(b) #defineisapreprocessordirectivethatisusedtodefineasymbolicconstant.
The symbolic constant defined, replaces the word / statement wherever it
appears in the program as a macro substitution.
Syntax: #definesymbolic_namevalue
Example: #define Pi 3.14
#defineWELCOME cout<<”HelloWorld !n”;
(Full 2 marks for illustrating the concept of #define using example)
OR
(1 mark if only definition is written)
(c) Corrected Program:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h> // Error 1
void main()
{ struct STUDENT
{ char stu_name[20];
char stu_sex;
int stu_age; //Error 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-16-320.jpg)


![282
(c) class ADMISSION
{
int AD_NO;
char NAME[20]; //or any constant size
char CLASS;
float FEES;
public:
void Read_Data()
{
do
{
cin>>AD_NO;
}while (AD_NO<10 || AD_NO>2000);
gets(NAME);
cin>>CLASS;
cin>>FEES;
}
void Display()
{
cout<<AD_NO;
cout<<NAME;
cout<<CLASS;
cout<<FEES;
}
void Draw_Nos();
};
(1 mark for proper syntax of class definition with correct class name
and a semicolon to end the class definition)
(1 mark for proper declaration of private members)
(1 mark for proper definition of Read_Data())
(1 mark for proper definition of Display())
Note: No marks should be deducted for
Not checking the range for AD_NO
Not declaring or defining Draw_Nos(). (Mentioned as Draw-
Nos() in the question paper)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-19-320.jpg)
![283
(d) (i) Read_pri_details(),Disp_pri_details()
(1 mark for correct function names)
(ii) 29 bytes
OR
33 bytes
(1 mark for correct answer)
(iii) Disp_pri_details(),Read_off_details(),Disp_off_details(),
Read_sta_details(),Disp_sta_details()
(2 marks for all correct member functions)
Note:
No partial marks to be given for any of the parts.
Ignore the constructor and function itself
3. (a) const int R = 100, C = 100;
void Arrayconvert(int A1D[], int N)
{
int A2D[R][C]={0};
for(int I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (int J = 0; J <N-I; J++)
A2D[I][J] = A1D[J];
}
OR
const int R = 100, C = 100;
void Arrayconvert(int A1D[], int N)
{
int A2D[R][C];
for(int I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (int J = 0; J <N; J++)
if (J<N-I)
A2D[I][J] = A1D[J];
else
A2D[I][J] = 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-20-320.jpg)
![284
OR
const int R = 100, C = 100;
void Arrayconvert(int A1D[], int N)
{
int A2D[R][C], I, J;
for(I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (J = 0; J <N; J++)
A2D[I][J] = 0;
for(I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (J = 0; J <N-I; J++)
A2D[I][J] = A1D[J];
}
OR
Any other equivalent code
(1 mark for function header)
(1 mark for correct use of nested loops)
( ½ mark for correctly assigning the values from 1D array to 2D array)
( ½ mark for assigning 0 to the rest of the elements)
Note: Ignore declaration of the 2D array.
(b) ForColumnwiseallocation
Address ofA[I][J] = BA+ W[ (J –LBC) x M + (I - LBR)]
Where
BA= BaseAddress
W = Size of each element in bytes = 8 bytes (given)
M = No. of rows in the 2DArray = 30 (given)
Address of MAT[5][7] given is 1000.
Assumption 1 : LBR=LBC=0
Therefore
1000 = BA + 8 (7 × 30 + 5)
= BA + 8 × 215
= BA + 1720
BA = 1000 – 1720
= -720
Therefore,
Base Address = - 720
Thus,Address of MAT[20][5] = -720 + 8 ( 5 × 30 + 20)
= -720 + 8 × 170
= -720 + 1360
= 640](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-21-320.jpg)
![285
Assumption 2 : LBR=LBC=1
Therefore
1000 = BA + 8 [(7-1) × 30 +(5-1)]
= BA + 8[6 × 30 + 4]
= BA + 8 ×184
= BA + 1472
BA = 1000 – 1472
= -472
Therefore,
Base Address = - 472
Thus,Address of MAT[20][5] = -472 + 8 ( 4 × 30 + 19)
= -472 + 8 × 139
= -472 + 1112
= 640
(2 marks for writing the correct column major formula or sustitution
of values in the correct formula)
(1 mark for calculating Base Address)
(1 mark for calculating final address of MAT[20][5])
(c) void queue::add( )
{
if ( (rear + 1) % 10 != front )
{
if (rear == -1 )
front = rear = 0 ;
else
rear = (rear + 1) %10;
cin>>data[rear];
}
else
cout<<”Queue full !! Overflow Error !!n”;
}
void queue::remove()
{
if (front != -1)
{
cout<< data[front]<<” deleted ”;
if(front==rear)
front=rear=-1;
else
front = (front+1)%10;
}
else
cout<<”Queue empty ! Underflow Error!!n”;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-22-320.jpg)
![286
OR
void queue::add( )
{
if ( (rear + 1) % 10 != front )//Ignoring –1
initial values
{
rear = (rear + 1) %10;
cin>>data[rear];
}
else
cout<<”Queue full !! Overflow Error !!n”;
}
void queue::remove()
{
if (front != rear) //Ignoring –1 initial values
{
front = (front+1)%10;
cout<< data[front]<<” deleted…”;
}
else
cout<<”Queue empty ! Underflow Error!!n”;
}
OR
void queue::add()
{ int item;
if((front==0 && rear==9) || front==rear+1)
cout<<”nQueue overflow error”;
else
{
cout<<”nEnter an item to add : “;
cin>>item;
if(front= =-1)
{ front=0;rear=0; }
else
rear=rear+1;
if(rear==10)
rear=0;
data[rear]=item;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-23-320.jpg)
![287
void queue::remove()
{ if((front==-1 )
cout<<”nQueue Underflow Error”;
else
{ int item=data[front];
if(front==rear)
front=rear=-1;
elseif(front==9)
front=0;
else
front=front+1;
cout<<”nDeleteditemis:“<<item;
}
}
OR
Anyotherequivalentcode
(2 marks for any correct add( )function code)
( ½ mark for checking Overflow condition)
(1 mark for changing the values of rear counter )
( ½ mark for assigning the new value at the correct position)
(2 marks for any correct remove( )function code)
(1 mark for checking Underflow condition)
(1 mark for changing the values of front counter)
Note: There is a conceptual contradiction for the function void
Delete(int ITEM) , thus the benefit of doubt is given to the student
and therefore the definition of the function is to be ignored .
(d) struct Node
{
float Data;Node *Link;
};
class Stack
{
Node *Top;
public:
Stack() { Top = NULL ; }
void Push( );void Pop ( );void Display ( );
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-24-320.jpg)

![289
(b) void countwords( )
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open(“Para.txt”);
char ch ;
int count = 1;
while(!fin.eof())
{
ch = fin.get();
if (ch == ‘ ’)
count ++;
}
cout<<”nNumber of words = “<<count; // Optional
fin.close(); //Optional
}
OR
void countwords( )
{
ifstream fin“Para.txt”);
char str[30] ;
int count = 0;
while(fin)
{
fin>>str;
count++;
}
cout<<”nNumber of words = “<<count; // Optional
fin.close(); //Optional
}
OR
void countwords( )
{
fstream fin;
fin.open(“Para.txt”, ios::in);
char ch[80] ;
int count = 1;
while(fin)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-26-320.jpg)
![290
fin.getline(str,80);
for(int i=0;str[i]!=’0’;i++)
if (ch == ‘ ’)
count++;
}
cout<<”nNumber of words = “<<count; // Optional
fin.close(); //Optional
}
OR
void countwords( )
{
fstream fin(“Para.txt”, ios::in);
char ch[80] ;
int count = 0;
while(fin)
{
fin.getline(str,80, ‘ ’);
count++;
}
cout<<”nNumber of words = “<<count; // Optional
fin.close(); //Optional
}
OR
Anyotherequivalentcode
(1/2 mark for opening file in correct mode either using ifstream or ios::in)
(1/2 mark for correct loop)
(1/2 mark for checking for blank space/equivalent code)
(1/2 mark for counting number of words)
(c) void update()
{
fstream f;
COLONY c;
char C_Code[10];
cout<<”nEnter the Colony Code : “;
cin>>C_Code; // OR gets(C_Code);
f.open(“COLONY.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
while(f.read((char*)&c,sizeof(COLONY)))
{
if(strcmp(c.Colony_Code, C_Code)==0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-27-320.jpg)



![295
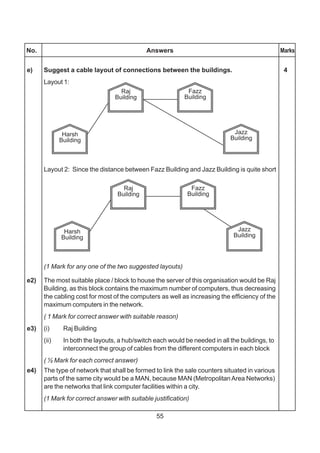
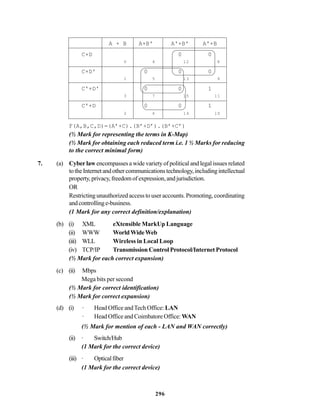
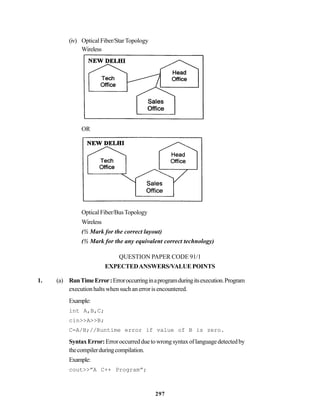
(d) (i) Star or Bus or any other valid topology or diagram.
(1 mark for mentioning any of the above topologies)
(1 mark for diagrammatic representation of any of the above topologies)
(ii) WingA,becausemaximumnumberofcomputersare locatedatWingA.
(1 mark for the correct answer)
OR
( ½ mark if only Wing A is mentioned without justification)
(ii) Hub/Switchinallthewings.
OR
CorrectdiagramdepictingplacementofHub/Switchinallthewings.
(1 mark for correct placement)
(iv) Coaxial cable / Modem / LAN / TCP-IP / Dialup/ DSL/ Leased Line
ORanyothervalidtechnology(anyone).
Note: Optical fiber, Satellite link and Microwave NOT to be
considered as valid answers.
(1 Mark for any valid technology)
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
EXPECTEDANSWERS/VALUEPOINTS
1. (a) (i) math.h / complex.h (ii) stdlib.h
(1/2 Marks for each correct Header File)
(b) —
Note:Astheterminlinefunctionisnotmentionedinthecurriculum,benefitof
doubt should be given to the students.
(Full 2 marks to be awarded to the students who have scored at least
1 mark in the entire Q. No. 1 i.e. from 1(a) to 1(f))
(c) #include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h> // Error 1 - needed for gets()
void main()
{
struct movie
{
char movie_name[20];
char movie_type;
int ticket_cost = 100; //Error 2 - assignment not
//possible inside structure definition
}MOVIE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-32-320.jpg)
![296
gets(MOVIE.movie_name);//Error 3 -members must be
//accessed using object
cin>>MOVIE.movie_type; //Error 4 -cant use gets for
//char variable and member must
//be accessed using object.
}
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
struct movie
{
char movie_name[20];
char movie_type;
int ticket_cost = 100; //Error 1 – initialization‘ not
//possible inside structure definition
}MOVIE;
cin.getline(MOVIE.movie_name,20);//Error 2 -members must
//be accessed using object
cin>>MOVIE.movie_type; //Error 3 -cant use gets for
//char variable and member must
//be accessed using object.
}
(1 mark for identifying and correcting any one Error)
(1 ½ mark for identifying and correcting any two errors)
(2 marks for identifying and correcting more than two errors)
OR
(1 mark for only identifying all errors)
(d) JackJill
JackJillJohn
(2 marks for any one correct line)
(Full 3 marks for both lines correct)
(½ mark to be deducted from full 3 marks, if endl is not considered)
(e) -2
(Full 2 marks for correct output)
OR
(Full 2 marks for mentioning values of First as 14 and Second as 16,
as representation of minus sign is not very prominent)
OR
(Full 2 marks for mentioning syntax error with justification as
insertion operator << expected in between First and Second)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-33-320.jpg)

![298
(c) class HOUSING
{
int REG_NO;
char NAME[20];
char TYPE;
float COST;
public:
void Read_Data();
void Display();
void Draw_Nos(HOUSING S);
};
void HOUSING::Read_Data()
{
cin>>REG_NO; //Validation not required
cin>>NAME; //OR gets(NAME);
cin>>TYPE; cin>>COST;
}
void HOUSING::Display()
{
cout<<REG_NO<<NAME<<TYPE<<COST<<endl;
}
void HOUSING::Draw_Nos();//Ignore
(1/2 mark for proper syntax of class definition with correct class name
and a semicolon to end the class definition)
(1/2 mark for mentioning the proper visibility modes (private / public))
(1 mark for proper declaration of private data members)
(1 mark for proper definition of Read_Data() with user entry for data
members OR declaring a local object and entering the values of data
members of this object )
(1 mark for proper definition of Display())
Note:As language of Third part of this question has ambiguity, it is
required to be ignored. Moreover, if anyone has partially attempted
thethirdpart(i.e.,Draw_nosfunction)andnotattempted/notcorrectly
attempted Read/Display function, he/she should be given 2 Marks
for Third part taking into consideration the marks for this question
should not exceed the max. marks allocated (i.e. 4 marks) to this
question 2 (c).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-35-320.jpg)
![299
(d) (i) Read_office_details
Disp_office_details.
(1 mark for correct names)
(ii) 29 bytes
OR
33 Bytes
(1 mark for correct answer)
(iii) Read_fur_details(),
Disp_fur_details,
Read_sofa_details(),
Disp_sofa_details(),
Disp_office_details()
Read_office_details() (Optional)
(2 marks for correct answer)
3. (a) const int R = 100, C = 100;
void Arrayconvert(int A1D[ ], int N)
{
int A2D[R][C]={0};
for(int I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (int J = 0; J <=I; J++)
A2D[I][J] = A1D[J];
}
( 1 mark for proper function header )
( 1 mark for proper use of loops)
( 1 mark for proper assignment of values)
(b) ForRowwiseallocation
Address ofA[I][J] = BA+ W( (I-LBR) x N + (J-LBC))
Where
BA= BaseAddress
W = Size of each element in bytes = 4 bytes (given)
N = No. of columns in the 2DArray = 10 (given)
Address of MAT[3][7] given is 1000.
Therefore
(Assumption 1: LBR = LBC = 0)
MAT[3][7]=100 = BA + 4 (10 (3-0) + (7-0))
= BA + 148
BA = 1000 – 148
= 852](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-36-320.jpg)
![300
Therefore,
Base Address = 852
Thus,Address of MAT[10][5] = 852 + 4 ( 10 (10-0) + (5-0))
= 852+420
= 1272
OR
(Assumption 2: LBR = LBC = 1)
MAT[3][7]=1000 = BA + 4 (10 (3-1) + (7-1))
= BA + 104
BA = 1000 – 104
= 896
Therefore,
Base Address = 896
Thus,Address of MAT[10][5] = 896 + 4 ( 10 (10-1) + (5-1))
= 896+376
= 1272
(1 mark for writing the correct formula / correct substituted values,
for row major properly, for calculating Base Address)
(1 mark for calculating correct Base Address)
(1 mark for writing the correct formula / correct substituted values,
for row major properly, for calculating Address of MAT [10][5] )
(1 mark for calculating correct address of MAT [10][5])
(c) void stack::push()
{
int n;
cout<<”Enter a value”;cin>>n;
if (top==10)
cout<<”Stack Overflow”;
else
data[++top]=n;
}
void stack::pop()
{
if (top==-1)
cout<<”Stack Underflow”;
else
cout<<data[top--];
}
void stack::Delete(int ITEM);//Ignore this part](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-37-320.jpg)
![301
[PushOperation]
(1/2 mark for checking overflow condition)
(1/2 mark for using increment in Top variable)
(1 mark for correct assignment of data in stack)
[PopOperation]
(1/2 mark for checking underflow condition)
(1/2 mark for using decrement in Top variable)
(1 mark for displaying or returning value of the popped element from
the stack)
Note:As language of Third part of this question has ambiguity with
respect to Stack Operation, it is required to be ignored. Moreover, if
anyone has partially attempted the third part (i.e. Delete function)
and not attempted/not correctly attempted Push/Pop should be given
2 Marks for Third part taking into consideration the marks for this
question should not exceed the max. marks allocated (i.e. 4 marks)
to this question 3 (c).
(d) struct Student
{
char Name[20];Student *Link;
};
class Queue
{
Student *FRONT, *REAR;
public:
Queue() { FRONT = NULL ; REAR = NULL}
void Insert( );
};
void Queue::Insert()
{
Student *Temp = new Student;
gets(Temp->Name);
Temp->Link = NULL;
if(REAR==NULL)
{ FRONT=Temp; REAR = Temp; }
else
{
REAR->Link = Temp;
REAR=Temp;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-38-320.jpg)

![303
OR
Any equivalent code that counts the number of words from the file
(1/2 Mark for opening the file in right mode)
(1/2 Mark for correct loop structure i.e. with a condition checking for
end of file)
(1/2 Mark for reading a character / line from the file)
(1/2 Mark for checking for space and incrementing the counter)
(c) void modify( )
{
fstream out;
out.open(“PRODUCT.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
PRODUCT P1;
int flag=0,stock;char PCode[10];
gets(PCode);
cin>>stock;
while (out.read((char*)&P1, sizeof(P1))
if (strcmp(P1.Product_code,Pcode)==0)
// strcmpi()may also be considered
{
flag=1;
P1.Stock=stock;
int Position=out.tellg( )-sizeof(P1);
out.seekp(Position);
//OR
out.seekp(-sizeof(P1),ios::cur);
out.write((char*)&P1, sizeof(P1);
}
}
if (flag==0) cout<<”Product Code does not match”;
//OR
if (!flag) cout<<”Product Code does not match”;
out.close();
}
OR
Any other equivalent code
(1/2 Mark for opening the file in ‘in’ as well as ‘out’ mode)
(1/2 Mark for declaring object and temporary variables required for
product code and stock)
(1/2 Marks for correct loop, check of end of file and reading of an
object from the file)
(1/2 Mark for correct comparison)
(1/2 Mark for identifying and moving the file pointer to the correct
position)
(1/2 Mark writing the modified/updated data on right position in the
file)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-40-320.jpg)
![304
5. (a) DDL–DataDefinitionLanguage
DML–DataManipulationLanguage
(1 Mark each for correct full form OR correctly explaining with the
help of examples)
(b) (i) SELECT FL_NO,NO_FLIGHTS FROM FLIGHTS
WHERE STARTING=’KANPUR’ AND ENDING=’BANGALORE’;
(1/2 Mark for using SELECT and FROM correctly)
(1/2 Mark for correct WHERE clause)
(ii) SELECT * FROM FLIGHTS ORDER BY FL_NO;
(1/2 Mark for using SELECT and FROM correctly)
(1/2 Mark for correct ORDER BY clause [ASC is optional])
(iii) SELECT FLIGHTS.FL_NO, FARE+FARE*TAX/100
FROM FLIGHTS, FARES WHERE FLIGHTS.STARTING=’DELHI’ AND
FLIGHTS.ENDING=’MUMBAI’ AND FLIGHTS.FL_NO=FARES.FL_NO;
*Assuming TAX% as TAX
(Full 1 Mark for correctly attempting any part of 5 (b))
(iv) SELECT MIN(FARE) FROM FARES WHERE AIRLINES=’INDIAN AIRLINES’;
(1/2 Mark for using SELECT and FROM with MIN function correctly)
(1/2 Mark for correct WHERE clause)
(v) FL_NO NO_FLIGHTS AIRLINES
IC302 8 IndianAirlines
AM501 1 JetAirways
IC701 4 IndianAirlines
(1 Mark for correct output, Ignore First header line)
(vi) 7
(1 Mark for correct output)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-41-320.jpg)
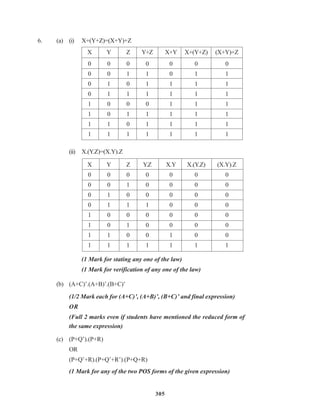
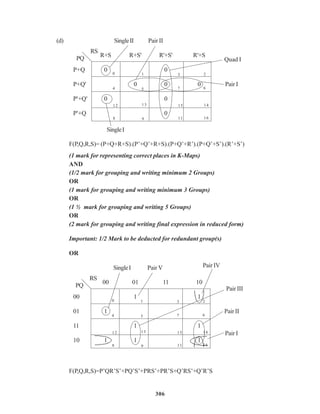
![307
(1 mark for representing correct places in K-Maps)
AND
(1/2 mark for grouping and writing minimum 2 Groups)
OR
(1 mark for grouping and writing minimum 4 Groups)
OR
(1 ½ mark for grouping and writing 6 Groups)
OR
(2 mark for grouping and writing final expression in reduced form)
Important: 1/2 Mark to be deducted for redundant group(s)
7. (a) OpticalFiber
Ethernet Cable or twisted pair cable or UTP or STP
Co-axial Cable
Infrared
Radio Link OR Radiowave
Microwave link OR Microwave
Satellite Link
[Any TWO of the mentioned above OR any other correct media]
(1/2 Mark for each correct answer)
(b) (i) XML ExtensibleMarkupLanguage
(ii) GSM GlobalSystemforMobilecommunication {ignorecommunication}
(iii) SMS ShortMessagingService {Message/Messagingbothacceptable}
(iv)MAN MetropolitanArea Network
(1/2 Mark for each correct answer)
(No marks for partially correct answers)
(c) Hackers:Computerenthusiastswhoenjoylearningaboutcomputersystems
andgetintoothersystem/networkforgainingmoreknowledgeormayfind
flawsinthesystemforrectificationpurposes.
Crackers:Maliciousprogrammerswhobreakintosecuresystemsforstealing
andcorrupting/spoilingdata.
(1/2 Mark for definition of each Hacker and Cracker)
OR
(Full 1 Mark for mentioning the difference)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-44-320.jpg)

![261
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language : C++
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
1. (a) DifferentiatebetweenaLogicalErrorandSyntaxError.Alsogivesuitable
examples of each in C++. 2
(b) Name theheaderfile(s)thatshallbeneeded for successful compilation of
thefollowingC++code: 1
void main( )
{
char Text[40];
strcpy(Text,”AISSCE”);
puts(Text);
}
(c) Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical error(s),
ifany.Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include <iostream.h>
const int Size 5;
void main()
{
int Array[Size];
Array = {50,40,30,20,10};
for(Ctr=0; Ctr<Size; Ctr++)
cout>>Array[Ctr];
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
int Numbers[] = {2,4,8,10};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-46-320.jpg)
![262
int *ptr = Numbers;
for (int C = 0; C<3; C++)
{
cout<< *ptr << “@”;
ptr++;
}
cout<<endl;
for(C = 0; C<4; C++)
{
(*ptr)*=2;
--ptr;
}
for(C = 0; C<4; C++)
cout<< Numbers [C]<< “#”;
cout<<endl;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void Indirect(int Temp=20)
{
for (int 1=10; I<=Temp; I+=5)
cout<<I<<” , “ ;
cout<<endl;
}
void Direct (int &Num)
{
Num+=10;
Indirect(Num);
}
void main()
{
int Number=20;
Direct(Number) ;
Indirect();
cout<< “ Number=” <<Number<<endl ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-47-320.jpg)
![263
(f) In the following C++ program what is the expected value of Myscore from
Options(i)to(iv)givenbelow.Justifyyouranswer. 2
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream.h>
void main( )
{
randomize();
int Score[] = {25,20,34,56, 72, 63}, Myscore;
Myscore = Score[2 + random(2)];
cout<<Myscore<<endl; }
(i) 25
(ii) 34
(iii) 20
(iv) None of the above
2. (a) Differentiate between Protected and Private members of a class in
context ofInheritanceusing C++. 2
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingclass: 2
class Science
{
char Topic[20];
int Weightage;
public:
Science ( ) //Function 1
{
strcpy (Topic, “Optics” );
Weightage = 30;
cout<<“Topic Activated”;
}
~Science( ) //Function 2
{
cout’<<”Topic Deactivated”;
}
(i) NamethespecificfeaturesofclassshownbyFunction1andFunction
2 in the above example.
(ii) How would Function 1 and Function 2 get executed ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-48-320.jpg)
![264
(c) DefineaclassTravelinC++withthedescriptiongivenbelow: 4
PrivateMembers:
T_Code oftypestring
No_of_Adults oftypeinteger
No_of_Children oftypeinteger
Distance oftypeinteger
TotalFare oftypefloat
PublicMembers:
• Aconstructortoassigninitialvaluesasfollows:
T_Code with the word “NULL”
No_of_Adults as 0
No_of_Children as 0
Distance as 0
TotalFare as 0
• AfunctionAssignFare( )whichcalculatesandassignsthevalue
of the data memberTotalFare as follows :
For each Adult
Fare (Rs) For Distance (Km)
500 >=1000
300 <1000 & >=500
200 <500
For each Child the above Fare will be 50% of the Fare mentioned in
the above table.
Forexample:
If Distance is 750, No_of_Adults = 3 and No_of_Children = 2
ThenTotalFare should be calculated as
No_of_Adults * 300 + No_of_Children * 150
i.e. 3 * 300 + 2 * 150 = 1200
• AfunctionEnterTraveK)toinputthevaluesofthedatamembers
T_Code, No_of_Adults, No_of_Children and Distance; and
invoketheAssignFare()function.
• Afunction ShowTraveK) which displays the content of all the
data members for aTravel.
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code : 4
class Teacher
{
char TNo[5], TName[20], DeptflO];
int Workload;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-49-320.jpg)
![265
protected:
float Salary;
void AssignSal(float);
public:
Teacher( ) ;
void TEntry( ) ;
void TDisplay( );
};
class Student
{
char Admno[10], SName[20], Stream[10];
protected:
int Attendance, TotMarks;
public:
Student( );
void SEntry( );
void SDisplay( );
};
class School : public Student, public Teacher
};
char SCode[10], SchName[20];
public:
School ( ) ;
void SchEntry( );
void SchDisplay( );
};
(i) Which type of Inheritance is depicted by the above example ?
(ii) Identifythememberfunctiion(s)thatcannotbecalleddirectlyfromthe
objectsofclassSchoolfromthefollowing:
TEntry()
SDisplay()
SchEntry()
(iii) Writenameofallthemember(s)accessiblefrommemberfunctionsof
class School.
(iv) IfclassSchoolwasderivedprivatelyfromclassTeacherandprivately
from class Student, then, name the member function(s) that could be
accessed through Objects of class School.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-50-320.jpg)
![266
3. (a) Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size.as
argumentsandreplaceselementshavingevenvalueswithitshalfandelements
havingoddvalueswithtwiceitsvalue. 4
Example:ifanarrayoffiveelementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
3, 4, 5, 16, 9
then the function should rearrange the content of the array as
6, 2, 10, 8, 18
(b) AnarrayArr[15][20]isstoredinthememoryalongtherowwitheachelement
occupying 4 bytes. Find out the BaseAddress and address of the element
Arr[3][2], if the elementArr[5][2] is stored at the address 1500. 4
(c) WriteafunctioninC++todeleteanodecontainingcustomer’sinformation,
from a dynamically allocated Queue of Customers implemented with
the helpofthefollowingstructure: 4
struct Customer
{
int CNo;
char CName[20];
Customer *Link;
};
(d) Write a functionin C++ whichaccepts a2D arrayofintegers andits size
asargumentsanddisplaystheelementsofmiddlerowandtheelementsof
middlecolumn. 2
[Assuming the 2DArray to be a square matrix with odd dimension
i.e. 3×3, 5×5, 7×7 etc...]
Example,ifthearraycontentis
3 5 4
7 6 9
2 1 8
Outputthroughthefunctionshouldbe:
Middle Row : 7 6 9
Middle Column : 5 6 1
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
15 3 2 + / 7 + 2 *
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows: 1
class Labrecord
{
int Expno;
char Experiment[20];
char Checked;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-51-320.jpg)

![268
(c) Given a binary file SPORTS.DAT, containing records of the following
structuretype:
struct Sports
{
char Event[20];
char Participant[10][30];
};
WriteafunctioninC++thatwouldreadcontentsfromthefileSPORTS.DAT
andcreatesafilenamedATHLETIC.DATcopyingonlythoserecordsfrom
SPORTS.DATwheretheeventnameis“Athletics”. 3
5. (a) What is the importance of a Primary Key in a table ? Explain with a suitable
example. 2
(b) Consider the following tables Consignor and Consignee. Write SQL
commandsforthestatements(i)to(iv)andgiveoutputsforSQLqueries(v)
to(viii). 6
TABLE : CONSIGNOR
CnorlD CnorName CnorAddress City
ND01 RSinghal 24,ABC Enclave NewDelhi
ND02 AmitKumar 123,PalmAvenue NewDelhi
MU15 RKohli 5/A, South Street Mumbai
MU50 S Kaur 27-K, Westend Mumbai
TABLE : CONSIGNEE
CneelD CnorlD CneeName CneeAddress CneeCity
MU05 ND01 RahulKishore 5, ParkAvenue Mumbai
ND08 ND02 PDhingra 16/J, Moore Enclave NewDelhi
KO19 MU15 APRoy 2A,CentralAvenue Kolkata
MU32 ND02 SMittal P245,AB Colony Mumbai
ND48 MU50 BPJain 13, Block D,AVihar NewDelhi
(i) TodisplaythenamesofallConsignorsfromMumbai.’
(ii) To display the CneelD, CnorName, CnorAddress, CneeName,
CneeAddress for every Consignee.
(iii) To display consignee details in ascending order of CneeName.
(iv) To displaynumberofconsignorsfromeachcity,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-53-320.jpg)
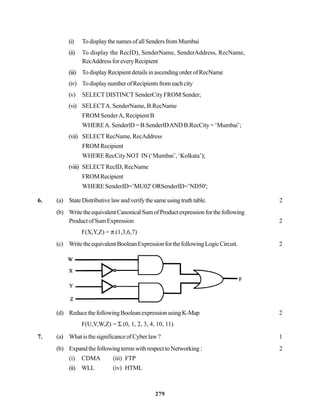
![271
In continuation of the above, the company experts have planned to install
thefollowingnumberofcomputersineachoftheiroffices:
HeadOffice 100
SalesOffice 20
TechOffice 50
KolkataOffice 50
AhmedabadOffice 50
CoimbatoreOffice 50
(i) Suggestnetworktype(outofLAN,MAN,WAN)forconnectingeach
ofthefollowingsetoftheiroffices:
• Head Office andTech Office
• Head Office and Coimbatore Office
(ii) Which device will you suggest to be procured by the company for
connecting all the computers within each of, their offices out of the
followingdevices?
• Modem
• Telephone
• Switch/Hub
(iii) Whichofthefollowingcommunicationmedia,willyousuggesttobe
procured by the company for connecting their local offices in New
Delhiforveryeffectiveandfastcommunication?
• EthernetCable
• OpticalFiber
• TelephoneCable
(iv) Suggestacable/wiringlayoutforconnectingthecompany’slocaloffices
located in New Delhi.Also,, suggest an effective method/technology
for connecting the company’s regional offices at “Kolkata”,
“Coimbatore”and“Ahmedabad”. 4
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) DifferentiatebetweenaRunTimeErrorandSyntaxError.Alsogivesuitable
examples of each in C++. 2
(b) Nametheheaderfile(s)thatshallbeneededforsuccessfulcompilationofthe
followingC++code 1
void main ( )
{
char String [20];
gets (String);
strcat (String, “CBSE”);
puts (String);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-56-320.jpg)
![272
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerror(s)ifany.
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
# include <iostream.h>
const int Max 10;
void main ( )
{
int Numbers [Max];
Numbers = { 20, 50,10, 30,40 } ;
for (Loc= Max-1 ; Loc > = 0 ; Loc - -)
cout>>Numbers [Loc];
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
# include < iostream.h>
void main ()
{
intArray[] = {4,6,10,12};
int *pointer = Array ;
for (int I=1 ; I<=3 ; I++)
{
cout<<*pointer<<#”;
pointer ++;
}
cout<<endl;
for (I=1 ; I<=4 ; I++)
{
(*pointer)*=3 ;
-- pointer;
}
for(I=l; I<5; I + + )
cout << Array [I-1] << “@”;
cout << endl;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
# include < iostream.h>
void Withdef (int HisNum = 30)
{
for (int 1=20 ; I<*= HisNum; I+=5)
cout<<I<<””;
cout<<endl;
}
void Control (int &MyNum)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-57-320.jpg)
![273
MyNum+=10;
Withdef(MyNum);
}
void main ()
{
int YourNum=20;
Control (YourNum);
Withdef();
cout<<”Number=”<<YourNum<<endl;
}
(f) InthefollowingC++programwhatistheexpectedvalueofMyMarksfrom
Options(i)to(iv)givenbelow.Justifyanswer. 2
#include<stdlib. h >
# include<iostream. h>
void main ()
{
randomize ();
int Marks [ ]= {99, 92, 94, 96, 93, 95}, MyMarks;
MyMarks = Marks [1 + random (2) ];
cout<<MyMarks<<endl;
}
(i) 99 (ii) 94
(iii) 96 (iv) None of the above
2. (a) DifferentiatebetweenConstructorandDestructorfunctionincontextof
Classes and Objects using C++ 2
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingclass 2
class Maths
{
char Chapter [20];
int Marks;
public:
Maths ( ) //Member Function 1
{
strcpy (Chapter, “Geometry”);
Marks = 10;
cout<<“Chapter Initialised”;
{
~Math () //Member Function 2
}
cout<<”Chapter Over”;
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-58-320.jpg)

![275
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code : 4
class Trainer
{
char TNo [5], TName [20], Specialisation [10];
int Days;
protected :
float Remuneration;
void AssignRem (float);
public :
Trainer ( ) ;
void TEntry ( );
void TDisplay ( );
};
class Learner
{
char Regno [10], LName [20], Program [10];
Protected :
int Attendance, Grade;
public:
Learner ( );
void LEntry ( );
void LDisplay ( );
};
class Institute : public Learner, public Trainer
{
char ICode[10], IName [20]; (
public:
Institute ( );
void IEntry ( );
void IDisplay ( );
};
(i) Which type of Inheritance is depicted by the above example?
(ii) Identifythememberfunction(s)thatcannotbecalleddirectlyfromthe
objectsofclassInstitutefromthefollowing
TEntry()
LDisplay()
IEntry()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-60-320.jpg)
![276
(iii) Writenameofallthemember(s)accessiblefrommemberfunctionsof
classInstitute.
(iv) IfclassInstitutewasderivedprivatelyfromclassLearnerandprivately
from classTrainer, then, name the member function(s) that could be
accessed through Objects of class Institute.
3. (a) Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as
argumentsandreplaceselementshavingoddvalueswiththriceitsvalueand
elementshavingevenvalueswithtwiceitsvalue.
Example:ifanarrayoffiveelementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
3, 4, 5, 16, 9
then the function should rearrange the content of the array as
9, 8, 15, 32, 27 4
(b) AnarrayArray[20][15]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwitheach
element occupying 8 bytes. Find out the BaseAddress and address of the
elementArray[2][3] if the elementArray [4] [5] is stored at the address
1000. 4
(c) Write a function in C++ to delete a node containing Book’s information,
fromadynamicallyallocatedStackofBooksimplementedwiththehelpof
thefollowingstructure. 4
struct Book
}
int BNo;
char BName[20];
Book *Next;
};
(d) Write a function in C++ which accepts a 2D array of integers and its size as
argumentsanddisplaystheelementswhichlieondiagonals. 2
[Assuming the 2DArray to be a square matrix with odd dimension
i.e. 3×3, 5×5, 7×7 etc.]
Example,ifthearraycontentis
5 4 3
6 7 8
1 2 9
Outputthroughthefunctionshouldbe:
Diagonal One : 5 7 9
Diagonal Two : 3 7 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-61-320.jpg)
![277
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
25 8 3 - / 6 * 10 +
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows: 1
class PracFile
{
intPracno;
char PracName[20];
int TimeTaken;
int Marks;
public:
// function to enter PracFile details
void EnterPrac( );
// function to display PracFile details
void ShowPrac( ):
// function to return TimeTaken
int RTime() {return TimeTaken;}
// function to assign Marks
void Assignmarks (int M)
{ Marks = M;}
};
void AllocateMarks( )
{ fstreamFile;
File.open(“MARKS.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
PracFile P;
int Record = 0;
while (File.read(( char*) &P, sizeof(P)))
{
if(P.RTime()>50)
P.Assignmarks(0)
else
P.Assignmarks(10)
______________ //statement 1
______________ //statement 2
Record + + ;
}
File.close();
}
IfthefunctionAllocateMarks()issupposedtoAllocateMarksfortherecords
in the file MARKS.DAT based on their value of the member TimeTaken.
Write C++ statements for the statement 1 and statement 2, where,
statement 1 is required to position the file write pointer to an appropriate
place in the file and statement 2 is to perform the write operation with the
modifiedrecord.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-62-320.jpg)
![278
(b) Write afunction in C++ to print the count of the word is as an
independentwordinattextfileDIALOGUE.TXT. 2
For example, if the content of the file DIALOGUE. TXT is
This is his book. Is this book good?
Then the output of the program should be 2.
(c) GivenabinaryfileGAME.DAT,containingrecordsofthefollowingstructure
type 3
struct Game
{
char GameName [20];
char Participant [10] [30];
};
WriteafunctioninC++thatwouldreadcontentsfromthefileGAME.DAT
and creates a file named BASKET.DAT copying only those records from
GAME.DATwherethegamenameis“BasketBall”
5. (a) Differentiatebetweenprimarykeyandalternatekey. 2
(b) Consider the following tables. Write SQL commands for the statements
(i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii) 6
TABLE:SENDER
SenderlD SenderName SenderAddress SenderCiry
ND01 RJain 2,ABCAppts NewDelhi
MU02 HSinha 12, Newtown Mumbai
MU15 S Jha 27/A, Park Street Mumbai
ND50 T Prasad 122-K, SDA NewDelhi
TABLE : RECIPIENT
RecID SenderlD RecName RecAddress RecCiry
KO05 ND01 R Bajpayee 5, CentralAvenue Kolkata
ND08 MU02 S Mahajan 116,AVihar NewDelhi
MU19 ND01 HSingh 2A,AndheriEast Mumbai
MU32 MU15 P K Swamy B5, C STerminus Mumbai
ND48 ND50 STripathi 13, B1 D, Mayur Vihar NewDelhi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-63-320.jpg)


![283
(b) string.h
stdio.h
(½ Mark for identifying each correct header file)
Note: Marks are not to be deducted if any additional header file is
mentioned
(c) #include<iostream.h>
const int Size =5;
void main( )
{
int Array[Size]={50,40,30,20,10};
for(int Ctr=0;Ctr<Size;Ctr++)
cout<<Array[Ctr];
}
(½ Mark for each correction)
OR
(1 Mark for identifying at least three errors, without suggesting
correction)
(d) 2 @ 4 @ 8 @
4 # 8 # 16 # 20 #
(1 Mark for each correct line of output)
Note:
· ½ Mark to be deducted for missing symbols in each line of output
· ½ Mark to be deducted if endl is not considered in the output
· As Borland C++ Compiler declares for loop variable locally,
the program will result in syntax errors. So, any student
specifying Variable C not declared OR mentioning that the
program will not RUN due to incorrect syntax should be
awarded full 2 Marks
(e) 10, 15, 20, 25, 30,
10, 15, 20,
Number=30
(1 Mark for each correct line of output)
Note:
· ½ Mark to be deducted for missing Commas (,) in each line of
output
· ½ Mark to be deducted if endl is not considered in the output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-68-320.jpg)
![284
(f) (ii) 34
(1 Mark for the correct answer)
(1 Mark for the correct justification)
2. (a) Base Class AccessSpecifier DerivedClass
Protected Private Private
Protected Protected
Public Protected
Private Private NotAccessible
Protected NotAccessible
Public NotAccessible
(1 mark each for correct explanation of Private and Protected
members)
Note: If the contents of the above table is explained correctly in any
format (with or without example) full 2 marks are to be awarded.
(b) (i) Function1:Constructor/DefaultConstructor
Function2:Destructor
(½ Marks for each correct answer)
(ii) Function 1 is executed or invoked automatically when an object of
class Science is created.
Function 2 is invoked automatically when the scope of an object of
class Science comes to an end.
OR
Example:
{
Science s1;//Constructor is invoked
} // the destructor is invoked
(½ Mark for each correct answer through explanation OR
example)
(c) class Travel
{
char TCode[5]; //OR char *Tcode;
int No_of_Adults;
int No_of_Children;
int Distance;
float TotalFare;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-69-320.jpg)
![285
public:
Travel();
void AssignFare();
void EnterTravel();
void ShowTravel();
};
Travel::Travel()
{
strcpy(TCode,”NULL”);// OR TCode[0]=’0’ OR strcpy(TCode,”0”)
// OR TCode=NULL if TCode is declared as char pointer
No_of_Adults = 0;
No_of_Children = 0;
Distance = 0;
TotalFare = 0;
}
void Travel::AssignFare()
{
if(Distance>=1000)
TotalFare = 500*No_of_Adults+250*No_of_Children;
else
if (Distance >= 500)
TotalFare = 300*No_of_Adults+150*No_of_Children;
else
TotalFare = 200*No_of_Adults+100*No_of_Children;
}
void Travel::EnterTravel()
{
gets(TCode); // or cin >> TCode;
cin>>No_of_Adults>>No_of_Children>>Distance;
AssignFare();
}
void Travel::ShowTravel()
{
cout<<TCode<<No_of_Adults<<No_of_Children
<<Distance<<TotalFare<<endl;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax of class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of constructor)
(1 Mark for checking all three conditions and calculating
TotalFare in AssignFare( ))
(½ Mark for correct EnterTravel( ) with proper invocation of
AssignFare( ))
(½ Mark for displaying all data Members including TotalFare
inside ShowTravel( ))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-70-320.jpg)
![286
(d) (i) MultipleInheritance
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(ii) None
OR
Allthefunctionscanbecalled.
(1 Mark for any of the correct answer)
(iii) Data Members: SCode, SchName, Attendance, TotMarks,
Salary
Member Functions: SchDisplay(), SchEntry(), SEntry(),
SDisplay( ), TEntry( ), TDisplay( ), AssignSal( )
( 1 Mark for all correct members)
NOTE:
· Mention of Constructor functions School(), Student() and
Teacher() to be ignored.
· No marks to be awarded for partially correct answers
(iv) SchEntry( ),SchDisplay( ).
( 1 Mark for all correct member functions)
NOTE:
· Constructor function School() to be ignored.
· No marks to be awarded for partially correct answers
3. (a) void Display(int NUM[],int N)
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i=i+1)
{
if(NUM[i]%2==0)
NUM[i]=NUM[i]/2;
else
NUM[i]=2*NUM[i];
}
}
OR
void Display(int NUM[],int N)
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i=i+1)
NUM[i]=(NUM[i]%2!=0)?2*NUM[i]:NUM[i]/2;
}
(1 Mark for correct Function Header with proper Arguments)
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(1 Mark for checking Even / Odd values)
(1 Mark for replacing array elements with proper values)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-71-320.jpg)
![287
(b) Assuming LBR=LBC=0
S=4 bytes
Number of Rows(N)=15
Number of Columns(M)=20
LOC(Arr[I][J]).= B +((I-LBR)*M+(J-LBC))*S
LOC(Arr[5][2]).= B +((5-0)*20+(2-0))*4
1500.= B +(100+2)*4
B.= 1500-408
B.= 1092
LOC(Arr[3][2].= 1092+((3-0)*20+(2-0))*4
..= 1092 + (62*4)
. .= 1092+248
.= 1340
OR
Assuming LBR=LBC=1
S=4 bytes
Number of Rows(N)=15
Number of Columns(M)=20
LOC(Arr[I][J]).= B +((I-LBR)*M+(J-LBC))*S
LOC(Arr[5][2]).= B +((5-1)*20+(2-1))*4
1500 .= B +(80+1)*4
B .= 1500-324
B .= 1176
LOC(Arr[3][2]).= 1176+((3-1)*20+(2-1))*4
. .= 1176 + (41*4)
.= 1176+164
.= 1340
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/correct substituted values, for
row major properly, for calculating Base Address)
(1 Mark for calculating correct Base Address)
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/correct substituted values, for
row major properly, for calculating Address of Arr[3][2])
(1 Mark for calculating correct Address of Arr[3][2])
(c) class QUEUE
{
Customer *Rear,*Front;
public:
QUEUE( ) { Rear=NULL; Front=NULL;}
void DELETE( );
~QUEUE( );
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-72-320.jpg)

![289
(d) //Function definition
void Display(int A[][100],int N)
{
cout<<”Middle Row:”<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<N;i=i+1)
cout<<A[N/2][i]<<” “;
cout<<endl;
cout<<”Middle Column:”<<endl;
for(i=0;i<N;i=i+1)
for(int i=0;i<N;i=i+1) – For Borland C++
cout<<A[i][N/2]<<” “;
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
(½ Mark for correct function header)
(½ Mark for correct loop)
(½ Mark for checking/printing middle row elements)
(½ Mark for checking/printing middle column elements)
(e) Evaluationofthegivenpostfixexpressionisexplainedbelow
Operator Scanned Stack Content
15 15
3 15, 3
2 15, 3, 2
+ 15, 5
/ 3
7 3, 7
+ 10
2 10, 2
* 20
OR
Anyothermethodofevaluatingthepostfixexpressionisshown.
(½ Mark for each operation correctly evaluated)
(Only 1 Mark is to be awarded if correct answer is given without
steps)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-74-320.jpg)
![290
4. (a) Statement 1:
File.seekg(-1*sizeof(L),ios::cur);
OR
File.seekg(Rec*sizeof(L));
OR
File.seekp(-1*sizeof(L),ios::cur);
OR
File.seekp(Rec*sizeof(L));
OR
Any equivalent correct method of calculating size of the record in place of
sizeofoperator.
Statement 2:
File.write((char *) &L,sizeof(L));
OR
Any equivalent correct method of calculating size of the record in place of
sizeofoperator.
(½ Mark for each correct statement)
(b) //Function to count the word in STORY.TXT file
void thewordCount()
{
ifstream Fil(“STORY.TXT”);
char String[20];
int C=0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>String;
if(strcmpi(String,”the”)==0)
C=C+1;
}
cout<<C<<endl;
Fil.close();
}
OR
void thewordCount()
{
ifstream Fil(“STORY.TXT”);
char String[20];
int C=0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>String;
if(strcmp(String,”the”)==0 || strcmp(String,”The”)==0)
C=C+1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-75-320.jpg)
![291
}
cout<<C<<endl;
Fil.close();
}
OR
void thewordCount()
{
ifstream F(“STORY.TXT”);
char Str[4];
int C=0;
while(F.getline(Str,4,’ ‘))
{
if(strcmp(Str,”the”)==0 || strcmp(Str,”The”)==0)
C=C+1;
}
cout<<C<<endl;
F.close();
}
(½ Mark for opening file in the correct mode)
(½ Mark for reading the content from the file and the loop)
(½ Mark for correct comparison)
(½ Mark for initialization and increment of the counter(variable))
Note:
Ignore case sensitivity in the comparison with “the” or “The”
(c) //Function to copy records from SPORTS.DAT to
//ATHELETIC.DAT
void SP2AT()
{
fstream IS,OA;
Sports S;
IS.open(“SPORTS.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in);
OA.open(“ATHLETIC.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::out);
while(IS.read((char*) &S,sizeof(S)))
{
if(strcmp(S.Event,”Athletics”)==0)
OA.write((char *)&S,sizeof(S));
}
IS.close();
OA.close();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-76-320.jpg)




![298
(½ Mark for each correct explanation of Runtime Error and Syntax
Error)
(½ Mark for each correct example of Runtime Error and Syntax Error)
OR
(Full 2 Marks for correct examples demonstrating the difference
between Runtime Error and Syntax Error)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded if Explanation with out supporting
examples)
(b) stdio.h
string.h
(½ Marks for identifying each correct header file)
Note: Ignore any other header files, if mentioned.
(c) #include<iostream.h>
const int Max = 10; //OR const int Max = 5;
void main()
{
int Numbers[Max]= {20,50,10,30,40};
// OR int Numbers[]= {20,50,10,30,40};
int Loc;
for(Loc=Max-1; Loc>=0; Loc—)
cout<<Numbers[Loc];
}
(½ Marks for each correction)
OR
(1 Mark for identifying at least three errors, without suggesting
correction)
(d) 4 # 6 # 10 #
12 @ 18 @ 30 @ 36 @
(1 Mark for each correct line of output)
Note:
· ½ Mark to be deducted for missing symbols in the output
· ½ Mark to be deducted if endl is not considered in the output
· As Borland C++ Compiler declares for loop variable locally,
the program will result in syntax errors. So, any student
specifying Variable I not declared OR mentioning that the
program will not RUN due to incorrect syntax should be
awarded full 2 Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-83-320.jpg)

![300
OR
Example:
{
Maths s1; //Constructor is invoked
} //Destructor is invoked
(½ Mark for each correct answer through explanation OR
example)
NOTE: If the error in declaration of the destructor is specified
then marks for the destructor function should be allocated.
(c) class Tour
{
char TCode[10]; //OR char *Tcode;
int NoofAdults;
int NoofKids;
int Kilometres;
float TotalFare;
public:
Tour()
{
strcpy(TCode,”NULL”); //OR TCode[0]=’0’OR strcpy(TCode,”0”)
//OR TCode=NULL if TCode is declared as char pointer
NoofAdults = 0;
NoofKids = 0;
Kilometres = 0;
TotalFare = 0;
}
void AssignFare();
void EnterTour();
void ShowTour();
};
void Tour::AssignFare()
{
if(Kilometres>=1000)
TotalFare = 500*NoofAdults+250*NoofKids;
else if (Kilometres >= 500)
TotalFare = 300*NoofAdults+150*NoofKids;
else
TotalFare = 200*NoofAdults+100*NoofKids;
}
void Tour::EnterTour()
{
gets(TCode); // or cin >> TCode;
cin>>NoofAdults>>NoofKids>>Kilometres;
AssignFare( );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-85-320.jpg)

![302
3. (a) void Replace( int Arr[], int Size)
{
for(int i =0; i<Size; i++)
if(Arr[i]%2 != 0 )
Arr[i] *= 3;
else
Arr[i] *= 2;
}
OR
void Replace( int Arr[], int Size)
{
for(int i =0; i<Size; i++)
Arr[i]%2 ? Arr[i] *= 2 : Arr[i] *= 3;
}
(1 Mark for correct Function Header with proper Arguments)
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(1 Mark for checking Even / Odd values)
(1 Mark for replacing with proper values)
(b) AddressofArray[i][j]alongthecolumn=
Base Address + W [( i – L1) + (j – L2) * M]
where,
W = size of each location in bytes = 8
L1 = Lower Bound of rows = 0
L2 = Lower Bound of columns = 0
M = Number of rows per column = 20
Address ofArray[4][5] = Base Address + 8 [ (4 – 0) +(5 – 0) * 20]
1000 = Base Address + 8 [104]
BaseAddress = 1000 – 8 x 104
= 1000 – 832
= 168
Address ofArray[2][3] = 168 + 8 [ (2 – 0) + (3 – 0) x 20]
= 168 + 8 x 62
= 168 + 496
= 664
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-87-320.jpg)
![303
AddressofArray[i][j]alongthecolumn=
Base Address + W [( i – L1) + (j – L2) * M]
where,
W = size of each location in bytes = 8
L1 = Lower Bound of rows = 1
L2 = Lower Bound of columns = 1
M = Number of rows per column = 20
Address ofArray[4][5] = Base Address + 8 [ (4 – 1) +(5 –1) * 20]
1000 = Base Address + 8 [83]
BaseAddress = 1000 – 8 x 83
= 1000 – 664
= 336
Address ofArray[2][3] = 336 + 8 [ (2 – 1) + (3 – 1) x 20]
= 168 + 8 x 41
= 168 + 328
= 496
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/ correct substituted values for
calculating Base Address)
(1 Mark for calculating correct Base Address)
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/ correct substituted values for
calculating Address of Arr[3][2])
(1 Mark for calculating correct Address of Arr[3][2])
(c) class Stack
{
Book *Top;
public:
Book() //Constructor to initialize Top
{ Top = NULL; }
void Push(); //Function to insert a node
void Pop(); //Function to delete a node
void Display(); //Function to display nodes of Stack
~Book(); //Destructor to delete all nodes
};
void Stack::Pop( )
{
if (Top != NULL)
{
Stack *Temp;
Temp = Top;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-88-320.jpg)
![304
//Ignore the following line while evaluation
cout<<Top->Bno<<Top->Bname<<”deleted”<<endl;
Top = Top ->Next;
delete Temp;
}
else
cout<<”Stack Empty”;
}
OR
void Pop(Book *&Top)
{
if(Top!=NULL)
{
Book *Temp = Top;
Top = Top ->Next;
delete Temp;
}
else
cout<<”Stack Empty”;
}
(½ Mark for declaring Top as member / passing Top to argument/
declaring it as a global variable)
(½ Mark for correct function header)
(1 Mark for checking Underflow)
(1 Mark for reassigning Top)
(1 Mark for deleting node)
(d) void Diagonals(int Arr[][100], int Size)
{
int Row, Col;
cout<<”Diagonal One: “;
for (Row = 0; Row < Size; Row++)
for (Col = 0; Col < Size; Col++)
if (Row == Col)
cout<<Arr[Row][Col];
cout<<”Diagonal Two: “;
for (Row = 0; Row < Size; Row++)
for (Col = 0; Col < Size; Col++)
if (Row + Col == Size - 1)
cout<<Arr[Row][Col];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-89-320.jpg)
![305
OR
void Diagonals(int Arr[][100], int Size)
{
int Loc;
cout<<”Diagonal One: “;
for (Loc = 0; Loc < Size; Loc++)
cout<<Arr[Loc][Loc];
cout<<”Diagonal Two: “;
for (Loc = 0; Loc < Size; Loc++)
cout<<Arr[Loc][Size-Loc-1];
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
(½ Marks for correct function header)
(½ Marks for correct loop(s))
(½ Marks for checking/printing right diagonal elements)
(½ Marks for checking/printing left diagonal elements)
(e) Operator Scanned Stack Content
25 25
8 25, 8
3 25, 8, 3
- 25, 5
/ 5
6 5, 6
* 30
10 30, 10
+ 40
OR
Anyothermethodofcorrectlyevaluatingthepostfixexpressionisshown.
(2 Marks is to be given for correct answer)
OR
(½ Mark for each operation correctly evaluated)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-90-320.jpg)
![306
4. (a) Statement1:
File.seekp(Record * sizeof(P));
OR
File.seekp(Record * sizeof(PracFile));
OR
File.seekp(-sizeof(P), ios::cur);
OR
File.seekg(Record * sizeof(P));
OR
File.seekg(Record * sizeof(PracFile));
OR
File.seekg(-sizeof(P), ios::cur);
OR
Any equivalent correct method of calculating size of the record in place of
sizeofoperator.
Statement2:
File.write((char*)&P, sizeof(P));
OR
File.write((char*)&P, sizeof(PracFile));
OR
Any equivalent correct method of calculating size of the record in place of
sizeofoperator.
(½ Mark for each correct statement)
(b) void CountIs()
{
ifstream Fil;
Fil.open(“DIALOGUE.TXT”);
char Word[10];
int Count =0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>Word;
if(strcmpi(Word,”is”)==0)
Count++;
}
cout<<Count;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-91-320.jpg)
![307
OR
void CountIs()
{
ifstream Fil;
Fil.open(“DIALOGUE.TXT”);
char Word[10];
int Count = 0;
while(Fil.getline(Word,10,’ ‘))
{
if(strcmpi(Word,”is”)==0)
Count++;
}
cout<<Count;
Fil.close(); //ignore
}
OR
void CountIs()
{
ifstream Fil;
Fil.open(“DIALOGUE.TXT”);
char ch, Word[10];
int Loc=0, Count = 0;
while(Fil.get(ch))
{
if(ch!=’ ‘)
{
Word[Loc] = ch;
Loc++;
}
else
{
Word[Loc] = ‘0’;
Loc = 0;
if(strcmpi(Word,”is”)==0)
Count++;
}
}
cout<<Count;
Fil.close(); //ignore
}
OR
Anyothercorrectdefinition
(½ Marks for opening DIALOGUE.TXT correctly)
(½ Marks for reading each word from the file)
(½ Marks for comparing with “is” / “Is” )
(½ Marks for printing the count of “is” / “Is”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-92-320.jpg)



![308
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language: C+ +
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) Whatisthedifferencebetween#defineandconst?Explainwithsuitable 2
example.
(b) Name the header files that shall be needed for the following code 1
voidmain()
{
char String [ ] = “Peace”;
cout<<setw (20) << String;
}
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerror(s)if
any.Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
First = 10, Second = 20;
Jumpto (First; Second);
Jumpto (Second);
}
void Jumpto (int N1, int N2=20)
{
N1 = N1 + N2;
cout<<N1>>N2;
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-97-320.jpg)
![309
voidmain()
{
char Text [ ] = “Mind@Work!”;
for (int I = 0; Text (I)! = ‘0’; 1++)
{
if(!isalpha(Text[I]))
Text [I] = ‘*’;
elseif(isupper(Text[I]))
Text [I] = Text [I] + 1 ;
else
Text (I) = Text [I+ 1];
}
cout<<Text;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
int U = 10, V = 20;
for (int I = 1; 1 < = 2; 1++)
{
cout<<“[1]=”<<U++<<“&”<<V–5<<endl;
cout<<“[2]=”<<++V<<“&”< <U+ 2< <endl;
}
}
(f) Inthefollowingprogram,findthecorrectpossibleoutput(s)fromtheoptions: 2
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
randomize ( ) ;
char City [ ] [10] = {“DEL”, “CHN”, “KOL”, “BOM”, “BNG”};
intFly;
for (int I=0;I<3;I++)
{
Fly=random (2)+ 1;
cout<<City[Fly]<<”:”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-98-320.jpg)
![310
}
}
outputs:
(i) DEL:CHN:KOL:
(ii) CHN:KOL:CHN:
(iii) KOL:BOM:BNG:
(iv) KOL:CHN:KOL:
2. (a) Differentiate between public and private visibility modes in context of
ObjectOrientedProgrammingusingasuitableexampleillustratingeach. 2
(b) Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following
program 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
classBazar
{
charType[20];
char Product[20];
intQty;
floatPrice;
Bazar ( ) //Function 1
{
strcpy(Type,“Electronic”);
strcpy(Product,“Calculator”);
Qty=10;
Price=225;
}
public:
void Disp ( ) / / Function 2
{
cout<<Type<<“-”<<Product<<“:”<<Qty
<<“@”<<Price<<endl;
}
};
voidmain()
{
BazarB; / /Statement 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-99-320.jpg)
![311
B. Disp ( ); / / Statement 2
}
(i) Will Statement 1 initialize all the data members for object B with the
values given in the Function I? (Yes OR No). Justify your answer
suggesting the correction(s) to be made in the above code.
(ii) What shall be the possible output when the program gets executed?
(Assuming, if required - the suggested correction(s) are made in the
program)
(c) DefineaclassGarmentsinC++withthefollowingdescriptions: 4
PrivateMembers:
GCode oftypestring
GType oftypestring
GSize oftypeinteger
GFabric oftypestring
GPrice oftypefloat
Afunction Assign ( ) which calculates and assigns the value of GPrice as
follows
For the value of GFabric as “COTTON”,
GType GPrice(Rs)
TROUSER 1300
SHIRT 1100
For GFabric other than “COTTON” the above mentioned
GPrice gets reduced by 10%.
PublicMembers:
Aconstructor to assign initial values of GCode, GType and GFabric
with the word “NOTALLOTTED” and GSize and GPrice with 0
A function Input ( ) to input the values of the data members GCode,
GType, GSize and GFabric and invoke theAssign ( ) function.
AfunctionDisplay()whichdisplaysthecontentofallthedatamembers
for a Garment.
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code: 4
classDolls
{
char DCode[5] ;
protected:
floatPrice;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-100-320.jpg)
![312
voidCalcPrice(float);
public:
Dolls();
void DInput ( ) ;
void DShow ( ) ;
} ;
classSoftDolls:publicDolls
{
char SDName[20] ;
floatWeight;
public:
SoftDolls ( ) ;
void SDInput ( ) ;
void SDShow ( ) ;
} ;
classElectronicDolls:publicDolls
{
char EDName[20] ;
charBatteryType[10];
intBatteries;
public:
ElectronicDolls();
void EDInput ( ) ;
void EDShow ( ) ;
} ;
(i) WhichtypeofInheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
(ii) How many bytes will be required by an object of the class
ElectronicDolls?.
(iii) Writenameofallthedatamembersaccessiblefrommemberfunctions
oftheclassSoftDolls
(iv) Write name of all the member functions accessible by an object of the
classElectronicDolls.
3. (a) Write a function in C++, which accepts an integer array and its size as
parameters and rearranges the array in reverse. Example: if an array of nine
elementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 7, 8, 12, 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-101-320.jpg)
![313
thenthefunctionshouldrearrangethearrayas
10, 12, 8, 7, 6, 1, 5, 2, 4 4
(b) An arrayArr[40][10] is stored in the memory along the column with each
element occupying 4 bytes. Find out the address of the locationArr[3][6]
if the locationArr[30][10] is stored at the address 9000 4
(c) Write a function in c++ to Insert an element into a dynamically allocated
Queue where each node contains a name (of type string) as data. 4
AssumethefollowingdefinitionofTHENODEforthesame.
structTHENODE
{
char Name[20] ;
THENODE*Link;
} ;
(d) Write a function in C++ to print the product of each column of a two
dimensionalintegerarraypassedastheargumentofthefunction. 2
Explain:ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
Then the output should appear as :
Product of Column 1 = 24
Product of Column 2 = 30
Product of Column 3 = 240
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression(ShowstatusofStack
after execution of each operation) : 2
4, 10, 5, +, *, 15, 3, /, –
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows: 1
classApplicant
{
longAId; //Applicant’sId](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-102-320.jpg)
![314
char Name [20] ; //Applicant’sName
floatScore; //Applicant’sScore
public:
voidEnroll();
void Disp ( ) ;
void MarksScore ( ); / /Function to change Score
longR_AId(){retumAId;)
} ;
void ScoreUpdate (long Id)
{
fstreamFile;
File.open(“APPLI.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
ApplicantA;
int Record = 0, Found = 0 ;
while (!Found && File.read((char*) &C, sizeof(c)))
{
if(Id ==A.R_AId ( ))
{
cout<<”Enter new Score” ;
A.MarksScore ( );
______________ / / Statement 1
______________ / /Statement 2
Found = 1;
}
Record ++;
}
if (Found ==1) cout<<”Record Updated”;
File.close ( ) ;
}
WritetheStatement1toposition theFilePointeratthebeginningoftheRecordfor
which the Applicant’s ld matches with the argument passed, and Statement2 to
write the updated Record at that position.
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the number of lowercase alphabets
present in a text file “BOOK.TXT”. 2
(c) GivenabinaryfilePHONE.DAT,containingrecordsofthefollowing
structuretype 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-103-320.jpg)
![315
classPhonlist
{
char Name [20] ;
charAddress[30];
charAreaCode[5];
char PhoneNo[15] ;
public:
void Register () ;
Void Show ( ) ;
int CheckCode (charAC [ ])
{
return strcmp (AreaCode,AC) ;
}
} ;
Write a functionTRANSFER ( ) in C++, that would copy all those records which
are havingAreaCode as “DEL” from PHONE.DATto PHONBACK.DAT.
5. (a) DifferentiatebetweenCandidateKeyandPrimaryKey incontextofRDBMS 2
(b) Consider the following tables Product and Client.Write SQLcommands for the
statement (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii) 6
TABLE: PRODUCT
TABLE:CLIENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-104-320.jpg)

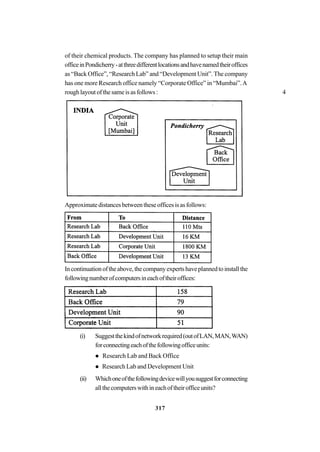
![318
Switch/Hub
Modem
Telephone
(iii) Whichofthefollowingcommunicationmedium,youwillsuggest
to be procured by the company for connecting their local office
units in Pondicherry for very effective (High Speed)
communication?
Telephone Cable
Optical Fiber
Ethernet Cable
(iv) Suggestacable/wiringlayoutforconnectingthecompany’slocal
office units located in Pondicherry.Also, suggest an effective
method/technology for connecting the company’s office unit
locatedinMumbai.
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
1. (a) What is the purpose of using a typedef command in C++. Explain with
suitableexample. 2
(b) Name the header files that shall be needed for the following code: 1
voidmain()
{
char Word [ ] =”Exam”;
cout<<setw(20)<<Word;
}
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s),ifany.
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
One = 10, Two = 20;
Callme(One;Two);
Callme(Two);
}
voidCallme(intArg1,intArg2=20)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-107-320.jpg)
![319
Arg1 =Arg1 +Arg2;
cout<<Arg1>>Arg2;
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
voidmain()
{
charMystring[]=“What@OUTPUT!”;
for(int I = 0; Mystring [I] ! =’ 0'; I++)
{
if(!isalpha(Mystring[I]))
Mystring [I] = ‘*’;
elseif(isupper(Mystring[I]))
Mystring[I]=Mystring[I]+1;
else
Mystring[I]=Mystring[I+1];
}
cout<<Mystring;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
intA=5, B=10;
for (int I = 1; I<=2; 1++)
{
cout<<“Linel=”<<A++<<“&”<<B–2<<endl;
cout<<“Line2=”<<++B<<“&”<<A+3<<endl;
}
}
(f) Inthefollowingprogram,findthecorrectpossibleoutput(s)fromtheoptions: 2
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-108-320.jpg)
![320
randomize();
charArea [] [10] = {‘‘NORTH”, ‘‘SOUTH”, “EAST”, “WEST”} ;
intToGo;
for (int I=0; 1<3; 1++)
{
ToGo = random(2) +1;
cout<<Area [ToGo]<<” : “;
}
}
outputs:
(i) SOUTH:EAST:SOUTH:
(ii) NORTH:SOUTH:EAST:
(iii) SOUTH:EAST:WEST:
(iv) SOUTH:EAST:EAST:
2. (a) Differentiatebetweenprivateand protectedvisibilitymodesincontextof
ObjectOrientedProgramminggivingasuitableexampleillustratingeach. 2
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
classRetail
{
char Category [20];
char Item [20];
intQty;
floatPrice;
Retail() //Function1
{
strcpy (Category, “Cereal”);
strcpy(Item,“Rice”);
Qty = 100;
Price = 25;
public:
void Show ( ) //Function2
{
cout<<Category<<“–”<<Item<<“:”<<Qty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-109-320.jpg)

![322
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code: 4
classToys
{
char TCode [5] ;
protected:
floatPrice;
voidAssign(float);
public:
Toys( ) ;
void TEntry ( ) ; ,
voidTDisplay();
} ;
classSoftTOYS:publicToys
{
char STName [ 20] ;
floatweight;
public:
SoftToys( ) ;
void STEntry ( ) ;
voidSTDisplay();
} ;
classElectronicToys:publicToys
{
char ETName[20];
intNo_of_Batteries;
public:
ElectronicToys();
void ETEntry ( ) ;
voidETDisplay();
} ;
(i) WhichtypeofInheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
(ii) How many bytes will be required by an object of the class SoftToys ?
(iii) Writenameofallthedatamembersaccessiblefrommemberfunctions
of the class SoftToys.
(iv) Writenameofallthememberfunctions,whichareaccessiblefroman
object of the class ElectronicToys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-111-320.jpg)
![323
3. (a) WriteafunctioninC++,whichacceptsanintegerarrayand its size as arguments
andswapstheelementsofeveryevenlocationwithitsfollowingoddlocation. 4
Example:ifanarrayofnineelementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 7, 9, 23, 10
thenthefunctionshouldrearrangethearrayas
4, 2, 6, 1, 7, 5, 23, 9, 10
(b) An arrayArr[50] [100] is stored in the memory along the row with each element
occupying2bytes.FindouttheaddressofthelocationArr[20][50],ifthelocation
Arr[10] [25] is stored at the address 10000. 4
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toDeleteanelementfromadynamicallyallocatedQueue
where each node contains a real number as data.
AssumethefollowingdefinitionofMYNODEforthesame.
struct MYNODE 4
{
floatNUM;
MYNODE*Link;
} ;
(d) Write a function in C++ to print the product of each row of a two dimensional
integer array passed as the argument of the function. 2
Example:ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
Then the output should appear as :
Product of Row 1= 8000
Product of Row 2= 6000
Product of Row 3= 3600
Product of Row 4= 2400
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression(ShowstatusofStack
after execution of each operation) : 2
5, 20, 15, –, *, 25, 2, *, +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-112-320.jpg)
![324
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows:
class Candidate
{
longCld; / /Candidate’ s Id
char CName [20]; / /Candidate’s Name
floatMarks; / /Candidate’s Marks
public:
void Enter ( ) ;
void Display ( ) ;
void MarksChange( ) ; / /Function to change marks
lond R_Cid( ) {return Cld; )
};
void MarksUpdate (long Id)
{
fstreamFile;
File.open(“CANDIDAT.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
Candidate C;
int Record=0, Found=0;
while (! Found && File.read ( (char*) &C, sizeof (C) ) )
{
if (Id= =C. R_Cld ( ) )
{
cout<<”EnternewMarks”;
C.MarksChange( ) ;
_______________ / /Statement 1
_______________ / /Statement 2
Found = 1;
}
Record++;
}
if (Found = 1) cout<<”Record Updated”;
File.close ( ) ;
}
WritetheStatement1topositiontheFilePointeratthebeginningoftheRecord
forwhichtheCandidate’sIdmatcheswiththeargumentpassed,andStatement
2 to write the updated Record at that position. 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-113-320.jpg)
![325
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the number of uppercase alphabets present
inatextfile“ARTICLE.TXT”. 2
(c) Given a binary file TELEPHON.DAT, containing records of the following
classDirectory:
classDirectory
{
char Name[20] ;
charAddress [30] ;
charAreaCode[5];
char Phone_No[15];
public:
void Register ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
int CheckCode(charAC[ ])
{
return strcmp (AreaCode,AC);
}
};
Write a function COPYABC( ) in C++, that would copy only those records
havingAreaCode as “123” fromTELEPHON.DATtoTELEBACK.DAT. 3
5. (a) Differentiate between Candidate Key and Alternate Key in context of
RDBMS. 2
(b) Consider the following tables Item and Customer.WriteSQLcommands
for the statements (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to
(viii). 6
TABLE : ITEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-114-320.jpg)

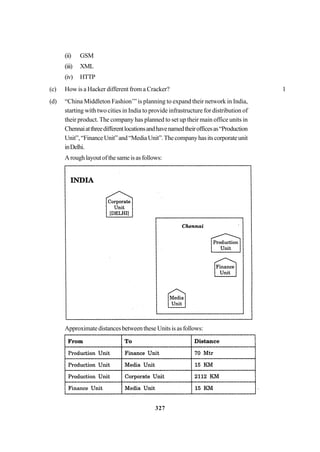


![330
(b) Name the header files that shall be needed for the following code 1
void main ( )
{
char String [ ] = “Peace”;
cout<<setw(20)<<String;
}
Ans: iostream.h
iomanip.h
(½ Mark for identifying each correct header file)
Note: Ignore any other header files, if mentioned.
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerror(s)ifany.
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include <iostream.h>
void main( )
{
First = 10 , Second = 20;
Jump to (First; Second) ;
Jumpto (Second);
}
void Jumpto(int N1, int N2=20)
{
N1 = N1 + N2;
cout<<N1>>N2;
}
Ans: #include <iostream.h>
void Jumpto(int N1, int N2=20); // Error 1
void main( )
{
int First = 10, Second = 20; // Error 2
Jumpto(First, Second); // Error 3
Jumpto(Second) ;
}
void Jumpto(int N1, int N2=20)
{
N1 = N1 + N2;
cout<<N1<<N2; // Error 4
}
OR
#include <iostream.h>
void Jumpto(int N1, int N2=20) // Error 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-119-320.jpg)
![331
{
N1 = N1 + N2;
cout<<N1<< N2; // Error 2
}
void main ( )
{
int First = 10, Second = 20; // Error 3
Jumpto(First, Second); // Error 4
Jumpto (Second) ;
}
(½ Mark for each correction)
OR
(1 Mark for identifying at least three errors, without suggesting
correction)
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void main ( )
{
char Text [ ] = “Mind@Work!”;
for (int I = 0; Text [I] !=’0’; I++)
{
if (!isalpha (Text [I])
Text [I] = ‘*’;
else if (isupper(Text [I]))
Text [I] = Text [I]+1;
else
Text (I) = Text [I+l];
}
cout<<Text;
}
Ans: Nnd@*Xrk!*
(½ Mark for N in the 1st position)
(½ Mark for nd in the 2nd and 3rd position)
(½ Mark for @ in the 4th position)
(½ Mark for * in the 5th position)
(½ Mark for Xrk!)
(½ Mark for * at the end)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-120-320.jpg)
![332
OR
(Fu1l 3 Marks If error is mentioned in the code for Text (I) after last else)
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
int U=10, V=20;
for (int I = 1; I<=2; I++)
{
cout<<“[1]=”<<U++<<“&”<<V–5<<endl;
cout<<“[2]=”<<++V<<“&”<<U+2<<endl;
}
}
Ans: [1]=10&15
[2]=21&13
[1]=11 &16
[2]=22&14
(½ Mark for each correct line of output)
Note:
½ Mark to be deducted for missing “=” and “&” symbols in the output.
½ Mark to be deducted if endl is not considered in the output
(f) Inthefollowingprogram,findthecorrectpossibleoutput(s)fromtheoptions: 2
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream.h>
void main( )
{
randomize( );
char City [ ] [10] = {“DEL”, “CHN”, “KOL”, “BOM”, “BNG”};
int Fly;
for (int I=0;1<3;1++)
{
Fly = random(2)+1;
cout<<City [Fly]<<”:”;
}
}
outputs:
(i) DEL:CHN:KOL:
(ii) CHN:KOL:CHN:
(iii) KOL:BOM:BNG:
(iv) KOL:CHN:KOL:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-121-320.jpg)

![334
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingprogram 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
class Bazar
{
char Type [20];
char Product [20];
int Qty;
float Price;
Bazar ( )
{ //Function 1
strcpy (Type,”Electronic”);
strcpy (Product,”Calculator”);
Qty = 10;
Price = 225;
}
public:
void Disp ( )
{ //Function 2
cout<<Type<<“-”<<Product<<“:”<<Qty
<<“@”<<Price<<endl;
}
};
void main ( )
{
Bazar B; //Statement 1
B. Disp ( ) ; //Statement 2
}
(i) Will Statement 1 initialize all the data members for object B with the
values given in the Function 1? (Yes OR No). Justify your answer
suggesting the correction(s) to be made in the above code.
Ans: No, since the constructor Bazar has been defined in private section
Suggested Correction: Constructor Bazar() to be ,defined in public
(½ Mark for identifying NO)
(½ Mark for justification and correction)
(ii) What shall be the possible output when the program gets executed?
(Assuming, if required - the suggested correction(s) are made in the
program)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-123-320.jpg)
![335
Ans: Iftheconstructorisdefinedasapublicmember,thefollowingoutputshallbe
generated:
Electronic-Calculator:10@225
(1 Mark for correct answer)
OR
(½ Mark each for the String and Numeric values)
(c) Define,aclassGarmentsinC++withthefollowingdescriptions: 4
PrivateMembers:
GCode oftypestring
GType oftypestring
GSize oftypeinteger
GFabric oftypestring
GPrice oftypefloat
Afunction Assign ( ) which calculates and assigns the value of GPrice as
follows
For the value ofGFabric as “COTTON”,
GType GPrice(Rs)
TROUSER 1300
SHIRT 1100
For GFabric other than “COTTON” the above mentioned
GPrice gets reduced by 10%.
PublicMembers:
Aconstructor to assign initial values of GCode, GType and GFabric
with the word “NOTALLOTTED” and GSize and GPrice with 0
A function Input ( ) to input the values of the data members GCode,
GType, GSize and GFabricl and invoke theAssign ( ) function.
AfunctionDisplay()whichdisplaysthecontentofallthedatamembers
for a Garment.
Ans:
class Garments
{
char GCode[10];
char GType[10];
int GSize;
char GFabric[10] ;
float GPrice;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-124-320.jpg)

![337
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(½ Mark for correct definition of constructor)
(1 Mark for correct definition of Assign( ))
(1 Mark for correct definition of Input( ) with proper invocation of Assign( ) function)
(½ Mark for correct definition of Display( ))
NOTE:
Deduct % Mark ifAssign( ) is not invoked properly inside Input( ) function
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code: 4
class Dolls
{
char DCode[5] ;
protected:
float Price;
void CalcPrice(float);
public:
Dolls ( );
void DInput ( ) ;
void DShow ( ) ;
} ;
class SoftDolls : public Dolls
{
char SDName[20] ;
float Weight;
public:
SoftDolls ( ) ;
void SDInput ( ) ;
void SDShow ( ) ;
} ;
class ElectronicDolls: public Dolls
{
char EDName[20] ;
char BatteryType[10];
int Batteries;
public:
ElectronicDolls ( ) ;
void EDInput ( ) ;
void EDShow ( ) ;
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-126-320.jpg)
![338
(i) WhichtypeofInheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
Ans: HierarchicalInheritance
OR
SingleLevelInheritance
(1 mark for mentioning any of the above mentioned type of Inheritance)
(ii) How many bytes will be required by an object of the class ElectronicDolls?
Ans: 41 bytes
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iii) Writenameofallthedatamembersaccessiblefrommemberfunctionsof
theclassSoftDolls
Ans: SDName,Weight, Price
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for partially correct answer
(iv) Write name of all the member functions accessible by an object of the class
ElectronicDolls.
Ans: EDInput( ), EDShow( ), DInput( ), DShow( )
(1 Mark for Correct answer)
Note:
Constructor functions ElectronicDolls( ) & Dolls( ) to be
Ignored.
No marks to be awarded for partially correct answers
3. (a) Write a function in C++, which accepts an integer array and its size as
parameters and rearranges the array in reverse. Example: if an array of nine
elementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 7, 8, 12, 10
thenthefunctionshouldrearrangethearrayas
10, 12, 8, 7, 6, 1, 5, 2, 4 4
Ans:
void Rearrange( int Arr [], int Size)
{
for (int i = 0; i<Size/2; i++)
{
int T = Arr[i];
Arr[i] = Arr[Size-1-i];
Arr[Size-1-i]=T;
}
}
OR
Any other correct equivalent function definition
(1 Mark for correct Function Header with proper Arguments)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-127-320.jpg)
![339
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(2 Marks for swapping the values correctly)
Note:
Deduct ½ Mark if loop runs till Size instead of Size/2 for swapping
Deduct ½ Mark if reversed values are stored in another array
(b) An arrayArr[40][10] is stored in the memory along the column with each
element occupying 4 bytes. Find out the address of the locationArr[3][6]
if the locationArr[30][10] is stored at the address 9000 4
Ans:
AddressofArray[i][j]alongthecolumn=
Base Address + W [( i - L1) + (j - L2) * M]
where,
W = size of each location in bytes = 4
L1 = Lower Bound of rows = 0
L2 = Lower Bound of columns = 0
M = Number of rows per column = 40
Address of Array[30][10] = Base Address + 4 * (30 + 10 * 40)
9000 = Base Address + 4 * 430
BaseAddress = 9000 - 4 x 430
= 9000 -1720
= 7280
Address ofArray[3][6] = 7280 + 4 * (3 + 6 * 40)
= 7280 + 4 * 243
= 7280 + 972
= 8252
OR
AddressofArray[i][j]alongthecolumn=
Base Address + W (( i - L1) + (j - L2) * M)
where,
W = size of each location in bytes = 4
L1 = Lower Bound of rows = 1
L2 = Lower Bound of columns = 1
M = Number of rows per column = 40
Address of Array[30][10] = Base Address + 4 * ((30 -1) +(10 -1) * 40)
9000 = Base Address + 4 * (29+9*40)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-128-320.jpg)
![340
9000 = Base Address + 4 * (29+360)
9000 = Base Address + 4 * (389)
BaseAddress = 9000 - 4 * 389
= 9000 -1556
= 7444
Address ofArray[3][6] = 7444 + 4 * ((3 -1) + (6 -1) * 40)
= 7444 + 4 * (2+5 * 40)
= 7444 + 4 * (2+200),
= 7444 + 4 * 202
= 7444 + 808
= 8252
OR
AddressofArray[i][j]alongthecolumn=
Address ofArray[x][y] + W [( i-x) + (j - y) * M]
where,
W = size of each location in bytes = 4
M = Number of rows per column = 40
i , j = Index value of the unknown element
x , y = Index value of the known element
Address ofArray[3][6] = Address of Array[30][10]+ 4 [(3 - 30) +(6 -10) * 40]
= 9000 + 4 [-27 -160]
= 9000 - 4 x 187
= 9000 -748
= 8252
(2 Marks for writing correct formula (for column major), substituting
formula with correct values and/or calculate Base Address)
(2 Marks for writing correct formula/correct substituted values, for
column major properly, for calculating Address of Arr[20][50])
(c) Write a function in c++ to Insert an element into a dynamically allocated
Queue where each node contains a name (of type string) as data. 4
AssumethefollowingdefinitionofTHENODEforthesame.
structTHENODE
{
char Name[20];
THENODE *Link;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-129-320.jpg)

![342
Rear = Temp;
}
else
{
Rear–>Link = Temp;
Rear = Temp;
}
}
(½ Mark for declaration of a temporary pointer to THENODE)
(½Markfornewallocationfortemporarypointer)
(½ Mark for assigning OR entering the value of NAME on temporary
pointer)
(½ Mark for assigning NULLto Temp->Link)
(½ Mark for checking Empty QUEUE)
(½ Mark for assigning Front and Rear in case of Empty QUEUE)
(½ Mark for assigning Rear ->Link with Temporary pointer when
QUEUEisnotEmpty)
(½MarkforreassigningRearwithTempwhentheQUEUEisnotEmpty)
(d) Write a function in C++ to print the product of each column of a two
dimensionalintegerarraypassedastheargumentofthefunction. 2
Explain:ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
Then the output should appear as :
Product of Column 1 = 24
Product of Column 2 = 30
Product of Column 3 = 240
Ans:
void ProdCol(int Arr[][100], int Row, int Col)
{
int i, j, Prod;
for (j = 0; j < Col; j++)
{
Prod=1;
for (i = 0; i < Row; i++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-131-320.jpg)
![343
Prod * = Arr[i][j];
cout<<“Product of Column”<<j<< “=” <<Prod<<endl;
}
}
OR
Any other correct equivalent function definition
(½ Mark for correct function header)
(½ Mark for correct loop(s))
(½ Mark for finding product of elements for each column correctly)
(½ Mark for printing the product in correct format)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression(ShowstatusofStack
after execution of each operation) : 2
4, 10, 5, +, *, 15, 3, /, –
Ans:
Operator Scanned Stack Content
4 4
10 4, 10
5 4, 10, 5
+ 4, 15
* 60
15 60, 15
3 60, 15, 3
/ 60, 5
- 55
OR
Anyothermethodofevaluatingcorrectlythepostfixexpressionisshowing
the Stack Status.
(½ Mark for each operation correctly evaluated showing the Stack Status)
OR
(½ Mark only to be given for writing correct answer without showing the
Stack Status)
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows: 1
class Applicant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-132-320.jpg)
![344
{
long AId; //Applicant’s Id
char Name [20] ; //Applicant’s Name
float Score; //Applicant’s Score
public:
void Enroll ( );
void Disp ( );
void MarksScore( ); //Function to change Score
long R_AId () {retumAId;)
} ;
void ScoreUpdate (long Id)
{
fstream File;
File.open (“APPLI.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
Applicant A;
int Record = 0, Found = 0 ;
while (!Found && File.read((char*) &C, sizeof(c)))
{
if(Id ==A.R_AId ( ))
{
cout<<”Enter new Score” ;
A.MarksScore ( );
______________ // Statement 1
______________ //Statement 2
Found = 1 .
}
Record ++;
}
if (Found ==1) cout<<”Record Updated”;
File.close ( ) ;
}
WritetheStatement1topositiontheFilePointeratthebeginningoftheRecord
forwhichtheApplicant’sldmatcheswiththeargumentpassed,andStatement2
to write the updated Record at that position.
Ans:
Statement 1 :
File.seekp (Record * sizeof (A));
OR
File.seekp (Record * sizeof (Applicant));
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-133-320.jpg)


![347
NOTE:
No Mark should be deducted if Count is not returned
(c) GivenabinaryfilePHONE.DAT,containingrecordsofthefollowing
structuretype 3
class Phonlist
{
char Name [20] ;
char Address[30];
char AreaCode[5];
char PhoneNo[15] ;
public:
void Register () ;
Void Show ( ) ;
int CheckCode (char AC[])
{
return strcmp (AreaCode, AC) ;
}
} ;
Write a function TRANSFER ( ) in C++, that would copy all those records
which are having AreaCode as “DEL” from PHONE.DAT to
PHONBACK.DAT.
Ans:
void TRANSFER() OR
{ ifstream fin (“PHONE.DAT”, ios: :binary);
Phonlist P; ofstream fin (“PHONBACK.DAT”, ios: :binary);
fstream fin,fout;
fin.open(“PHONE.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in);
fout.open(“PHONBACK.DAT”, ios:: binary | ios::out);
while (fin.read((char*)&P, sizeof(P)))
{
if (P. CheckCode(“DEL”) ==0)
fout.write((char*)& P,sizeof(P));
}
fin.close(); //ignore
fout.close(); //ignore
}
OR OR
void TRANSFER() ifstream fin (“PHONE.DAT”, ios: :binary);
{ ofstream fin (“PHONBACK.DAT”, ios: :binary);
Phonlist P;
fstream fin, fout;
fin. open (“PHONE. DAT”, ios: : binary | ios: : in);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-136-320.jpg)

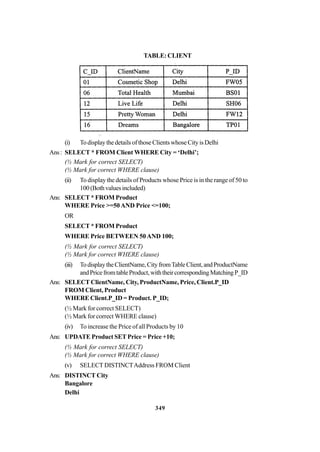

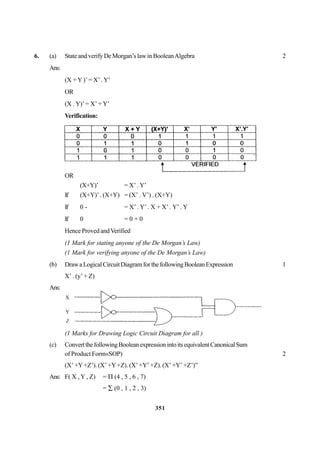

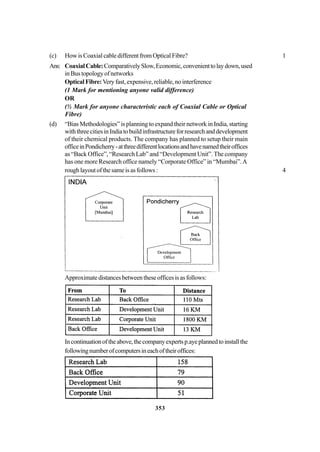

![355
MARKING SCHEME
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
EXPECTEDANSWERS
1. (a) What is the purpose of using a typedef command in C++. Explain with
suitableexample. 2
Ans: Typedef:
Thiskeywordallowscreatingsynonymsoraliasesforpreviouslydefineddata
types
Thegeneralformoftypedefis
typedefold_namenew_name;
OR
typedef is used for renaming a data type.
Example:
typedef char STR [80];
OR
typedef signed char SMALLNUM;
OR
typedef float REAL;
OR
typedef long int BIGNUM;
OR
typedef int MAT[2][3] ;
(1 Mark for definition of typedef)
(1 Mark for example of typedef)
OR
(Full 2 Marks for an example with an appropriate explanation)
(b) Name the header files that shall be needed for the following code: 1
void main ( )
{
char Word [ ] =”Exam”;
cout<<setw(20)<<Word;
}
Ans:
iostream.h
iomanip.h
(½ Mark for identifying each correct header file)
Note: Marks are not to be deducted if any additional header file is mentioned](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-144-320.jpg)
![356
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s),ifany.
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include <iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
One = 10, Two = 20;
Callme (One;Two) ;
Callme (Two) ;
}
void Callme (int Arg1, int Arg2=20)
{
Arg1 = Arg1 + Arg2;
cout<<Arg1>> Arg2;
}
Ans:
#include <iostream.h>
void Callme (int,int Arg2=20); //Error 1
void main ()
{
int One=10,Two=20; //Error 2
Callme(One,Two); //Error 3
Callme (Two);
}
void Callme (int Argl, int Arg2=20)
{
Argl=Argl +Arg2 ;
cout<<Argl<<Arg2; //Error 4
}
(½ Mark for each correction)
OR
(1 Mark for only identifying at least three errors, without suggesting
correction)
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void main ( )
{
char Mystring[ ] =“What@OUTPUT!” ;
for(int I = 0; Mystring [I] ! =’ 0'; I++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-145-320.jpg)
![357
if (!isalpha (Mystring[I]))
Mystring [I] = ‘*’;
else if (isupper (Mystring[I]))
Mystring [I] = Mystring[I] +1;
else
Mystring [I] = Mystring [I+1];
}
cout<<Mystring;
}
Ans:
Xat@*PVUQVU*
(½ Mark for X in the first position)
(½ Mark for at in the 2nd & 3rd positions)
(½ Mark for @ in the 4th position)
(½ Mark for * in the 5th position)
(½ Mark for PVUQvu)
(½ Mark for * at the end)
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram:
#include<iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
int A=5, B=10;
for (int I = 1; I<=2; 1++)
{
cout<< “Linel=”<<A++<<“&”<<B–2<<endl;
cout<<“Line2=”<<++B<<“&”<<A+3<<endl;
}
}
Ans:
Line1=5&8
Line2=11&9
Line1=6&9
Line2=12&10
(½ Mark for each correct line of output)
Note: .
½ Mark to be deducted for missingAmpersand (&) in each line of output
½ Mark to be deducted if endl is not considered in the output
(f) Inthefollowingprogram,findthecorrectpossibleoutput(s)fromtheoptions:
#include<stdlib.h>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-146-320.jpg)
![358
#include<iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
randomize() ;
char Area [] [10] = {‘‘NORTH”, ‘‘SOUTH”, “EAST”, “WEST”} ;
int ToGo;
for (int I=0; 1<3; 1++)
{
ToGo = random(2) +1;
cout<<Area [ToGo]<<” : “;
}
}
(i) SOUTH:EAST:SOUTH:
(ii) NORTH:SOUTH:EAST:
(iii)SOUTH:EAST:WEST:
(iv) SOUTH:EAST:EAST:
Ans:
(i)and(iv)
(2 Mark for the correct answer)
OR
(1 Mark for anyone of the option)
2. (a) Differentiatebetweenprivateand protectedvisibilitymodesincontextof
ObjectOrientedProgramminggivingasuitableexampleillustratingeach.
Ans: Private Visibility Mode Protected Visibility Mode
Themembersinprivatevisibility Themembersinprotectedvisibility
modes are not accessible to modes are not accessible to objects
objectsaswellasderivedclasses but are accessible in derived classes
class A
{
int x;
protected:
int y;
public:
void display(void) ;
} ;
class B:public A
{
int a;
public:
int b;
void readit(void) ;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-147-320.jpg)
![359
(1 mark for anyone correct difference given above)
(1 mark for correct example).
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingprogram:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
class Retail
{
char Category [20];
char Item [20];
int Qty;
float Price;
Retail ( ) // Function 1
{
strcpy (Category, “Cereal”);
strcpy (Item, “Rice”);
Qty = 100;
Price = 25;
}
public:
void Show ( ) // Function 2
{
cout<<Category<<“–”<<Item<<“ : ”<<Qty
<<“@”<<Price<<endl;
}
};
void main ( )
{
Retail R; // Function 1
R. Show ( );. // Function 2
}
Ans: i) No, since the constructor Retail has been defined in private section.
Suggested Correction: Constructor RetailO to be defined in public
section of class.
(½ mark for identifying No)
(½ mark for justification)
Ans: ii) Cereal-Rice:100@25
(1 full mark for the correct answer)
(c) DefineaclassClothinginC++withthefollowingdescriptions:
PrivateMembers:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-148-320.jpg)
![360
Code of type string
Type of type string
Size of type integer
Material of type string
Price of type float
AfunctionCalc_Price()whichcalculatesandassignsthevalueofPrice
asfollows:
For the value of Material as “COTTON” :
Type Price (Rs.)
TROUSER 1500
SHIRT 1200
ForMaterialotherthan“COTTON”theabovementionedPrice
gets reduced by 25%.
PublicMembers:
Aconstructor to assign initial values of Code, Type and Material with the
word “NOTASSIGNED” and Size and Price with 0.
Afunction Enter( ) to input the values of the data members Code,Type, Size
and Material and invoke the CalcPrice( ) function.
A function Show( ) which displays the content of all the data members for a
Clothing.
Ans:
class Clothing
{
char Code[25];
char Type[25];
int Size;
char Material[30];
float Price;
Public:
Clothing() ;
void Calc_Price() ;
void Enter() ;
void Show() ;
};
Clothing::Clothing()
{
strcpy(Code,”NOT ASSIGNED”);
strcpy(Type,”NOT ASSIGNED”);
Size=0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-149-320.jpg)
![361
strcpy (Material, “NOT ASSIGNED”);
Price=0;
}
void Clothing:: Calc_Price()
{
if (strcmp(Type, “TROUSER”) ==0 && strcmp (Material,“COTTON”)==0)
Price=1500;
else if (strcmp(Type, “SHIRT”) ==0 && strcmp(Material,”COTTON”)==O)
Price=1200;
else if (strcmp(Type, “TROUSER”) ==0 && strcmp(Material,”COTTON”)!=O)
Price=1500*0.75;
else if (strcmp(Type,”SHIRT”)==0) && strcmp(Material,”COTTON”)!= 0)
Price=1200*0.75;
}
void Clothing::Enter()
{
gets(Code) ; // or cin >> Code;
gets(Type) ; // or cin >> Type;
cin>>Size;
gets(Material) ;// or cin >> Material;
Calc_Price() ;
}
void Clothing::Show()
{
cout<<Code<<Type<<Size<<Material<<Price<<endl;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(½MarkforcorrectdefinitionoffunctionCalc_price())
(½ Mark for constructor)
(1 Mark for calculation of correct Price for each condition)
(½ Mark for correct Enter() with proper invocation of Calc_Price())
(½MarkfordisplayingalldataMembersinfunctionShow())
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following code:
class Toys
{
char TCode [5] ;
protected:
float Price;
void Assign (float);
public:
Toys( ) ;
void TEntry ( ) ; ,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-150-320.jpg)
![362
void TDisplay () ;
} ;
class SoftTOYS: public Toys
{
char STName [ 20] ;
float weight;
public:
SoftToys( ) ;
void STEntry ( ) ;
void STDisplay ( );
} ;
class ElectronicToys: public Toys
{
char ETName[20];
int No_of_Batteries;
public:
ElectronicToys( ) ;
void ETEntry ( ) ;
void ETDisplay ( ) ;
} ;
(i) Whichtypeofinheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
Ans: HierarchicalInheritance
OR
SingleLevelInheritance
(1 Mark to be given for mentioning any of the above mentioned type of
inheritance)
(ii) How many bytes will be required by an object of the class softToys?
Ans:
33
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iii) Writenameofallthedatamember(s)accessiblefrommemberfunctions
of class SoftToys.
Ans: Data Members: Price, STName, Weight
(1 Mark for all correct members)
NOTE:
No marks to be awarded for partially correct answers
(iv) Writenameofallthememberfunctions,whichareaccessiblefroman
object of the class ElectronicToys.
Ans:
Member Functions: TEntry ( ) , TDisplay ( ) , ETEntry ( ) , ETDisplay ( )
(1 Mark for correct answer)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-151-320.jpg)
![363
NOTE:
ConstructorsToys() & ElectronicToys(), it mentioned to be ignored.
No marks to be awarded for partially correct answers
3. (a) WriteafunctioninC++,whichacceptsanintegerarrayand its size as arguments
andswapstheelementsofeveryevenlocationwithitsfollowingoddlocation. 4
Example:ifanarrayofnineelementsinitiallycontainstheelementsas
2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 7, 9, 23, 10
thenthefunctionshouldrearrangethearrayas
4, 2, 6, 1, 7, 5, 23, 9, 10
Ans:
void Display (int NUM[ ], int N)
{
int T;
for (int I=0; I<N–l; I+=2)
{
T=N[I] ;
N[I]=N[I+1] ;
N[I+1] = T ;
}
}
(1 Mark tor correct Function Header with proper Arguments)
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(2 Marks for swapping values correctly with/without a temporary variable)
(b) An arrayArr[50] [100] is stored in the memory along the row with each element
occupying2bytes.FindouttheaddressofthelocationArr[20][50],ifthelocation
Arr[10] [25] is stored at the address 10000.
Ans:
Assuming LBR=LBC=0
S=2 bytes
Number of Rows (N)=50
Number of Columns (M)=100
LOC (Arr [I] [J]) =B + (I*M+J)*S
LOC (Arr [10] [25])=B +(10*100+25)*2
10000 = B +(1000+25)*2
B = 10000-2050
B = 7950
LOC (Arr [20] [50]) = 7950+(20*100+50)*2
= 7950 + (2050*2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-152-320.jpg)
![364
= 7950+4100
= 12050
OR
Assuming LBR=LBC=1
S=2 bytes
Number of Rows (N)=50
Number of Columns (M) =100
LOC (Arr [I] [J]) =B +((I-LBR)*M+(J-LBC))*S
LOC (Arr [10] [25]) =B +((10–1)*100+(25–1))*2
10000 = B +(900+24)*2
B = 10000-1848
B = 8152
LOC (Arr [20] [50]) = 8152+ ((20-1)*100+ (50-1))*2
= 8152 + (1949*2)
= 8152+3898
= 12050
(2 Mark for writing correct formula(for row major), substituting formula
with correct values and calculate Base Address)
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/correct substituted values, for row
major properly, for calculating Address of Arr[20][50])
(1 Mark for calculating correct Address of Arr[20][50])
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toDeleteanelementfromadynamicallyallocatedQueue
where each node contains a real number as data.
AssumethefollowingdefinitionofMYNODEforthesame.
struct MYNODE
{
float NUM;
MYNODE *Link;
} ;
Ans:
class QUEUE
{
MYNODE *Rear,*Front;
public:
QUEUE() { Rear=NULL; Front=NULL;}
void DELETE();
~QUEUE() ;
};
//Function definition DELETE()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-153-320.jpg)

![366
(d) Write a function in C++ to print the product of each row of a two dimensional
integer array passed as the argument of the function.
Example:ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
Then the output should appear as :
Product of Row 1= 8000
Product of Row 2= 6000
Product of Row 3= 3600
Product of Row 4= 2400
Ans:
// Function definition
void Display(int A[ ][3], int M, int N)
{
int I, J;
long int T; // OR int T;
cout<<“Performing Calculation:”<<endl;
for (I=0; I<M; I=I+1)
{
T=1;
for (J=0; J<N; J=J+1)
T=T*A[M][N] ;
cout<<”Product of Row “<<I+1<<”= “<<T<<endl;
}
}
OR
Any other correct equivalent function definition
(1/2 mark for correct function header)
(1/2 mark for correct loops)
(1/2 mark for calculating product)
(1/2 mark for correct initialization of T after every inner loop)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression(ShowstatusofStack
after execution of each operation) :
5, 20, 15, –, *, 25, 2, *, +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-155-320.jpg)
![367
Ans: Evaluationofthegivenpostfixexpressionisexplainedbelow
Operator Scanned Stack Content
5 5
20 5, 20
15 5, 20,15
- 5, 5
* 25
25 25, 25, 2
2 25, 25, 2
* 25, 50,
+ 75
OR
Any other method of evaluating the postfix expression is shown.
(2 Marks to be given for correct answer)
(½ Mark for each operation correctly evaluated)
(Only 1 Mark is to be awarded if correct answer is given without steps)
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefully,andanswerthequestion
thatfollows:
class Candidate
{
long Cld; / /Candidate’ s Id
char CName [20];/ /Candidate’s Name
float Marks; / /Candidate’s Marks
public:
void Enter ( ) ;
void Display ( ) ;
void MarksChange( ) ; / /Function to change marks
lond R_Cid( ) {return Cld; )
};
void MarksUpdate (long Id)
{
fstream File;
File.open (“CANDIDAT.DAT”,ios: :binary | ios: :in | ios: :out);
Candidate C;
int Record=0, Found=0;
while (! Found && File.read ( (char*) &C, sizeof (C) ) )
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-156-320.jpg)

![369
//R fstream Fi1;
//Fil.open(“ARTICLE. TXT”, ios : : in) ;
Char ch;
int c=0;
while(Fil) // OR while (!Fi1.eof())
Fil.get(ch) ; //OR ch = Fil.get();
if (isupper(ch))
//OR if (ch>=65 && ch<=90) OR if (ch>=‘A’&&ch<=‘Z’)
c++;
}
cout<<”Number of alphabets in uppercase”<<c<<endl.;
Fil.close() ;
}
OR
void theUpperAlphaCount()
{
ifstream Fil(“ARTICLE.TXT”);
//R fstream Fil;
//Fil.open(“ARTICLE. TXT”, ios:: in) ;
char ch;
int c=0;
while (Fil.get(ch))
{
if (isupper(ch))
//OR if (ch>=65 && ch<=90) OR if (ch>=‘A’ && ch<=‘Z’)
c++;
}
cout<<“Number of alphabets in uppercase”<<c<<endl;
Fil.close();
}
(½ Mark for opening file in the correct mode)
(½ Mark for reading the content from the file and the loop)
(½ Mark for correct comparison)
(½Markforinitializationandincrementofthecounter(variable))
(c) Given a binary file TELEPHON.DAT, containing records of the following
classDirectory:
class Directory
{
char Name[20] ;
char Address[30] ;
char AreaCode[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-158-320.jpg)
![370
char Phone_No[15];
public:
void Register ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
int CheckCode(char AC[ ])
{
return strcmp (AreaCode, AC);
}
};
Write a function COPYABC( ) in C++, that would copy only those records
havingAreaCode as “123” fromTELEPHON.DATtoTELEBACK.DAT.
Ans:
//Function to copy records from TELEPHON.DAT to
//TELEBAC.DAT
void COPYABC()
{
fstream IS, OA;
IS.open(“TELEPHON.DAT”, ios::binary|ios: :in);
OA.open(“TELEBACK. DAT”, ios::binary | ios:: out);
Directory D;
while (IS.read((char*)& D,sizeof(D)))
{
if (D. CheckCode(“123”)==0)
OA.write((char *)& D,sizeof(D));
}
IS.close() ;
OA.close() ;
}
OR
Anyotherequivalentcode
(½ Mark for opening each file in the correct mode)
(½ Mark for reading the content from the file)
(½ Mark for the correct loop)
(½ Mark for the correct comparison with “123”)
(½ Mark for writing the content to the second file)
5. (a) Differentiate between Candidate Key and Alternate Key in context of
RDBMS.
Ans: Candidate Key: It is the one that is capable of becoming primary key i.e., a
columnorsetofcolumnsthatidentifiesarowuniquelyintherelation.
Alternate Key:Acandidate key that is not selected as a primary key is called
anAlternateKey.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-159-320.jpg)
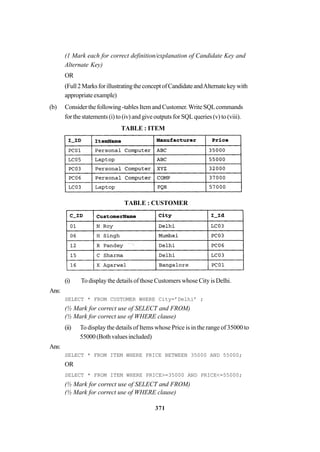



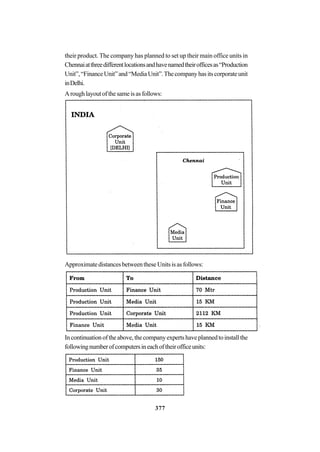
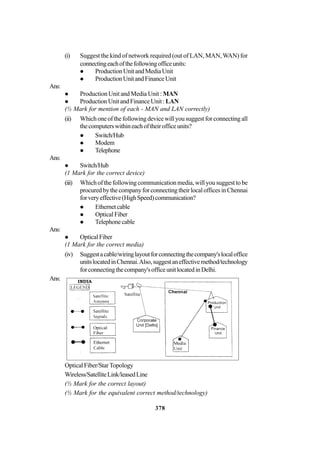
![310
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language: C+ +
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) What is the difference between call by value and call by reference? Give an
exampleinC++toillustrateboth. 2
(b) Writethenamesoftheheaderfilestowhichthefollowingbelong: 1
(i) puts( )
(ii) sin()
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include [iostream.h]
#include [stdio.h]
class Employee
{
int EmpId = 901;
char EName [20] ;
public
Employee ( ) { }
void Joining () {cin>>EmpId; gets (EName);}
void List ( ) {cout<<EmpId<<“ : ”<<EName<<endl;}
} ;
void main ( )
{
Employee E ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-168-320.jpg)
![311
Joining.E ( ) ;
E. List ( )
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
int X[ ] = {10, 25, 30, 55, 100};
int *p = X ;
while ( *p < 110)
{
if (*p%3 ! = 0)
*p = *p + 1 ;
else
*p = *p + 2 ;
p++;
}
for(int I = 4 ; 1>= 1 ; I - -)
{
cout << X[I] << “*” ;
if ( I%3 = = 0) cout<<endl ;
}
cout<<X[0]*3<<endl ;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void Encode (char Info [ ], int N) ;
void main ( )
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-169-320.jpg)
![312
char Memo [ ] = “Justnow” ;
Encode(Memo, 2) ;
cout<<Memo<<endl ;
}
void Encode(char Info[ ], int N)
{
for (int I = 0 ; Info[I] != ‘0’ ; 1++)
if (1%2= =0)
Info[I] = Info[I] –N ;
else if (islower(Info[I]))
Info[I] = toupper(Info[I]) ;
else
Info[I] = Info[I] +N ;
}
(f) Studythefollowingprogramandselectthepossibleoutputfromit: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int LIMIT = 4 ;
void main ( )
{
randomize ( ) ;
int Points;
Points = 100 + random(LIMIT) ;
for (int P=Points ; P>=100 ; P– –)
cout<<P<<“#” ;
cout<<endl;
}
(i) 103#102#101#100#
(ii) 100#101#102#103#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-170-320.jpg)

![314
PrivateMembers
Rno //Data member to store Room No
Name //Data member to store customer name
Charges //Data member to store per day charges
Days //Data member to store number of days of stay
COMPUTE( ) //A function to calculate’ and return Amount as
Days*Charges and if the value of Days*Charges is more than 11000
then as 1.02*Days*Charges
PublicMembers
Getinfo() //A function to enter the content Rno, Name,
//Charges and Days
Dispinfo() //A function to display Rno, Name, Charges,
//Days andAmount (Amount to be displayed by
//calling function COMPUTE ( ) )
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class FaceToFace
{
char CenterCode [10] ;
public:
void Input ( ) ;
void Output ( ) ;
} ;
class Online
{
char website [50] ;
public:
void SiteIn ( ) ;
void SiteOut ( ) ;
} ;
class Training: public FaceToFace, private Online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-172-320.jpg)
![315
{
long Tcode ;
float charge;
int period;
public:
void Register ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
} ;
(i) WhichtypeofInheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
(ii) WritenamesofallthememberfunctionsaccessiblefromShow()functionof
classTraining.
(iii) WritenameofallthemembersaccessiblethroughanobjectofclassTraining.
(iv) Is the function Output( ) accessible inside the function SiteOut( ) ? Justify
youranswer.
3. (a) Write a function SORTPOINTS( ) in C++ to sort an array of structure Game
in descending order of Points using Bubble Sort. 3
Note:AssumethefollowingdefinitionofstructureGame
struct Game
{
long PNo; //Player Number
char PName [20] ;
long Points;
} ;
Sample content of the array (before sorting)
PNo PName Points
103 RitikaKapur 3001
104 JohnPhilip 2819
101 RaziaAbbas 3451
105 TarunKumar 2971](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-173-320.jpg)
![316
Sample content of the array (after sorting)
PNo PName Points
101 RaziaAbbas 3451
103 Ri tika Kapur 3001
105 TarunKumar 2971
104 JohnPhilip 2819
(b) An array S[40][30]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwith each of the
element occupying 4 bytes, find out the base address and address of element
S[20][15], if an element S[15][10] is stored at the memory location 7200. 4
(c) Write a function QUEINS( ) in C++ to insert an element in a dynamically
allocatedQueuecontainingnodesofthefollowinggivenstructure: 4
struct Node
{
int PId ; //Product Id
char Pname [20] ;
NODE *Next ;
} ;
(d) DefineafunctionSWAPCOL()inC++toswap(interchange)thefirstcolumn
elements with the last column elements, for a two dimensional integer array
passed as the argument of the function. 3
Example:Ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
2 1 4 9
1 3 7 7
5 8 6 3
7 2 1 2
After swapping of the content of 1st column and last column, it should be :
9 1 4 2
7 3 7 1
3 8 6 5
2 2 1 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-174-320.jpg)
![317
(e) Convert the following infix expression to its equivalent postfix expression
showingstackcontentsfortheconversion: 2
X–Y /(Z + U) * V
4. (a) Observe the program segment given below carefully and fill in the blanks
markedasLine1andLine2usingfstreamfunctionsforperformingthere-
quired task. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Stock
{
long Ino ; //Item Number
char Item [20] ;//Item Name
int Qty ; //Quantity
public:
void Get(int) ;//Function to enter the content
void show ( ) ;//Function to display the content
void Purchase (int Tqty)
{
Qty + = Tqty ;
} //Function to increment in Qty
long KnowIno ( ) {return Ino ;}
} ;
void Purchaseitem (long PINo, int PQty)
//PINo -> Ino of the item purchased
//PQty -> Number of item purchased
{
fstream File;
File.open(“ITEMS.DAT”, ios :: binarylios ::
inlios :: out);
int Pos = –1 ;
Stock S ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-175-320.jpg)

![319
class USER
{
int Uid ; //User Id
char Uname [20];//User Name
char Status; //User Type: A Active I Inactive
Public:
void Register ( ) ;//Function to enter the content
void show ( ) ; //Function to display all data
members
char Getstatus ( ) {return Status;}.
} ;
5. (a) What are candidate keys in a table? Give a suitable example of candidate
keys in a table. 2
(b) Consider the following tables GARMENT and FABRIC. Write SQL
commands for the statements (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries
(v)to(viii) 6
Table:GARMENT
Table : FABRIC
FCODE TYPE
F04 POLYSTER
F02 COTTON
F03 SILK
F01 TERELENE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-177-320.jpg)

![323
int StudentId = 1001;
char Name [20] ;
public
MyStudent( ){ }
void Register ( ) {cin>>StudentId; gets (Name) ;}
void Display ( ) {cout<<StudentId<< “:” <<Name<<end1;}
} ;
void main ( )
{
MyStudent MS ;
Register.MS( ) ;
MS.Display( ) ;
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
int A[ ] = {10, 15, 20, 25, 30}
int *p = A;
while (*p < 30)
{
if (*p%3 ! = 0)
*p = *p + 2 ;
else
*p = *p + 1;
p++;
}
for (int J = 0; J<=4; J++)
{
cout << A[J] << “*” ;
if ( J%3 = = 0) cout<<end1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-181-320.jpg)
![324
}
Cout<<A[4] * 3<<end1;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void Secret (char Mig [ ], int N);
void main ( )
{
char SMS[ ] = “rEPorTmE” ;
Secret{SMS,2);
cout<<SMS<<end1;
}
void Secret(char Msg[ ], int N)
{
for (int C=0; Msg[C] ! =’ 0' ;C++)
if (C%2==0)
Msg[C] = Msg[C]+N;
else if (isupper(Msg[C]))
Msg[C] = tolower(Msg[C]);
else
Msg[C] = Msg[C]-N;
}
(f) Studythefollowingprogramandselectthepossibleoutputfromit: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int MAX=3 ;
void main ( )
{
randomize( ) ;
int Number ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-182-320.jpg)

![326
(i) WhichmemberfunctionoutofFunction1,Function2,Function3andFunction
4shownintheabovedefinitionofclassJobiscalledautomatically,whenthe
scope of an object gets over? Is it known as Constructor OR Destructor OR
Overloaded Function OR Copy Constructor?
(ii) Job P ; //Line 1
Job Q(P) ; //Line 2
WhichmemberfunctionoutofFunction1,Function2,Function3andFunction
4 shown in the above definition of class Job will be called on execution of
statementwrittenasLine2?Whatisthisfunctionspecificallyknownasoutof
Destructor or Copy Constructor or Default Constructor?
(c) DefineaclassHOTELinC++withthefollowingdescription: 4
PrivateMembers:
Rno //Data member to store Room No
Name //Data member to store customer name
Tariff //Data member to store per day charges
NOD //Data member to store number of days of stay
CALC( ) //Afunction to calculate and returnAmount as NOD*Tariff
and if the value of NOD*Tariff is more than 10000 then as
1.05*NOD*Tariff
PublicMembers
Checkin ( ) / /Afunction to enter the content Rno, Name,
/ / Tariff and NOD
Checkout( ) / /Afunction to display Rno, Name, Tariff,
/ /NOD andAmount (Amount to be displayed by
//callingfunctionCALC())
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class Regular
{
char SchoolCode[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-184-320.jpg)
![327
public:
void InRegular( );
void OutRegular( );
} ;
class Distance
{
char StudyCentreCode [‘5] ;
public:
void InDistance( );
void OutDistance ( );
} ;
class Course: public Regular, private Distance
{
char Code [ 5] ;
float Fees;
int Duration;
public:
void InCourse( );
void OutCourse( );
} ;
(i) WhichtypeofInheritanceisshownintheaboveexample?
(ii) Write names of all the member functions accessible from OutCourse
functionofclassCourse.
(iii) Write name of all the members accessible througb an object of class
Course.
(iv) IsthefunctionInRegular()accessibleinsidethefunctionInDistance()?
Justifyyouranswer.
3. (a) WriteafunctionSORTSCORE()inC++tosortanarrayofstructureExaminee
in descending order of Score using Bubble Sort. 3
Note:AssumethefollowingdefinitionofstructureExaminee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-185-320.jpg)
![328
struct Examinee
{
long RollNo;
char Name [20] ;
float Score;
} ;
Sample Content of the array (before sorting)
Sample Content of the array (after sorting)
(b) An array T[50][20] is stored in the memory along the column with each of
the elements occupying 4 bytes. Find out the base address and address of
element T[30][15], if an element T[25][10] is stored at the memory location
9800. 4
(c) Write a function QUEDEL( ) in C++ to display and delete an element from
a dynamically allocated Queue containing nodes of the following given
structure: 4
struct NODE
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-186-320.jpg)
![329
int Itemno;
char Itemname[20];
NODE *Link;
} ;
(d) Define a function SWAPARR( ) in C++ to swap (interchange) the first row
elements with the last row elements, for a two dimensional integer array
passed as the argument of the function. 3
Example:Ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
5 6 3 2
1 2 4 9
2 5 8 1
9 7 5 8
After swapping of the content of first row and last row, it should be as follows:
9 7 5 8
1 2 4 9
2 5 8 1
5 6 3 2
(e) Convert the following infix expression to its equivalent postfix expression
showingstackcontentsfortheconversion: 2
A + B * (C – D) / E
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmarked.
asLine1andLine2usingfstreamfunctionsforperformingtherequiredtask. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Library
{
long Ano; //Ano - Accession Number of the Book
char Title[20]; //Title - Title of the Book
int Qty; //Qty - Number of Books in Library
public:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-187-320.jpg)

![331
Example:
Ifthecontentofthefile“NOTES.TXT”isasfollows:
It is very important to know that
smokingisinjurioustohealth.
Let us take initiative to stop it.
ThefunctionCOUNT_TO()willdisplaythefollowingmessage:
Count of -to- in file: 3
Note: In the above example, ‘to’ occurring as a part of word stop is not
considered.
(c) Write a function in C++ to read and display the detail of all the members
whose membership type is ‘L’or ‘M’from a binary file “CLUB.DAT”.
Assume the binary file “CLUB.DAT” contains objects of class CLUB,
whichisdefinedasfollows: 3
class CLUB
{
int Mno; //Member Number
char Mname [20]; //Member Name
char Type;//Member Type:L Life Member M Monthly Member G Guest
public:
void Register();//Function to enter the content
void Display(); //Function to display all data
members char WhatType() {return Type;}.
} ;
5. (a) What is the purpose of a key in a table? Give an example of a key in a table. 2
(b) Consider the following tables DRESS and MATERIAL. Write SQL
commands for the statements (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v)
to(viii). 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-189-320.jpg)
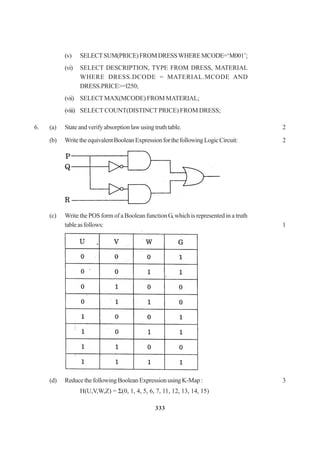




![338
Ans (i) stdio.h (ii) math. h
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include [iostream.h]
#include [stdio.h]
class Employee
{
int EmpId=901;
char EName [20] ;
public
Employee(){}
void Joining() {cin>>EmpId; gets (EName);}
void List () {cout<<EmpId<<” : “<<EName<<endl;}
};
void main ()
{
Employee E;
Joining.E();
E.List()
}
Ans #include <iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
class Employee
{ int EmpId;
char EName[20];
public :
Employee() {EmpId=901;}
void Joining() {cin>>EmpId; gets (EName);}
void List () {cout<<EmpId<<”: “<<EName<<endl;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-196-320.jpg)
![339
};
void main ()
{ Employee E;
E.Joining ();
E.List ();
}
(½ Mark for writing both header files inside < >)
(½ Mark for removing = 901 from int Empld = 901;)
(½Markforwriting:afterpublicand;afterE.List())
(½MarkforwritingE.Joining();correctly)
Note: ½markforidentifyinganytwoerrorswithoutvalidcorrectionand1
markforidentifyingallfiveerrorswithoutvalidcorrection
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void main ()
{
int X[] = {10,25,30,55,110};
int *p = X;
while ( *p < 110)
{
if ( *P%3 != 0 )
*p=*p+1;
else
*p = *p + 2;
p++;
}
for(int I = 4; I>=l ; I--)
{
cout << X[I] << “*" ;
if ( I%3 == 0) cout<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-197-320.jpg)
![340
}
cout<<X[0] * 3<<endl;
}
Ans 1110*56*
32*26*33
(½ Mark for each correct value)
(½ Mark for all correct endl and *)
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void Encode (char Info [ ], int N) ;
void main ( )
{
char Memo [ ] = “Justnow” ;
Encode (Memo, 2) ;
cout<<Memo<<endl ;
}
void Encode (char Info [ ], int N)
{
for (int I = 0 ; Info[I] !=‘0’ ; 1++)
if (1%2= =0)
Info[I] = Info[I] –N ;
else if (islower(Info[I]))
Info[I] = toupper(Info[I]) ;
else
Info[I] = Info[I] +N ;
}
Ans HuqTlOu
(½ Mark for writing H, U as the first two characters)
(½ Mark for writing q, T as the next two characters)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-198-320.jpg)


![343
Number=N;
}
void main ()
{
Play P; //Call for constructor
P.Disp (); P.Change(90,80) ;
Play Q(P); //Copy constructor call
Q.Disp();
Play R=Q; //Copy constructor ca11 [same as P1ay R(Q);]
R. Disp();
}
(1 Mark for correct explanation of Copy Constructor)
(1 Mark for a valid example of Copy Constructor)
Note: Member function other than the constructors are optional
(b) Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class:
class WORK 2
{
int WorkId;char WorkType ;
public:
-WORK ( ) //Function 1
{ cout<<”Un-Allocated”<<endl ;}
void status ( ) //Function 2
{ cout<<WorkId<<”: “<<WorkType<<endl ;}
WORK ( ) //Function 3
{ WorkId = 10; WorkType=’T’ ; }
WORK(WORK &W) //Function 4
{
WorkId=W. WorkId+12;WorkType=W. WorkType+l
}
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-201-320.jpg)

![345
Dispinfo() //A function to display Rno, Name, Charges,
//Days andAmount (Amount to be displayed by
//calling function COMPUTE ( ) )
Ans class RESORT
{
int Rno;
char Name [20];
float Charges;
int Days;
float COMPUTE();
public:
void Getinfo() ;
void Dispinfo();
};
void RESORT::Getinfo()
{
cin>>Rno;
gets (Name);
cin>>Charges;
cin>>Days;
}
void RESORT::Dispinfo()
{
cout<<Rno<<” “<<Name<<“ “<<Charges<<” “<<Days<<
COMPUTE()<<endl;
}
float RESORT::COMPUTE(}
{
float Amount = Charges*Days;
if (Amount>11000)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-203-320.jpg)
![346
Amount = 1.02*Days*Charges;
return Amount;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of COMPUTE ( )) .
(1 Mark for correct definition of Dispinfo( ) with proper invocation of
COMPUTEOfunction)
(1 Mark for correct definition of Getinfo( ))
NOTE: Deduct ½ Mark if COMPUTE( ) is not invoked properly inside
Dispinfo()function
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class FaceToFace
{
char CenterCode [10] ;
public:
void Input ( ) ;
void Output ( ) ;
} ;
class Online
{
char website [50] ;
public:
void SiteIn ( ) ;
void SiteOut ( ) ;
} ;
class Training: public FaceToFace, private Online
{
long Tcode ;
float charge;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-204-320.jpg)

![348
is accessible inside the function InDistance( ) ONLYfor an object of the derived class OR in
contextofInheritance)
NOTE: No mark to be awarded if onlyYES is written without any justification.
3. (a) Write a function SORTPOINTS( ) in C++ to sort an array of structure Game
in descending order of Points using Bubble Sort. 3
Note:AssumethefollowingdefinitionofstructureGame
struct Game
{
long PNo; //Player Number
char PName [20] ;
long Points;
} ;
Sample content of the array (before sorting)
PNo PName Points
103 RitikaKapur 3001
104 JohnPhilip 2819
101 RaziaAbbas 3451
105 TarunKumar 2971
Sample content of the array (after sorting)
PNo PName Points
101 RaziaAbbas 3451
103 Ri tika Kapur 3001
105 TarunKumar 2971
104 JohnPhilip 2819
Ans void SORTPOINTS(Game G[], int N)
{
Game Temp;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-206-320.jpg)
![349
for (int I = 0; I<N-l; I++)
for (int J = 0; J<N-I-l; J++)
if(G[J].Points < G[J+l].Points)
{
Temp = G[J];
G[J] = G[J+l];
G[J+l] = Temp;
}
{
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
( ½ Mark for correct Function Header)
( ½ Mark for each correct loop)
( 1 Mark for correct comparison of adjacent elements)
( ½ Mark for swapping the values correctly)
Note:
Deduct ½ Mark if sorted in ascending order instead of descending order
Deduct ½ Mark if only Points is swapped instead of the whole Structure
Deduct ½ Mark ifTemp is not declared with correct data type
(b) An array S[40][30]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwith each of the
element occupying 4 bytes, find out the base address and address of element
S[20][15], if an element S[15][10] is stored at the memory location 7200. 4
Ans Loc(S[I][J]) = Base(S)+W(I+J*N)
Loc(S[15][10]) = Base(S)+4(15+10*40)
Base(S) = 7200-4*415
Base(S) = 7200-1660
Base(S) = 5540
Loc(S[20][15]) = Base(S)+4(20+15*40)
Loc(S[20][15]) = 5540 + 4(20+15*40)
= 5540 + 4(20+600)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-207-320.jpg)
![350
= 5540 + 4*620
= 5540 + 2480
= 8020
OR
Address of S[i][j]=BaseAddress + W[(i-L1) + ( j - L2) *M]
Address of S[15] [10] = BaseAddress+ 4[(15–0)+(10 - 0)*40]
7200= Base Address + 4 [415]
Base Address = 7200 - 4 * 415
= 7200 - 1660
= 5540
Address of S[20][15]= 5540 + 4 [(20 - 0) + (15 - 0) x 40]
= 5540 + 4 x 620
= 5540 + 2480
= 8020
OR
Address of Sri] [j] along the column =
Base Address + W [( i - L1) + (j - L2) * M]
Address of S[15)[10] = BaseAddress + 4[(15 - 1)+(10-1) x 40]
7200= Base Address + 4 [374]
Base Address = 7200 - 4 x 374
= 7200 - 1496
= 5704
Address of 5[20)[15] = 5704 + 4 [(20 - 1) + (15 - 1) x 40]
= 5704 + 4 x 579
= 5704 + 2316
= 8020
(1Markforwritingcorrectformula(forcolumnmajor)ORsubstitutingformula
with correct values for calculating correct BaseAddress)
(1 Mark for calculating correct BasgAddress)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-208-320.jpg)
![351
(1 Mark for writing correct formula/correct substituted values, for column
major properly, for calculatingAddress of 5[20][15])
(1 Mark for calculating correct address of 5[20][15])
(c) Write a function QUEINS( ) in C++ to insert an element in a dynamically
allocatedQueuecontainingnodesofthefollowinggivenstructure: 4
struct Node
{
int PId ; //Product Id
char Pname [20] ;
NODE *Next ;
} ;
Ans class Queue
{
Node *Front, *Rear;
public:
QUEUE() //Constructor to initia1ize Front and Rear
{
Front = NULL;
Rear = NULL;
}
void QUEINS(); //Function to insert a node
void QUEDEL(); //Function to de1.ete a node
void QUEDISP(); //Function to disp1ay nodes
~Queue(); //Destructor to de1ete a11 nodes
} ;
void Queue::QUEINS( )
{
Node *Temp;
Temp = new Node;
cin>>Temp->PId;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-209-320.jpg)

![353
(½ Mark for assigning NULLtoTemp->Next)
(½ Mark for checking Empty Queue)
(½ Mark for assigning Front withTemp in case of empty queue)
(½ Mark for assigning Rear ->Next withTemp when queue is not empty)
(½ Mark for assigning RearwithTemp)
(d) DefineafunctionSWAPCOL()inC++toswap(interchange)thefirstcolumn
elements with the last column elements, for a two dimensional integer array
passed as the argument of the function. 3
Example:Ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
2 1 4 9
1 3 7 7
5 8 6 3
7 2 1 2
After swapping of the content of 1st column and last column, it should be :
9 1 4 2
7 3 7 1
3 8 6 5
2 2 1 7
Ans void SWAPCOL(int A[][100], int M, int N)
{
int Temp, I;
for(I=O; I<M; I++)
{
Temp = A [I][0] ;
A[I][0] = A[I][N-l];
A[I][N-l] = Temp;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-211-320.jpg)
![354
OR
void SWAPCOL(int A[4][4])
{
int Temp, I;
for(I=O; I<4; I++)
{
Temp = A[I][0];
A[I][0] = A[I][3];
A[I][3] = Temp;
}
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition.
(1 Mark for correct function header)
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(1Markforswappingthefirstcolumnwithlastcolumncorrectly)
(e) Convert the following infix expression to its equivalent postfix expression
showingstackcontentsfortheconversion: 2
X–Y /(Z + U) * V
Ans X - Y / (Z + U) * v
= (X - ((Y / (Z + U)) * v))
Element Scanned Stack Postfix
(
X X
- -
(
(
Y XY
/ -/
(](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-212-320.jpg)

![356
#include <fstream.h>
class Stock
{
long Ino ; //Item Number
char Item [20] ;//Item Name
int Qty ; //Quantity
public:
void Get(int) ;//Function to enter the content
void show ( ) ;//Function to display the content
void Purchase (int Tqty)
{
Qty + = Tqty ;
} //Function to increment in Qty
long KnowIno ( ) {return Ino ;}
} ;
void Purchaseitem (long PINo, int PQty)
//PINo -> Ino of the item purchased
//PQty -> Number of item purchased
{
fstream File;
File.open(“ITEMS.DAT”, ios :: binarylios ::
inlios :: out);
int Pos = –1 ;
Stock S ;
while (Pos = = –1 && File.read((char*) &S, sizeof (S)))
if (S. KnowIno( ) ==PINo)
{
S. Purchase (PQty); //To update the number of Items
Pos = File.tellg ( ) -sizeof (S) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-214-320.jpg)

![358
Example:
Ifthecontentofthefile“MEMO.TXT”isasfollows:
I will do it, if you
request me to do it.
It would have been done much earlier.
ThefunctionCOUNT_DO()willdisplaythefollowingmessage:
Count of -do- in file : 2
Note: In the above example, ‘do’ occurring as a part of word done is not
considered.
Ans void COUNT_DO ()
{
ifstream Fi1;
Fil.open(“MEMO.TXT”);
char Word[80];
int Count =0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>Word;
if (strcmp (Word, “do”) ==0)
Count++;
}
cout<<”Count of -do- in file:”<<Count;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}
OR
void COUNT_TO ()
{
ifstream Fi1(“MEMO.TXT”);
//OR fstream Fi1;
OR ifstream Fil(“MEMO.TXT”);
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-216-320.jpg)
![359
//Fi1.open (“NOTES. TXT”, ios::in);
char. STR[10];
int c=0;
whi1e(Fi1.qet1ine(STR,10, ‘ ‘))
{
if (strcmpi (STR, “to”) =0)
c++;
}
Fi1.c1ose();//Ignore
cout<<”Count of -to- in file : “<<c<<end1;
}
OR
void COUNT_DO ()
{
ifstream Fi1;
Fil.open(“MEMO.TXT”);
char Word[80],Ch;
int Count =0, I=0;
while(Fi1.get(Ch))
{
if (Ch! = ‘ ‘)
Word[I++] = Ch;
else
{
Word[I] = ‘0’;
if (strcmp (Word, “do”) ==0)
Count++;
I=O;
}
}
OR ifstream Fil(“MEMO.TXT”);
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-217-320.jpg)
![360
cout<<”Count of -do- in file:”<<Count;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}
OR
Anyothercorrectfunctiondefinition
(½ Mark for opening MEMO. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (Whichever method adopted) from the file)
(½ Mark for comparing the word with ‘do’ and incrementing counter)
(½ Mark for displaying the number of ‘do’with/without theText Message)
(c) Write a function in C++ to read and display the detail of all the users whose
statusis‘A’(i.e.Active)fromabinaryfile“USER.DAT”.Assumingthebinary
file “USER.DAT” is containing objects of class USER, which is definedas
follows: 3
class USER
{
int Uid ; //User Id
char Uname [20];//User Name
char Status; //User Type: A Active I Inactive
Public:
void Register ( ) ;//Function to enter the content
void show ( ) ; //Function to display all data
members
char Getstatus ( ) {return Status;}.
} ;
Ans void DisplayActive ()
{
USER U;
ifstream fin;
fin.open (“USER.DAT”, ios::binary);
OR
ifstream fin (“USER.DAT”, ios::binary);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-218-320.jpg)

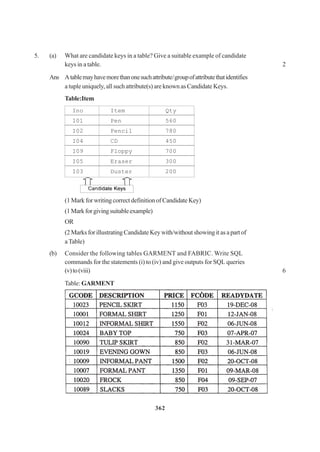


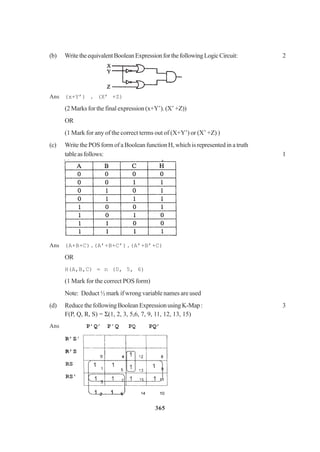




![370
void main ()
{
int P=6;
Seventimes(P);//p is actual parameter
}
(½ Mark for each correct explanation of Actual Parameter and Formal
Parameter)
(½ Mark for each correct example of Actual Parameter and Formal
Parameter)
OR
(Full 2 Marks for correct examples demonstrating the difference between
Actual Parameter and Formal Parameter)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded for Explanation given without supporting
examples)
(b) Writethenamesoftheheaderfilestowhichthefollowingbelong: 1
(i) setw( )
(ii) sqrt( )
Ans (i) iomanip.h (ii) math.h
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include <iostream.h>
include <stdio.h>
class MyStudent
{
int StudentId = 1001;
char Name [20] ;
public
MyStudent( ){ }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-228-320.jpg)
![371
void Register ( ) {cin>>StudentId; gets (Name) ;}
void Display ( ) {cout<<StudentId<< “:” <<Name<<end1;}
} ;
void main ( )
{
MyStudent MS ;
Register.MS( ) ;
MS.Display( ) ;
}
Ans # include <iostream.h>
# include <stdio.h>
class MyStudent
{ int StudentId;
char Name[20];
public :
MyStudent() {StudentId = 1001;}
void Register(){ cin>>StudentId; gets (Name);}
void Display () {cout«StudentId<<”:“<<Name<<endl;}
};
void main ()
{
MyStudent MS;
MS. Register ();
MS. Display () ;
}
(½Markforwritingbothincludeas#include)
(½ Mark for removing = 1001 from int StudentId = 1001;)
(½Markforwriting:afterpublic)
(½ Mark for writing MS. Register ( ) ; correctly)
Note: ½ mark for identifying any two errors without valid correction and
1markforidentifyingallfiveerrorswithoutvalidcorrection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-229-320.jpg)
![372
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void main ( )
{
int A[ ] = {10, 15, 20, 25, 30}
int *p = A;
while (*p < 30)
{
if (*p%3 ! = 0)
*p = *p + 2 ;
else
*p = *p + 1;
p++;
}
for (int J = 0; J<=4; J++)
{
cout << A[J] << “*” ;
if ( J%3 = = 0) cout<<end1;
}
Cout<<A[4] * 3<<end1;
}
Ans 12*
16*22*27*
30*90
(1 Mark for each line with correct values)
Note:
Deduct½Markifany/all‘*’missing
Deduct ½ Mark if endl is not considered at the right positions
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-230-320.jpg)
![373
void Secret (char Mig[ ], int N);
void main ( )
{
char SMS[ ] = “rEPorTmE” ;
Secret{SMS,2);
cout<<SMS<<end1;
}
void Secret(char Msg[ ], int N)
{
for (int C=0; Msg[C] !=’ 0' ;C++)
if (C%2==0)
Msg[C] = Msg[C]+N;
else if (isupper(Msg[C]))
Msg[C] = tolower(Msg[C]);
else
Msg[C] = Msg[C]-N;
}
Ans teRmttoe
(½ Mark for writing t,e as the first two characters)
(½ Mark for writing R,m as the next two characters)
(½ Mark for writing t,t as the next two characters)
(½ Mark for writing o,e as the next two characters)
(f) Studythefollowingprogramandselectthepossibleoutputfromit: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int MAX=3 ;
void main ( )
{
randomize( ) ;
int Number ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-231-320.jpg)



![377
Ans class HOTEL
{
int Rno;
char Name[20];
float Tariff;
int NOD;
float CALC() ;
public:
void Checkin() ;
void Checkout() ;
} ;
float HOTEL::CALC()
{
float Amount = Tariff*NOD;
if (Amount>10000)
Amount = 1.05*NOD*Tariff;
return Amount;
}
void HOTEL::Checkin()
{
cin>>Rno;
gets (Name);
cin>>Tariff;
cin>>NOD;
}
void HOTEL::Checkout()
{
cout<<Rno<<” “<<Name<<“ “<<Tariff<<” “<<NOD<<
CALC ()<<endl;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-235-320.jpg)
![378
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of CALC( ))
(1 Mark for correct definition of Checkout( ) with proper invocation of
CALC()function)
(1 Mark for correct definition of Checkin())
NOTE:Deduct½MarkifCALC()isnotinvokedproperlyinsideCheckout()
function
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class Regular
{
char SchoolCode[10];
public:
void InRegular( );
void OutRegular( );
} ;
class Distance
{
char StudyCentreCode [5] ;
public:
void InDistance( );
void OutDistance( );
} ;
class Course: public Regular, private Distance
{
char Code [ 5] ;
float Fees;
int Duration;
public:
void InCourse( );
void OutCourse( );
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-236-320.jpg)

![380
Note:AssumethefollowingdefinitionofstructureExaminee
struct Examinee
{
long RollNo;
char Name[20] ;
float Score;
} ;
Sample Content of the array (before sorting)
Sample Content of the array (after sorting)
I
Ans void SORTSOORE (Examinee E[ ], int N)
{
Examinee Temp;
for (int I = 0; I<N-l; I++)
for (int J = 0; J<N-I-l; J++)
if(E[J].Score < E[J+l].Score)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-238-320.jpg)
![381
Temp = E[J];
E[J] = E[J+l];
E[J+l] = Temp;
}
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
( ½ Mark for correct Function Header)
( ½ Mark for each correct loop)
( 1 Mark for correct comparison of adjacent elements)
( ½ Mark for swapping the values correctly)
Note:
Deduct ½ Mark if sorted in ascending order instead of descending order
Deduct ½ Mark if only Score is swapped instead of the whole Structure
Deduct ½ Mark ifTemp is not declared with correct data type
(b) An array T[50][20] is stored in the memory along the column with each of
the elements occupying 4 bytes. Find out the base address and address of
element T[30][15], if an element T[25][10] is stored at the memory location
9800. 4
Ans Loc(T[I][J]) = Base(T)+W(I+J*N)
Loc(T[25][10]) = Base(T)+4(25+10*50)
Base(T) = 9800-4*525
Base(T) = 9800-2100
Base(T) = 7700
Loc(T[30][15]) = Base(T)+4(30+15*50)
Loc(T[30][15]) = 7700 + 4(30+15*50)
= 7700 + 4(30+750)
= 7700 + 4*780
= 7700 + 3120
= 10820](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-239-320.jpg)
![382
OR
Address of T[i][j]=BaseAddress + W [(i - L1) + (j - L2) * M]
Address of T[25] [10] = BaseAddress + 4[(25 - 0)+(10 - 0)*50]
9800 = Base Address + 4 [525]
Base Address = 9800 - 4 * 525
= 9800 - 21.00
= 7700
Address of T[30][15]= 7700 + 4 [(30 - 0) + (15 - 0) x 50]
= 7700 + 4 x 780
= 7700 + 3120
= 10820
OR
Address of T[i][j] along the column =
Base Address + W [( i - L1) + (j - L2) * M]
Address of T[25][10]=BaseAddress + 4[(25 - 1) +(10 -1) x 50]
9800= Base Address + 4 [474]
Base Address = 9800 - 4 x 474
= 9800 - 1896
= 7904
Address of T[30][15] = 7904 + 4 [(30 - 1) + (15 - 1) x 50]
= 7904 + 4 x 729
= 7904 + 2916
= 10820
(1Markforwritingcorrectformula(forcolumnmajor)ORsubstitutingformula
with correct values for calculating correct BaseAddress)
(1 Mark for calculating correct BaseAddress)
(1Markforwritingcorrectformula(forcolumnmajor)ORsubstitutingformula
with correct values for calculatingAddress ofT[30][15])
(1 Mark for calculating correct address of T[30][15])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-240-320.jpg)
![383
(c) Write a function QUEDEL( ) in C++ to display and delete an element from
a dynamically allocated Queue containing nodes of the following given
structure: 4
struct NODE
{
int Itemno;
char Itemname[20];
NODE *Link;
} ;
Ans class Queue
{
Node *Front, *Rear;
public:
QUEUE() //Constructor to initialize Front and Rear
{ Front = NULL;
Rear = NULL;
}
void QUEINS(); //Function to insert a node
void QUEDEL(); //Function to delete a node
void QUEDISP(); //Function to display nodes
~Queue(); //Destructor to delete all nodes
};
void Queue::QUEDEL( )
{
if (Front!=NULL)
{
NODE *Temp=Front;
cout<<Front->Itemno<<” “;
cout<<Front->Itemname<<”Deleted“;
Front=Front->Link;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-241-320.jpg)

![385
Example:Ifthetwodimensionalarraycontains
5 6 3 2
1 2 4 9
2 5 8 1
9 7 5 8
After swapping of the content of first row and last row, it should be as follows:
9 7 5 8
1 2 4 9
2 5 8 1
5 6 3 2
Ans void SWAPARR(int A[][100], int M, int N)
{
int Temp, Ji
for (J=0; J<N; J++)
{
Temp = A[0)[J] ;
A[0][J] = A[M-1][J];
A[M-l][J] = Temp;
}
}
OR
void SWAPARR(int A[4][4])
{
int Temp, J;
for (J=0; J<4; J++)
{
Temp = A[0][J];
A[0][J] = A[3][J];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-243-320.jpg)
![386
A[3][J] = Temp;
}
}
OR
Anyotilercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
(1 Mark for correct function header)
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(1 Mark for swapping the first row with last row correctly)
(e) Convert the following infix expression to its equivalent postfix expression
showingstackcontentsfortheconversion: 2
A + B * (C – D) / E
Ans A + B * (C - D) / E
= (A+ ( (B* (C-D) ) / E) )
Element Scanned Stack Postfix
(
A A
+ +
(
(
B AB
* +*
(
C ABC
- +*-
D ABCD
) +* ABCD-
) + ABCD-*
/ +/
E ABCD-*E
) + ABCD-*E/
) ABCD-*E/+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-244-320.jpg)
![387
OR
Element Scanned Stack Postfix
( (
A ( A
+ (+ A
B (+ AB
* (+* AB
( (+*( AB
C (+*( ABC
- (+*(- ABC
D (+*(- ABCD
) (+* ABCD-
/ (+/ ABCD-*
E (+/ ABCD-*E
) ABCD-*E/+
OR
Any other method for converting the given infix expression to its equivalent
postfixexpressionshowingtheStackStatus.
(½ Mark for correctly converting expression up to each operator)
(1 Mark only to be given for writing correct answer without showing the
Stack Status)
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmarked.
asLine1andLine2usingfstreamfunctionsforperformingtherequiredtask. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Library
{
long Ano; //Ano - Accession Number of the Book
char Title[20]; //Title - Title of the Book
int Qty; //Qty - Number of Books in Library
public:
void Enter (int); //Function to enter the content](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-245-320.jpg)


![390
Fil.open (“NOTES.TXT”, ios::in);
char Word[80]; OR ifstream Fil(“NOTES.TXT”);
int Count =0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>Word;
if (strcmp(Word, “to”)==0)
Count++;
}
Fil.close(); //Ignore
cout<<”Count of -to- in file:”<<Count;
}
OR
void COUNT_TO ()
{
ifstream Fil(“NOTES.TXT”); OR
fstream Fil;
char STR[10]; Fil.open(“NOTES.TXT”,ios::in);
int c=0;
while (Fil.getline(STR, 10, ‘ ’))
{
if (strcmpi (STR, “to”) ==0)
c++;
}
Fil.close();//Ignore
cout<<“Count of -to- in file:”<<c<<end1;
}
OR
void COUNT_TO ()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-248-320.jpg)
![391
{
ifstream Fil; OR ifstream Fi1(“NOTES.TXT”);
Fil.open(“NOTES.TXT”)
char Word[80],Ch;
int Count =0, I=0;
while(Fil.get(Ch))
{
if (Ch!= ‘ ‘)
Word [I++] = Ch;
else
{
Word[I] = ‘0’;
if (strcmp (Word, “to”) ==0)
Count++;
I=O;
}
}
Fil.close(); //Ignore
cout<<”Count of -to- in file: “<<Count;
}
OR
Anyothercorrectfunctiondefinitionperformingthedesiredoperation
(½ Mark for opening NOTES. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (Whichever method adopted) from the file)
(½Markforcomparingthewordwith‘to’andincrementingcounter)
(½Markfordisplayingthenumberof‘to’with/withouttheTextMessage)
(c) Write a function in C++ to read and display the detail of all the members
whose membership type is ‘L’or ‘M’from a binary file “CLUB.DAT”.
Assume the binary file “CLUB.DAT” contains objects of class CLUB,
whichisdefinedasfollows: 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-249-320.jpg)
![392
class CLUB
{
int Mno; //Member Number
char Mname [20]; //Member Name
char Type; //Member Type: L Life Member M Monthly Member G Guest
public:
void Register();//Function to enter the content
void Display(); //Function to display all data members
char WhatType() {return Type;}.
} ;
Ans void DisplayL_M()
{
CLUB C;
fstream fin;
fin. open (“CLUB.DAT”, ios::binary|ios::in);
OR
ifstream fin (“CLUB.DAT”, ios::binary);
while(fin.read((char*)&C, sizeof(C))
{
if(C.WhatType()==’L’||C.WhatType()==’M’)
C .Display ();
}
fin.close(); //Ignore
}
OR
void Disp1ayL_M ()
{
CLUB C;
fstream fin;
fin.open (“CLUB.DAT”, ios::binary | ios::in);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-250-320.jpg)

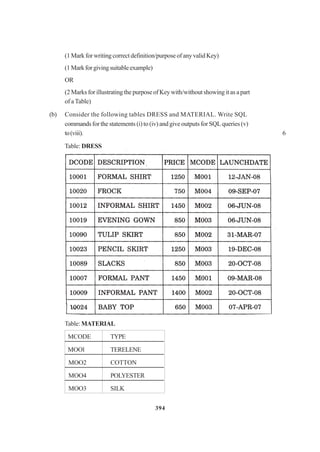


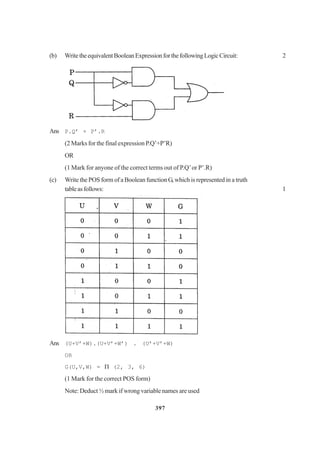
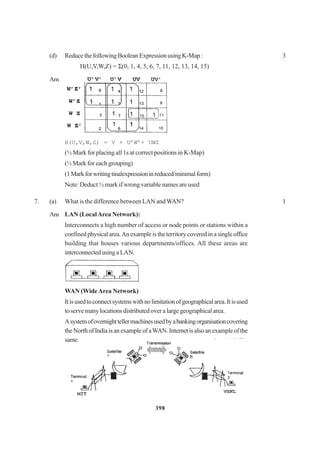



![302
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language: C+ +
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) What is the difference between automatic type conversion and type casting?
Also, give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both. 2
(b) WhichC++headerfile(s)willbeessentiallyrequiredtobeincludedtorun/
execute the following C++ code? 1
void main( )
{
int Eno=123, char Ename[ ]=”Rehan Swamp”;
cout<<setw(5)<<Eno<<setw(25)<<EName<<endl;
}
(c) Rewritethefollowingc++programcodeafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s)
(ifany).Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include <iostream.h>
class TRAIN
{
long TrainNo;
char Description[25];
public
void Entry ( )
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-260-320.jpg)

![304
}
void main ( )
{
POINT P1={15, 25, 5}, P2={10, 30, 20};
StepIn(P1);
StepOut(P2,4);
cout<<P1.X<<“,”<<P1.Y<<“,”<<P1.Z<<endl;
cout<<P2.X<<“,”<<P2.Y<<“,”<<P2.Z<<endl;
StepIn(P2,12);
cout<<P2.X<<“,”<<P2.Y<<“,”<<P2.Z<<endl;
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void ChangeIt(char Text[ ], char C)
{
for (int K=0;Text[K]!='0';K++)
{
if (Text[K]>=’F’ && Text[K]<=’L’)
Text[K]=tolower(Text[K]);
else
if (Text[K]=’E’ || Text[K]==’e’)
Text[K]= =C;
else
if (K%2==O)
Text[K]=toupper(Text[K]);
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-262-320.jpg)
![305
Text[K]=Text[K-l];
}
}
void main ( )
{
char OldText[ ]=”pOwERALone”;
ChangeIt(OldText,’%’);
cout<<“New TEXT:”<<OldText<<endl;
}
(f) Thefollowingcodeisfromagame,whichgeneratesasetof4randomnumbers.
Yallavisplayingthisgame,helphimtoidentifythecorrectoption(s)outofthe
fourchoicesgivenbelowasthepossiblesetofsuchnumbersgeneratedfrom
the program code so that he wins the game. Justify your answer. 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int LOW=15;
void main ( )
{
randomize( ) ;
int POINT=5, Number;
for (int 1=1;I<=4;I++)
{
Number=LOW+random(POINT) ;
cout<<Number<<“:” ;
POINT--;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-263-320.jpg)
![306
(i) 19:16:15:18:
(ii) 14:18:15:16:
(iii) 19:16:14:18:
(iv) 19:16:15:16:
2. (a) What do you understand by Polymorphism.?Also, give an example in C++
toillustratethesame. . 2
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingclass: 2
class TEST
{
int Regno, Max, Min, Score;
public:
TEST() //Function 1
{
Regno= 101;Max=100;Min=40;Score=75;
}
TEST(int Pregno,int Pscore) //Function 2
{
Regno=Pregno;Max=100;Min=40;Score=Pscore;
}
~TEST() //Function 3
{
cout<<“TEST Over”<<endl;
}
void Display() //Function 4
{
cout<<Regno<<“:”<<Max<<“:”<<Min<<endl;
cout<<“[Score]”<<Score<<endl;
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-264-320.jpg)
![307
(i) As per Object Oriented Programming, which. concept is illustrated by
Function 1 and Function 2 together?
(ii) WhatisFunction3specificallyreferredas?Whendoyouthink,Function3
willbeinvoked/called?
(c) DefineaclassITEMinC++withfollowingdescription: 4
PrivateMembers
Code of type integer (Item Code)
Inameoftypestring(ItemName)
Price of type float (Price of each item)
Qtyoftypeinteger(Quantityof iteminstock)
Offer of type float (Offer percentage on the item)
AmemberfunctionGetOffer()tocalculateOfferpercentageasperthe
followingrule:
If Qty<=50 Offer is 0
If 50<Qty<=100 Offer is 5
If Qty>100 Offer is 10
PublicMembers
A function GetStock() to allow user to enter values for Code, Iname,
Price,QtyandcallfunctionGetOffer()tocalculatetheoffer
AfunctionShowItem()toallowusertoviewthecontentofallthedata
members
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
classChairperson
{
long CID; //Chairperson Identification Number
char CName[20];
protected:
char Description [40];
void Allocate();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-265-320.jpg)
![308
public:
Chairperson();
void Assign();
void Show();
};
class Director
{
int DID; //Director ID
char Dname[20];
protected:
char Profile[30];
public:
Director();
void Input();
void output();
};
class Company: private Chairperson, public Director
{
int CID; //Company ID
char City[20], Country[20];
public:
Company();
void Enter();
void Display();
};
(i) Whichtypeofinheritanceoutofthefollowingisspecificallyisillustratedin
the above C++ code?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-266-320.jpg)
![309
(a) SingleLevelInheritance
(b) MultiLevelInheritance
(c) MultipleInheritance
(ii) Write the names of data members, which are accessible by objects of class
typeCompany.
(iii) Write the names of all member functions, which are accessible by objects of
class type Company.
(iv) Writethenamesofallmembers,whichareaccessiblefrommemberfunctions
of class Director.
3. (a) Write a function CHANGEO in C++, which accepts an array of integer and
its size as parameters and divide all those array elements by 7 which are
divisibleby7andmultiplyother-arrayelementsby3. 3
Sample Input Data of the array
ContentofthearrayafterCalling CHANGE()function
(b) An arrayP[50][60]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwitheach of the
elementoccupying2bytes,findoutthememorylocationfortheelementP[10]
[20], if the BaseAddress of the array is 6800. 3
(c) Write a completeprograminc++toimplement a dynamically allocated Stack
containingnamesofCountries. 4
(d) Write a function int SKIPSUM(intA[ ] [3], int N,int M) in C++ to find and
return the sum of elements from all alternate elements of a two-dimensional
arraystartingfromA[0][0]. 2
Hint:
Ifthefollowingisthecontentofthearray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-267-320.jpg)
![310
The function SKIPSUM() should add elementsA[0][0],A[0][2],A[1][l],
A[2][0] andA[2][2].
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
(Show status of Stack after each operation)
False, True, NOT, OR, True, False,AND, OR
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanks mar-
ked as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using tellg() and seekp() functions for
performingtherequiredtask. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Client
{
long Cno; char Name[20], Email[30] ;
public:
//Function to allow user to enter the Cno, Name,
Email
void Enter() ;
//Function to allow user to enter (modify) Email
void Modify() ;
long ReturnCno() {return Cno;}
};
void ChangeEmail()
{ Client C;
fstream F;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-268-320.jpg)
![311
F.open (“INFO.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
long Cnoc;//Client’s no. whose Email needs to be
changed
cin>>Cnoc;
while (F.read((char*)&C, sizeof(C)))
{
if (Cnoc= =C.ReturnCno())
{
C.Modify();
//Statement 1
int Pos = __________//To find the current
position of file pointer
// Statement 2
_______________//To move the file
pointer to write the
//modified record
back onto the file
//for the desired Cnoc
F.write((char*)&C, sizeof(C));
}
}
F.close();
}
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the words “this” and “these” present in a
textfile“ARTICLE.TXT”. 2
[Note that the words “this” and “these” are complete words]
(c) Write a function in C++ to search and display details of all flights, whose
destination is“Mumbai”fromabinary file “FLIGHT.DAT”.Assuming the
binaryfileiscontainingtheobjectsofthefollowingclass. 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-269-320.jpg)
![312
class FLIGHT
{
int Fno; //Flight Number
char From[20]; //Flight Starting Point
char To[20]; //Flight Destination
public:
char* GetFrom() {return From;}
char* GetTo() {return To;}
void Enter() {cin>>Fno;gets(From);gets(To);}
void Display(){cout<<Fno<<“:”<<From<<“:”<<To<<endl;}
};
5. (a) What do you understand by Candidate Keys in a table? Give a suitable
exampleofCandidateKeysfromatablecontainingsomemeaningfuldata. 2
(b) Consider the following tables STORE and SUPPLIERS
and answer (bl) and (b2) parts of this question:
Table:STORE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-270-320.jpg)
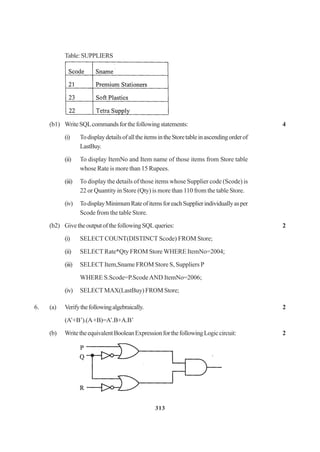

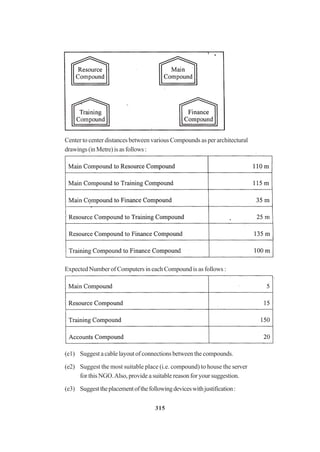
![316
(i) Repeater
(ii) Hub/Switch
(e4) The NGO is planning to connect its International office situated in
Mumbai,whichoutofthefollowingwiredcommunicationlink,youwill
suggestforaveryhighspeedconnectivity?
(i) TelephoneAnalogLine
(ii) OpticalFiber
(iii) EthernetCable
(f) Writethefullformsofthefollowing: 1
(f1) GNU
(f2) XML
(g) Write one advantage of each for Open Source Software and Proprietary
Software. 1
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
1. (a) What is the difference between call by value and call by reference?Also,
give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both. 2
(b) WhichC++headerfile(s)willbeessentiallyrequiredtobeincludedtorun/
executethefollowingC++code: 1
void main()
{
int Rno=24; char Name[] =”Amen Singhania”;
cout<<setw(lO)<<Rno<<setw(20)<<Name<<endl;
}
(c) RewritethefollowingC++programcodeafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s)
(ifany).Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include <iostream.h>
class FLIGHT
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-274-320.jpg)
![317
long FlightCode;
char Description[25];
public
void AddInfo()
{
cin>>FlightCode; gets (Description) ;
{
void ShowInfo()
(
cout<<FlightCode<<“:”<<Description<<endl;
}
} ;
void main()
{
FLIGHT F;
AddInfo.F(); ShowInfo.F();
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include <iostream.h>
struct THREE_D
{int X,Y,Z;};
void MoveIn(THREE_D &T, int Step=l)
}
T.X+=Step;
T.Y-=Step;
T.Z+=Step;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-275-320.jpg)
![318
}
void MoveOut(THREE_D &T, int Step=l)
{
T.X-=Step;
T.Y+=Step;
T.Z-=Step;
}
void main ()
{
THREE_D Tl={lO,20,5},T2={30,lO,40};
MoveIn(T1);
MoveOut(T2,5);
cout<<Tl.X<<“,”<<Tl.Y<<“,”<<T1.Z<<endl;
cout<<T2.X<<“,”<<T2.Y<<“,”<<T2.Z<<endl;
MoveIn(T2,l0);
cout<<T2.X<<“,”<<T2.y<<“,”<<T2.Z<<endl;
}
(e) Find.theoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void MyCode (char Msg [], char CH)
{
for (int (Cnt=O;Msg[Cnt]!=’0';Cnt++)
{
if (Msg[Cnt]>=’B’ && Msg[Cnt]<=’G’)
Msg[Cnt]=tolower(Msg[Cnt]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-276-320.jpg)
![319
else
if (Msg[Cnt]==’A’|| Msg[Cnt]==’a’)
Msg[Cnt]=CH;
else
if (Cnt%2==0)
Msg[Cnt]=toupper(Msg[Cnt]);
else
Msg[Cnt]=Msg[Cnt-l];
}
}
void main ()
{
char MyText [] =” ApEACeDriVE”;
MyCode(MyText,’@’);
cout<<“NEW TEXT:”<<MyText<<endl;
}
(f) Thefollowingcodeisfromagame,whichgeneratesasetof4randomnumbers.
Prafulisplayingthisgame,helphimtoidentifythecorrectoption(s)outofthe
fourchoicesgivenbelowasthepossiblesetofsuchnumbersgeneratedfrom
the program code so that he wins the game. Justify your answer. 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int LOW=25;
void main ()
{
randomize();
int P01NT=5,Number;
for (int I=1;I<=4;I++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-277-320.jpg)

![321
{
cout<<“Exam Over”<<endl;
}
void Show () //Module 4
{
cout<<Rno<<“:”<<MaxMarks<<“:”<<MinMarks<<endl;
cout<<“[Marks Got]”<<Marks<<endl;
}
};
(i) As per Object Oriented Programming, which concept is illustrated by
Module 1 and Module 2 together?
(ii) What is Module 3 referred as ? When do you think, Module 3 will be
invoked/called?
(c) DefineaclassSTOCKinC++withfollowingdescription: 4
PrivateMembers
ICode of type integer (Item Code)
Item of type string (Item Name)
Price of type float (Price of each item)
Qty of type integer (Quantity in stock)
Discountoftypefloat(Discountpercentageontheitem)
AmemberfunctionFindDisc()tocalculatediscountasperthefollowing
rule:
If Qty<=50 Discountis0
If 50<Qty<=100 Discountis5
If Qty>100 Discountis10
PublicMembers
A function Buy() to allow user to enter values for ICode, Item, Price,
QtyandcallfunctionFindDisc()tocalculatetheDiscount.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-279-320.jpg)
![322
A function ShowAll( ) to allow user to view the content of all the data
members.
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class Director
{
long DID; //Director Identification Number
char Name[20];
protected:
char Description[40];
void Allocate();
public:
Director();
void Assign();
void Show();
} ;
class Ractory:public Director
}
int FID; //Factory ID
char Address[20];
protected:
int NOE; //No. of Employees
public:
Factory();
void Input();
void Output();
};
class ShowRoom:private Factory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-280-320.jpg)
![323
{
int SID; //Showroom ID
char City[20];
public:
ShowRoom();
void Enter();
void Display();
};
(i) Whichtypeofinheritanceoutofthefollowingisillustratedintheabove
C++ code?
(a) SingleLevelInheritance
(b) MultiLevelInheritance
(c) MultipleInheritance
(ii) Write the names of data members, which are accessible by objects of
class type ShowRoom.
(iii) Writethenamesofallmemberfunctionswhichareaccessiblebyobjects
of class type ShowRoom.
(iv) Write the names of all members, which are accessible from member
functionsofclassFactory.
3. (a) Write a function REASSIGNO in C++, which accepts an array of integers
and its size as parameters and divide all those array elements by 5 which are
divisibleby5andmultiplyotherarrayelementsby2. 3
Sample Input Data of the array
ContentofthearrayaftercallingREASSIGNOfunction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-281-320.jpg)
![324
(b) An array T[90][100] is stored in the memory along the column with each of
the elementsoccupying4bytes.Findoutthememorylocationfortheelement
T[10][40], if the BaseAddress of the array is 7200. 3
(c) Write a complete program in C++ to implement a dynamically allocated
QueuecontainingnamesofCities. 4
(d) Write a function intALTERSUM (int B[ ] [5], int N, int M in C++ to find
andreturnthesumofelementsfromallalternateelementsofatwo-dimensio-
nalarraystartingfromB[0][0]. 2
Hint:
Ifthefollowingisthecontentofthearray
The function should add elements B[0][0], B[0][2], B[l][l], B[2][0] and
B[2][2].
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
(Show status of Stack after each operation)
True, False, NOT, OR, False, True, OR,AND
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmar-
ked as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using tellg() and seekp() functions for
performingtherequiredtask. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Customer
{
long Cno;char Name[20],Mobile[12];
public:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-282-320.jpg)

![326
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the words “to” and “the” present in a text file
“POEM.TXT”. 2
[Note that the words “to” and “the” are complete words]
(c) Write a function in C++ to search and display details. of all trains, whose
destinationis“Delhi”.fromabinaryfile“TRAIN.DAT”.Assumingthebinary
fileiscontainingtheobjectsofthefollowingclass. 3
class TRAIN
{
int Tno; // Train Number
charFrom[20]; // Train Starting Point
charTo [20]; // Train Destination
public:
char* GetFrom(){return From;}
char* GetTo(){return To;}
void Input(){cin>>Tno;gets(From);gets(To);}
void Show(){cout<<Tno<<“:”<<From<<“:”<<To<<endl;}
};
5. (a) WhatdoyouunderstandbyPrimaryKey?GiveasuitableexampleofPrimary
Keyfromatablecontainingsomemeaningfuldata. 2
(b) Consider the following tables STOCK and DEALERS and answer (b1) and
(b2) parts of this question:
Table: STOCK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-284-320.jpg)

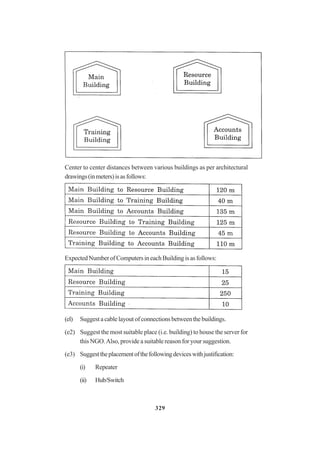


![332
int A=1, B=2;
float C = (float)A/B; //Type Casting
cout<<C;
OUTPUT:
0.5
(½ Mark for each correct explanation ofAutomatic Type Conversion and
TypeCasting)
(½ Mark for each correct example ofAutomaticType Conversion andType
Casting)
OR
(Full2Marksforcorrectexample(s)demonstratingthemeaningof/difference
betweenAutomaticType Conversion andType Casting)
OR
(Only 1 Mack to be awarded if Explanation without supporting examples)
Note:Outputisoptional
(b) WhichC++headerfile(s)willbeessentiallyrequiredtobeincludedtorun/
execute the following C++ code? 1
void main( )
{
int Eno=123, char Ename[ ]=”Rehan Swamp”;
cout<<setw(5)<<Eno<<setw(25)<<EName<<endl;
}
Ans. (i) iostream.h (ii) iomanip.h
OR
iomanip.h - (As iostream.h is included in iomanip.h)
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
OR
(Full 1 Mark for mentioning only iomanip.h )
Note: Ignore any other header files, if mentioned.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-290-320.jpg)
![333
(c) Rewritethefollowingc++programcodeafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s)
(ifany).Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include <iostream.h>
class TRAIN
{
long TrainNo;
char Description[25];
public
void Entry ( )
{
cin >>TrainNo; gets(Description);
}
Void Display ( )
{
cout<<TrainNo<<“:”<<Description<<endl;
}
};
void main( )
{
TRAIN T;
Entry. T( ); Display. T( );
}
Ans. #include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
class TRAIN
{
long TrainNo;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-291-320.jpg)
![334
char Description [25];
public:
void Entry ()
{
cin>>TrainNo; gets (Description);
}
void Display ()
{
cout<<TrainNo<<“:”<<Description<<end1;
}
};
void main ()
{
TRAIN T;
T.Entry(); T.Display();
}
(½ Mark for writing # before include<iostream.h>
(½ Mark for writing # include <stdio.h>
(½ Mark for writing: after public)
(½ Mark for writing T.Entry(); and T.Display(); correctly)
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#inc1ude <iostream.h>
struct POINT
{int X, Y, Z;};
void StepIn(POINT & P, int Step=1)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-292-320.jpg)

![336
Note:
Deduct (½ Mark if any/all ‘,’ missing
Deduct (½ Mark if endl is not considered at the right positions
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void ChangeIt(char Text[ ], char C)
{
for (int K=0;Text[K]!='0';K++)
{
if (Text[K]>=’F’ && Text[K]<=’L’)
Text[K]=tolower (Text[K]);
else
if (Text[K]=’E’ || Text[K]==’e’)
Text[K]==C;
else
if (K%2==O)
Text[K]=toupper(Text[K]);
else
Text[K]=Text[K-l];
}
}
void main ( )
{
char OldText[ ]=”pOwERALone”;
ChangeIt(OldText,’%’);
cout<<“New TEXT:”<<OldText<<endl;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-294-320.jpg)



![340
~TEST() //Function 3
{
cout<<“TEST Over”<<endl;
}
void Display() //Function 4
{
cout<<Regno<<“:”<<Max<<“:”<<Min<<endl;
cout<<“[Score]”<<Score<<endl;
}
};
(i) As per Object Oriented Programming, which. concept is illustrated by
Function 1 and Function 2 together?
Ans. Polymorphism
OR
FunctionOverloading
OR
ConstructorOverloading
(1 Mark for naming the concept correctly)
(ii) WhatisFunction3specificallyreferredas?Whendoyouthink,Function3
willbeinvoked/called?
Ans. Destructor, invoked or called when scope of an Object gets over.
(½ Mark for naming Destructor correctly)
(½ Mark for mentioning correctly when it is invoked)
(c) DefineaclassITEMinC++withfollowingdescription: 4
PrivateMembers
Code of type integer (Item Code)
Inameoftypestring(ItemName)
Price of type float (Price of each item)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-298-320.jpg)
![341
Qtyoftypeinteger(Quantityof iteminstock)
Offer of type float (Offer percentage on the item)
AmemberfunctionGetOffer()tocalculateOfferpercentageasperthe
followingrule:
If Qty<=50 Offer is 0
If 50<Qty<=100 Offer is 5
If Qty>100 Offer is 10
PublicMembers
A function GetStock() to allow user to enter values for Code, Iname,
Price,QtyandcallfunctionGetOffer()tocalculatetheoffer
AfunctionShowItem()toallowusertoviewthecontentofallthedata
members
Ans. classITEM
{
int Code;
char Iname [20] ;
floatPrice;
intQty;
floatOffer;
voidGetOffer();
public:
void GetStock ()
{
cin>>Code;
gets (Iname) ; // OR cin.getline (Iname, 80) ; OR cin>>Iname;
cin>>Price>>Qty;
GetOffer();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-299-320.jpg)
![342
}
void ShowItern ( )
{
cout<<Code<<Iname<<Price<<Qty<<Offer;
};
voidITEM::GetOffer()
{
if(Qty<=50)
Offer = 0;
else if (Qty <=100)
Offer = 5; / /OR Offer = 0.05;
else
Offer = 10; / /OR Offer = 0.1;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of GetOffer())
(1 Mark for correct definition of GetStock () with proper invocation of GetOffer()
function)
(1 Mark for correct definition of Showltem())
NOTE:
Deduct ½ Mark if GetOffer() is not invoked properly inside GetStock()function
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
classChairperson
{
long CID; //Chairperson Identification Number
char CName[20];
protected:
char Description [40];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-300-320.jpg)
![343
void Allocate();
public:
Chairperson();
void Assign();
void Show();
};
class Director
{
int DID; //Director ID
char Dname[20];
protected:
char Profile[30];
public:
Director();
void Input();
void output();
};
class Company: private Chairperson, public Director
{
int CID; //Company ID
char City[20], Country[20];
public:
Company();
void Enter();
void Display();
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-301-320.jpg)

![345
3. (a) Write a function CHANGEO in C++, which accepts an array of integer and
its size as parameters and divide all those array elements by 7 which are
divisibleby7andmultiplyother-arrayelementsby3. 3
Sample Input Data of the array
ContentofthearrayafterCalling CHANGE()function
Ans. void CHANGE (int A[ ], int N)
{
for(int I = 0; I<N; I++)
{
if (A[I]%7 = = 0)
A [I] = A [I] /7;
else
A[I] = A[I] * 3;
}
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
( ½ Mark for correct Function Header)
(½ Mark for correct loop)
(½ Mark for correct checking of divisibility of array elements by 7)
(½ Mark for correct else OR correct checking of non divisibility of array elements by 7)
(½ Mark for each correct assignment)
(b) An arrayP[50] [60]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwitheach of the
elementoccupying2bytes,findoutthememorylocationfortheelementP[10]
[20], if the BaseAddress of the array is 6800. 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-303-320.jpg)
![346
Ans.Loc(P[I] [J]) = Base(P)+W(I+J*M)
i Loc(P[10][20]) = Base(P)+ 2(10+20*50)
Loc(P[10] [20]) = 68OO + 2(10+20*50)
= 6800 + 2 (10+1000)
= 6800 + 2*1010
= 6800 + 2020
= 8820
OR
Address of P[i] [j] = BaseAddress + W((i–L1)+(j–L2)*M)
Address of P[10] [20]= 6800 + 2((10-0)+(20-0)x50)
= 6800 + 2 x 1010
= 6800 + 2020
= 8820
OR
Address of P[I] [J] along the column
= BaseAddress + W((I–LBR)+(J–LBC)*M)
(where N is the number of rows, LBR = LBC = 1)
Address of P[10][20]=6800+2((10-1)+(20-l)x50)
= 6800 + 2 ( 9 + 19 x 50 )
= 6800 + 2 x 959
= 6800 + 1918
= 8718
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for column major) OR substituting
formula with correct values for calculating Address)
(2 marks for calculating correct address)
(c) Write a completeprograminc++toimplement a dynamically allocated Stack
containingnamesofCountries. 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-304-320.jpg)
![347
Ans. #include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
struct Node
{
char Country [20] ;
Node *Link;
};
class Stack
{
Node *Top;
public:
Stack() {Top = NULL;}
void Push() ;
void Pop() ;
void Display() ;
~Stack () ;
};
void Stack::Push()
{
Node *Temp = new Node;
gets(Temp -> Country);
Temp -> Link = Top;
Top = Temp;
}
void Stack::Pop()
{
if (Top !=NULL)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-305-320.jpg)

![349
void main ( )
{
Stack ST; char Ch;
do
{
cout<<“p/O/D/Q” ;
cin>>Ch;
switch (Ch)
{
case ‘P’ : ST.Push(); break;
case ‘O’ :ST.Pop(); break;
case ‘D’ :ST.Disp();
}
} while (Ch!=’Q’);
}
(d) Write a function int SKIPSUM(intA[ ] [3], int N,int M) in C++ to find and
return the sum of elements from all alternate elements of a two-dimensional
arraystartingfromA[0][0]. 2
Hint:
Ifthefollowingisthecontentofthearray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-307-320.jpg)
![350
The function SKIPSUM() should add elementsA[0][0],A[0][2],A[1][l],
A[2][0] andA[2][2].
Ans. int SKIPSUM(int A[ ][ 3 ], int N,int M)
{
int S=0:
for(int I = 0; 1< N; 1++)
for (int J = (I%2)?1:0; J<M; J = J+2)
S = S + A [I][J];
return S;
}
OR
int SKIPSlJM(int A[ ][3], int N, int M)
{
int S=0;
for (int I = 0; 1< N; I++)
for (int J = (I%2==0)? 0:1 ; J<M; J = J+2)
S = S + A [I][J];
return S;
}
OR
int SKIPSUM(int A[][3], int N, int M)
{
int I,J, S=O;
for (I = 0; 1 < N; 1++)
{
if (I%2) //OR (1%2 !=0 ) OR (I%2 == 1)
J = l;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-308-320.jpg)
![351
else
J = 0;
for ( ; J<M; J = J+2)
S = S + A[I][J];
}
return S;
}
OR
int SKIPSUM(int A[][3], int N, int M)
{
int S=0, C=0;
for(int I = 0; 1< N; 1++)
for (int J = 0; J<M; J++ )
{
if (C%2 == 0)
S = S + A[I][J];
C++;
}
return S;
}
OR
int SKIPSUM(int A[][3], int N, int M)
{
int S=0, C=l;
for(int I = 0; I<N; I++)
for (int J = 0; J<M; J++ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-309-320.jpg)
![352
{
if (C%2 != 0)
S = S + A[I][J];
C++;
}
return S;
}
OR
int SKIPSUM (int A[][3], int N, int M)
{
int S=0;
for(int I = 0; l< N; l++)
for (int J = 0; J<M; J++ )
{
if ((I+J)%2 == 0)
S = S + A[I][J];
}
return S;
}
OR
Anyothercorrectequivalentfunctiondefinition
(½ Mark for correct function header)
(½ Mark for each correct loop)
(½ Mark for checking alternate cells)
(½ Mark for finding Sum of elements)
(½ Mark for returning the Sum)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-310-320.jpg)

![355
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanks mar-
ked as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using tellg() and seekp() functions for
performingtherequiredtask. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Client
{
long Cno; char Name[20], Email[30] ;
public:
//Function to allow user to enter the Cno, Name,
Email void Enter() ;
//Function to allow user to enter (modify) Email
void Modify() ;
long ReturnCno() {return Cno;}
};
void ChangeEmail()
{ Client C;
fstream F;
F.open (“INFO.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
long Cnoc;//Client’s no. whose Email needs to be
changed cin>>Cnoc;
while (F.read((char*)&C, sizeof(C)))
{
if (Cnoc==C.ReturnCno())
{
C.Modify();
//Statement 1
int Pos = __________//To find the current
position of file pointer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-313-320.jpg)
![356
// Statement 2
_______________//To move the file
pointer to write the
//modified record
back onto the file
//for the desired Cnoc
F.write((char*)&C, sizeof(C));
}
}
F.close();
}
Ans. Statement1:
F. tellg ();
Statement2:
F. seekp(Pos-sizeof(C)) ;
OR
F.seekp(-sizeof(C), ios::cur);
OR
Anyequivalentcorrectmethod
(½ Mark for each correct statement)
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the words “this” and “these” present in a
textfile“ARTICLE.TXT”. 2
[Note that the words “this” and “these” are complete words]
Ans. void COUNT ( )
{
ifstream Fil;
OR ifstream Fil(“ARTICLE.TXT”);
Fil.open(“ARTICLE.TXT”);
char Word [80]
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-314-320.jpg)
![357
int C1 = 0, C2 = 0
while (!Fil.eop())
{
Fil>>Word;
if (strcmp(Word,“this”) ==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcmp(Word,“these”) ==0)
C2++;
}
cout<<“Count of -this- in file:”<<Cl;
cout<<“Count of -these- in file:”<<C2;
OR cout<<“Count of -this- and —these- -in file:"<<Cl+C2;
Fil.close(); //gnore
}
OR
void COUNT( )
{ OR
if stream Fil(“ARTICLE.TXT”); ifstream Fil;
char Word[80] ; Fil.open(“ARTICLE. TXT”) ;
int C = 0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{ Fil>>Word;
if (strcmp(Word,“this”)==0||strcmp(Word,“these”) ==0)
C++;
}
cout<<“Count of -this- and -these- in file:"<<C;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-315-320.jpg)
![358
}
OR
void COUNT( )
{
ifstream Fil(“ARTICLE.TXT”);
//OR fstream Fil;
// Fil. open(“ARTICLE. TXT”, ios: : in);
char STR[l0];
int Cl=0, C2=0;
while (Fil.getline (STR,l0, ''))
{
if (strcmp(STR,“this”)==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcmp(STR,“these”)==0)
C2++;
}
}
cout<<“Count of -this- in file:”<<Cl;
cout<<“Count of -these- in file:”<<C2;
Fil.close() ;//Ignore
} OR cout<<“Count of -this- and -these- in file:”<<Cl+C2;
OR
void COUNT ( )
{
ifstream Fil;
OR ifstreamFil(“ARTICLE.TXT");
Fil. open(“ARTICLE.TXT”);
char Word[80] ,Ch;
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-316-320.jpg)
![359
int Cl =0, C2 = 0, I=O;
while(Fil.get(Ch))
{
if (Ch! = ' ')
Word[I++] = Ch;
else
{
Word[I] = ‘0’;
if (strcmp (Word,“this”)==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcmp(Word,“these”)==0)
C2++;
I=0,
}
}
cout<<“Count of -this- in file:" <<Cl;
cout<<“Count of -these- in file:" <<C2;
OR
cout<<“Count of -this- and -these- in file: “<<Cl+C2;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}
OR
Anyothercorrectfunctiondefinition
(½ Mark for opening ARTICLE. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (Whichever method adopted) from the file)
(½ Mark for comparing the word with ‘this’and ‘these’and incrementing
counter(s)
(½ Mark for displaying the individual count of ‘this’ and ‘these’ or the
total count of ‘this’ and ‘these’ with/without the Text Message)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-317-320.jpg)
![360
(c) Write a function in C++ to search and display details of all flights, whose
destination is“Mumbai”fromabinary file “FLIGHT.DAT”.Assuming the
binaryfileiscontainingtheobjectsofthefollowingclass. 3
class FLIGHT
{
int Fno; //Flight Number
char From[20]; //Flight Starting Point
char To[20]; //Flight Destination
public:
char* GetFrom() {return From;}
char* GetTo() {return To;}
void Enter() {cin>>Fno;gets(From);gets(To);}
void Display(){cout<<Fno<<“:”<<From<<“:”<<To<<endl;}
};
Ans. void Read ()
{
FLIGHT F;
ifstream fin;
fin.open(“FLIGHT.DAT”, ios::binary) ;
OR ifstream fin (“FLIGHT. DAT”, iC;s: :binary) ;
while(fin.read((char*)&F, sizeof(F)))
{
if (strcmp(F. GetTo(),“Mumbai”))
F.Display() ;
}
fin.close(); //Ignore
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-318-320.jpg)

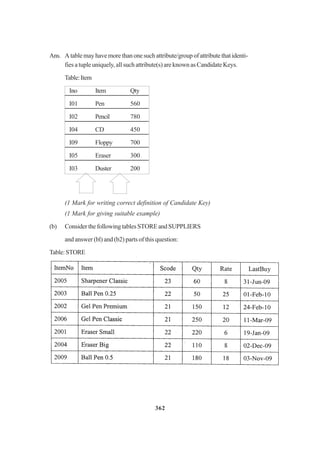


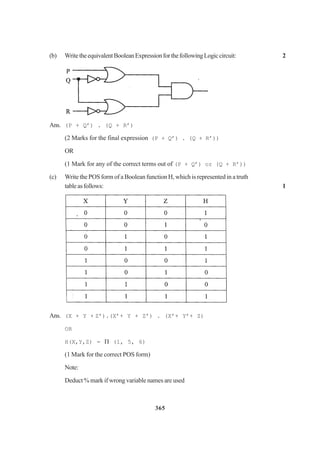


![371
vcid Caloulato(int A,int & B )// A is oall by value,
{ // B is call by roforonco
A++;
a+=A;
}
(½ Mark for each corroct explanatIon of Call by va/ueand Call by referenco)
(½ Mark for each corroct examplo,of Call by value and Call by reference)
OR
(Full 2 Marks for correct examples demonstrating tho dlfferonce botween
Call by value and Call by roforonce)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded for ExplanatIon glvon without supporting examples)
(b) WhichC++headerfile(s)willbeessentiallyrequiredtobeincludedtorun/
executethefollowingC++code: 1
void main()
{
int Rno=24; char Name [] =” Amen Singhania”;
cout<<setw(lO)<<Rno<<setw(20)<<Name<<endl;
}
Ans. iostream.h
iomanip.h
OR
iomanip.h - (As iostream.h is included in iomanip.h)
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
OR
(Full Mark for mentioning only iomanip.h )
Note: Ignore any other header files, if mentioned.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-329-320.jpg)
![372
(c) RewritethefollowingC++programcodeafterremovingthesyntaxerror(s)
(ifany).Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include <iostream.h>
class FLIGHT
{
long FlightCode;
char Description[25];
public
void AddInfo ( )
{
cin>>FlightCode; gets (Description) ;
{
void ShowInfo ()
(
cout<<FlightCode<<“:”<<Description<<endl;
}
} ;
void main()
{
FLIGHT F;
AddInfo.F(); ShowInfo.F();
}
Ans. #include <iostream.h> / / Error 1
#include <stdio.h> / / Error 2
class FLIGHT
{
long FlightCode;
not required if gets( ) is re-
placed with cin.getline( ) or
cin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-330-320.jpg)
![373
char Description[25];
public : / / Error 3
void AddInfo ( )
{
cin>>FlightCode; gets (Description) ;
}
void ShowInfo ( )
{
cout<<FlightCode<<”:”<<Description<<endl;
}
} ;
void main ( )
{
FLIGHT F;
F.AddInfo( ) ; F. ShowInfo ( ) ; / / Error 4
}
(½ Mark for each correction)
OR
(1 mark for identifying at least three errors, without suggesting correction)
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include <iostream.h>
struct THREE_D
{int X,Y,Z;};
void MoveIn(THREE_D &T, int Step=l)
}
T.X+=Step;
T.Y-=Step;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-331-320.jpg)

![375
(e) Find.theoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void MyCode (char Msg [], char CH)
{
for (int (Cnt=O;Msg[Cnt]!=’0';Cnt++)
{
if (Msg[Cnt]>=’B’ && Msg[Cnt]<=’G’)
Msg[Cnt]=tolower(Msg[Cnt]);
else
if (Msg[Cnt]==’A’|| Msg[Cnt]==’a’)
Msg[Cnt]=CH;
else
if (Cnt%2==0)
Msg[Cnt]=toupper(Msg[Cnt]);
else
Msg[Cnt]=Msg[Cnt-l];
}
}
void main ()
{
char MyText [] =” ApEACeDriVE”;
MyCode(MyText,’@’);
cout<<“NEW TEXT:”<<MyText<<endl;
}
Ans. NEW TEXT :@@e@ccddIIe
(½ Mark for writing @,@,e as the first three characters)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-333-320.jpg)

![377
I POINT Number
Minimum Maximum
1 5 25 29
2 4 25 28
3 3 25 27
4 2 25 26
Theonlyoptionthatsatisfiesthesevaluesisoption(iv).
(1 Mark for mentioning correct option)
(1 Mark for any valid justification)
Note: Only ½ Mark to be given if only options (i) & (iv) are mentioned as
correct options; no other combination of options is acceptable;
2. (a) What do you understand by Data Encapsulation and Data Hiding ?’Also,
giveanexampleinC++toillustrateboth. 2
Ans. Data Encapsulation:Wrapping up of data and functions together in a single
unit is known as Data Encapsulation. In a class, we wrap up the data and
functionstogetherinasingleunit.
DataHidina:Keepingthedatainprivate/protectedvisibilitymodeoftheclass
to prevent it from accidental change is known as Data Hiding.
class Computer
{
char CPU[lO] ;int RNM; //Data Hiding
public: //Data Encapeulation
void STOCK();
void SHOW();
};
(½ MarkforeachcorrectexplanationofDataEncapsulationandDataHiding)
(½ Marie for each correct example of Data Encapsulation and Data Hiding)
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-335-320.jpg)
![378
(2 Marks for explaining the concept of the terms through suitable examples)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded for Explanation given without any example)
(b) Answerthequestions(i)and(ii)aftergoingthroughthefollowingclass: 2
class Exam
{
int Rno,MaxMarks,MinMarks,Marks;
public:
Exam ( ) //Module 1
{
Rno=101;MaxMarks=l00;MinMarks=40;Marks=75;
}
Exam (int Prno, int Pmarks) //Module 2
{
Rno=Prno;MaxMarks=l00;MinMarks=40;Marks=Pmarks;
}
~Exam () //Module 3
{
cout<<“Exam Over”<<endl;
}
void Show () //Module 4
{
cout<<Rno<<“:”<<MaxMarks<<“:”<<MinMarks<<endl;
cout<<“[Marks Got]”<<Marks<<endl;
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-336-320.jpg)

![380
A function ShowAll() to allow user to view the content of all the data
members.
Ans. class STOCK
{
int ICode,Qty;
char Item[20];
float Price,Discount;
void FindDisc();
public:
void Buy();
void ShowAll();
} ;
void STOCK::Buy()
{
cin>>ICode;
gets(Item);
cin>>Price;
cin»Qty;
FindDisc();
}
void STOCK::FindDisc()
{
if (Qty<=50)
Discount=0;
else if (Qty<=100)
Discount=5; // =0.05;
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-338-320.jpg)
![381
Discount=10; // =0.1;
}
void STOCK::ShowAll()
{
cout<<ICode<<’t’<<Item<<’t’<<Price<<’t’<<Qty
<<’t’<<Discount<<endl;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of FindDisc())
(1 Mark for correct definition of Buy() with proper invocation of
FindDisc() function)
(1 Mark for correct definition of ShowAll())
NOTE:
Deduct ½ Mark if FindDisc() is not invoked properly inside Buy() function
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
class Director
{
long DID; //Director Identification Number
char Name[20];
protected:
char Description[40];
void Allocate () ;
public:
Director() ;
void Assign () ;
void Show () ;
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-339-320.jpg)
![382
class Ractory:public Director
}
int FID; //Factory ID
char Address[20];
protected:
int NOE; //No. of Employees
public:
Factory();
void Input ();
void Output ();
};
class ShowRoom:private Factory
{
int SID; //Showroom ID
char City[20];
public:
ShowRoom();
void Enter ();
void Display ();
};
(i) WhichtypeofinheritanceoutofthefollowingisillustratedintheaboveC++
code?
(a) SingleLevelInheritance
(b) MultiLevelInheritance
(c) MultipleInheritance
Ans. (b) MultilevelInheritance
(1 Mark for mentioning correct option)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-340-320.jpg)

![384
Ans. void REASSIGN (int Arr[ ], int Size)
{
for (int i=0;i<Size;i++)
if (Arr[i]%5==0)
Arr[i]/=5;
else
Arr[i]*=2;
}
OR
void REASSIGN(int Arr[ ],int Size)
{
for (int i=0;i<Size;i++)
Arr[i]%5 ? Arr[i]/=5 : Arr[i]*=2;
}
OR
Any other correct equivalent function definition
( ½ Mark for correct Function Header)
( ½ Mark for correct loop)
( ½ Mark for correct checking of divisibility of array elements by 5)
( ½ Mark for correct placing of else OR correct checking of non divisibil-
ity of array elements by 5)
(½ Mark for each correct assignment)
(b) An array T[90][100] is stored in the memory along the column with each of
the elementsoccupying4bytes.Findoutthememorylocationfortheelement
T[10][40], if the BaseAddress of the array is 7200. 3
Ans. Loc(T[I][J)) = Base(T)+W(I+J*N)
(where N is the number of rows, LBR = LBC = 0)
= 7200 + 4[10 + 40 x 90]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-342-320.jpg)
![385
= 7200 + 4[10+3600]
= 7200 + 4 x 3610
= 7200 + 14440
= 21640
OR
Address of T[I][J] along the column
= BaseAddress + W [(I-LBR)+(J-LBC)* N]
(where N is the number of rows, LBR=LBC = 1)
Address of T[10][40]=BaseAddress + 4[ (10 - 1) +(40 - l)x 90]
= 7200+4[9 + 39 x 90]
= 7200+4[9 + 3510]
= 7200+4 x 3519
= 7200+14076
= 21276
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for column major) OR. substituting
formula with correct values for calculating Address)
(2 marks for calculating correct address)
(c) Write a complete program in C++ to implement a dynamically allocated
QueuecontainingnamesofCities. 4
Ans. #include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
struct NODE
{
char City[20];
NODE *Next;
};
class Queue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-343-320.jpg)


![388
NODE *Temp=Front;
Front=Front->Next; delete Temp;
}
}
void main ()
{
Queue QU; char Ch;
do
{
:
:
} while (Ch!=’Q’);
}
(4 Marks for correct program)
OR
(Full 4 Marks for correct logic of either Insertion OR Deletion functions
for Dynamically Allocated Queue.)
OR
(2 Marks for defining class with Constructor, function prototypes for
Insertion & deletion and Destructor or equivalent using Structures.)
(d) Write a function intALTERSUM (int B[ ] [5], int N, int M in C++ to find
andreturnthesumofelementsfromallalternateelementsofatwo-dimensio-
nalarraystartingfromB[0][0]. 2
Hint:Ifthefollowingisthecontentofthearray:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-346-320.jpg)
![389
The function should add elements B[0][0], B[0][2], B[l][l], B[2][0] and
B[2][2].
Ans. //Sample Code 1
int ALTERSUM(int B[][5] ,int N,int M)
{
int Sum=0;
for (int I=0;I<N;I++)
for (int J=(I%2==0)?0:1;J<M;J+=2)
Sum+=B[I][J] ;
return Sum;
}
OR
//Sample Code 2
int ALTERSUM(int B[][5],int N,int M)
{
int Sum=0,J=0;
for (int I=0;I<N;I++)
{
for (;J<M;J+=2)
Sum+=B[I][J] ;
J-=M;
}
return Sum;
}
OR
//Sample Code 3
int ALTERSUM(int B[][5],int N,int M)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-347-320.jpg)
![390
{
int *P=&B[0][0],Sum=0;
for (int I=0;I<M*N;I+=2)
{
Sum+=(*P);
P+=2;
}
return Sum;
}
OR
//Sample Code 4
int ALTERSUM (int B[][5], int N, int M)
{
int S=0, C=0;
for(int I = 0; 1< N; 1++)
for (int J = 0; J<M; J++ )
{
if (C%2 == 0)
S = S + B[I][J];
C++;
}
return S;
}
OR
//Sample Code 5
int ALTERSUM(int B[][5],int N,int M)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-348-320.jpg)
![391
int Sum=0;
for (int I=0;1<N;1++)
for (int J=0;J<M;J++)
if ((1+J)%2==0)
Sum+=B [I][J] ;
return Sum;
}
OR
//Sample Code 6
int ALTERSUM(int B[][5],int N,int M)
{
int Sum=0;
for (int I=0;1<N;1++)
for (int J=0;J<M;J++)
{
if ((1%2==0 && J%2=0)||(1%2!=0 && J%2!=0))
Sum+=B [I][J] ;
}
return Sum;
}
Note: Kindly note Sample Code 5 and 6 will not work in case of Even Di-
mensionalArrays, but keeping in view of the Sample given for 3x3 array
thesolutionisacceptable.
(½ Mark for correct loops)
(1 Mark for finding Sum of alternate cells)
(½ Mark for returning the Sum)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
(Show status of Stack after each operation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-349-320.jpg)


![394
#include <fstream.h>
class Customer
{
long Cno;char Name[20],Mobile[12];
public:
//Function to allow user to enter the Cno, Name,
Mobile
void Enter();
//Function to allow user to enter (modify) mobile
number void Modify();
//Function to return value of Cno
long GetCno () {return Cno;}
};
void ChangeMobile()
{
Customer C;
fstream F;
F.open(“CONTACT.DAT”,ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
long Cnoc; //Customer no. whose mobile number needs
to be changed cin>>Cnoc;
while (F.read((char*)& C,sizeof(C)))
{
if (Choc==C.GetCno())
{
C.Modify ();
//Statement 1
int Pos=_____________//To find the current
position of file pointer
//Statement 2
_____//To move the file pointer to write the
//modified record back onto the file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-352-320.jpg)
![395
//for the desired Cnoc
F.write((char*)&C,sizeof(C));
}
}
F. close( ) ;
}
Ans. Statement 1:
File.tellg() ;
Statement 2:
File.seekp(Pos-sizeof(C));
OR
File.seekp(-l*sizeof(C) ,ios::cur);
(½ Mark for each correct Statement)
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the words “to” and “the” present in a text file
“POEM.TXT”. 2
[Note that the words “to” and “the” are complete words]
Ans. void COUNT ()
{
ifstream Fil;
Fil. open (“POEM.TXT”); OR ifstream Fil (“POEM. TXT”);
char Word[80] ;
int Cl = 0, C2 = 0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>Word;
if (strcmp (Word, “to”) ==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcmp (Word, “the”) ==0)
C2++;
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-353-320.jpg)
![396
}
cout<<”Count of -to- in file:" <<Cl;
cout«”Count of -the- in file:”«C2;
OR cout<<”Count of -to- and -the- in file:”<<Cl+C2;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}
OR
void COUNT ( )
{
ifstream Fil(“POEM.TXT”);
// OR fstream Fil;
// Fil.open(“POEM.TXT”,ios::in);
char STR[l0];
int Cl=O, C2=0;
while (Fil.getline(STR,l0,''))
{
if (strcmp (STR, “to”) ==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcmp(STR, “the”) ==0)
C2++;
}
cout<<”Count of -to- in file:”<<Cl;
cout<<”Count of -the- in file:”<<C2;
OR cout<<”Count of -to- and -the- in file:”<<Cl+C2;
Fil.close(); //Ignore
}
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-354-320.jpg)
![397
OR
void COUNT()
{
ifstream Fil;
OR ifstream Fill(“POEM.TXT”);
Fil. open (“POEM.TXT”);
char Word[BO], Chi
int Cl =0, C2=0, 1=0;
while(Fil.get(Ch))
{
if (Ch! = ‘ ‘)
Word[1++] = Chi
else
{
Word[I] = ‘0’;
if (strcmp (Word, “to”) ==0)
Cl++;
else if (strcrap (Word, “the”) ==0)
C2++;
1=0;
}
}
cout<<”Count of -to- in file:”<<Cl;
cout<<”Count of -the- in file:”<<C2;
OR cout«”Count of -to- and -the- in
Fil.close(); //1gnore
}
OR
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-355-320.jpg)
![398
Any-othercorrectfunctiondefinition
(½ Mark for opening POEM. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (using any method) from the file)
(½ Mark for comparing the word with ‘to’ and ‘the’ )
(½ Mark for incrementing counter(s))
(c) Write a function in C++ to search and display details. of all trains, whose
destinationis“Delhi”.fromabinaryfile“TRAIN.DAT”.Assumingthebinary
fileiscontainingtheobjectsofthefollowingclass. 3
class TRAIN
{
int Tno; // Train Number
charFrom[20]; // Train Starting Point
charTo [20]; // Train Destination
public:
char* GetFrom (){return From;}
char* GetTo (){return To;}
void Input () {cin>>Tno;gets(From);gets(To);}
void Show () {cout<<Tno<<“:”<<From<<“:”<<To<<endl;}
};
Ans. void Read ( )
{
TRAIN T;
ifstream fin;
fin. open (“TRAIN.DAT”, ios::binary);
OR ifstream fin (“TRAIN.DAT”, ios::binary);
while(fin.read((char*)&T, sizeof(T)))
{
if(strcmp(T.GetTo() ,”Delhi”)==O)
T.Show() ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-356-320.jpg)

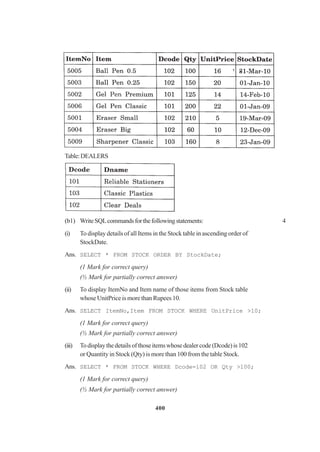


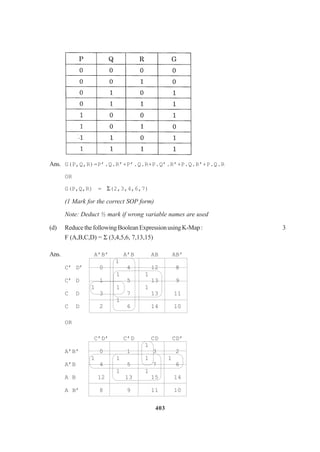

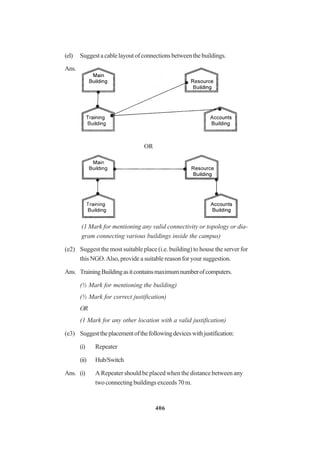

![314
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Programming Language: C+ +
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91/1
1. (a) What is the difference between LocalVariable and Global Variable?
Also, give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both. 2
(b) Writethenamesoftheheaderfiles,whichis/areessentiallyrequiredtorun/
executethefollowingC++code:
voidmain()
{
char C, String [ ] = "Excellence Overload";
for (int I=0; String [ I ] ! = ' 0'; I ++ )
if (String [I] ==' ')
cout<<end1;
else
{
C=toupper(String[I]);
cout<<C ;
}
}
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include[iostream.h]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-366-320.jpg)
![315
typedef char Text(80) ;
voidmain()
{
TextT="Indian";
intCount=strlen(T);
cout<<T<<'has'<<Count<< 'characters' <<end1;
}
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#inc1ude<iostream.h>
voidChangeArray(intNumber,intARR[],intSize)
{
for (int L =0; L<Size; L++)
if(L<Number)
ARR [L] +=L;
e1se
ARR [L] *=L;
}
void Show (intARR [ ], int Size)
{
for (int L=0; L<Size; L++)
(L%2!=0) ?cout<<ARR[L] <<"#": cout<<ARR[L]<<end1 ;
}
voidmain()
{
int Array [ ] = {30, 20, 40, 10, 60, 50};
ChangeArray (3,Array, 6) ;
Show (Array, 6) ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-367-320.jpg)
![316
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
int Track [ ] = {10, 20, 30, 40}, *Striker ;
Stxiker=Track:
Track [1] += 30 ;
cout<<"Striker>"<<*Striker<<end1;
Striker – =10 ;
Striker++ ;
cout<<"Next@"<<*Striker<<end1 ;
Striker+=2 ;
cout<<"Last@"<<*Striker<<end1;
cout<< "Reset To" <<Track[0] <<end1 ;
}
(f) Go through the C++ code shown below, and find out the possible output or
outputs from the suggested Output Options (i) to (iv).Also, write the least
value and highest value, which can be assigned to the variable Guess. 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
voidmain()
{
randomize ( ) ;
intGuess,High=4;
Guess=random{High)+50;
for{int C=Guess ; C<=55 ; C++)
cout<<C<<"#";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-368-320.jpg)
![317
}
(i) 50 # 51 # 52 # 53 # 54 # 55 #
(ii) 52 # 53 # 54 # 55
(iii) 53 # 54 #
(iv) 51 # 52 # 53 # 54 # 55
2. (a) Differentiatebetweenmembers,whicharepresentwithintheprivatevisibility
modewiththosewhicharepresentwithinthepublicvisibilitymodes. 2
(b) Write the output of the following C++ code.Also. write the name of feature
of Object Oriented Programming used in the following program jointly
illustratedbythefunction[I]to[IV]. 2
#include<iostream.h>
void Print ( ) //Function[I]
{
for (int K=1 ; K<=60 ; K++) cout<< "-" ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
voidPrint(intN) //Function[II]
{
for (int K=1 ; K<=N ; L++) cout<<"*" ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
voidPrint(intA,int.B) //Function[III]
{
for (int K=1. ;K<=B ;K++) cout <<A*K ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
void Print (char T, int N) //Function[IV]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-369-320.jpg)

![319
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
classStrident
(
intRno;
char Name [20] ;
floatMarks;
protected:
void Result( ) ;
public:
Student( ) ;
void Register( ); void Display( ) ;
} ;
classFaculty
{
long FCode;
char FName[20];
protected:
floatPay;
public:
Faculty ( ) ;
void Enter ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
} ;
class Course : public Student, private Faculty
{
long CCode [10]; char CourseName [50] ;
char StartDate[8], EndDate[8] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-371-320.jpg)
![320
public:
Course ( ) ;
void Commence ( ) ;
void CDetail ( ) ;
} ;
(i) Which type of inheritance is illustrated in the above C++ code?
(ii) Writethenamesofthealldatamembers,whichis/areaccessiblefrom
memberfunctionCommenceofclassCourse.
(iii) Writethenamesofmemberfunctions,whichareaccessiblefromobjects
of class Course.
(iv) Write the name of all the members, which are accessible from objects
ofclassFaculty.
3 (a) Write a Get1From2 ( ) function in C++ to transfer the content from two
arrays FIRST[ ] and SECOND[ ] to arrayALL[ ]. The even places (0, 2, 4,
...) of arrayALL[ ] should get the content from the array FIRST[ ] and odd
places (1, 3, 5, ) of the arrayALL[] should get the content from the array
SECOND[ ]. 3
Example:
If the FIRST[ ] array contains
30, 60, 90
And the SECOND[ ] array contains
10, 50, 80
TheALL[]arrayshouldcontain
30, 10, 60, 50, 90, 80
(b) AnarrayP[20][50]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwitheachofits
element occupying 4 bytes, find out the 1ocation of P[15][10], if P[0][0] is
stored at 5200. 3
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toperformInsert:operationonadynamicallyallocated
Queue containing Passenger details as given in the following definition of
NODE. 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-372-320.jpg)
![321
struct NODE
{
longPno; //passengerNumber
char Pname[20] ; //passenger Name
NODE *Link.;
} ;
(d) Write a COLSUM( ) function in C++ to find sum of each column of a NxM
Matrix. 2
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
50, 60, + , 20, 10, -, *
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmarked
as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using seekg( ), seekp( ), tellp( ) and tellg( )
functionsforperformingtherequiredtask. 1
#include<fstream.h>
class PRODUCT
{
int Pno; char Pname[20); int Qty;
public:
void ModifyQty( ) ;
//ThefunctionistomodifyquantityofaPRODUCT
} ;
voidPRODUCT::ModifyQty()
{
fstreamFile;
Fil.open("PRODUCT.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
intMPno;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-373-320.jpg)

![323
long ModelNo ;
float RAM, HDD ;
char Details [120] ;
public:
void StockEnter ( )
{cin>>ModelNo>>RAM>>HDD;gets(Details);}
void StockDisplay ( )
{cout<<ModelNo<<RAM<<HDD<<Details<<endl;}
long ReturnModelNo ( ) {return ModelNo ;}
} ;
5 (a) What do you understand by Union & Cartesian Product operations in rela-
tionalalgebra? 2
Consider the following tables WORKER and PAYYLEVELand answer
(b) and (c) parts of this question: 4
Table:WORKER
ECODE NAME DESIG PLEVEL DOJ DOB
11 RadheShyam Supervisor P001 13- Sep- 2004 23-Aug-1981
12 Chander Nath Operator P003 22-Feb-2010 12-Jul-1987
13 Fizza Operator P003 14-Jun-2009 14-0ct-1983
15 AmeenAhmed Mechanic P002 21-Aug-2006 13-Mar-1984
18 Sanya Clerk P002 19-Dec-2005 09-Jun-1983
Table:PAYLEVEL
PLEVEL PAY ALLOWANCE
P001 26000 12000
P002 22000 10000
P003 12000 6000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-375-320.jpg)
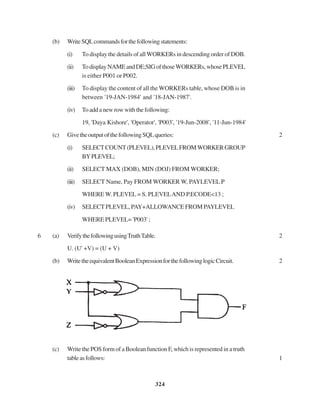


![327
COMPUTER SCIENCE
QUESTION PAPER CODE 91
1. (a) What isthedifferencebetweenTypeCastingandAutomaticTypeconversion?
Also, give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both. 2
(b) Write the names of the header files, which is/are essentially required torun/
executethefollowingc++code: 1
voidmain()
{
charCH,Text[]="+veAttitude";
for (int I=0 ; Text[I] ! ='0' ;I++)
if (Text[I]== ' ')
cout<<end1;
else
{
CH=toupper (Text [I]) ;
cout<<CH;
}
}
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include<iostream.h>
typedef char [80] String;
voidmain()
{
StringS="Peace";
intL=strlen(S);
cout<<S<< 'has'<<L<< 'characters'<<end1;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-379-320.jpg)
![328
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void SwitchOver(intA[ ], int N, int Split)
{
for (int K=0 ; K<N; K++)
if(K<Split)
A(K]+ =K;
else
A [K]*=K;
}
void Display (intA[ ], int N)
{
for (int K=0 ; K<N ; K++)
(K%2==0)? cout<<A[K]<<"%":cout<<A(K]<<end1;
}
voidmain()
{
int H[ ]= {30,40,50,20,10,5};
SwitchOver (H, 6, 3);
Display(H,6);
}
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
int *Queen, Moves [ ] = {11, 22, 33, 44};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-380-320.jpg)
![329
Queen = Moves;
Moves [2] + = 22;
Cout<< "Queen @"<<*Queen<<end1;
*Queen - = 11;
Queen + = 2;
cout<< "Now @"<<*Queen<<end1;
Queen++;
cout<<"Finally@"<<*Queen«end1;
cout<< "New Origin @"<<Moves[0]<<end1;
}
(f) Go through the C++ code shown below, and find out the possible output or
outputsfromthesuggestedOutputOptions(i)to(iv).Also,writetheminimum
andmaximumvalues,whichcanbeassignedtothevariableMyNum. 2
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
voidmain()
{
randomize ( ) ;
intMyNum,Max=5;
MyNum = 20 + random (Max) ;
for (int N=MyNum; N<=25;N++)
cout<N<"*";
}
(i) 20*21*22*23*24*25
(ii) 22*23*24*25*
(iii) 23*24*
(iv) 21*22*23*24*25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-381-320.jpg)
![330
2. (a) DifferentiatebetweenConstructorandDestructorfunctionwithrespectto
ObjectOrientedProgramming. 2
(b) Write the output of the following C++ code.Also, write the .name of feature
of Object Oriented Programming used in the following program jointly
illustratedbythefunction[I]to[IV] 2
#include<iostream.h>
void Line ( ) //Function[I]
{
for (int L=1;L<=80;L++) cout<<"-";
cout<<end1;
}
voidLine(intN) //Function[II]
{
for(intL=l;L<=N;L++) Cout<<"*";
cout<<endl;
}
void Line (char C, int N) //Function[III]
{
for(intL=l;L<=N;L++) cout<<C;
cout<<end1;
}
void Line (int M, int, N) //Function[IV]
{
for (int L=1;L<=N;L++) cout<<M*L;
cout<<end1;
}
voidmain()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-382-320.jpg)

![332
intRollno:
char SName[20];
floatMarksl;
protected:
void Result ( ) ;
public:
Student ( ) ;
void Enroll ( ) ;void Display ( ) ;
} ;
classTeacher
{
longTCode;
char TName [20];
protected:
floatSalary;
public:
Teacher ( );
void Enter ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
} ;
class Course: public Student, private Teacher
}
long CCode [10]; char CourseName [50];
char StartDate [8] , EndDate [8];
public:
Course ( ) ;
void Commence ( );
void CDetail ( ) ;
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-384-320.jpg)
![333
(i) Write the names of member functions, which are accessible from objects of
class Course
(ii) Writethenamesofallthedatamembers,whichis/areaccessiblefrommember
functionCommenceofclassCourse
(iii) Write the names of all the-members, which are accessible from objects of
classTeacher.
(iv) Which type of Inheritance is illustrated in the above C++ code?
3. (a) Write a Get2From1() function in C++ to transfer the content from one array
ALL[] to two different arrays Odd[] and Even[]. The Odd[] array should
contain the values from odd positions (1,3,5,...) ofALL[] and Even [] array
should contain the values from even positions (0, 2, 4,…..) ofALL[]. 3
Example
IftheALL[]arraycontains
12, 34, 56, 67, 89, 90
The Odd[] array should contain
34, 67, 90
And the Even [] array should contain
12, 56, 89
(b) An array G[50][20] is stored in the memory along the row with each of its
elementsoccupying8bytes.FindoutthelocationofG[10][15],ifG[0][0]is
stored at 4200. 3
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toperformDelete operationona dynamicallyallocated
QueuecontainingMembersdetailsasgiveninthefollowingdefinitionofNODE: 4
struct NODE
{
longMno //MemberNumber
char Mname[20]; //Member Name
NODE*Link;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-385-320.jpg)
![334
(d) WriteaDSUMOfunctioninC++tofindsumofDiagonalElementsfroma
NxN Matrix. 2
(Assuming that the N is a odd number)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
True, False, NOT,AND, True, True,AND,OR
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmarked
as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using seekg( ), seekp( ) tellp( ) and tellg( )
functionsforperformingtherequiredtask. 1
#include<fstream.h>
classITEM
{
intIno;charIname[20];floatPrice;
public:
voidModifyPrice();//Thefunctionistomodify
price of a particular ITEM
} ;
voiditem::ModiyPrice()
{
fstreamFile;
File.open("ITEM.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out)||;
intCIno;
cout<<"ItemNotomodifyprice:";cin>>CIno;
while(file.read((char*)this,sizeof(ITEM)))
{
if(CIno==Ino)
{
cout<<"PresentPrice:"<<Price<<end1;
cout<<"Changedprice:";cin>>Price;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-386-320.jpg)
![335
int FilePos = __________ ; //Statement 1,
___________________; //Statement 2
File.write((char*)this,sizeof(ITEM));
// Re-writing the record
}
}
File.close ( ) ;
}
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the no. of "He" or "She" words present in a
textfile"STORY.TXT". 2
Ifthefile"STORY.TXT"contentisasfollows:
Heisplayingintheground.Sheis
Playingwithherdolls.
Theoutputofthefunctionshouldbe
CountofHe/Sheinfile:2
(c) Write a function in C++ to search for a camera from a binary file
"CAMERA.DAT" containing the objects of class" CAMERA (as defined
below). The user should enter the Model No and the function should search
display the details of the camera. 3
classCAMERA
{
longModelNo;
floatMegaPixel;
intZoom;
charDetails[120];
public:
voidEnter(){cin>>ModelNo>>MegaPixel>>Zoom;gets(Details);}
voidDisplay()
{cout<<ModelNo<<MegaPixel<<Zoom<<Details<<endl;}
long GetModelNo ( ) {return ModelNo;}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-387-320.jpg)
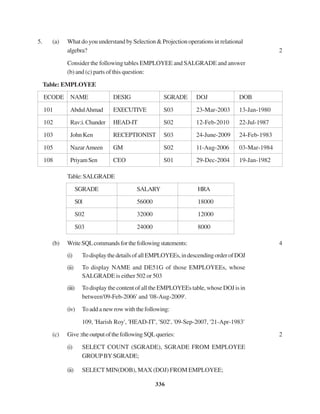




![341
void Fun ( )
{
int L = 25; // Local variable of function Fun ( ) assigned value 25
G=5; // GlobalVariable is accessed and assigned value 5
Cout<<G<<endl; //Value of global variable is displayed as 5
Cout<<L<<endl; //Value of local variable is displayed as 25
}
voidmain()
{
Fun ( ) ; //Functioncall
G = G + 5; //Globalvariableisincrementedby5
cout<<G<<endl; // Global variable is displayed as 10
}
(½ Mark for each correct explanation of Local Variable and Global
Variable)
(½ Mark for each correct example of Local variable and Global Variable)
OR
(Full 2 Maries for correct example(s) demonstrating the meaning of /
difference between Local Variable and Global Variable)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded if Explanation without supporting examples)
(b) Writethenamesoftheheaderfiles,whichis/areessentiallyrequiredtorun/
executethefollowingC++code:
voidmain()
{
char C, String [ ] = "Excellence Overload";
for (int I=0; String [ I ] ! = ' 0'; I ++ )
if (String [I] ==' ')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-393-320.jpg)
![342
cout<<end1;
else
{
C=toupper(String[I]);
cout<<C ;
}
}
Ans iostream.h
ctype.h
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
#include[iostream.h]
typedef char Text(80) ;
voidmain()
{
TextT="Indian";
intCount=strlen(T);
cout<<T<<'has'<<Count<< 'characters' <<end1;
}
Ans #include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef char Text [80];
voidmain()
{
TextT="Indian";
intCount=str1en(T);
cout<<T<< "has" <<Count<< "cbaracters"<<end1 ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-394-320.jpg)
![343
}
(½Markforwriting#include<iostream.h>
(½Markforwriting#include<string.h>
(½ Mark for writing typedef char Text(80];
(½Markforwriting"has"and"characters")
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#inc1ude<iostream.h>
voidChangeArray(intNumber,intARR[],intSize)
{
for (int L =0; L<Size; L++)
if(L<Number)
ARR [L] +=L;
e1se
ARR [L] *=L;
}
void Show (intARR [ ], int Size)
{
for (int L=0; L<Size; L++)
(L%2!=0) ?cout<<ARR[L] <<"#": cout<<ARR[L]<<end1 ;
}
voidmain()
{
int Array [ ] = {30, 20, 40, 10, 60, 50};
ChangeArray (3,Array, 6) ;
Show (Array, 6) ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-395-320.jpg)
![344
Ans 30
21#42
30#240
250#
(½ Mark for each correct value)
Note:
Deduct ½ Mark for not writing # at proper places
Deduct ½ Mark for not considering endl at proaer places
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
int Track [ ] = {10, 20, 30, 40}, *Striker ;
Stxiker=Track:
Track [1] += 30 ;
cout<<"Striker>"<<*Striker<<end1;
Striker – =10 ;
Striker++ ;
cout<<"Next@"<<*Striker<<end1 ;
Striker+=2 ;
cout<<"Last@"<<*Striker<<end1;
cout<< "Reset To" <<Track[0] <<end1 ;
}
Ans Striker>10
Next@50
Last@40
Reset to 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-396-320.jpg)


![347
{
Base B;
B.Assign(); //Accessible
}
(1MarkforcorrectexplanationORexampleillustratingnonaccessibilityof
PrivateMembersinsideDerivedclass)
(1MarieforcorrectexplanationORexampleillustratingaccessibilityofPublic
Members inside Derived Class and to object of the class)
(b) Write the output of the following C++ code.Also. write the name of feature
of Object Oriented Programming used in the following program jointly
illustratedbythefunction[I]to[IV]. 2
#include<iostream.h>
void Print ( ) //Function[I]
{
for (int K=1 ; K<=60 ; K++) cout<< "-" ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
voidPrint(intN) //Function[II]
{
for (int K=1 ; K<=N ; L++) cout<<"*" ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
voidPrint(intA,int.B)
{
for (int K=1. ;K<=B ;K++) cout <<A*K ;
cout<<end1 ;
}
void Print (char T, int N) //Function[IV]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-399-320.jpg)

![349
Amember functionAssignRem( ) to assign Remarks as per the Score
obtained by a candidate. Score range and the respective Remarks are
shownasfollows:
Score Remarks
>=50 Selected
less than 50 Not selected
PublicMembers
A function ENTER ( ) to allow user to enter values for RNo, Name,
Score&callfunctionAssignRem()toassigntheremarks.
AfunctionDISPLAY()toallowusertoviewthecontentofallthedata
members.
Ans class Candidate
{
longRNo;
char Name[20];
float Score;
char Remarks[20];
voidAssignRem();
public:
voidEnter();
voidDisplay();
} ;
voidCandidate::AssignRem()
{
if (Score>=50)
strcpy(Remarks,"Selected");
else
strcpy(Remarks,"Not Selected") ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-401-320.jpg)
![350
void Candidate: : Enter ( )
{
cin>>RNo ;
gets (Name) ; cin>>Score;
AssignRem();
}
voidCandidate::Display()
{
cout<<RNo<<Name<<Score<<Remarks<<end1;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declaration of data members)
(1 Mark for correct definition of AssignRem())
(1 Mark for correct definition of Enter() with proper invocation of
AssignRem() function)
(1 Mark for correct definition of Display())
NOTE:
Deduct ½ Mark to be deducted if Assignrem() is not invoked properly
inside Enter( ) function
No marks to be deducted if member function definitions are written
inside the class
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing:
classStrident
(
intRno;
char Name [20] ;
floatMarks;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-402-320.jpg)
![351
protected:
void Result( ) ;
public:
Student( ) ;
void Register( ); void Display( ) ;
} ;
classFaculty
{
long FCode;
char FName[20];
protected:
floatPay;
public:
Faculty ( ) ;
void Enter ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
} ;
class Course : public Student, private Faculty
{
long CCode [10]; char CourseName [50] ;
char StartDate[8], EndDate[8] ;
public:
Course ( ) ;
void Commence ( ) ;
void CDetail ( ) ;
} ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-403-320.jpg)
![352
(i) Which type of inheritance is illustrated in the above C++ code?
Ans MultipleInheritance
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(ii) Writethenamesofthealldatamembers,whichis/areaccessiblefrom
memberfunctionCommenceofclassCourse.
Ans CCode, CourseName, StartDate, EndDate, Pay
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for any other alternative answer
(iii) Writethenamesofmemberfunctions,whichareaccessiblefromobjects
of class Course.
Ans Commence( ), CDetail( ), Register( ), Display( )
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for any other alternative answer
Constructor functions to be ignored
(iv) Write the name of all the members, which are accessible from objects
ofclassFaculty.
Ans Enter( ), Show( )
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for any other alternative answer
Constructor functions to be iqnored
3 (a) Write a Get1From2 ( ) function in C++ to transfer the content from two
arrays FIRST[ ] and SECOND[ ] to arrayALL[ ]. The even places (0, 2, 4,
...) of arrayALL[ ] should get the content from the array FIRST[ ] and odd
places (1, 3, 5, ) of the arrayALL[] should get the content from the array
SECOND[ ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-404-320.jpg)
![353
Example:
If the FIRST[ ] array contains
30, 60, 90
And the SECOND[ ] array contains
10, 50, 80
TheALL[]arrayshouldcontain
30, 10, 60, 50, 90, 80
Ans void Get1From2 (intALL[],int FIRST[],int SECOND[],
intN,intM)
{
for(int I=0,J=0,K=0;i<N+M; I++)
if(I%2==0)
ALL[I]=FIRST[J++];
else
ALL[I]=SECOND[K++];
}
OR
voidGet1From2(intALL[],intFIRST[],intSECOND[],
int N, int M)
{
int J=0,K=0;
for(int I=0;i<N+M; I++)
{
if(I%2==0)
{
ALL [I] =FIRST [J] ;
J++;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-405-320.jpg)
![354
else
{
ALL[I]=SECOND[K];
K++;
}
}
}
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(½ Mark for checking even locations)
(½ Mark for checking even locations or writing else for odd locations)
( 1 Mark for incrementing FIRST and SECOND Array Locations)
(b) AnarrayP[20][50]isstoredinthememoryalongthecolumnwitheachofits
element occupying 4 bytes, find out the 1ocation of P[15][10], if P[0][0] is
stored at 5200. 3
Ans AssuminqLBR=LBC=0
B=5200
W=4 bytes
Number of Rows(N)=20
NumberofColumns(M)=50
LOC(Arr[I] [J]) = B +(I + J*N)*W
LOC(Arr[15][10]) = 5200+(15+10*20)*4
= 5200 + (215*4)
= 5200 + 860
= 6060
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for row major) OR substituting
formula with correct values for calculating Address)
(2 marks for calculating correct address)
Note:
1 Mark to be awarded for writing only the correct answer (i.e. 6060)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-406-320.jpg)
![355
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toperformInsert:operationonadynamicallyallocated
Queue containing Passenger details as given in the following definition of
NODE. 4
struct NODE
{
longPno; //passengerNumber
char Pname[20] ; //passenger Name
NODE *Link.;
} ;
Ans class Queue
{
NODE *Front, *Rear;
public:
Queue ( ) {Front = NULL; Rear = NULL; }
void QueInsert ( ) ;
void QueDel ( ) ;
void QueDis ( ) ;
~Queue ( ) ;
} ;
void Queue: : QueInsert ( )
{
NODE*Temp=new NODE;
cin>>Temp->Pno; gets (Temp->Pname) ;
Temp->Link = NULL;
Rear->Li.nk = Temp;
Rear = Temp ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-407-320.jpg)
![356
(1 Mark for creating a new NODE dynamically)
(1 Mark for assigning NULL to Link of new NODE)
(1 Mark for linking the Rearmost NODE to the new NODE)
(1 Mark for making the new NODE as the Rearmost NODE)
(d) Write a COLSUM( ) function in C++ to find sum of each column of a NxM
Matrix. 2
Ans void COLSUM(intA[] [100], int N, int M)
{
intSUMC;
for (int j=0; j<M; j++)
{
SUMC = 0;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
SUMC = SUMC + A[i] [j] ;
Cout<< "Sum of Column "<<j<<" = "<<SUMC ;
}
}
(½ Mark for writing correct outer loop)
(½ Mark for initializing SUMC with 0 for each column)
(½ Mark tor writing correct inner loop)
(½ Mark for finding sum of each column)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
50, 60, + , 20, 10, -, *
Ans ElementScanned STACK
50 50
60 50, 60
+ 110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-408-320.jpg)


![359
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the no. of "Me" or "My" words present in a
textfile"DIARY.TXT". 2
Ifthefile"DIARY.TXT"contentisasfollows:
My first book was Me and My
family. It gave me chance to be
known to the world.
Theoutputofthefunctionshouldbe
Count of Me/My in file : 4
Ans void COUNT ( )
{
ifstreamFil("DIARY.TXT");
char STR [10] ;
int count = 0 ;
while(!Fil.eof())
{
Fil>>STR;
if (strcmp (STR, "Me")==0 | | strcmp (STR, "My") ==0)
count++;
}
Cout<<"CountofMe/Myinfile:"<<count<<end1;
Fil.close( ) ; //Ignore
}
OR
Any other correct function definition performing the desired operation
(½ Mark for opening DIARY. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (Whichever method adopted) from, the file)
(½ Mark for comparing the word with 'Me' and 'My' and incrementing counter)
(½ Mark for displaying the number of 'Me/My' with/without the Text Message)
NOTE:
Ignore case sensitivity check for Me/My](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-411-320.jpg)
![360
(c) Write a function in C++ to search for a laptop from a binary file
"LAPTOP.DAT"containingtheobjectsofclassLAPTOP(asdefinedbelow).
The user should enter the Model No and the function should search and
display the details of the laptop. 3
classLAPTOP
{
long ModelNo ;
float RAM, HDD ;
char Details [120] ;
public:
void StockEnter ( )
{cin>>ModelNo>>RAM>>HDD;gets(Details);}
void StockDisplay ( )
{cout<<ModelNo<<RAM<<HDD<<Details<<endl;}
long ReturnModelNo ( ) {return ModelNo ;}
} ;
Ans void Search( )
{
LAPTOPL;
longmodelnum;
cin>>modelnum;
ifstreamfin;
fin.open("LAPTOP.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in);
while(fin.read((char*)&L,sizeof(L)))
{
if(L.ReturnModelNo()==modelnum)
L.StockDisplay ( ) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-412-320.jpg)

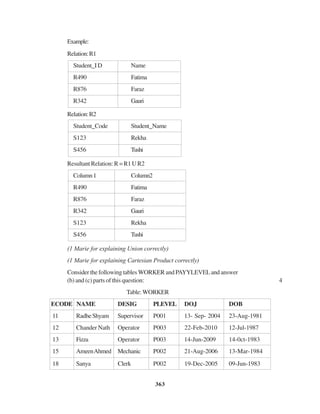
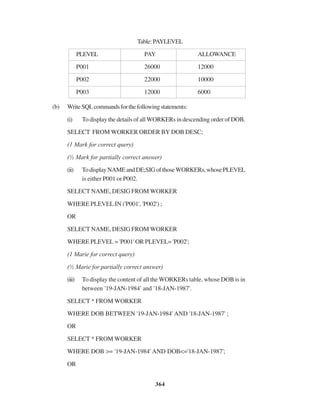

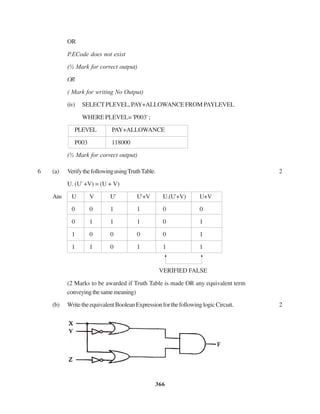



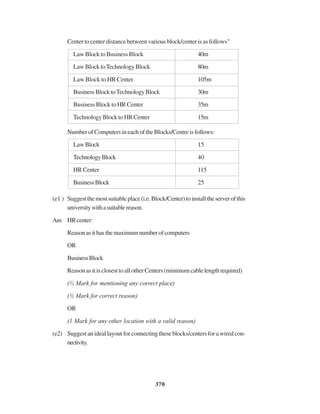
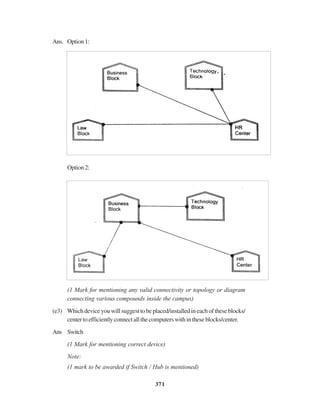

![373
int N = 65;
char C = N; //Automatic type conversion ; conversion
cout<<C;
Type Casting: It is an explicit process of conversion of a data from one type
to another. For example
intA=1, B=2;
float C = (float)A/B; //Type Casting
cout<<C;
(½ Mark for each correct explanation of Automatic Type Conversion
and Type Casting)
(½ Mark for each correct example of Automatic Type Conversion and
Type Casting)
OR
(Full 2 Marks for correct example(s) demonstrating the meaning of /
difference between Automatic Type Conversion and Type Casting)
OR
(Only 1 Mark to be awarded if Explanation is given without supporting
example)
(b) Write the names of the header files, which is/are essentially required torun/
executethefollowingc++code:
voidmain()
{
charCH,Text[]="+veAttitude";
for (int I=0 ; Text[I] ! ='0' ;I++)
if (Text[I]== ' ')
cout<<end1;
else
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-425-320.jpg)
![374
CH=toupper (Text [I]) ;
cout<<CH;
}
}
Ans iostream.h
ctype.h
(½ Mark for writing each correct header file)
(c) Rewritethefollowingprogramafterremovingthesyntacticalerrors(ifany).
Underlineeachcorrection. 2
include<iostream.h>
typedef char [80] String;
voidmain()
{
StringS="Peace";
intL=strlen(S);
cout<<S<< 'has'<<L<< 'characters'<<end1;
}
Ans #include<string.h>
#include<iostream.h>
typedef char String [80];
voidmain()
{
String S = "Peace";
intL=strlen(S);
cout<<S<< "has" << L << "characters"<<end1;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-426-320.jpg)
![375
(½ Mark for writing # include<string.h>
(½ Mark for adding # before include<iostream.h>
(½ Mark for writing typedef char string[80];)
(½ Mark for writing "has" and "characters")
(d) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 3
#include<iostream.h>
void SwitchOver(intA[ ], int N, int Split)
{
for (int K=0 ; K<N; K++)
if(K<Split)
A(K]+ =K;
else
A [K]*=K;
}
void Display (intA[ ], int N)
{
for (int K=0 ; K<N ; K++)
(K%2==0)? cout<<A[K]<<"%":cout<<A(K]<<end1;
}
voidmain()
{
int H[ ]= {30,40,50,20,10,5};
SwitchOver (H, 6, 3);
Display(H,6);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-427-320.jpg)
![376
Ans 30%41
52%60
40%25
(1 Mark for each line with correct values)
Note:
Deduct½Markifany/all'%tmissing
Deduct ½ Mark if endl is not considered at the right positions
(e) Findtheoutputofthefollowingprogram: 2
#include<iostream.h>
voidmain()
{
int *Queen, Moves [ ] = {11, 22, 33, 44};
Queen = Moves;
Moves [2] + = 22;
Cout<< "Queen @"<<*Queen<<end1;
*Queen - = 11;
Queen + = 2;
cout<< "Now @"<<*Queen<<end1;
Queen++;
cout<<"Finally@"<<*Queen«end1;
cout<< "New Origin @"<<Moves[0]<<end1;
}
Ans Queen @11
Now @55
Finally@44
New origin @0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-428-320.jpg)

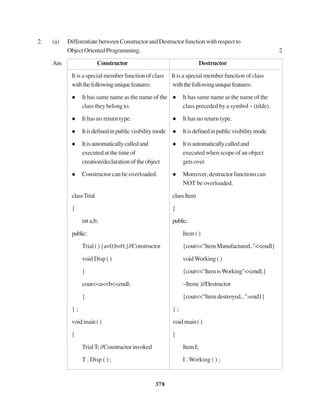
![379
} for (int C=0; C<2; C++)
{
ItemJ;
J.Working ( ) ;
}// Call of Destructor for J
}// Call of Destructor for I
(1 Marie for correct explanation OR example illustrating a Constructor)
(1 Marie for correct explanation OR example illustrating a Destructor)
(b) Write the output of the following C++ code.Also, write the .name of feature
of Object Oriented Programming used in the following program jointly
illustratedbythefunction[I]to[IV] 2
#include<iostream.h>
void Line ( ) //Function[I]
{
for (int L=1;L<=80;L++) cout<<"-";
cout<<end1;
}
voidLine(intN) //Function[II]
{
for(intL=l;L<=N;L++) Cout<<"*";
cout<<endl;
}
void Line (char C, int N) //Function[III]
{
for(intL=l;L<=N;L++) cout<<C;
cout<<end1;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-431-320.jpg)
![380
void Line (int M, int, N) //Function[IV]
{
for (int L=1;L<=N;L++) cout<<M*L;
cout<<end1;
}
voidmain()
{
intA=9, B=4, C=3;
char K= '#' ;
Line(K,B);
Line(A,C);
}
Ans ####
91827
PolymorphismORFunctionOverloading
(½ Mark for writing each correct line of output)
(1 Mark for writing the feature. name correctly)
(c) DefineaclassApplicantinC++withfollowingdescription: 4
PrivateMembers
Adata memberANo (Admission Number) of type long
A data member Name of type string
Adata memberAgg (Aggregate Marks) of type float
A data member Grade of type char
AmemberfunctionGradeMe()tofindtheGradeaspertheAggregate
Marks obtained by a student. EquivalentAggregate Marks range and
the respective Grades are shown as follows:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-432-320.jpg)
![381
AggregateMarks Grade
>=80 A
less than 80 and >=65 B
less than 65 and >=50 C
less than 50 D
PublicMembers
AfunctionENTER()toallowusertoentervaluesforANo,Name,Agg
& call function GradeMe() to find the Grade.
Afunction_RESULT()toallowusertoviewthecontentofallthedata
members.
Ans classApplicant
{
longANo;
char Name [20] ;
floatAgg;
char Grade;
void Grademe ( ) ;
public:
void Enter ( ) ;
void Result ( ) ;
} ;
voidApplicant::GradeMe()
{
if(Agg>=80)
Grade=' A' ;
elseif(Agg>=65)
Grade=' B' ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-433-320.jpg)

![383
(d) Answerthequestions(i)to(iv)basedonthefollowing: 4
classStudent
{
intRollno:
char SName[20];
floatMarksl;
protected:
void Result ( ) ;
public:
Student ( ) ;
void Enroll ( ) ;void Display ( ) ;
} ;
classTeacher
{
longTCode;
char TName [20];
protected:
floatSalary;
public:
Teacher ( );
void Enter ( ) ;
void Show ( ) ;
} ;
class Course: public Student, private Teacher
}
long CCode [10]; char CourseName [50];
char StartDate [8] , EndDate [8];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-435-320.jpg)

![385
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for a partially correct answer
Constructorfunctionstobeignored
iv) Which type of Inheritance is illustrated in the above C++ code?
Ans MultipleInheritance
(1 Mark for correct answer)
Note:
No marks to be awarded for a partially correct answer
3. (a) Write a Get2From1() function in C++ to transfer the content from one array
ALL[] to two different arrays Odd[] and Even[]. The Odd[] array should
contain the values from odd positions (1,3,5,...) ofALL[] and Even [] array
should contain the values from even positions (0, 2, 4,…..) ofALL[]. 3
Example
IftheALL[]arraycontains
12, 34, 56, 67, 89, 90
The Odd[] array should contain
34, 67, 90
And the Even [] array should contain
12,56,89
Ans voilGet2From1(intAll[],intEven[],intOdd[],intSize)
{
int J=0,K=0;
for (int I=0 ;I<Size; 1++)
{
if(I%2==0)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-437-320.jpg)
![386
Even[J]=All[I];
J++;
}
else
{
Odd[K]=All[I);
K++;
}
}
}
(1 Mark for correct loop)
(½ Mark for checking even locations)
(½ Mark for checking odd locations or writing else for even locations)
(½ Mark for assigning elements to the corresponding Even and Odd Array)
(½ Mark for incrementing Even and Odd Array Locations)
(b) An array G[50][20] is stored in the memory along the row with each of its
elementsoccupying8bytes.FindoutthelocationofG[10][15],ifG[0][0]is
stored at 4200. 3
Ans AssumingLBR=LBC=0
B=4200
W=8 bytes
Number of Rows(N)=50
Number of Columns (M)=20
LOC(Arr[I] [J]) = B +(I*M + J) *W
LOC (Arr [10] [15]) = 4200+ (10*20+15)*8
= 4200 + (215*8)
= 4200+1720
= 5920](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-438-320.jpg)
![387
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for row major)
OR substituting formula with correct values for calculating Address)
(2 marks for calculating correct address)
Note:
1 mark to be awarded for writing only the correct answer i.e. 5920, without
showinganyformula/calculation.
(c) WriteafunctioninC++toperformDelete operationona dynamicallyallocated
QueuecontainingMembersdetailsasgiveninthefollowingdefinitionofNODE: 4
struct NODE
{
longMno //MemberNumber
char Mname[20]; //Member Name
NODE*Link;
};
Ans class Queue
{
NODE *Front, *Rear;
public:
Queue ( ) {Front = NULL; Rear = NULL; }
void QueAdd ( );
void QueDel ( );
void QueDis ( );
~Queue();
} ;
void Queue: :QueDel ( )
{
if(Front!=NULL)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-439-320.jpg)
![388
{
NODE *Temp=Front;
cout<<Front->Mno<< " " ;
cout<<Front->Mname<<"Deleted";
Front=Front->Link;
deleteTemp;
if (Front==NULL) Rear=NULL;
}
else
cout<<"Underflow!Queueisempty..";
}
(1 Mark for checking Empty Queue)
(½ Mark for assigning Front to Temp)
(1 Mark for reassigning Front with Front->Link)
(1 Mark for deleting Temp)
(½ Mark for assigning Rear with NULL if Queue becomes Empty)
(d) WriteaDSUMOfunctioninC++tofindsumofDiagonalElementsfroma
NxN Matrix. 2
(Assuming that the N is a odd number)
Ans void DSUM (intA[ ] [100] ,int N)
{
int SUMR =0, SUML=0;
for(inti=0;i<N;i++}
{
SUMR=SUMR +A[i] [i] ;
SUML = SUML +A[i] [N-1-i] ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-440-320.jpg)
![389
cout<< " Sum of Diagonal Elements = "<<SUMR + SUML –
A[N/2] [N/2] ;
}
OR
void DSUM (intA[] [100], int N)
{
int SUMR =0, SUML=0;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
SUMR = SUMR +A[i] [i] ;
SUML = SUML +A[i] [N-1-i] ;
}
cout<<"SumofRightDiagonalElements="<<SUMR<<end1;
cout<<"SumofLeftDiagonalElements="<<SUML<<end1;
}
OR
void DSUM (intA[] [100] , int N)
{
int SUMR =0, SUML=0;
for (int i = 0; i<N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j<N; j++)
{
if(i==j)
SUMR=SUMR +A[i] [j] ;
else if (i+j == N-1)
SUML= SUML+A[i] [j];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-441-320.jpg)
![390
}
}
cout<< "Sum of Diagonal Elements ="<< SUMR + SUML-A[N/2] [N/2];
}
(½ Mark for writing correct Function Header)
(½ Mark for writing correct loop)
(1 Mark for finding sum of Right Diagonal Elements and/or Left Diagonal
Elements)
(e) Evaluatethefollowingpostfixnotationofexpression: 2
True, False, NOT,AND, True, True,AND,OR
Ans Element Scanned STACK Status
True TRUE
False TRUE,FALSE
NOT TRUE,TRUE
AND TRUE
True TRUE,TRUE
True TRUE,TRUE,TRUE
AND TRUE,TRUE
OR TRUE
FinalResult:TRUE
(½ Mark for evaluating each operator correctly)
OR
(½ Mark only for writing TRUE as the final answer without showing
any calculation/Stack)
4. (a) Observetheprogramsegmentgivenbelowcarefullyandfilltheblanksmarked
as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using seekg( ), seekp( ) tellp( ) and tellg( )
functionsforperformingtherequiredtask. 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-442-320.jpg)
![391
#include<fstream.h>
classITEM
{
intIno;charIname[20];floatPrice;
public:
voidModifyPrice();//Thefunctionistomodify
price of a particular ITEM
} ;
voiditem::ModiyPrice()
{
fstreamFile;
File.open("ITEM.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out)||;
intCIno;
cout<<"ItemNotomodifyprice:";cin>>CIno;
while(file.read((char*)this,sizeof(ITEM)))
{
if(CIno==Ino)
{
cout<<"PresentPrice:"<<Price<<end1;
cout<<"Changedprice:";cin>>Price;
int FilePos = __________ ; //Statement 1,
___________________; //Statement 2
File.write((char*)this,sizeof(ITEM));
// Re-writing the record
}
}
File.close( ) ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-443-320.jpg)
![392
Ans Option 1
Statement 1: File.tellp ( ) ; OR File. tellg ( ) ;
Statement 2: File.seekp (FilePos - sizeof (ITEM) ) ;
OR File.seekp(-sizeof(ITEM),ios::cur));
OR File.seekg(FilePos-sizeof(ITEM));
OR. File.seekg(-sizeof(ITEM),ios::cur));
Ogtion2
Statement 1: File. tellp ( ) – sizeof (ITEM) ;
OR File.tellg()-sizeof(ITEM);
Statement 2: File.seekp (FilePos) ;
OR File.seekg (FilePos) ;
(½ Mark for writing Statement 1 correctly)
(½ Mark for writing Statement 2 correctly)
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the no. of "He" or "She" words present in a
textfile"STORY.TXT". 2
Ifthefile"STORY.TXT"contentisasfollows:
Heisplayingintheground.Sheis
Playingwithherdolls.
Theoutputofthefunctionshouldbe
CountofHe/Sheinfile:2
Ans void COUNT ( )
{
ifstreamFil("STORY.TXT");
char STR [10];
int count = 0;
while(!Fil.eof())
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-444-320.jpg)
![393
Fil>>STR;
if (strcmp (STR, "He") ==0 | | strcmp (STR, "She") = =0)
count++;
}
Cout<<"CountofHe/Sheinfile:"<<count<<end1;
Fil.close();//Ignore
}
OR
Anyothercorrectfunctiondefinitionperformingthedesiredoperation
(½ Mark for opening STORY. TXT correctly)
(½ Mark for reading each word (Whichever method adopted) from the file)
(½ Mark for comparing the word with 'He' and 'She' and incrementing counter)
(½ Mark for displaying the count of 'He/She' with/without the Text Message)
Note:IgnorecasesensitivityforHe/She
(c) Write a function in C++ to search for a camera from a binary file
"CAMERA.DAT" containing the objects of class" CAMERA (as defined
below). The user should enter the Model No and the function should search
display the details of the camera. 3
classCAMERA
{
longModelNo;
floatMegaPixel;
intZoom;
charDetails[120];
public:
voidEnter(){cin>>ModelNo>>MegaPixel>>Zoom;gets(Details);}
voidDisplay()
{cout<<ModelNo<<MegaPixel<<Zoom<<Details<<endl;}
long GetModelNo ( ) {return ModelNo;}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-445-320.jpg)

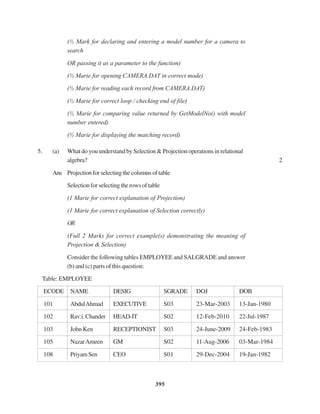


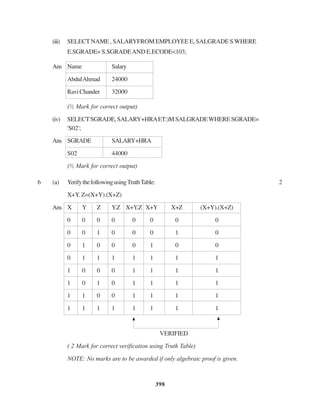
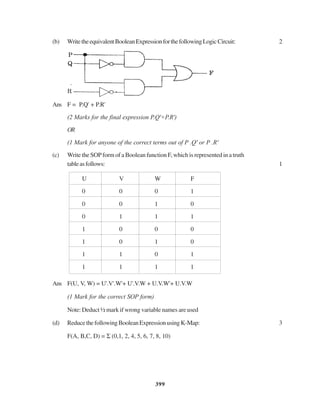



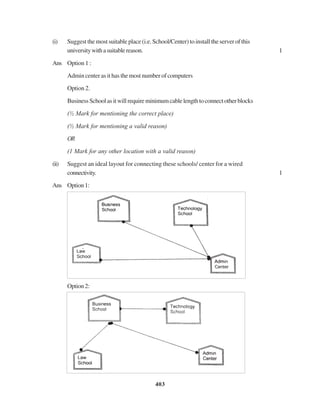

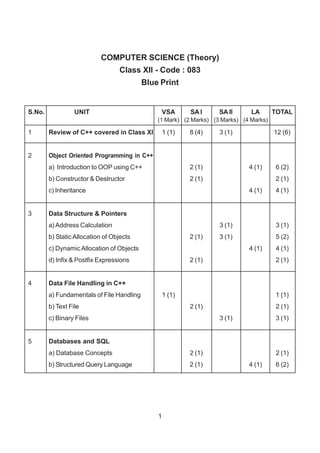
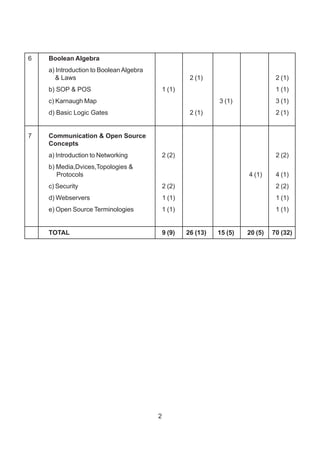
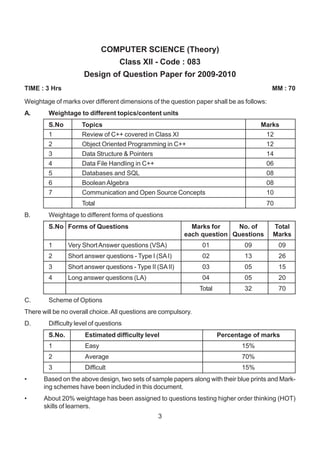
![4
COMPUTER SCIENCE (Theory) - Class XII
Sample Question Paper–I
Subject Code - 083
TIME : 3 Hrs MM : 70
1.
(a) What is the difference between Global Variable and Local Variable? Also, give
a suitable C++ code to illustrate both. 2
(b) Which C++ header file(s) will be essentially required to be included to run /
execute the following C++ code: 1
void main()
{
char Msg[ ]="Sunset Gardens";
for (int I=5;I<strlen(Msg);I++)
puts(Msg);
}
(c) Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical errors (if any).
Underline each correction. 2
#include [iostream.h]
class MEMBER
{
int Mno;float Fees;
PUBLIC:
void Register(){cin>>Mno>>Fees;}
void Display{cout<<Mno<<" : "<<Fees<<endl;}
};
void main()
{
MEMBER M;
Register();
M.Display();
}
No. Questions Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-460-320.jpg)
![5
No. Questions Marks
(d) Find the output of the following program: 3
#include <iostream.h>
struct GAME
{ int Score, Bonus;};
void Play(GAME &g, int N=10)
{
g.Score++;g.Bonus+=N;
}
void main()
{
GAME G={110,50};
Play(G,10);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl;
Play(G);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl;
Play(G,15);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl;
}
(e) Find the output of the following program: 2
#include <iostream.h>
void Secret(char Str[ ])
{
for (int L=0;Str[L]!='0';L++);
for (int C=0;C<L/2;C++)
if (Str[C]=='A' || Str[C]=='E')
Str[C]='#';
else
{
char Temp=Str[C];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-461-320.jpg)
![6
No. Questions Marks
Str[C]=Str[L-C-1];
Str[L-C-1]=Temp;
}
}
void main()
{
char Message[ ]="ArabSagar";
Secret(Message);
cout<<Message<<endl;
}
(f) In the following program, if the value of Guess entered by the user is 65, what
will be the expected output(s) from the following options (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)? 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int Guess;
randomize();
cin>>Guess;
for (int I=1;I<=4;I++)
{
New=Guess+random(I);
cout<<(char)New;
}
}
(i) ABBC
(ii) ACBA
(iii) BCDA
(iv) CABD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-462-320.jpg)

![8
No. Questions Marks
(c) Define a class TEST in C++ with following description: 4
Private Members
• TestCode of type integer
• Description of type string
• NoCandidate of type integer
• CenterReqd (number of centers required) of type integer
• A member function CALCNTR() to calculate and return the number of centers as
(NoCandidates/100+1)
Public Members
• Afunction SCHEDULE() to allow user to enter values for TestCode,
Description, NoCandidate & call function CALCNTR() to calculate the number of
Centres
• A function DISPTEST() to allow user to view the content of all the data members
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following: 4
class PUBLISHER
{
char Pub[12];
double Turnover;
protected:
void Register();
public:
PUBLISHER();
void Enter();
void Display();
};
class BRANCH
{
char CITY[20];
protected:
float Employees;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-464-320.jpg)
![9
No. Questions Marks
public:
BRANCH();
void Haveit();
void Giveit();
};
classAUTHOR : private BRANCH , public PUBLISHER
{
int Acode;
charAname[20];
floatAmount;
public:
AUTHOR();
void Start();
void Show();
};
(i) Write the names of data members, which are accessible from objects belong-
ing to classAUTHOR.
(ii) Write the names of all the member functions which are accessible from ob-
jects belonging to class BRANCH.
(iii) Write the names of all the members which are accessible from member func-
tions of classAUTHOR.
(iv) How many bytes will be required by an object belonging to classAUTHOR?
3. (a) Write a function in C++ to merge the contents of two sorted arrays A & B into
third array C. Assuming array A and B are sorted in ascending order and the
resultant array C is also required to be in ascending order.
(b) An array S[40][30] is stored in the memory along the row with each of the ele-
ment occupying 2 bytes, find out the memory location for the element S[20][10],
if the Base Address of the array is 5000.
(c) Write a function in C++ to perform Insert operation in a dynamically
allocated Queue containing names of students.
(d) Write a function in C++ to find the sum of both left and right diagonal ele-
3
3
4
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-465-320.jpg)
![10
No. Questions Marks
ments from a two dimensional array (matrix).
(e) Evaluate the following postfix notation of expression:
20, 30, +, 50, 40, - ,*
4.
(a) Observe the program segment given below carefully and fill the blanks
marked as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using seekp() and seekg() functions
for performing the required task. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Item
{
int Ino;char Item[20];
public:
//Function to search and display the content from a particular record number
void Search(int );
//Function to modify the content of a particular record number
void Modify(int);
};
void Item::Search(int RecNo)
{
fstream File;
File.open("STOCK.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in);
______________________ //Statement 1
File.read((char*)this,sizeof(Item));
cout<<Ino<<"==>"<<Item<<endl;
File.close();
}
void Item::Modify(int RecNo)
{
fstream File;
File.open("STOCK.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in|ios::out);
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-466-320.jpg)
![11
No. Questions Marks
cout>>Ino;cin.getline(Item,20);
______________________ //Statement 2
File.write((char*)this,sizeof(Item));
File.close();
}
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the number of lines present in a text file
"STORY.TXT". 2
(c) Write a function in C++ to search for a BookNo from a binary file "BOOK.DAT",
assuming the binary file is containing the objects of the following class. 3
class
{
int Bno;
char Title[20];
public:
int RBno(){return Bno;}
void Enter(){cin>>Bno;gets(Title);}
void Display(){cout<<Bno<<Title<<endl;}
};
5.
(a) What do you understand by Degree and Cardinality of a table? 2
Consider the following tables ACTIVITY and COACH and answer
(b) and (c) parts of this question:
Table: ACTIVITY
A Code ActivityName Stadium Participants Prize Schedule
Num Money Date
1001 Relay 100x4 StarAnnex 16 10000 23-Jan-2004
1002 High jump StarAnnex 10 12000 12-Dec-2003
1003 Shot Put Super Power 12 8000 14-Feb-2004
1005 Long Jump StarAnnex 12 9000 01-Jan-2004
1008 Discuss Throw Super Power 10 15000 19-Mar-2004](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-467-320.jpg)
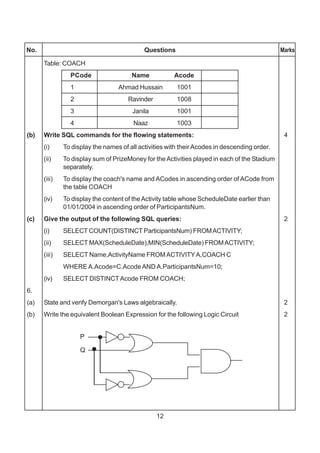
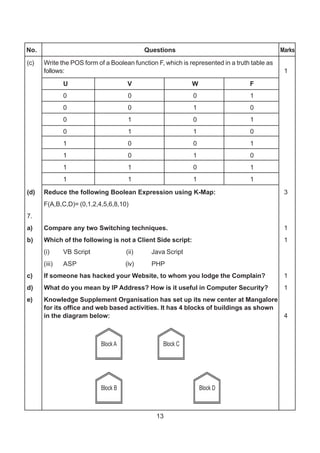
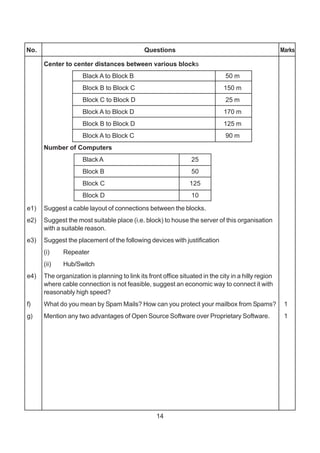


![17
(e) #agaSbarr 2
(2 Marks for correct line of output)
(f) (i) ABBC 2
(2 Marks for mentioning correct option)
2.
(a) Data Encapsulation: Wrapping up of data and functions together in a single unit is 2
known as Data Encapsulation. In a class, we wrap up the data and functions together
in a single unit.
Data Hiding: Keeping the data in private visibility mode of the class to prevent it from
accidental change is known as Data Hiding.
class Computer
{
char CPU[10];int RAM;
public: Data Encapsulation
void STOCK();
void SHOW();
};
( ½ Mark each for appropriate definitions)
(1 Mark for appropriate example showing both)
(b) i) Destructor, it is invoked as soon as the scope of the object gets over. 2
( ½ Mark for mentioning destructor)
( ½ Mark for remaining answer)
ii) Constructor Overloading (or Function Overloading or Polymorphism)
Seminar S1; //Function 1
Seminar S2(90); //Function 3
( ½ Mark for mentioning the correct concept)
( ½ Mark for the example)
No. Answers Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-473-320.jpg)
![18
(c) class TEST 4
{
int TestCode;
char Description[20];
int NoCandidate,CenterReqd;
void CALCNTR();
public:
void SCHEDULE();
void DISPTEST();
};
void TEST::CALCNTR()
{
CenterReqd=NoCandidate/100 + 1;
}
void TEST::SCHEDULE()
{
cout<<"Test Code :";cin>>TestCode;
cout<<"Description :";gets(Description);
cout<<"Number :";cin>>NoCandidate;
CALCNTR();
}
void TEST::DISPTEST()
{
cout<<"Test Code :"<<TestCode<<endl;
cout<<"Description :"<<Description<<endl;
cout<<"Number :"<<NoCandidate<<endl;;
cout<<"Centres :"<<CenterReqd<<endl;;
}
(½ Mark for correct syntax for class header)
(½ Mark for correct declarations of data members)
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of function CALCNTR())
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of SCHEDULE() with a call for CALCNTR())
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of DISPTEST())
(d) (i) None of data members are accessible from objects belonging to class 4
AUTHOR.
No. Answers Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-474-320.jpg)
![19
No. Answers Marks
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(ii) Haveit(), Giveit()
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iii) Data members: Employees,Acode, Aname,Amount
Member function: Register(), Enter(), Display(), Haveit(), Giveit(), Start(), Show(),
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iv) 70
(1 Mark for correct answer)
3. (a) voidAddNSave(int A[ ],int B[ ],int C[ ],int N,int M, int &K) 3
{
int I=0,J=0;
K=0;
while (I<N && J<M)
if (A[I]<B[J])
C[K++]=A[I++];
else
if (A[I]>B[J])
C[K++]=B[J++];
else
{
C[K++]=A[I++];
J++;
}
for(;I<N;I++)
C[K++]=A[I];
for (;J<M;J++)
C[K++]=B[J];
}
( ½ Mark for correct Function Header)
( ½ Mark for correct initialization of required variables)
( ½ Mark for correct formation of loop)
( ½ Mark for appropriate conditions and assignments in the loop)
( ½ Mark for appropriately transferring the remaining elements from first array)
( ½ Mark for appropriately transferring the remaining elements from second array)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-475-320.jpg)
![20
No. Answers Marks
(b) Given, 3
W=2
N=40
M=30
Base(S)=5000
Row Major Formula:
Loc(S[I][J]) =Base(S)+W*(M*I+J)
Loc(S[20][10]) =5000+2*(30*20+10)
=5000+2*(600+10)
=5000+1220
=6220
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for column major) OR substituting formula with
correct values)
(1 Mark for writing calculation step - at least one step)
(1 Mark for correct address)
(c) struct NODE 4
{
char Name[20];
NODE *Link;
};
class QUEUE
{ NODE *R,*F;
public:
QUEUE();
void Insert();
void Delete();
};
void QUEUE::Insert()
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-476-320.jpg)
![21
No. Answers Marks
NODE *Temp;
Temp=new NODE;
gets(Temp->Name);
Temp->Link=NULL;
if (Rear==NULL)
{
Rear=Temp;
Front=Temp;
}
else
{
Rear->Link=Temp;
Rear=Temp;
}
}
(1 Mark for creating a new node and assigning/entering appropriate values in it)
(1 Mark for checking if Queue is Empty)
(1 Mark for assigning Rear and Front as Temp - if Queue is Empty)
(1 Mark for eassigning Rear->Link as Front and Rear as Temp)
(d) void DiagSum(int M[][4],int N,int M) 2
{
int SumD1=0,SumD2=0;
for (int I=0;I<N;I++)
{
SumD1+=M[I][I];SumD2+=M[N-I-1][I];
}
cout<<"Sum of Diagonal 1:"<<SumD1<<endl;
cout<<"Sum of Diagonal 2:"<<SumD2<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-477-320.jpg)
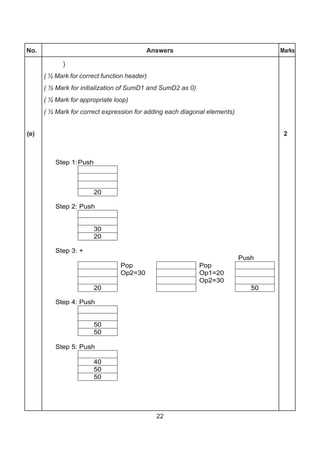
![23
(½ Mark for correctly evaluating each operator)
(½ Mark for the correct result)
4. a) 1
File.seekg(RecNo*sizeof(Item)); //Statement 1
File.seekp(RecNo*sizeof(Item)); //Statement 2
(½ Mark for each correct Statement)
(b) 2
void CountLine()
{
ifstream FIL("STORY.TXT");
int LINES=0;
char STR[80];
No. Answers Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-479-320.jpg)

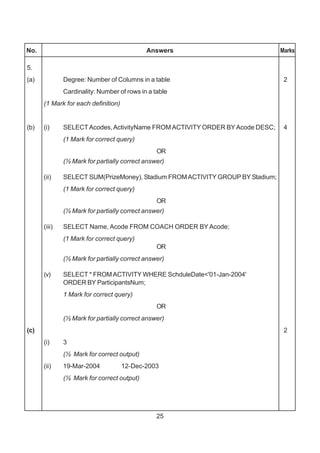

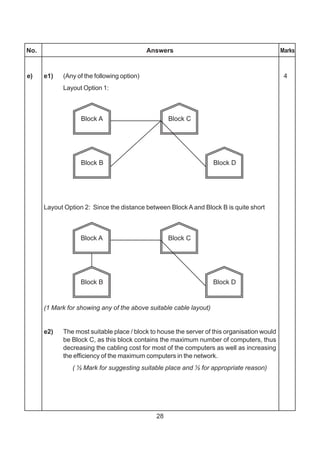
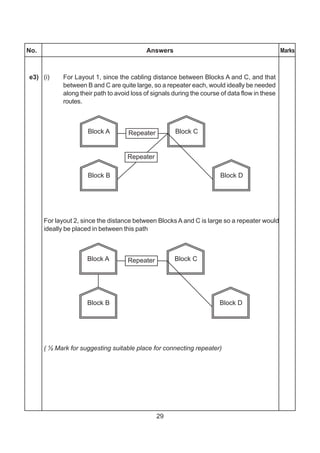
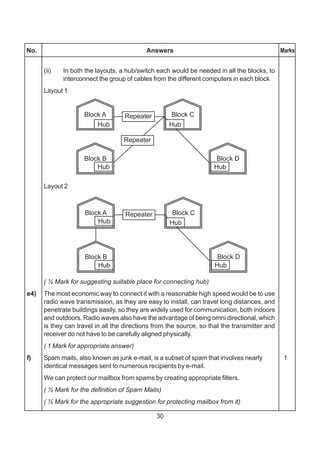

![32
No. Questions Marks
COMPUTER SCIENCE (Theory) - Class XII
Sample Question Paper–II
Subject Code - 083
TIME : 3 Hrs MM : 70
1.
(a) What is the difference between Actual Parameter and Formal Parameters?
Also, give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both 2
(b) Write the names of the header files to which the following belong: 1
(i) frexp() (ii) isalnum()
(c) Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical errors (if any).
Underline each correction. 2
#include <iostream.h>
struct Pixels
{ int Color,Style;}
void ShowPoint(Pixels P)
{ cout<<P.Color,P.Style<<endl;}
void main()
{
Pixels Point1=(5,3);
ShowPoint(Point1);
Pixels Point2=Point1;
Color.Point1+=2;
ShowPoint(Point2);
}
(d) Find the output of the following program: 3
#include <iostream.h>
void Changethecontent(intArr[ ], int Count)
{
for (int C=1;C<Count;C++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-488-320.jpg)
![33
No. Questions Marks
Arr[C-1]+=Arr[C];
}
void main()
{
intA[]={3,4,5},B[]={10,20,30,40},C[]={900,1200};
Changethecontent(A,3);
Changethecontent(B,4);
Changethecontent(C,2);
for (int L=0;L<3;L++) cout<<A[L]<<'#';
cout<<endl;
for (L=0;L<4;L++) cout<<B[L] <<'#';
cout<<endl;
for (L=0;L<2;L++) cout<<C[L] <<'#';
}
(e) Find the output of the following program: 2
#include <iostream.h>
struct Game
{
char Magic[20];int Score;
};
void main()
{
Game M={"Tiger",500};
char *Choice;
Choice=M.Magic;
Choice[4]='P';
Choice[2]='L';
M.Score+=50;
cout<<M.Magic<<M.Score<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-489-320.jpg)
![34
No. Questions Marks
Game N=M;
N.Magic[0]='A';N.Magic[3]='J';
N.Score-=120;
cout<<N.Magic<<N.Score<<endl;
}
(f) In the following program, if the value of N given by the user is 20, what
maximum and minimum values the program could possibly display? 2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int N,Guessnum;
randomize();
cin>>N;
Guessnum=random(N-10)+10;
cout<<Guessnum<<endl;
}
2.
(a) What do you understand by Polymorphism? Give a suitable example of the
same. 2
(b) Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following program: 2
class Match
{
int Time;
public:
Match()
//Function 1
{
Time=0;
cout<<"Match commences"<<end1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-490-320.jpg)

![36
No. Questions Marks
more than 2000 2200
Public Members
" A function FEEDINFO() to allow user to enter values for Flight Number,
Destination, Distance & call function CALFUEL() to calculate the quantity of Fuel
" AfunctionSHOWINFO()toallowusertoviewthecontentofallthedatamembers
(d) Answer the questions (i) to (iv) based on the following: 4
class CUSTOMER
{
int Cust_no;
char Cust_Name[20];
protected:
void Register();
public:
CUSTOMER();
void Status();
};
class SALESMAN
{
int Salesman_no;
char Salesman_Name[20];
protected:
float Salary;
public:
SALESMAN();
void Enter();
void Show();
};
class SHOP : private CUSTOMER , public SALESMAN
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-492-320.jpg)
![37
No. Questions Marks
char Voucher_No[10];
char Sales_Date[8];
public:
SHOP();
void Sales_Entry();
void Sales_Detail();
};
(i) Write the names of data members which are accessible from objects belonging to
class CUSTOMER.
(ii) Write the names of all the member functions which are accessible from objects
belonging to class SALESMAN.
(iii) Write the names of all the members which are accessible from member functions of
class SHOP.
(iv) How many bytes will be required by an object belonging to class SHOP?
3.
(a) Write a function in C++ to combine the contents of two equi-sized arrays A
and B by adding their corresponding elements as the formula A[i]+B[i]; where
value i varies from 0 to N-1 and transfer the resultant content in the third same
sized array C. 3
(b) An array P[20][30] is stored in the memory along the column with each of the
element occupying 4 bytes, find out the Base Address of the array, if an
element P[2][20] is stored at the memory location 5000. 3
(c) Write a function in C++ to perform Push operation on a dynamically allocated
Stack containing real numbers. 4
(d) Write a function in C++ to find sum of rows from a two dimensional array. 2
(e) Evaluate the following postfix notation of expression: 2
True, False,AND, True, True, NOT, OR,AND
4.
(a) Observe the program segment given below carefully and fill the blanks marked
as Statement 1 and Statement 2 using seekg() and tellg() functions for
performing the required task. 1
#include <fstream.h>
class Employee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-493-320.jpg)
![38
No. Questions Marks
{
int Eno;char Ename[20];
public:
//Function to count the total number of records
int Countrec();
};
int Item::Countrec()
{
fstream File;
File.open("EMP.DAT",ios::binary|ios::in);
______________________ //Statement 1
int Bytes =
______________________ //Statement 2
int Count = Bytes / sizeof(Item);
File.close();
return Count;
}
(b) Write a function in C++ to count the number of alphabets present in a text file
"NOTES.TXT". 2
(c) Write a function in C++ to add new objects at the bottom of a binary file
"STUDENT.DAT", assuming the binary file is containing the objects of the
following class. 3
class STUD
{
int Rno;
char Name[20];
public:
void Enter(){cin>>Rno;gets(Name);}
void Display(){cout<<Rno<<Name<<endl;}
};
- To take the file pointer to
the end of file.
- To return total number of
bytes from the beginning of
file to the file pointer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-494-320.jpg)
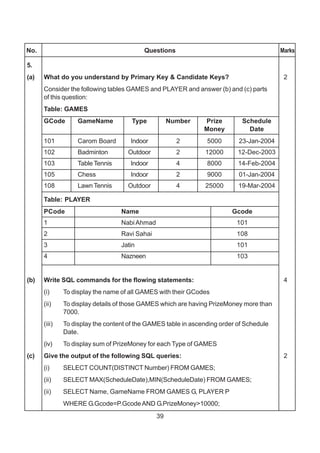
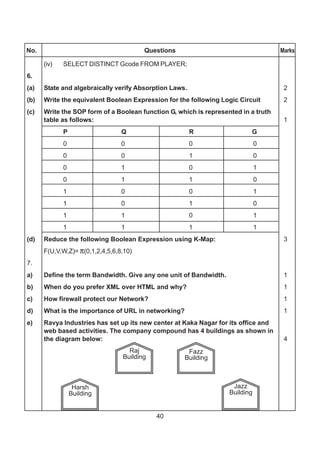
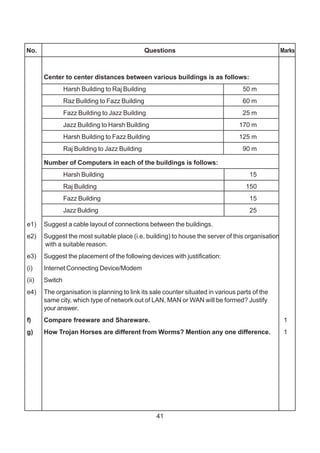


![44
No. Answers Marks
2.
(a) Polymorphism: It is a method of using the same operator or function (method) to work 2
using different set of inputs. Function overloading is one of the examples of polymor-
phism, where more than one function carrying same name behave differently with
different set of parameters passed to them.
void Display()
{
cout<<"Hello!"<<endl;
}
void Display(int N)
{
cout<<2*N+5<<endl;
}
(1 Mark each for appropriate definition)
(1 Mark for appropriate example)
(b) i) Copy constructor, It will help to copy the data from one object to another. 2
( ½ Mark for mentioning copy constructor)
( ½ Mark for remaining answer)
ii) Match M; //Function 1
Match N(10); //Function 3
( ½ Mark for each statement)
(c) class FLIGHT 4
{
int Fno;
char Destination[20];
float Distance, Fuel;
void CALFUEL();
public:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-500-320.jpg)

![46
No. Answers Marks
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of function CALFUEL())
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of FEEDINFO() with a call for CALFUEL())
(1 Mark for appropriate definition of SHOWINFO())
(d) 4
(i) None of data members are accessible from objects belonging to class
AUTHOR.
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(ii) Enter(), Show()
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iii) Data members: Voucher_No, Sales_Date, Salary
Member function:Sales_Entry(),Sales_Detail(),Enter(),Show(),Register(),
Status()
(1 Mark for correct answer)
(iv) 66
(1 Mark for correct answer)
3. (a) voidAddNSave(intA[ ],int B[ ],int C[ ],int N) 3
{
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
C[i]=A[i]+B[i];
}
(1 Mark for correct Function Header with appropriate parameters)
(1 Mark for appropriate loop)
(1 Mark for correct expression for addition of corresponding elements)
(b) Given, 3
W=4
N=20
M=30
Loc(P[2][20])=5000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-502-320.jpg)
![47
No. Answers Marks
Column Major Formula:
Loc(P[I][J]) =Base(P)+W*(N*J+I)
Loc(P[2][20]) =Base(P)+4*(20*20+2)
Base(P) =5000 -4*(400+2)
=5000-1608
=3392
(1 Mark for writing correct formula (for column major) OR substituting formula with
correct values)
(1 Mark for writing calculation step - at least one step)
(1 Mark for correct address)
(c) struct NODE 3
{
float Data; NODE *Link;
};
class STACK
{
NODE *Top;
public:
STACK();
void Push();
void Pop();
void Display();
~STACK();
};
void STACK::Push()
{
NODE *Temp;
Temp=new NODE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-503-320.jpg)
![48
No. Answers Marks
cin>>Temp->Data;
Temp->Link=Top;
Top=Temp;
}
(1 Mark for declaring Temp pointer)
(1 Mark for creating a new node and assigning/entering appropriate values in it)
(1 Mark for connecting link part of new node to top)
(1 Mark for assigning Top as the new node i.e. Temp)
(d) void MatAdd(int M[][4],int N,int M) 2
{
for (int R=0;R<N;R++)
{
int SumR=0;
for (int C=0;C<M;C++)
SumR+=M[C][R];
cout<<SumR<<endl;
}
}
( ½ Mark for correct function header)
( ½ Mark for appropriate outer loop)
( ½ Mark for appropriate inner loop)
( ½ Mark for correctly initializing SumR and calculatin the sum)
(e) 2
(½ Mark for correctly evaluating each operator)
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbsemarkingscheme2006-2011-160325122354/85/Cbse-marking-scheme-2006-2011-504-320.jpg)