ITC Limited is an Indian conglomerate established in 1910 that manufactures cigarettes and has diversified into other businesses including hotels, paper, agriculture, and IT. This presentation focuses on ITC's cigarette manufacturing plant in Kolkata and discusses its holistic environmental management practices.
The plant generates various wastes from cigarette manufacturing processes, packaging, and other on-site activities. These wastes pose environmental and health risks if not properly managed. ITC implements waste recycling and sells recyclable materials. For tobacco waste, the company reuses usable tobacco and sells dust to vendors. Canteen waste is also sold or used as animal feed.
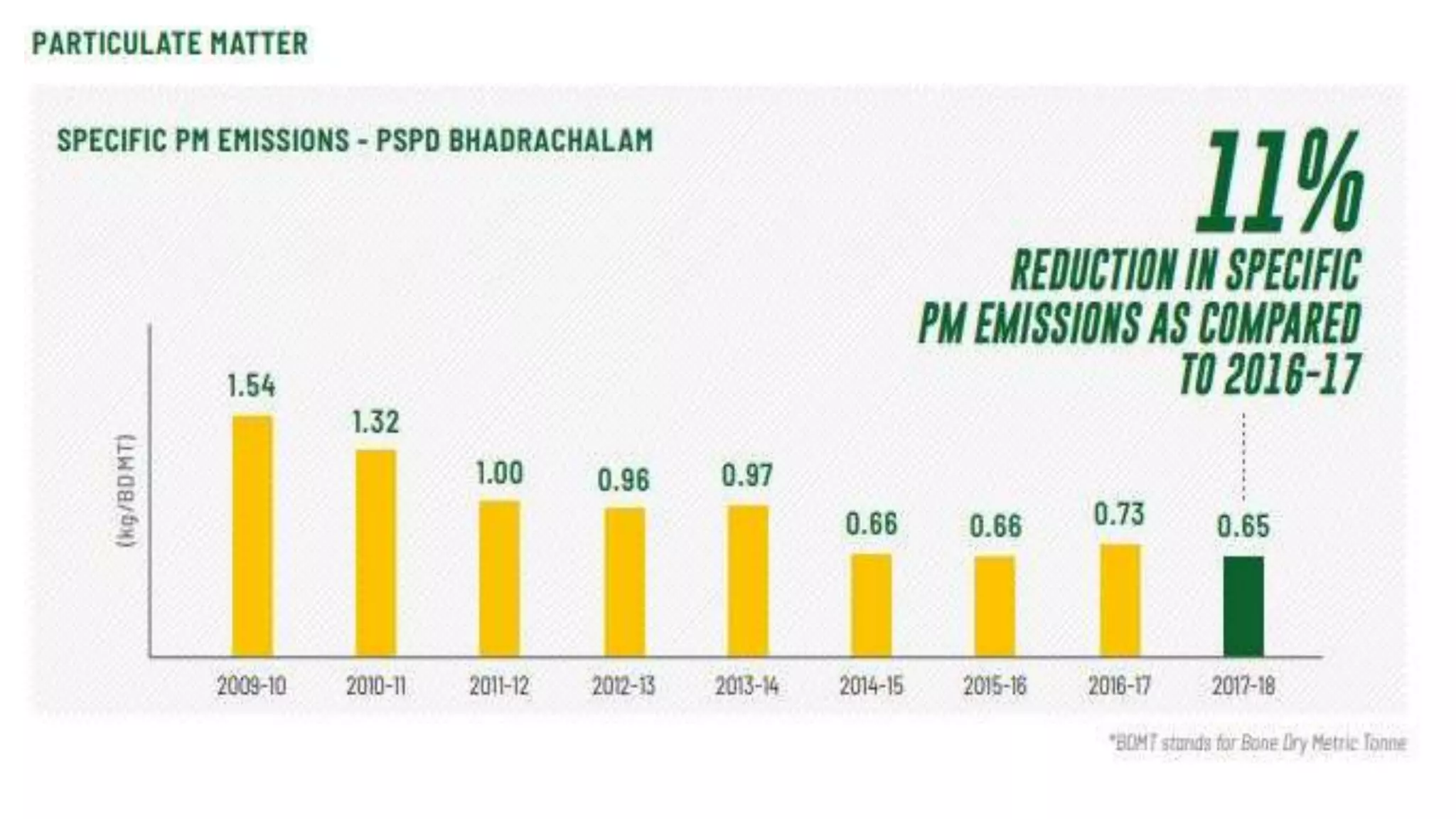
ITC's holistic management includes practices to treat air emissions,