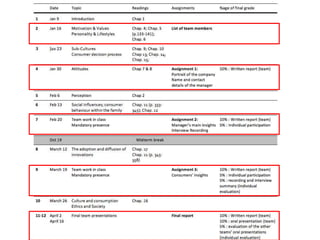
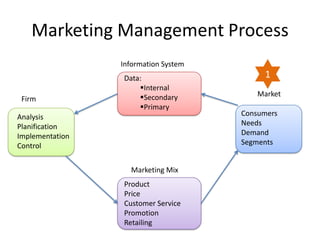
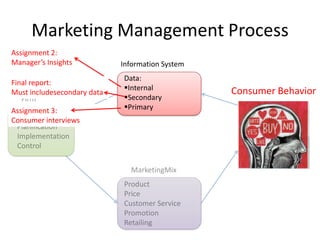
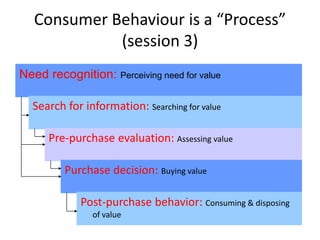
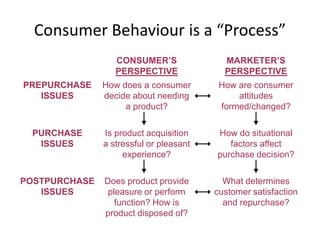
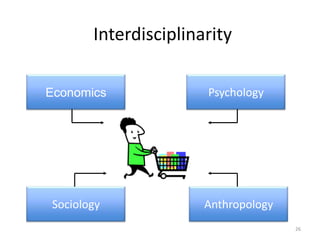
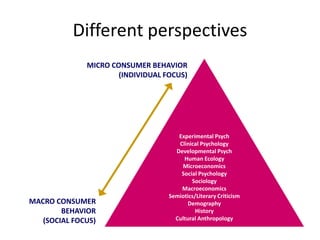
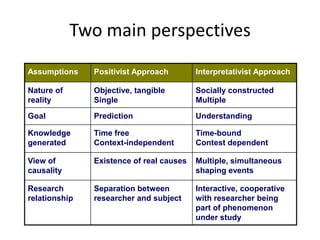
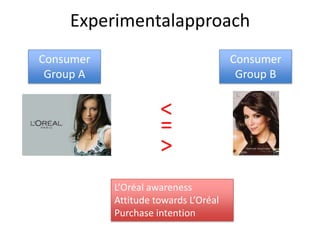
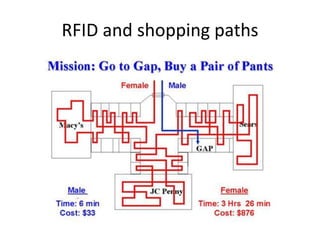
This document provides an overview and agenda for a consumer behavior course. It introduces the instructor, Sandra Laporte, and outlines her areas of expertise. The document then reviews the course objectives, which are to understand how consumer behavior insights can benefit managers and develop analytical skills. It outlines the group project, where students will create a consumer profile for a brand. Finally, it introduces the topic of consumer behavior, defining it and outlining some of the key influences on consumer decision-making that will be covered throughout the course.