- Develop extensive root systems to absorb water from deeper soil layers.
du
- Have thick cuticle and sunken stomata to reduce transpiration.
- Possess water storage tissues like succulents.
.e
- Droop or shed leaves during drought.
w
w
Animals:
- Migrate to areas with available water.
w
- Enter state of aestivation or hibernation during drought.
- Concentrate urine to reduce water loss.
- Obtain water from metabolic processes like respiration.
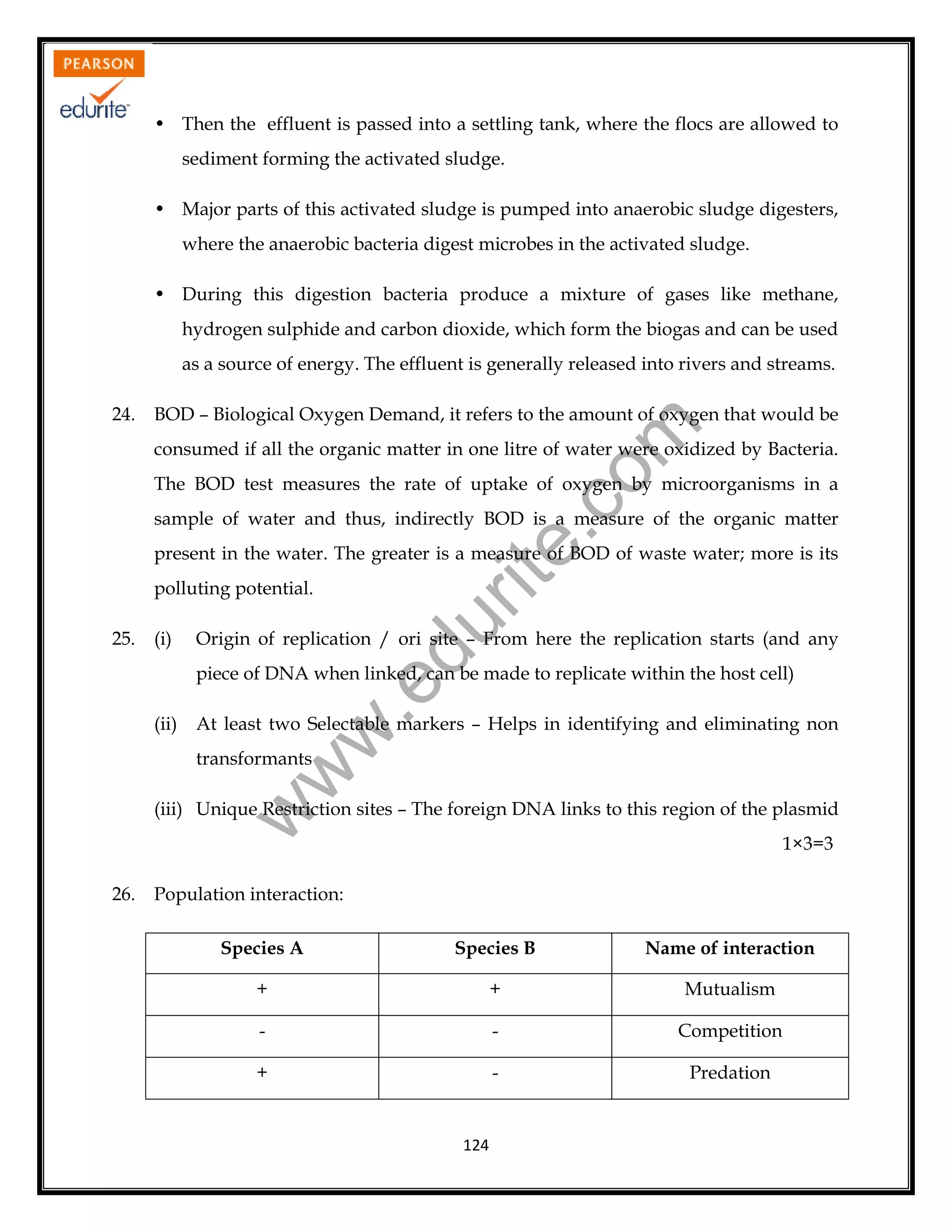
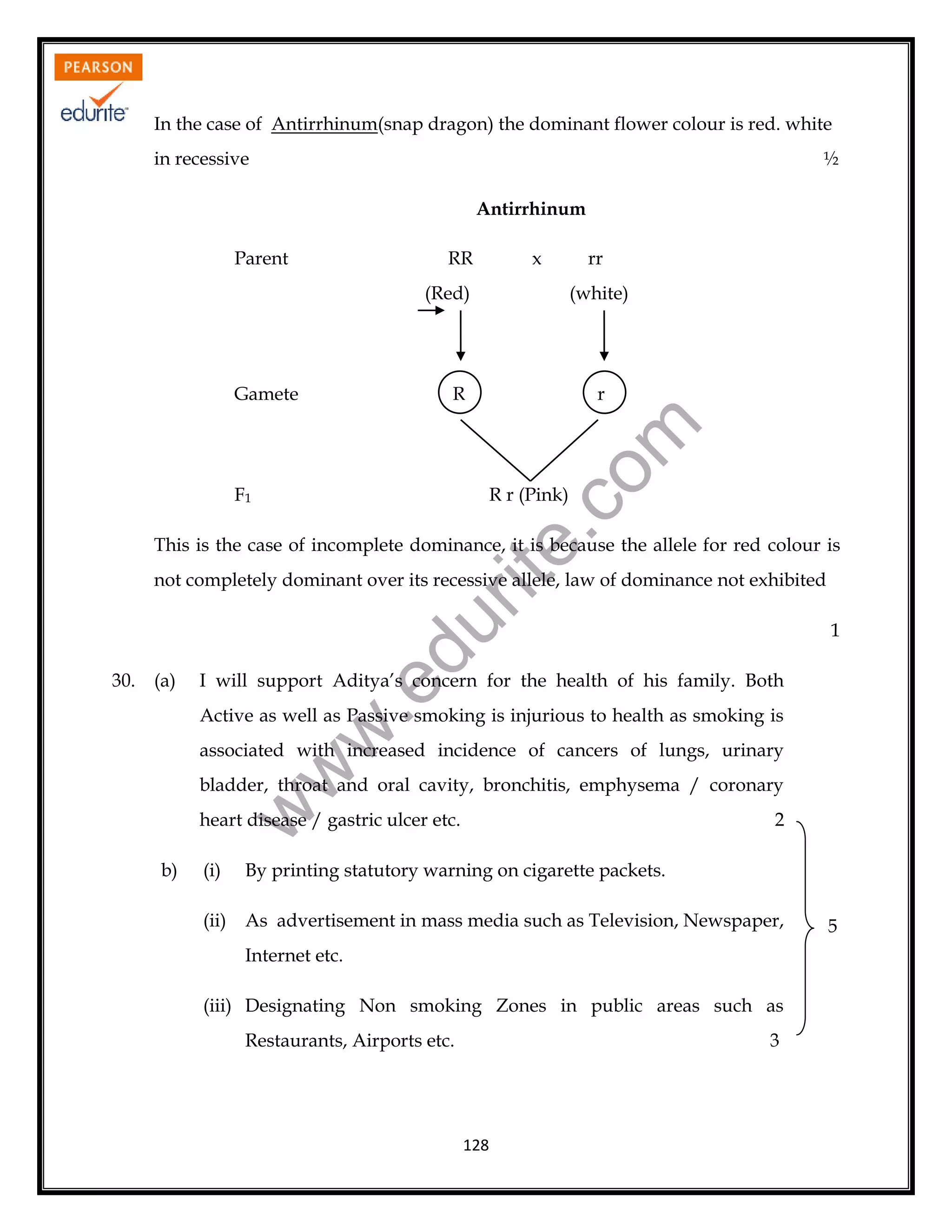
28. (a) Labelled diagram of sectional view of human ovary showing:
- Ovarian surface