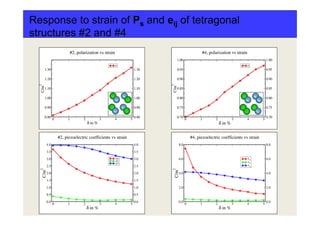
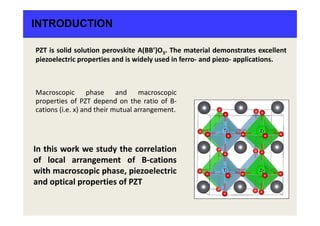
This study systematically analyzed the effect of local ordering of B-cations (Zr and Ti) on the electronic, optical, and piezoelectric properties of PbZrxTi1-xO3 (PZT) using density functional theory calculations. The most stable structure found was a tetragonal phase with P4mm symmetry. Other stable phases included a polar orthorhombic phase and a non-polar triclinic phase. Analysis showed that different arrangements of B-cations led to variations in the electronic structure, polarization, and piezoelectric response of the materials. In particular, large piezoelectric coefficients e15 and e33 were associated with specific planar and axial arrangements of

![OPTICAL AND ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE
PROPERTIES
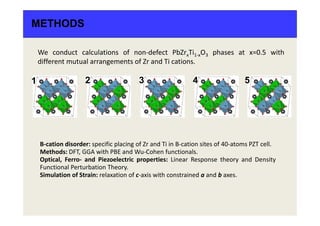
We have found a strong intermixing of Zr
and Ti d-states in our structures which
can give optical applications while PZT is
doped by non-isovalent cations
Optical band gap Eg~3.5 eV (from
optical spectra) does not show
significant dependence on Zr/Ti
arrangement, in agreement with
experimental results for thin films[*]
* M.P. Moret, M.A.C. Devillers, K. Wörhoff, P.K. Larsen, Journal of Applied Physics 92, 468 (2002).
Top of VB: oxygen 2p-states
Bottom of CB: Ti, Zr d-states
HOMO, #5 (FE) LUMO, #5 (FE)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bodanovemrs2012-150122045651-conversion-gate01/85/cBodanov-emrs2012-5-320.jpg)
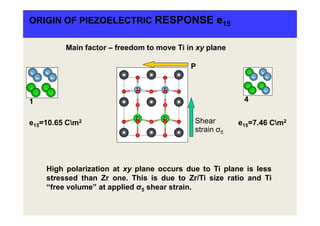
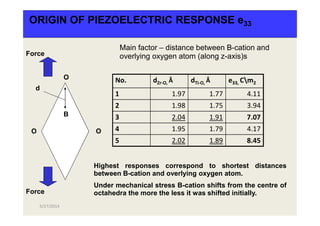
![1 2 3 4 5
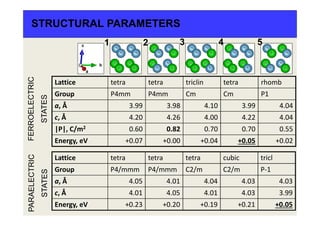
PIEZOELECTRIC PROPERTIES
e15 10.65 3.66 0.37 7.46 0.49
e31 0.27 0.37 -2.00 0.37 -0.35
e33 4.11 3.94 7.07 4.17 8.45
ε11 488.23 126.56 56.87 375.40 79.59
ε33 13.77 13.94 136.53 14.47 79.93
|P| 0.60 0.82 0.70 0.70 0.55
Pdirection [001] [001] [552] [001] [111]
tetra tetra triclin tetra rhomb
Piezoelectric coefficients, C/m2
Static dielectric permittivity
Spontaneous polarization, C/m2
Exp:
e33=11.9 Cm2
Low temperature,
pylycrystal Zr/Ti
50:50 *
Exp:
|P|=0.75 Cm2
single domain
crystal **
* Z. Q. Zhuang, M. J. Haun, S. J. Jang, and L. E. Cross, 6th IEEE International Symposium on
the Applications of Ferroelectrics, 1986, p. 394.
21 43 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bodanovemrs2012-150122045651-conversion-gate01/85/cBodanov-emrs2012-6-320.jpg)