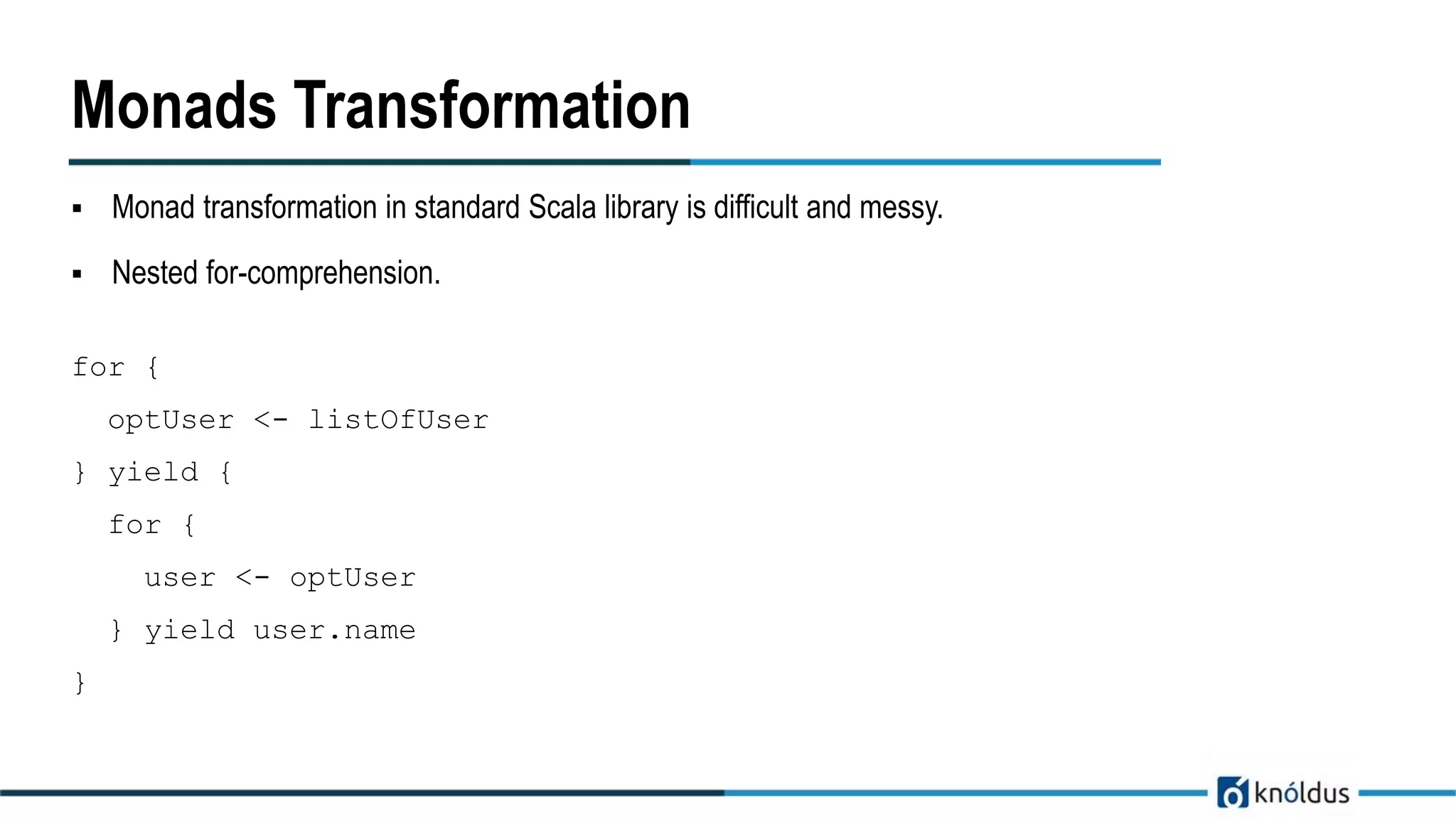
The document discusses the Cats library in Scala, focusing on functional programming abstractions such as type classes, monoids, semigroups, functors, and monads. It elaborates on defining and implementing type classes and various operations associated with them, as well as providing examples and use cases in Scala. Additionally, it highlights the use of monad transformers for simplifying nested data structures and computations.



![The Type Class
Type classes were first introduced in Haskell as a new approach to ad-hoc polymorphism.
Type classes in Haskell are based on Hindley–Milner type system.
Scala's type inference is based on Local Type Inference.
object Math {
trait NumberLike[A] {
def add(a: A, b: A): A
def subtract(a: A, b: A): A
def multiply(a: A, b: A): A
def divide(a: A, b: A): A
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-5-2048.jpg)
![Type Class Instances [Example]
object Math {
trait NumberLike[A] {
def add(a: A, b: A): A
def subtract(a: A, b: A): A
def multiply(a: A, b: A): A
def divide(a: A, b: A): A
}
implicit val intLike: NumberLike[Int] = new
NumberLike[Int] {
override def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a + b
override def subtract(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a - b
override def multiply(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a * b
override def divide(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a / b
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-7-2048.jpg)
(implicit ev: NumberLike[A]) =
ev.add(a, b)
}
DoTheMath.addition(1,2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-8-2048.jpg)
![Type class in Cats
Cats is written using a modular structure.
It allows us to choose which type classes, instances, and interface methods we want to use.
import cats.Show
import cats.instances.int._
val showInt: Show[Int] = Show.apply[Int]
val intToString: String = showInt.show(1)
import cats.syntax.show._
123.show](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-9-2048.jpg)
![Defining Custom Instances
import java.util.Date
implicit val dateShow: Show[Date] =
Show.show(date => s"${date.getTime}ms since the epoch.")
dateShow.show(new Date())
Result:
res2: String = 1532873812098ms since the epoch.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-10-2048.jpg)
![trait Monoid[A] {
def combine(x: A, y: A): A
def empty: A
}
A monoid for a type A is:
an operation on combine with type (A, A) => A
an element empty of type A
Must follow associative law.
Must follow identity law.
Monoids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-11-2048.jpg)
![Monoids [Few Example]
// Example Addition
1 + 1 = 2
1 + 0 = 1 & 0 + 1 = 1
1 + (1 + 2) = 4
(1 + 1) + 2 = 4
Integer Addition
Integer Multiplication
String Concatatination
// Example Concatenation
“1” + “1” = “11”
“1” + “” = “1” & “” + “1” = “1”
“1” + (“1” + “2”) = “112”
(“1” + “1”) + “2” = “112”
// Example Subtraction
(4 – 2) – 2 = 0
4 – (2 – 2) = 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-12-2048.jpg)
![Semigroup
trait Semigroup[A] {
def combine(x: A, y: A): A
}
A semigroup is just the combine part of a monoid
For example NonEmptyList or Positive Integer
trait Monoid[A] extends Semigroup[A] {
def empty: A
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-13-2048.jpg)
![Monoids and Semigroup in Cats
Type Class
The monoid type class is cats.kernel.Monoid , which is aliased as cats.Monoid.
Monoid extends cats.kernel.Semigroup , which is aliased as cats.Semigroup.
Instance
import cats.Monoid
import cats.instances.string._
Monoid[String].combine("Hello ", " World")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-14-2048.jpg)
![Monoids and Semigroup in Cats
Syntax
●Cats provides syntax for the combine method (|+| operator).
import cats.instances.option._
import cats.syntax.semigroup._
val result = Option(1) |+| Monoid[Option[Int]].empty
Result = Option(1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-15-2048.jpg)

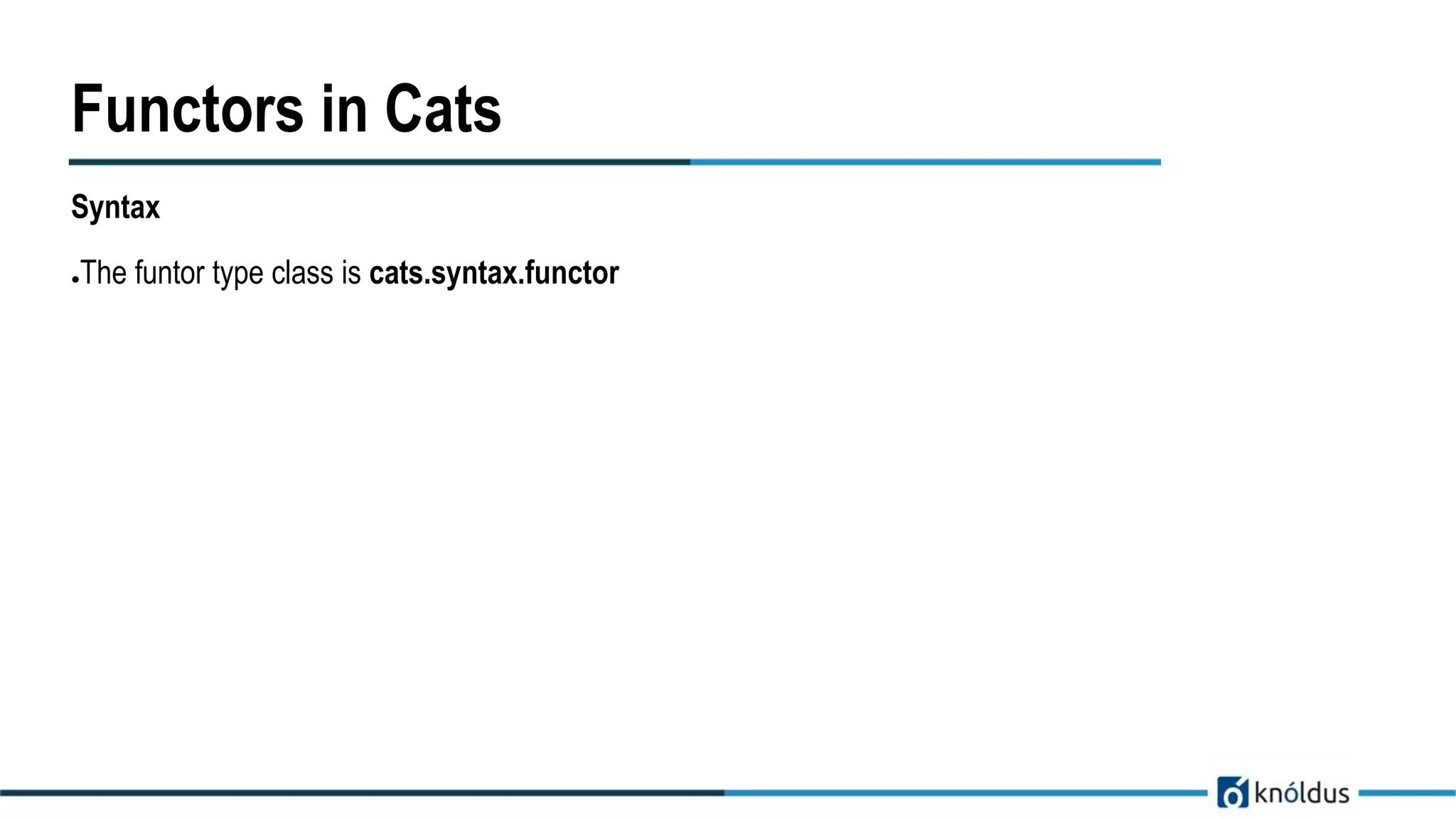
![Functors in Cats
Type Class
●The funtor type class is cats.Functor.
import cats.Functor
Functor[Option].map(Option(1))(_ + 2)
Instance
import cats.Functor
import cats.instances.option._
val optionIncrementFunc = Functor[Option].lift((x:Int) => x + 1)
val result = optionIncrementFunc(Option(2))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-17-2048.jpg)
![Monads Definition
trait Monad[F[_]] {
def pure[A](value: A): F[A]
def flatMap[A, B](value: F[A])(func: A => F[B]): F[B]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-20-2048.jpg)
![Monads in Cats
Type Class
The monad type class is cats.Monad.
import cats.Monad
Monad[Option].pure(3)
Instance
import cats.Monad
import cats.instances.option._
Monad[Option].flatMap(Option(3))(a => Some(a + 2))
// Option[Int] = Some(5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cats-in-scala-prabhatkashyap-180801101048/75/Cats-in-Scala-21-2048.jpg)