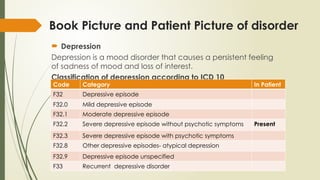
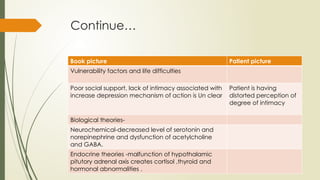
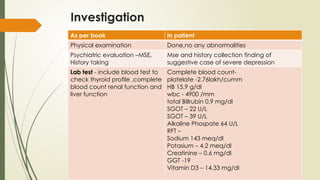
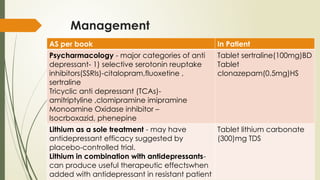
The document presents a case study of a patient diagnosed with a severe depressive episode, detailing symptoms, classification, etiology, interventions, and management strategies. It discusses the clinical features such as low mood, negative cognition, and potential psychotic symptoms, as well as diagnostic criteria based on ICD-10. It also covers treatment options including pharmacology, psychotherapy, and nursing management to address risks including suicide.