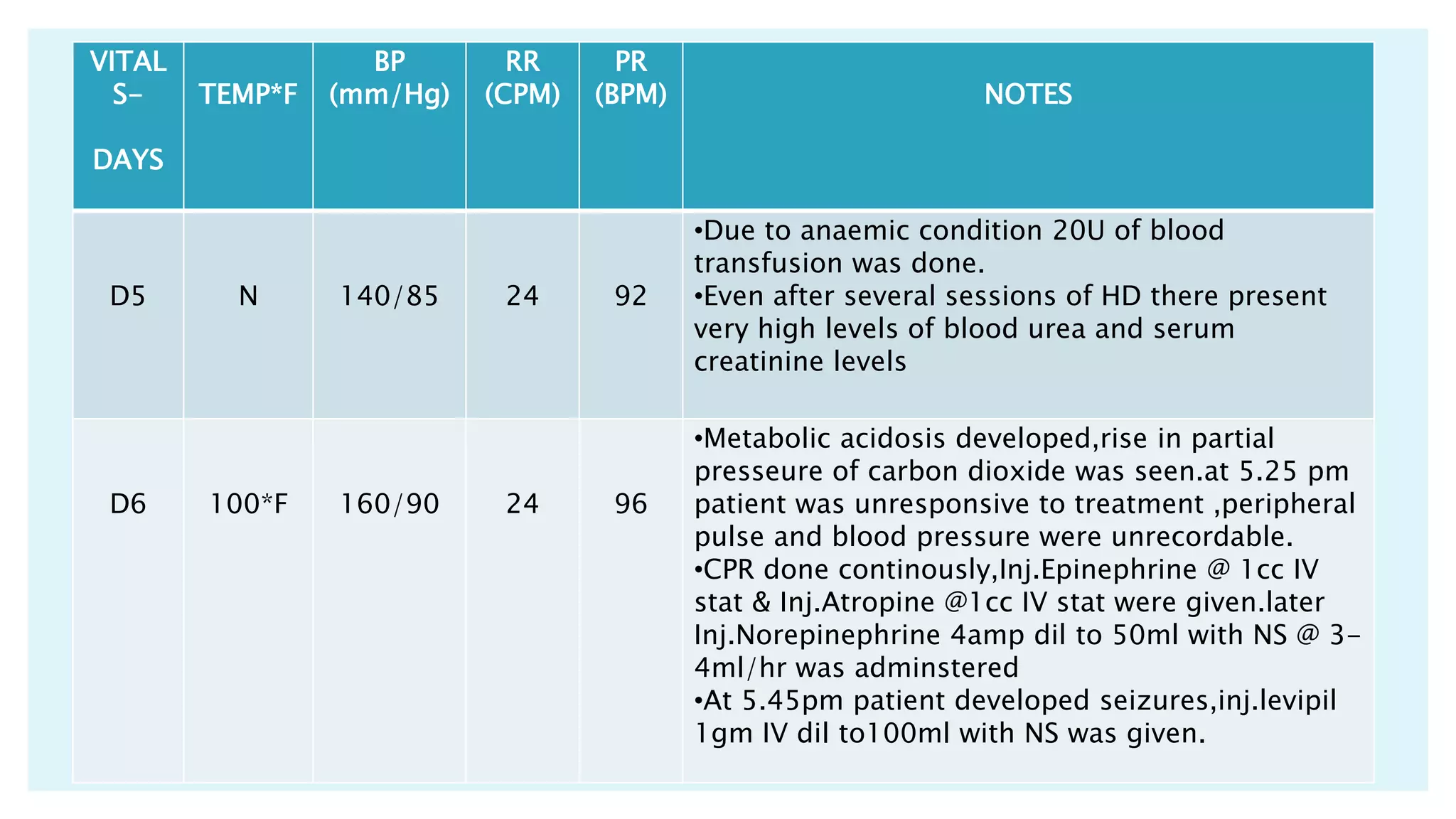
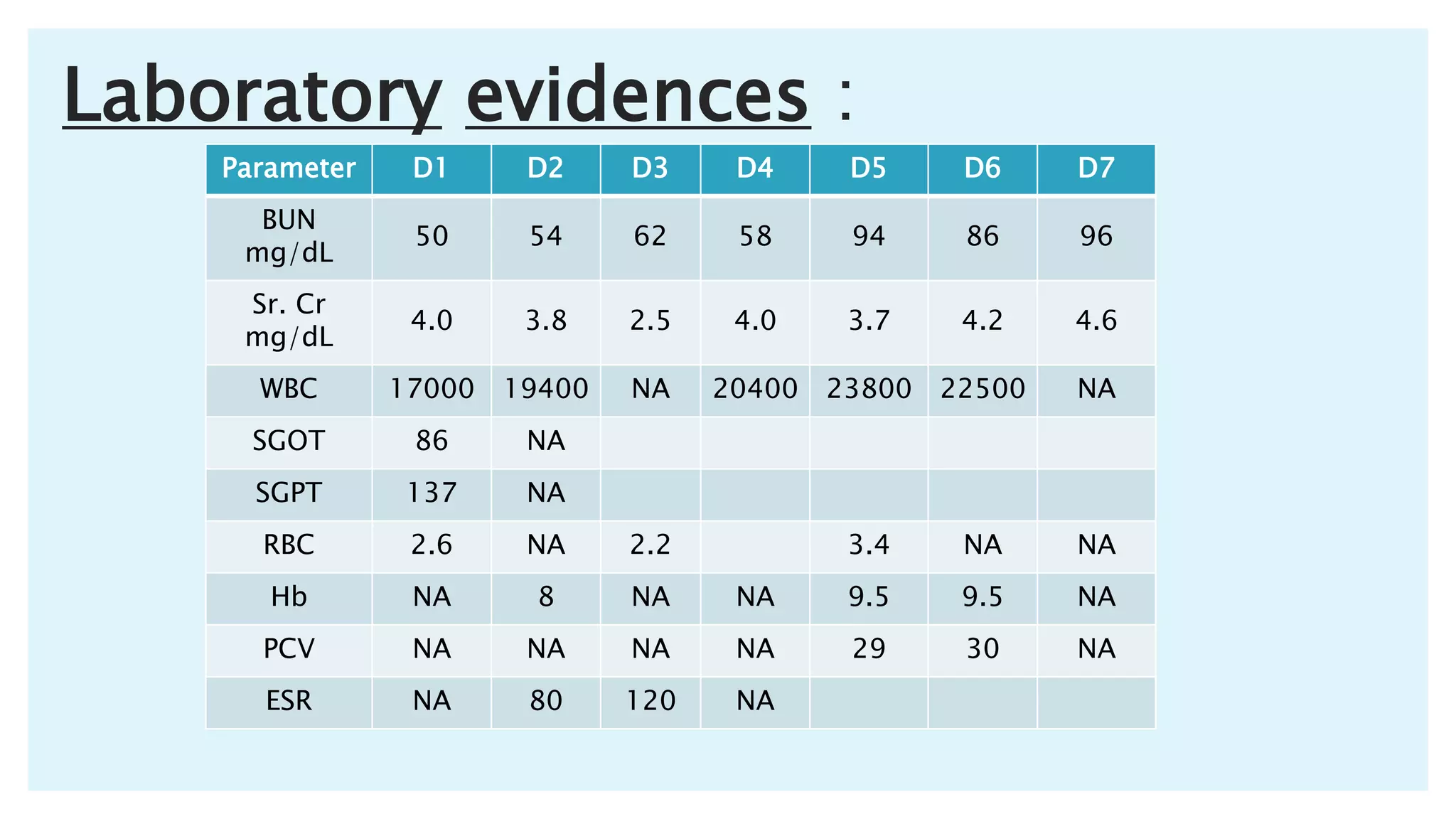
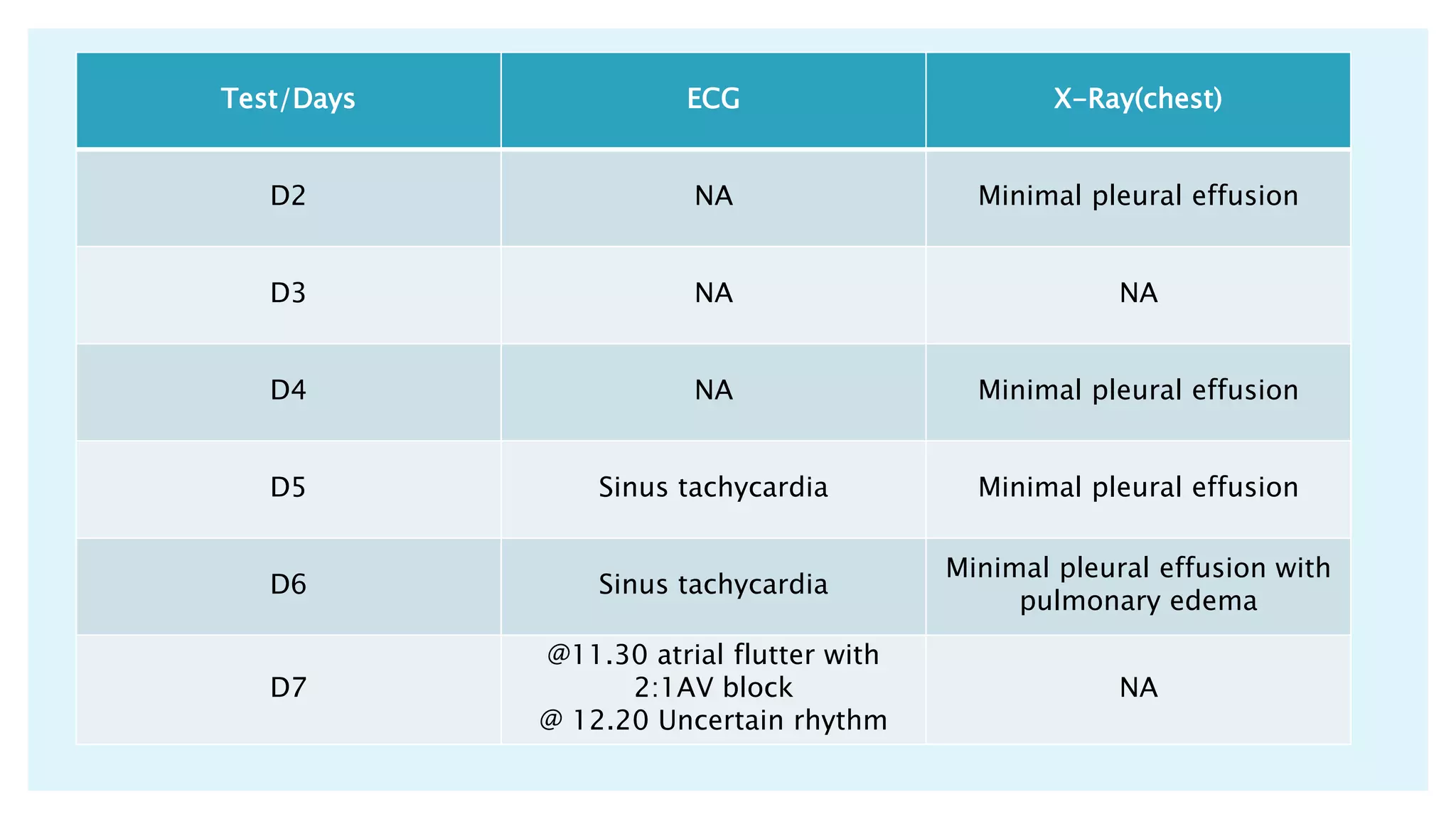
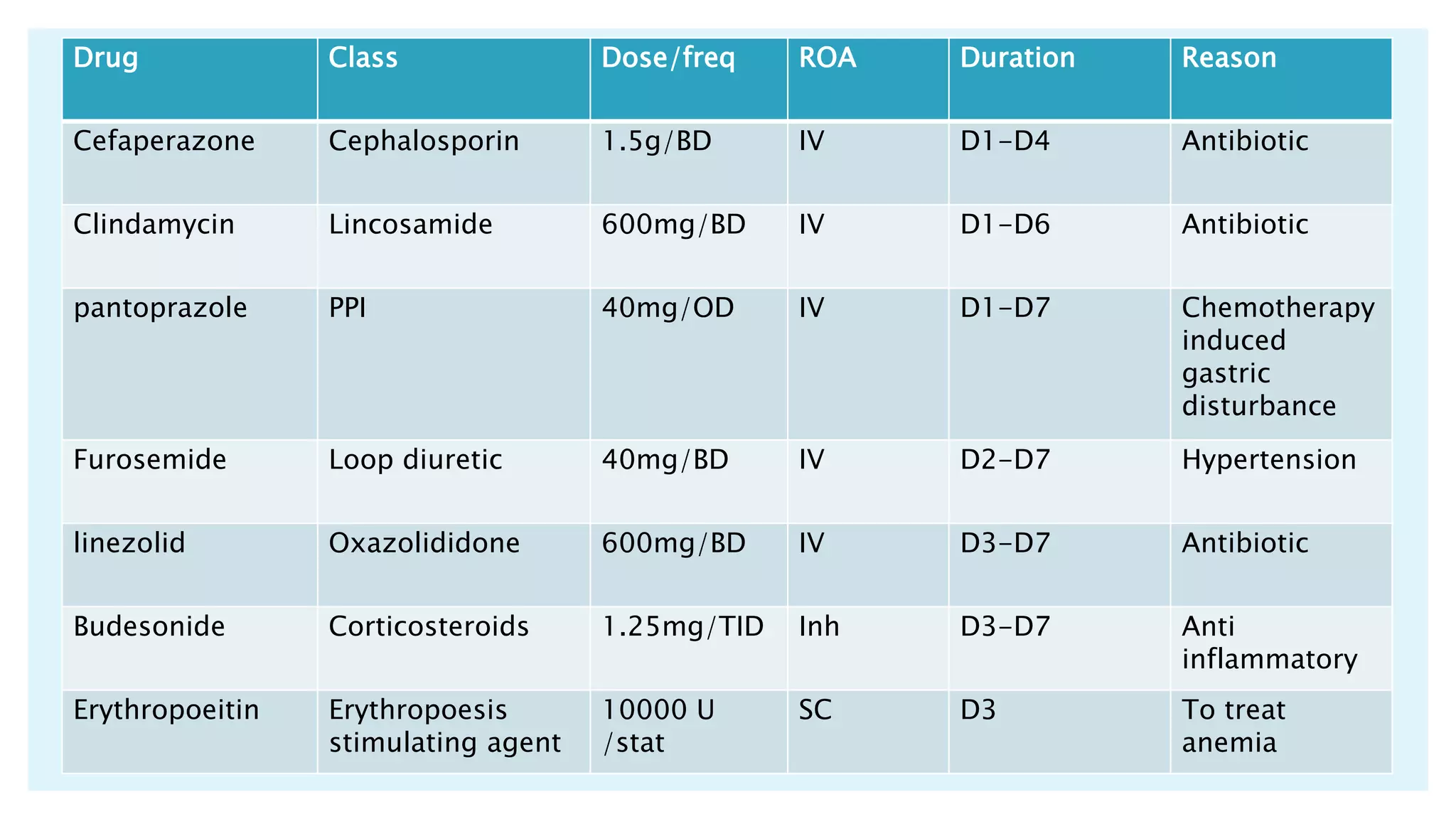
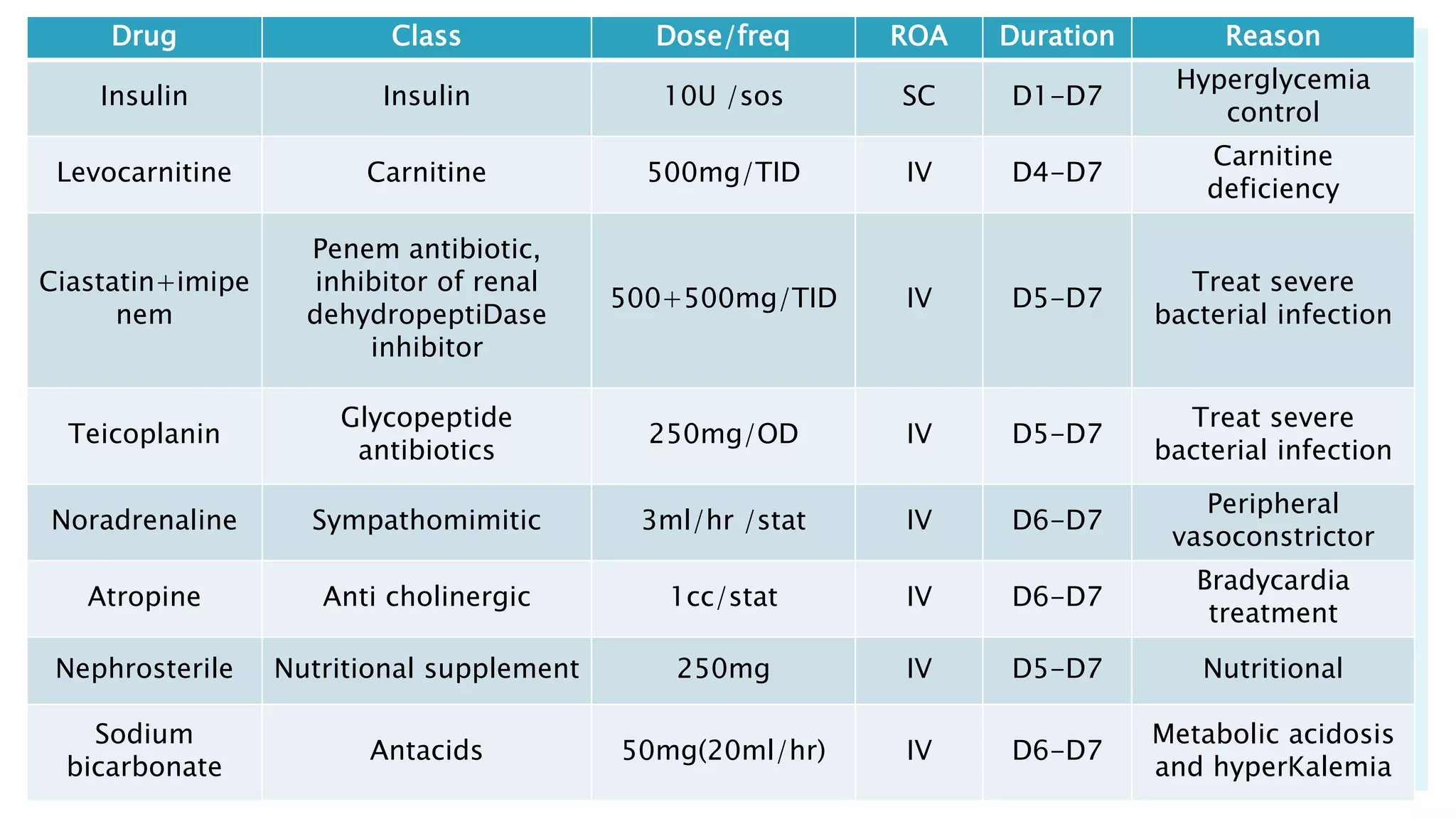
The document describes a case presentation of a 57-year-old female patient with end stage renal disease (ESRD) secondary to hypertension and diabetes. She was admitted with oliguria, shortness of breath, and elevated creatinine levels. Her treatment included hemodialysis to manage her ESRD. Her condition deteriorated over time with complications including metabolic acidosis, anemia, and eventually cardiopulmonary failure leading to her death. The case outlines her medical history, treatment plan involving hemodialysis and medications, monitoring, diet plan, and progression of her condition.