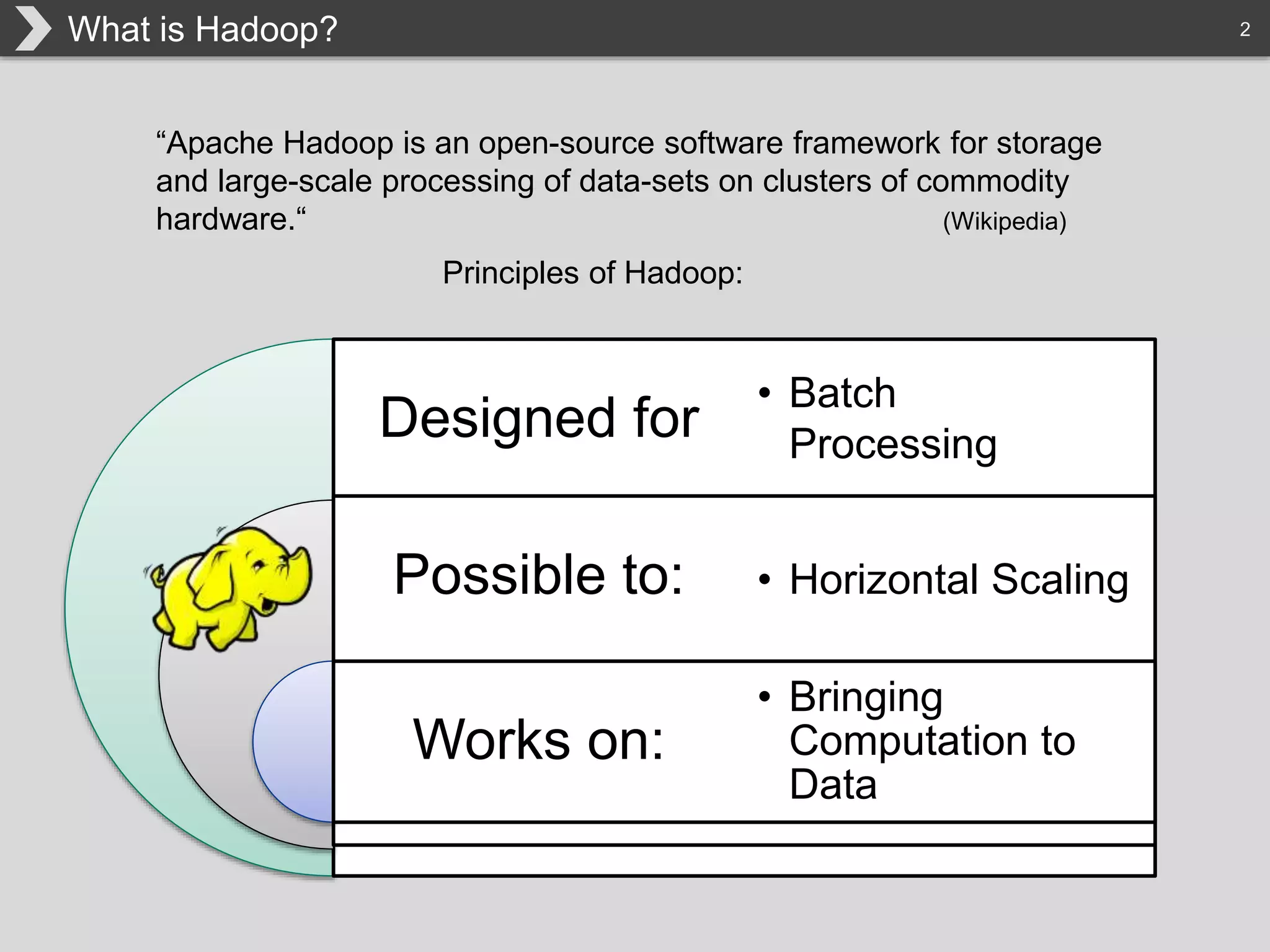
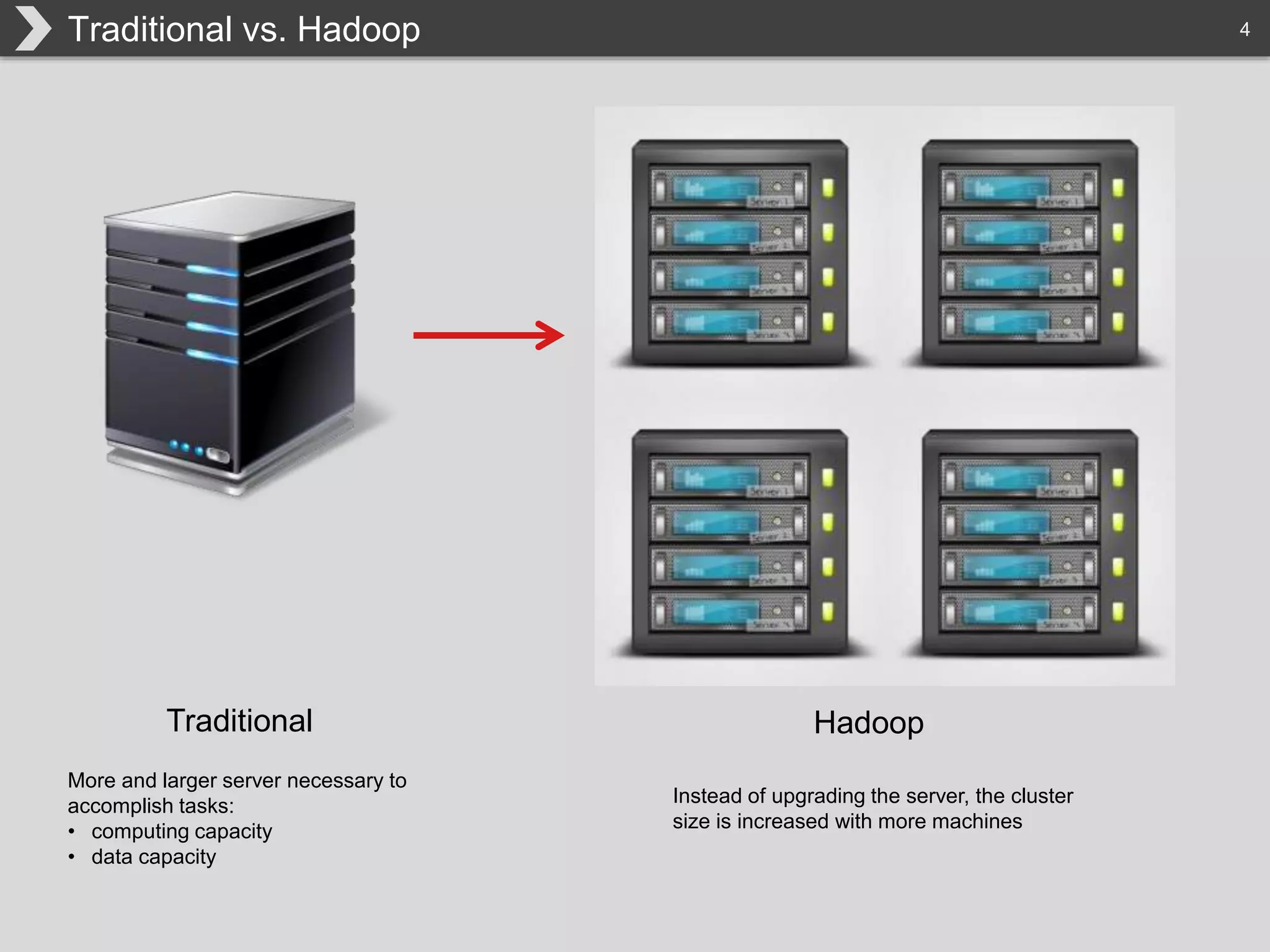
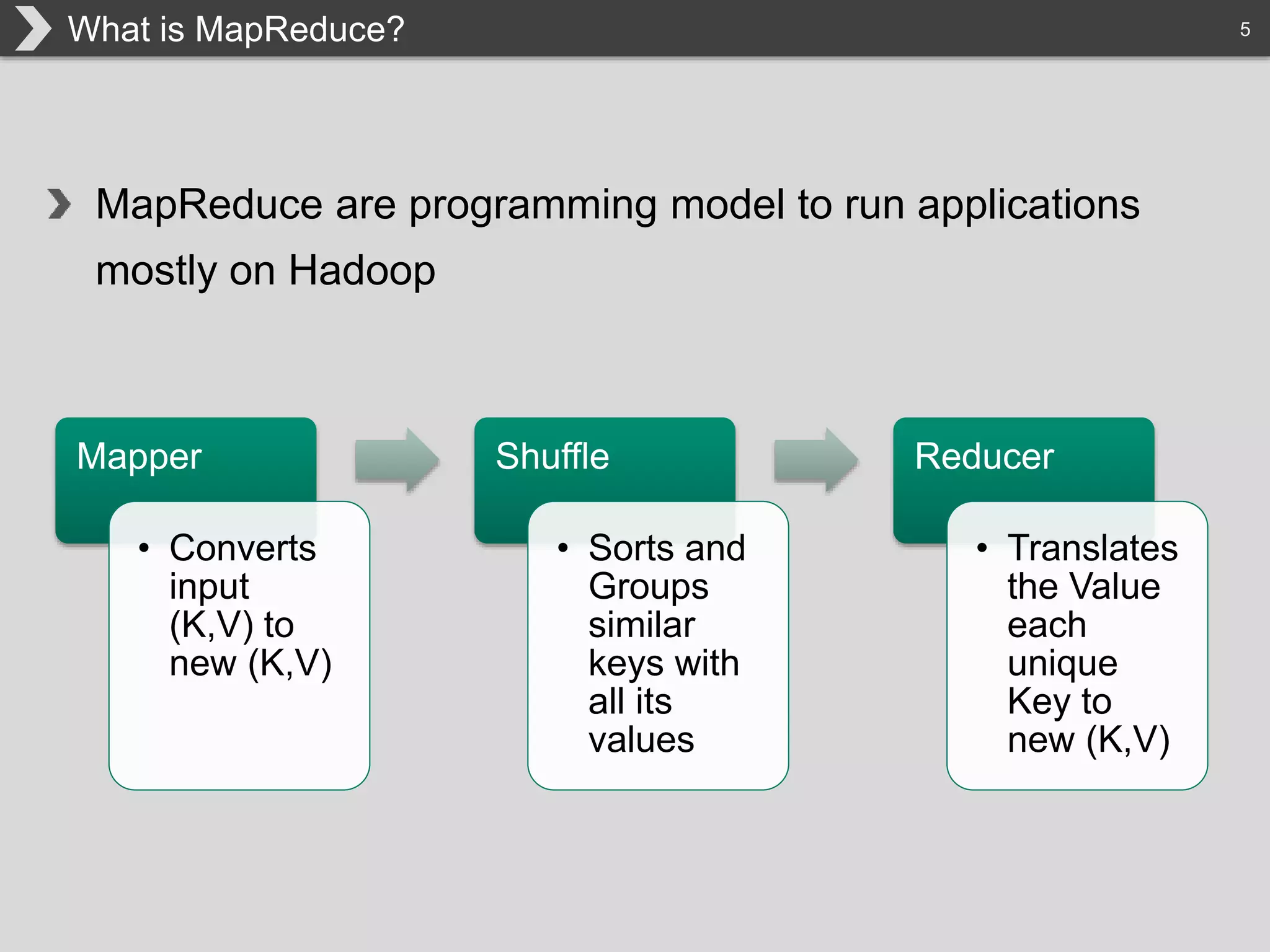
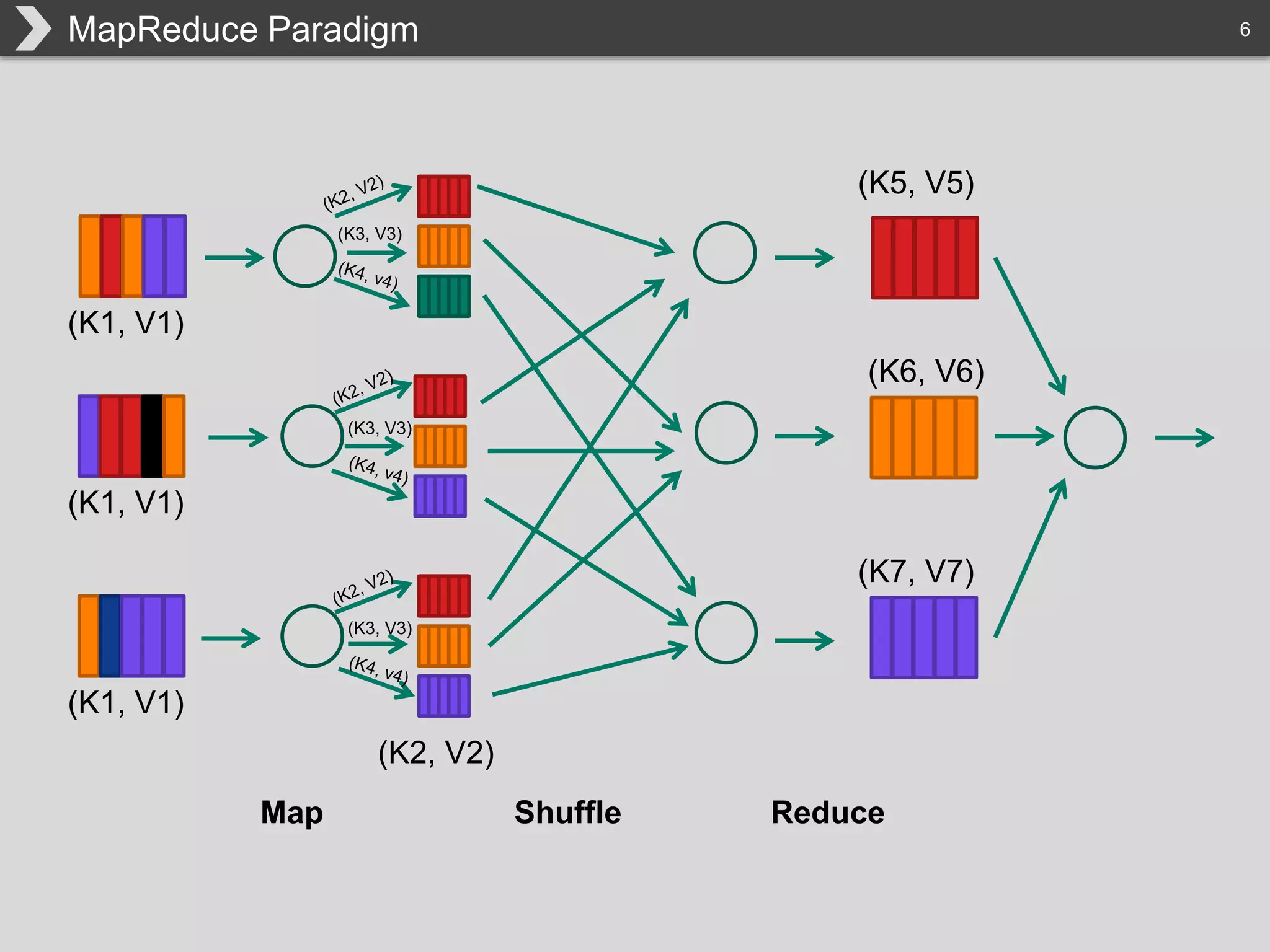
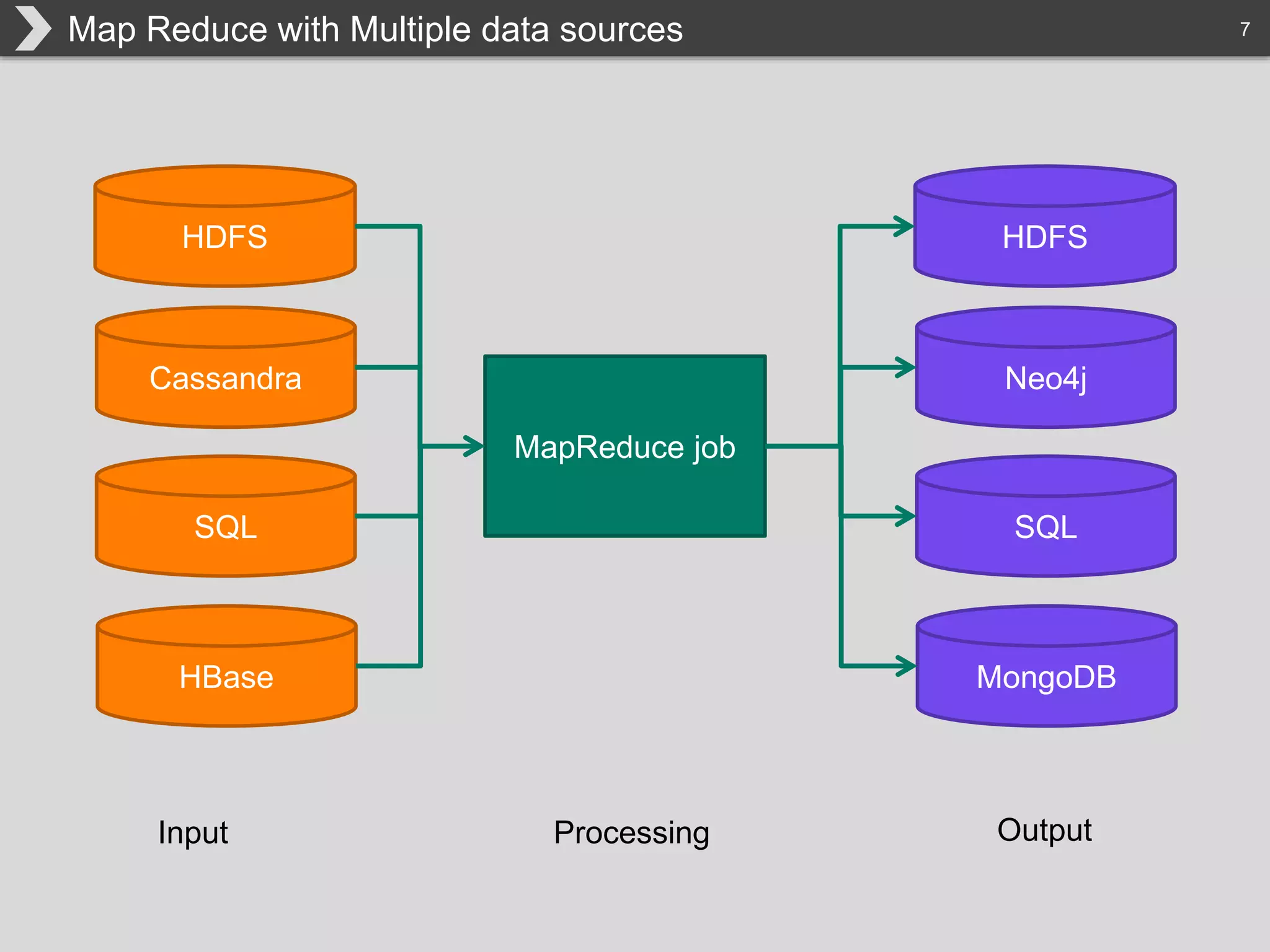
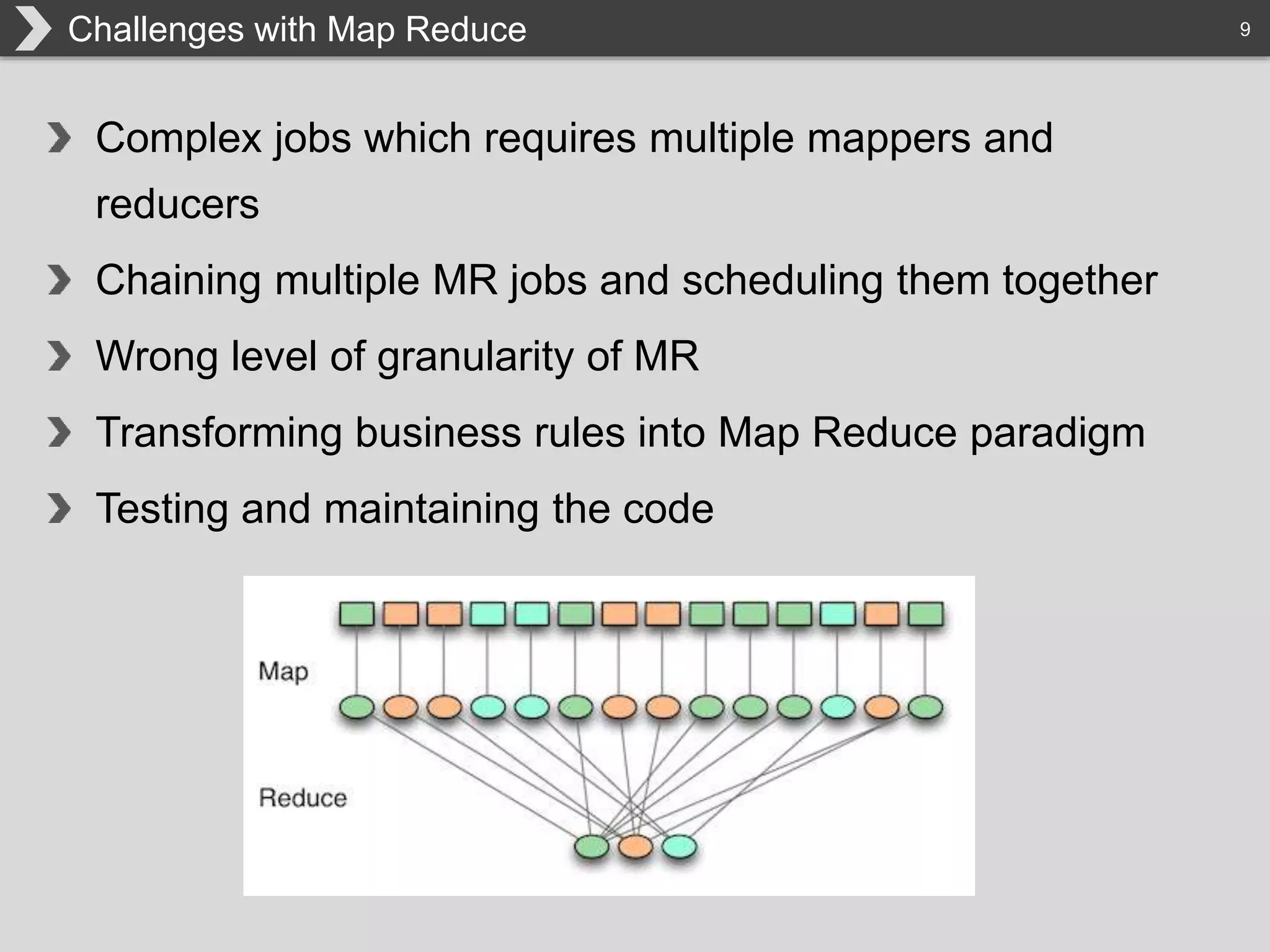
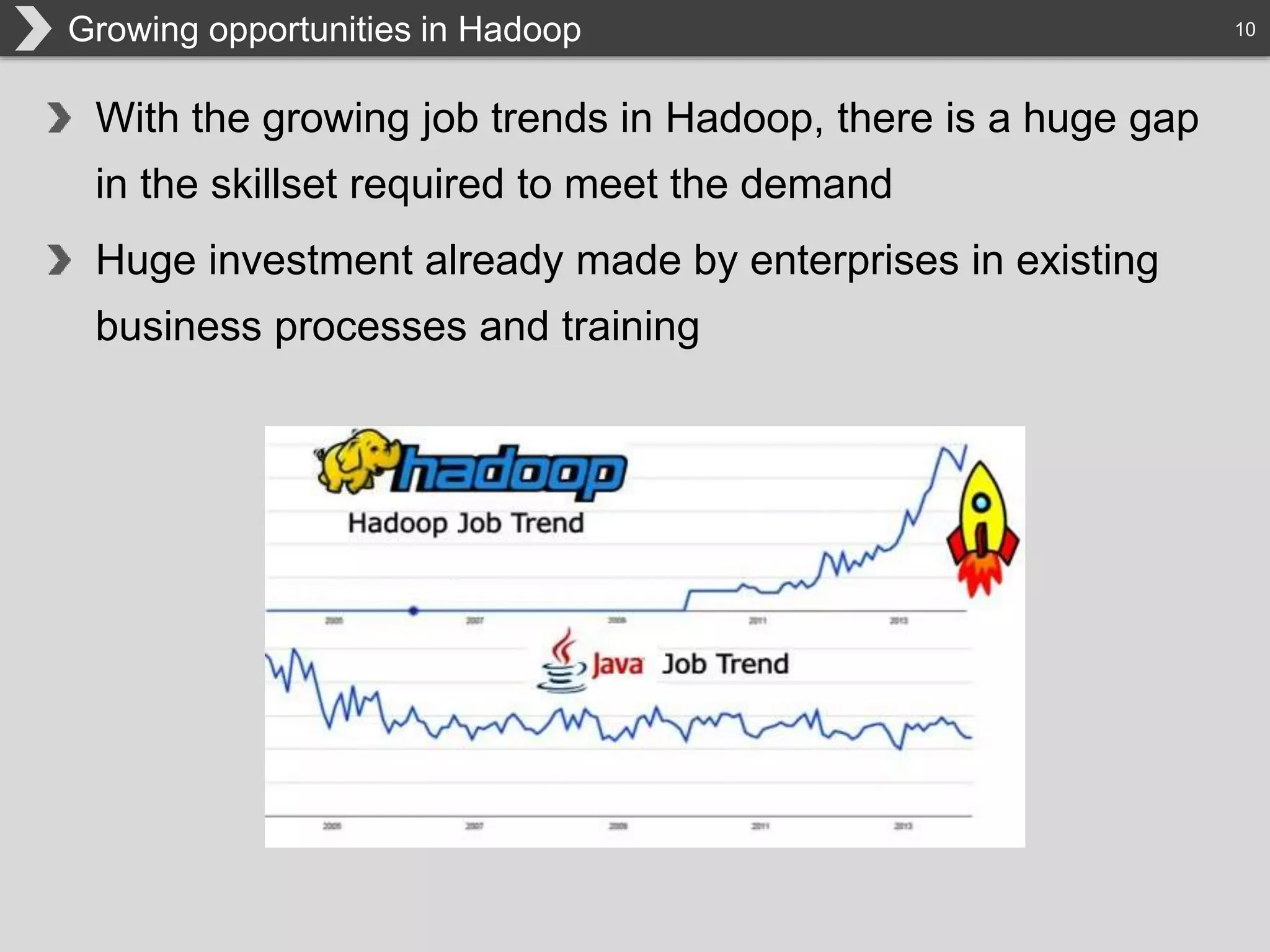
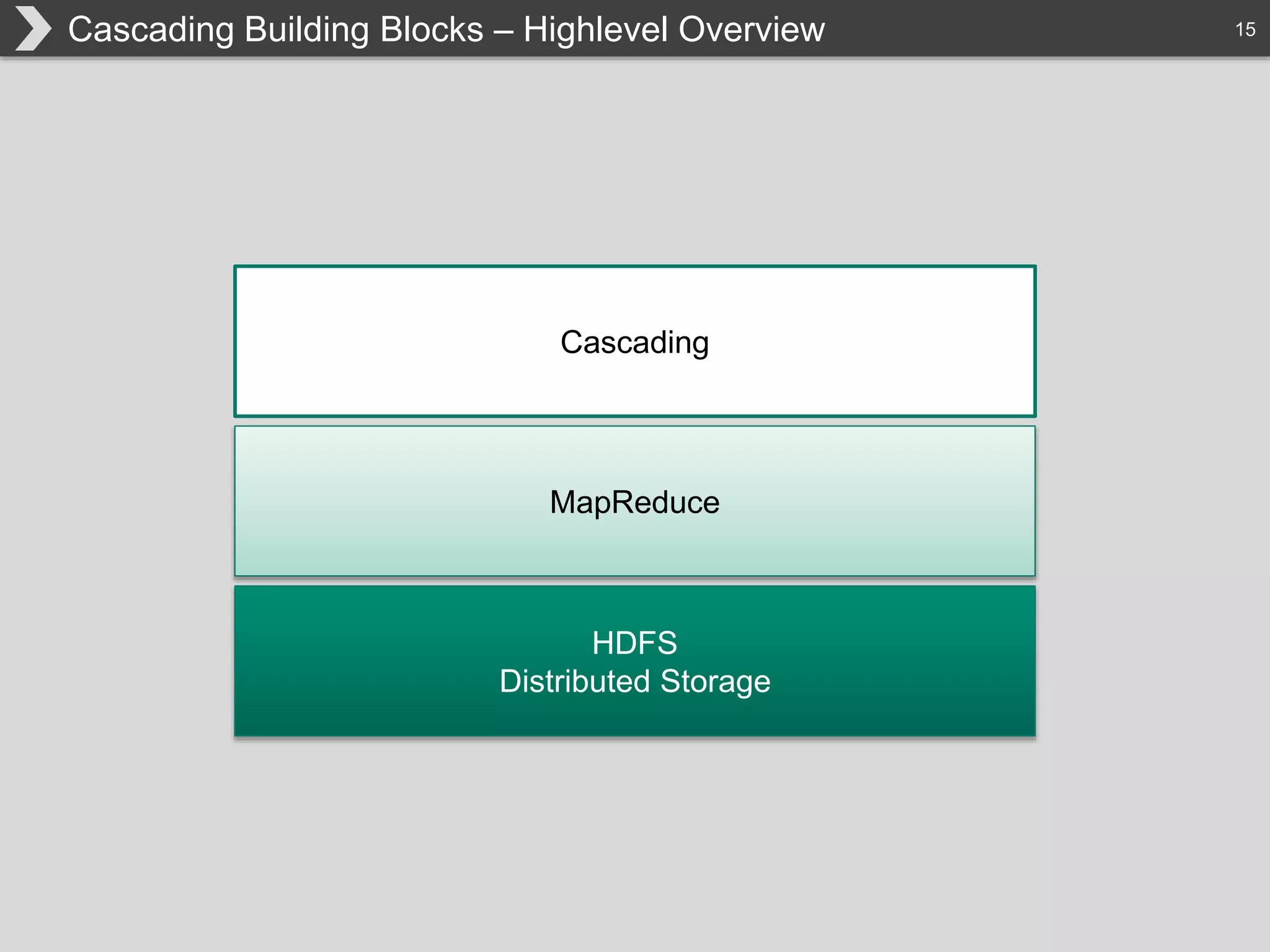
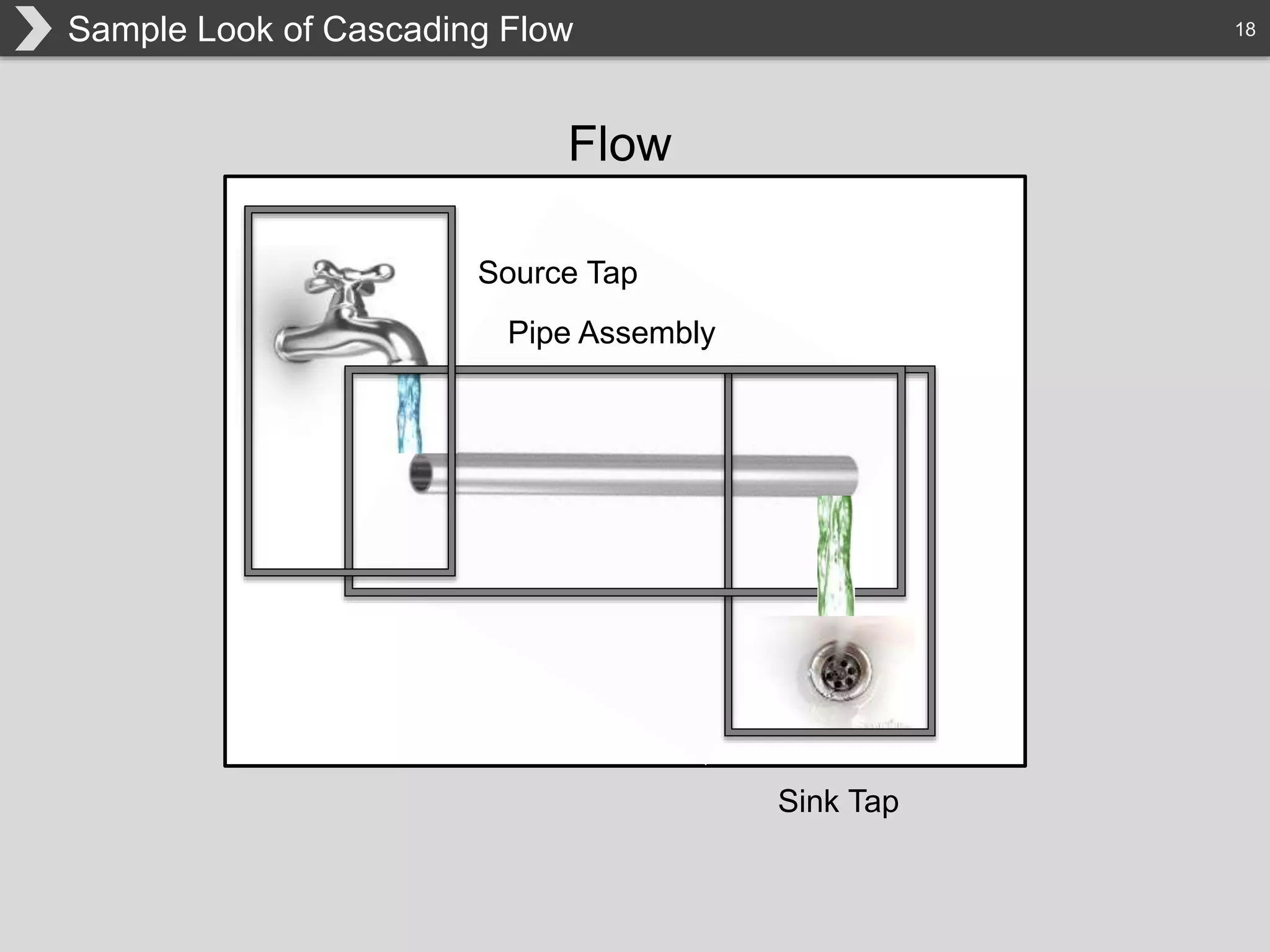
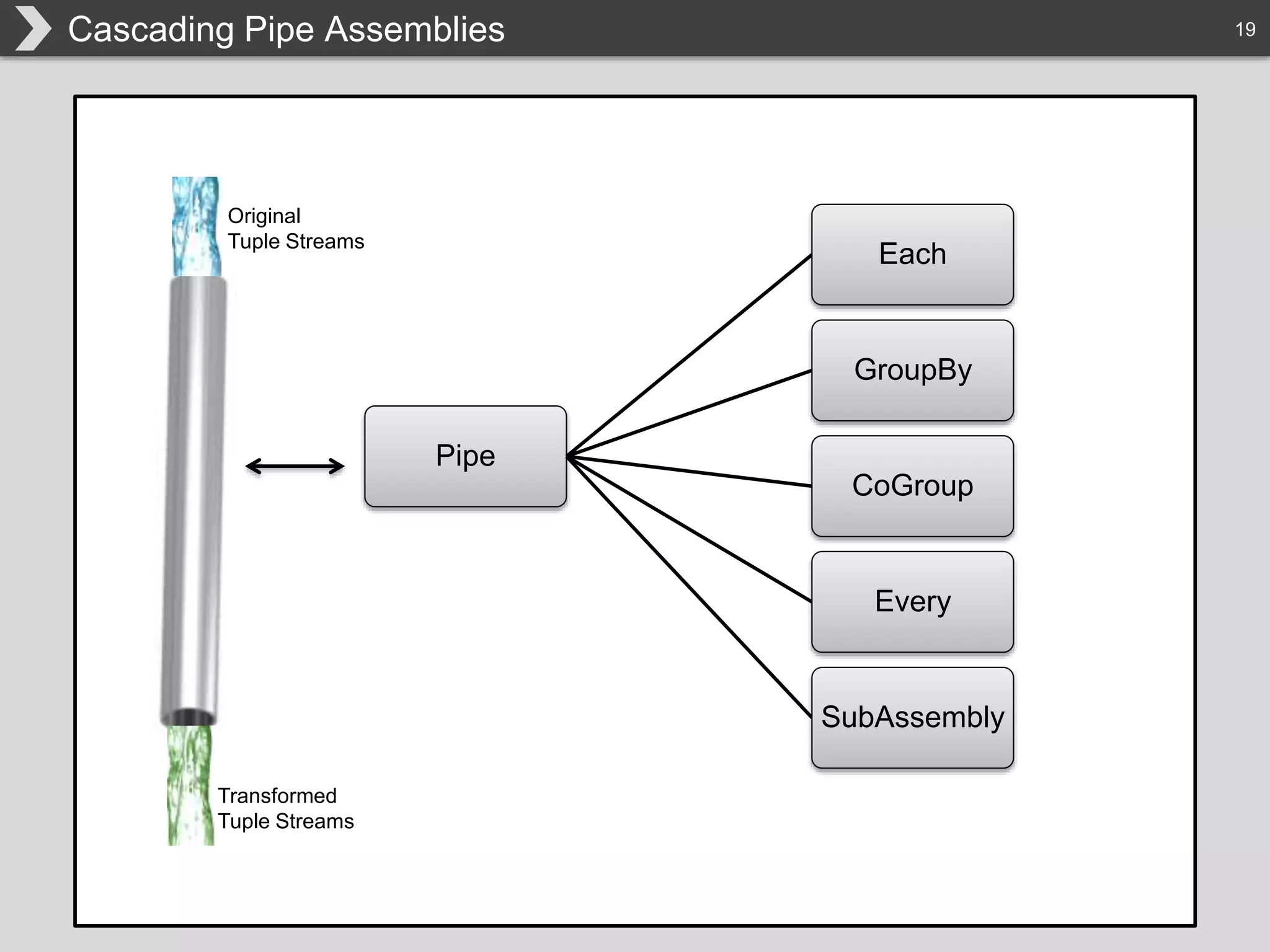
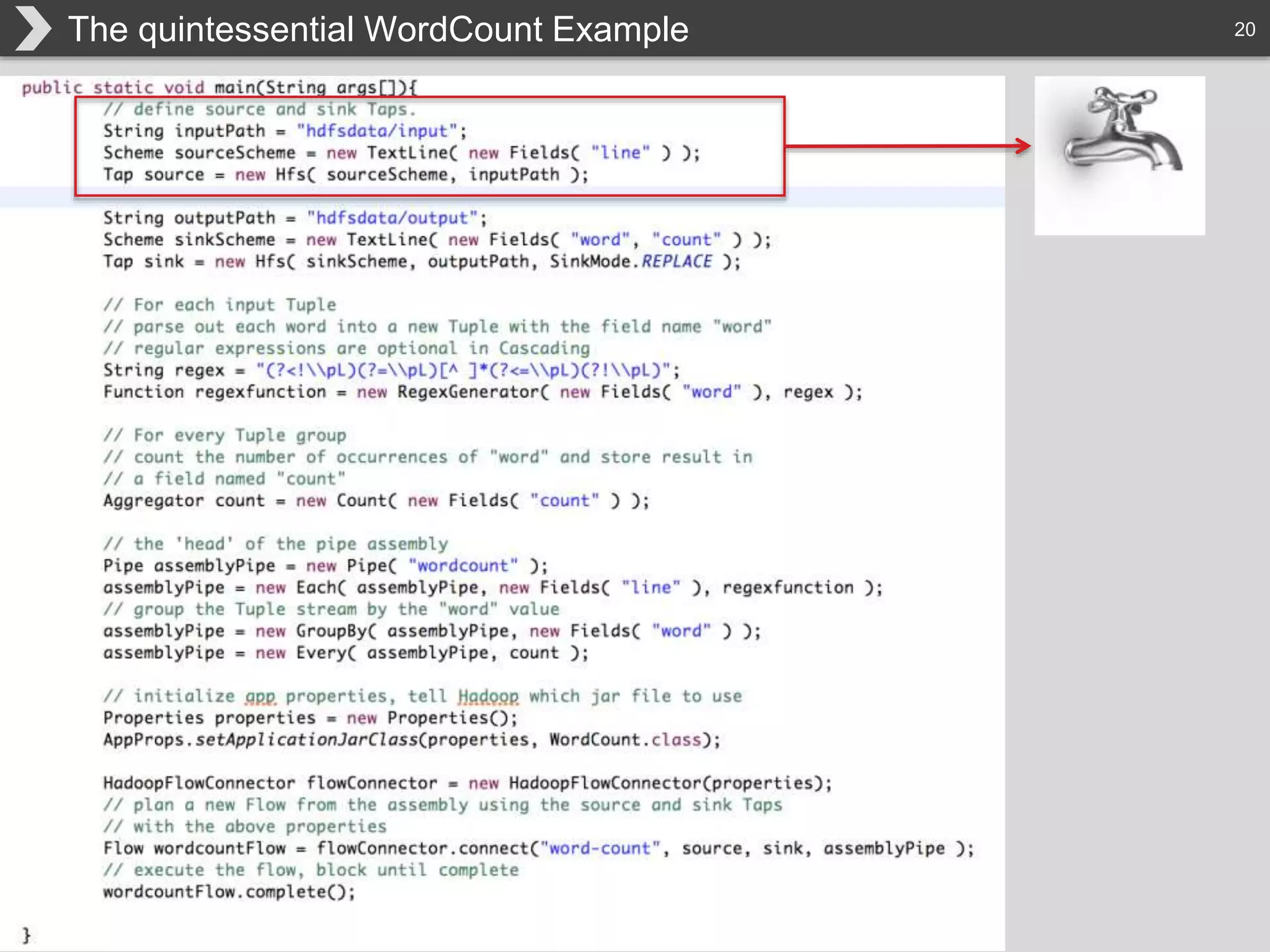
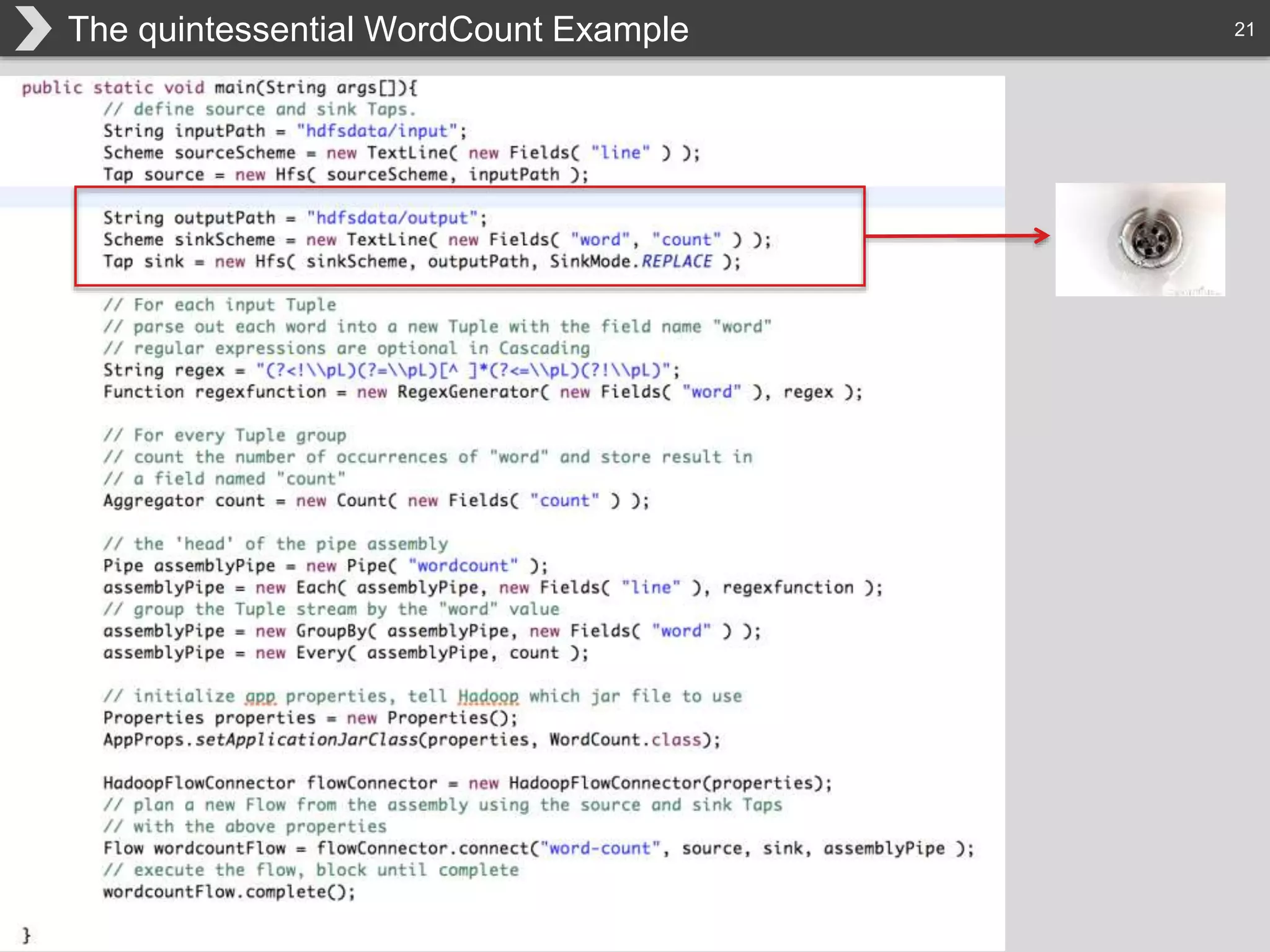
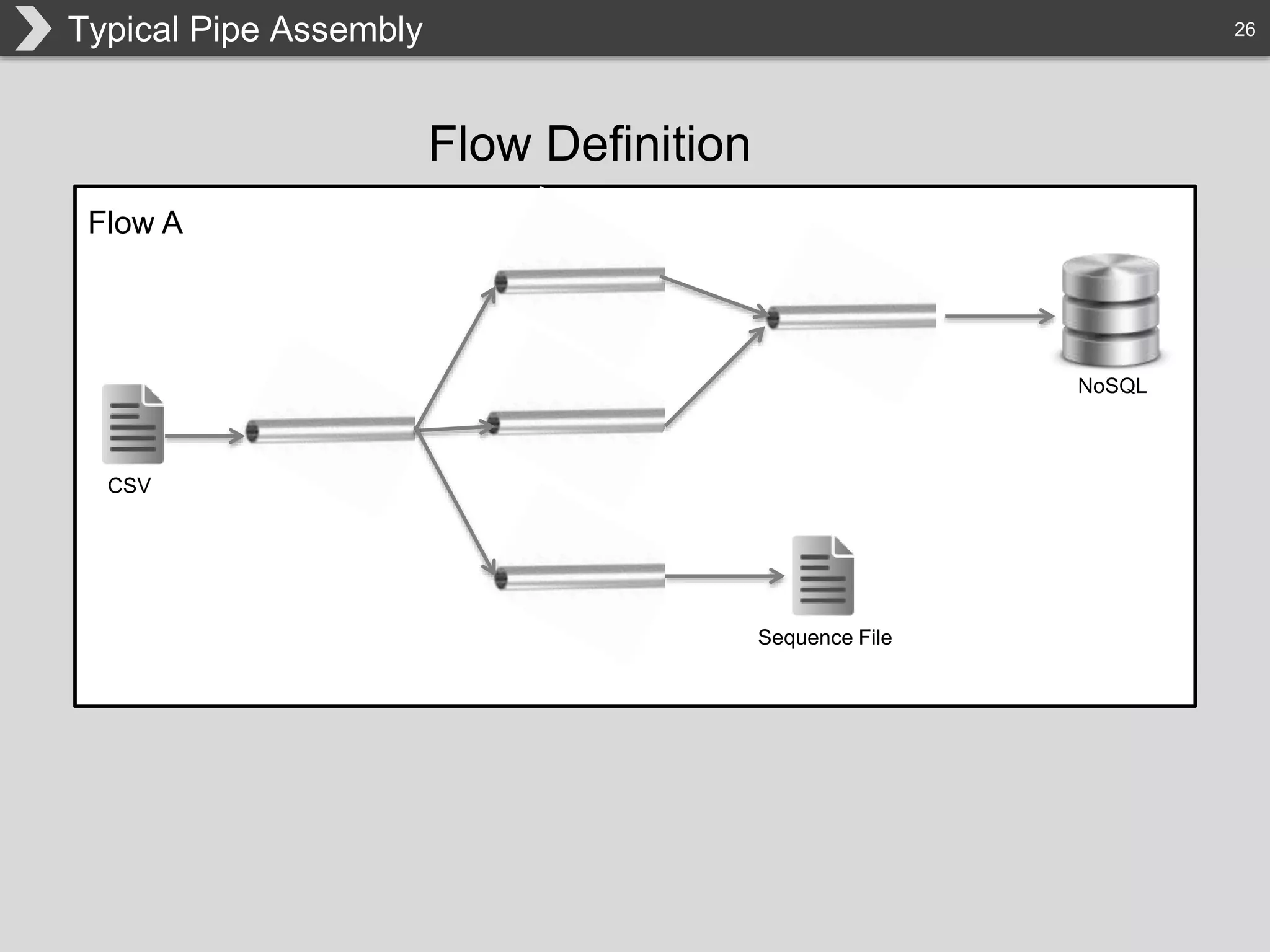
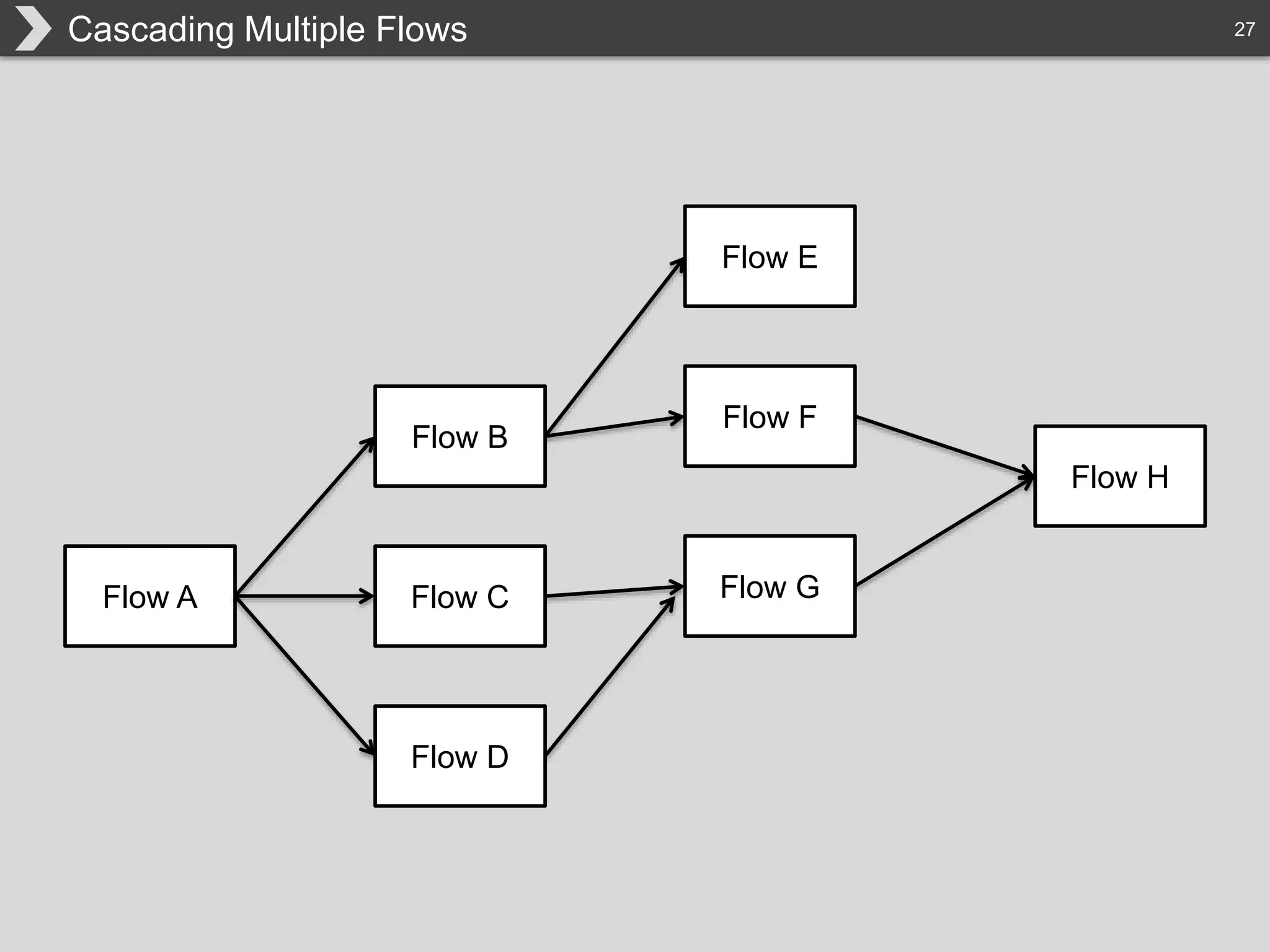
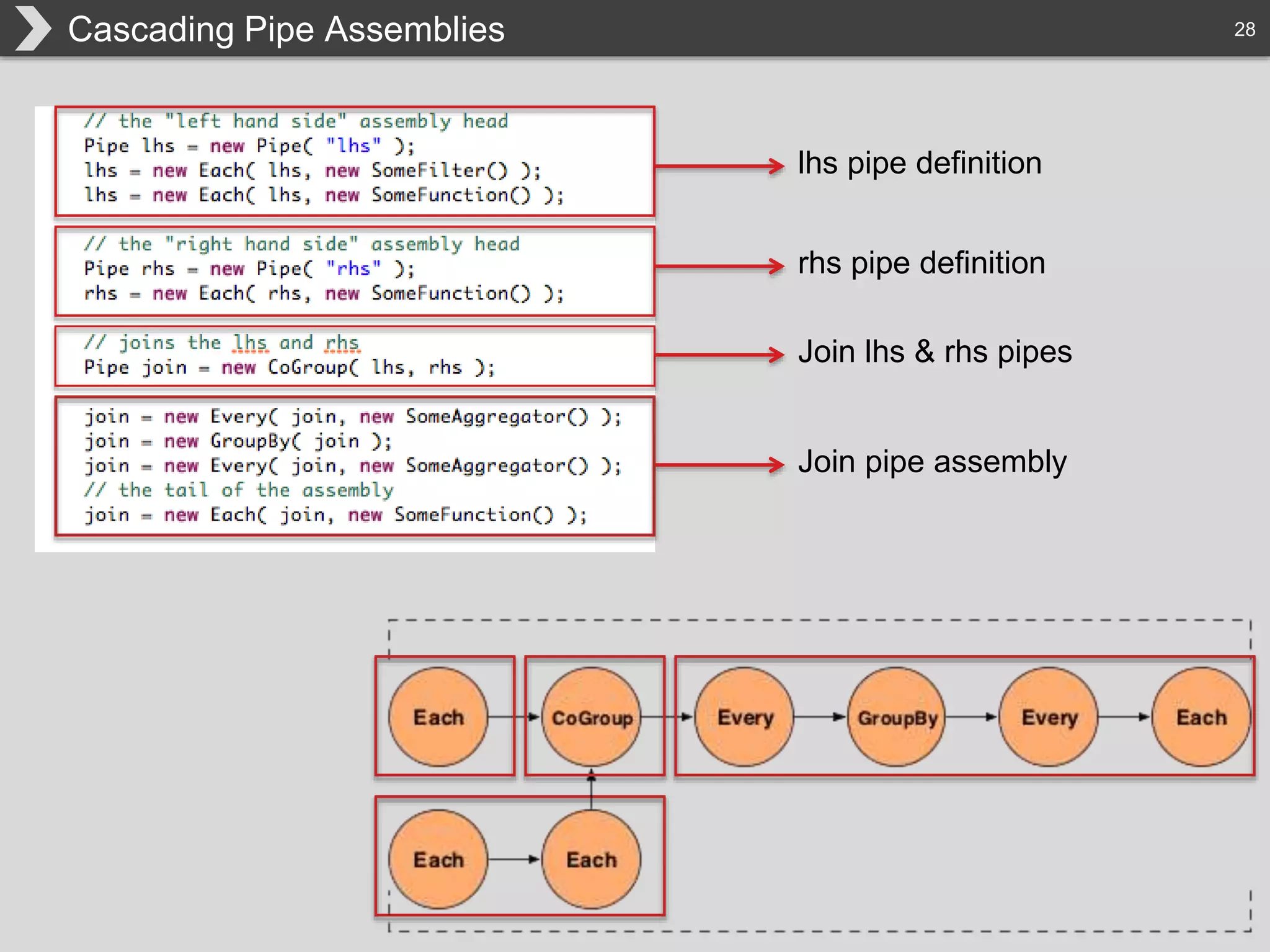
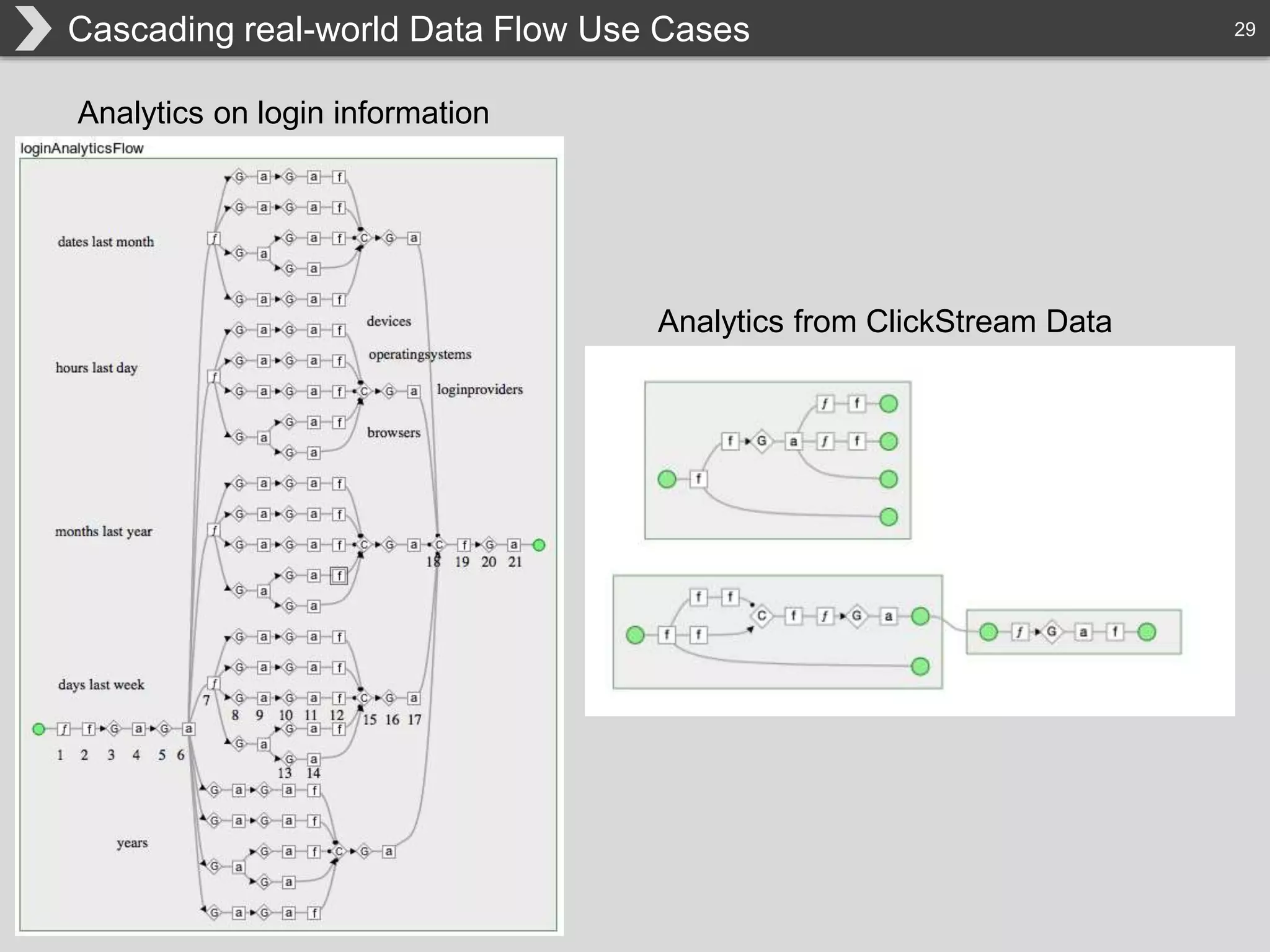
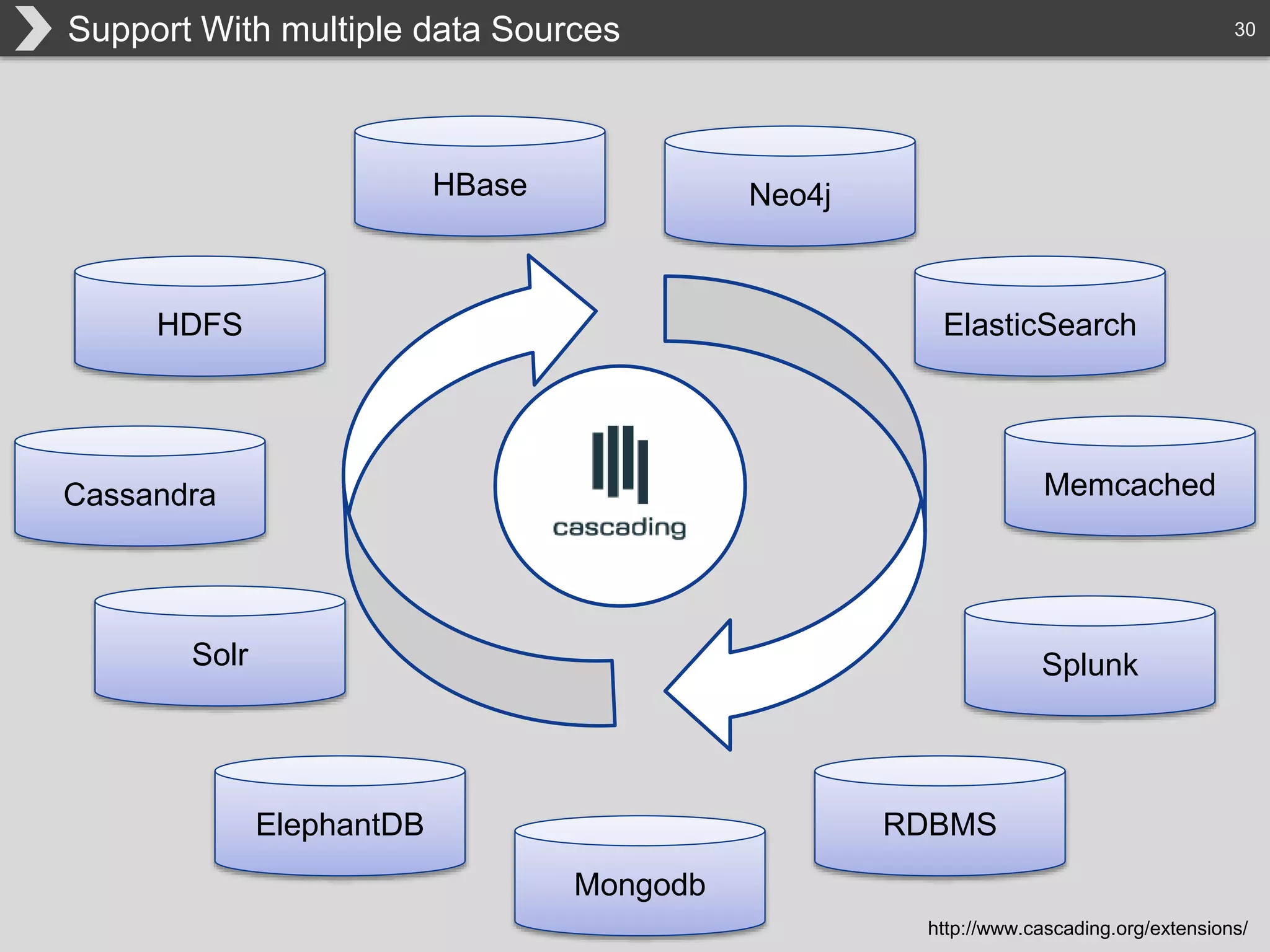
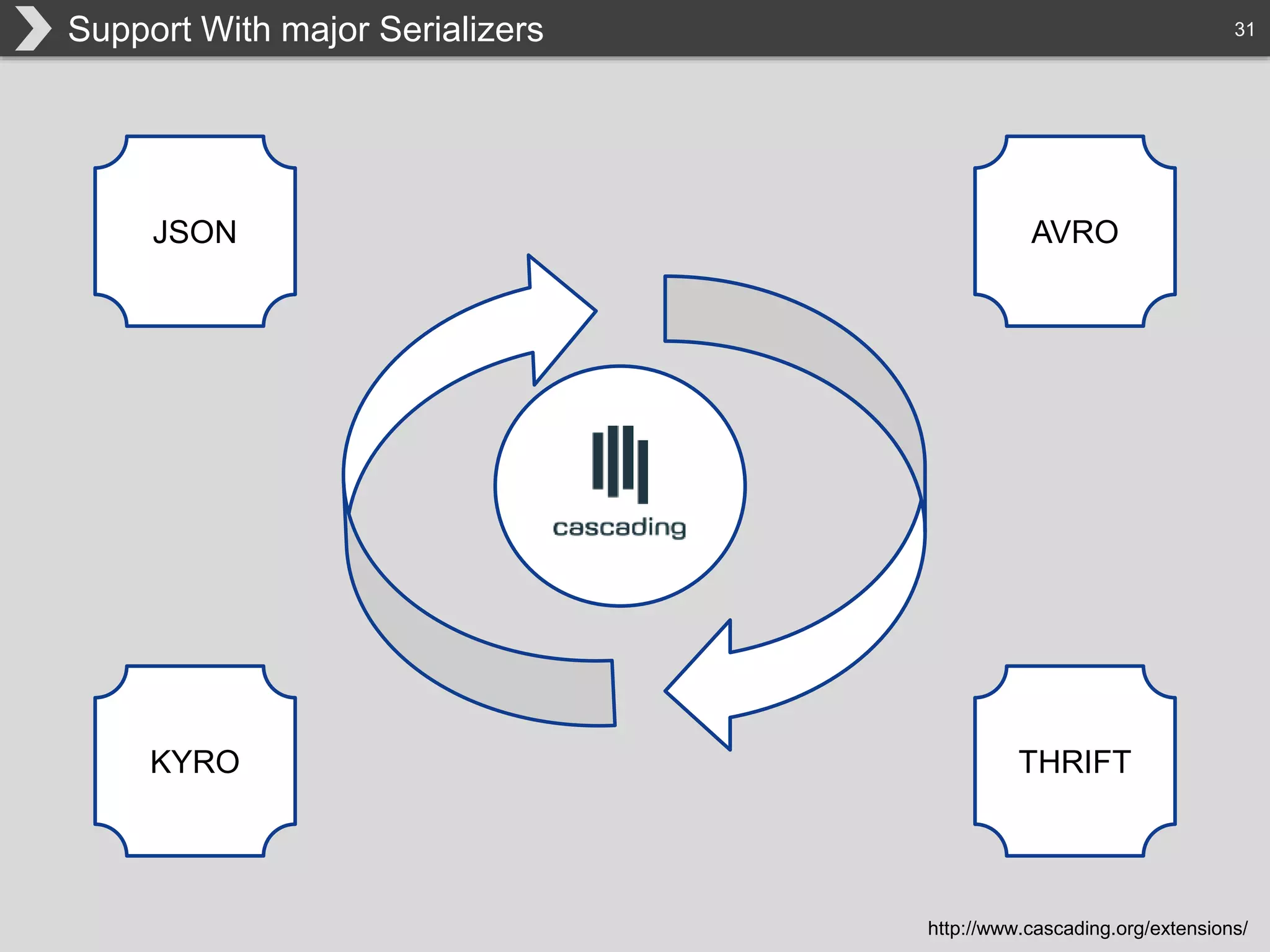
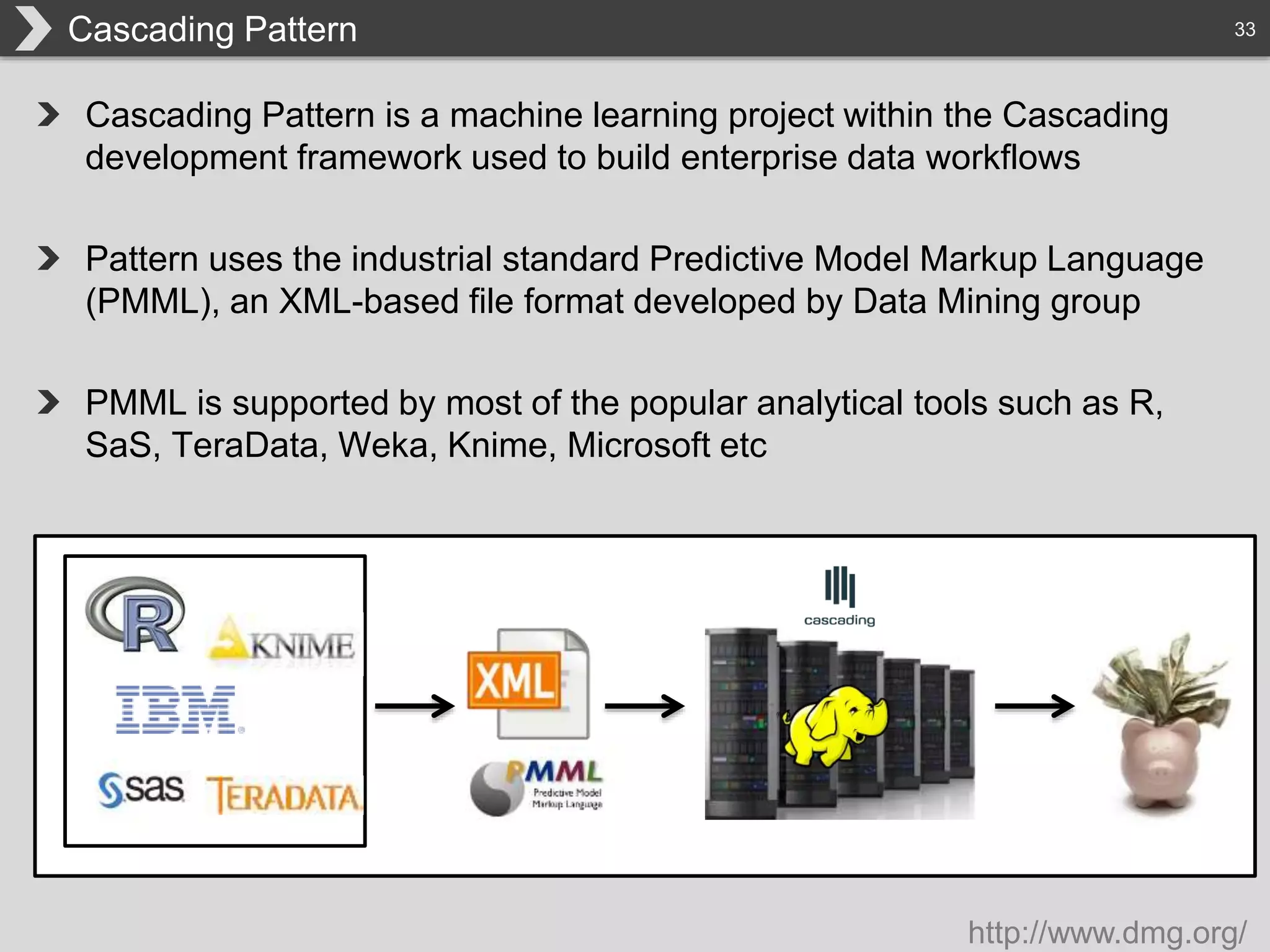
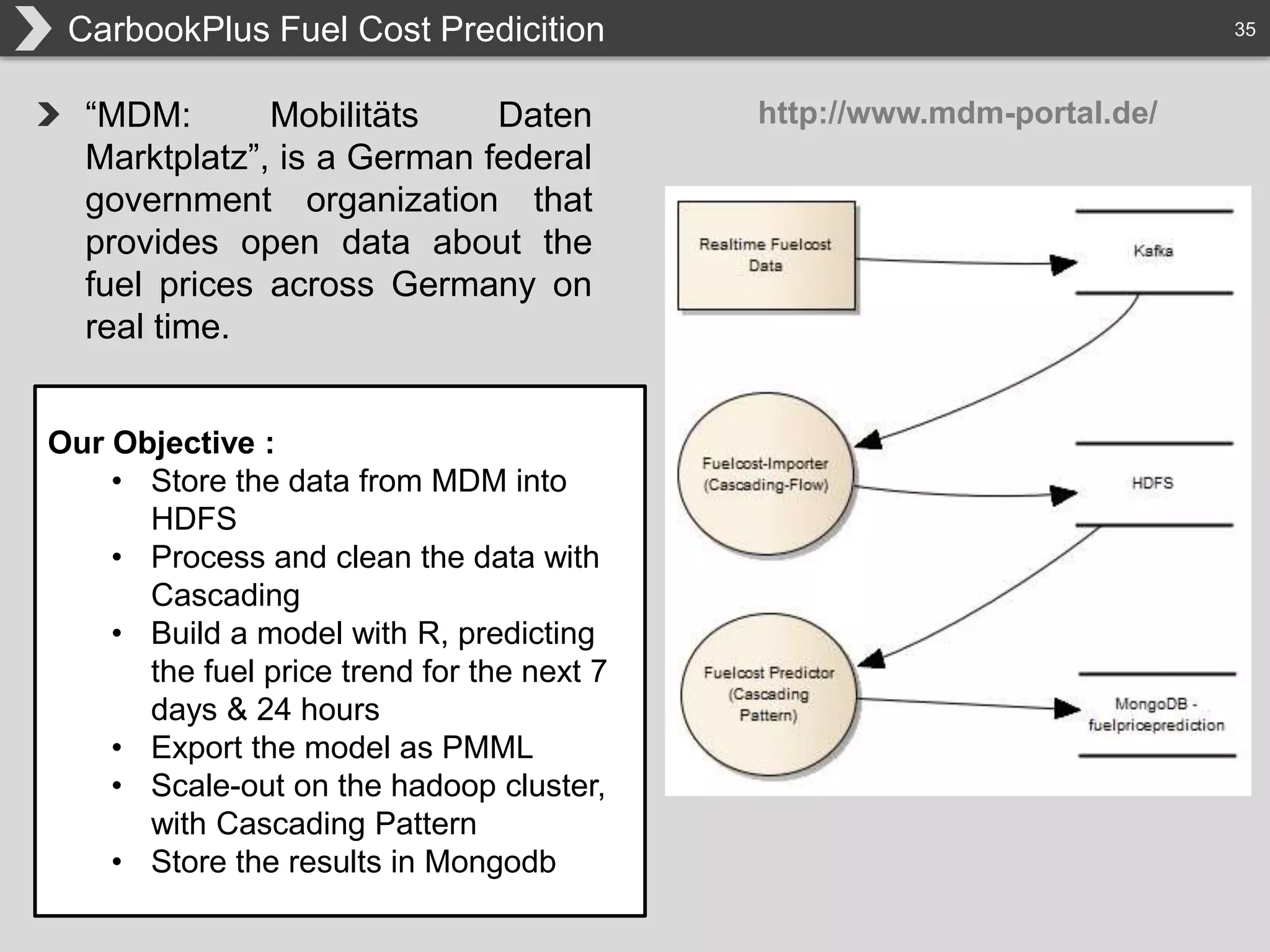
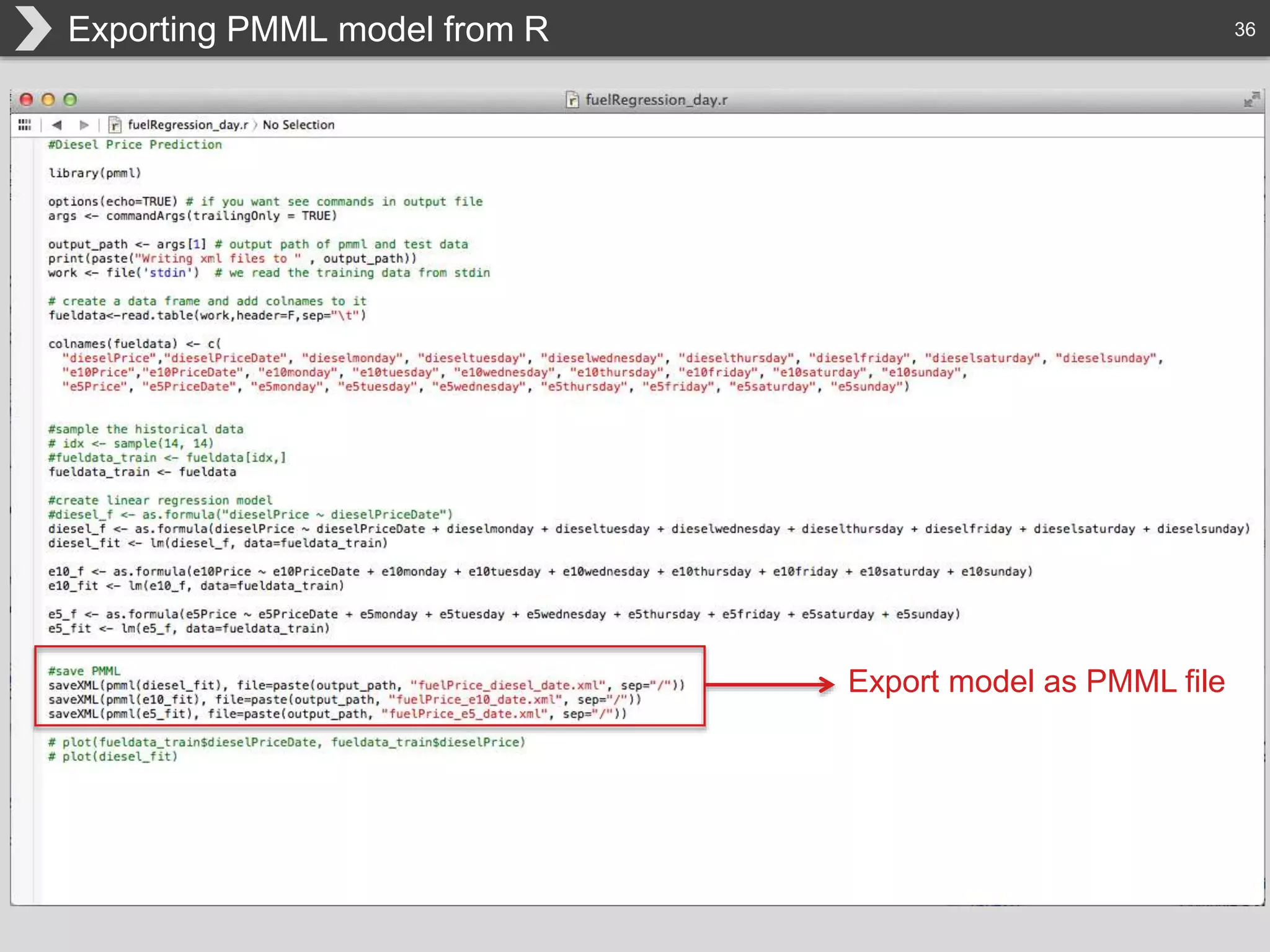
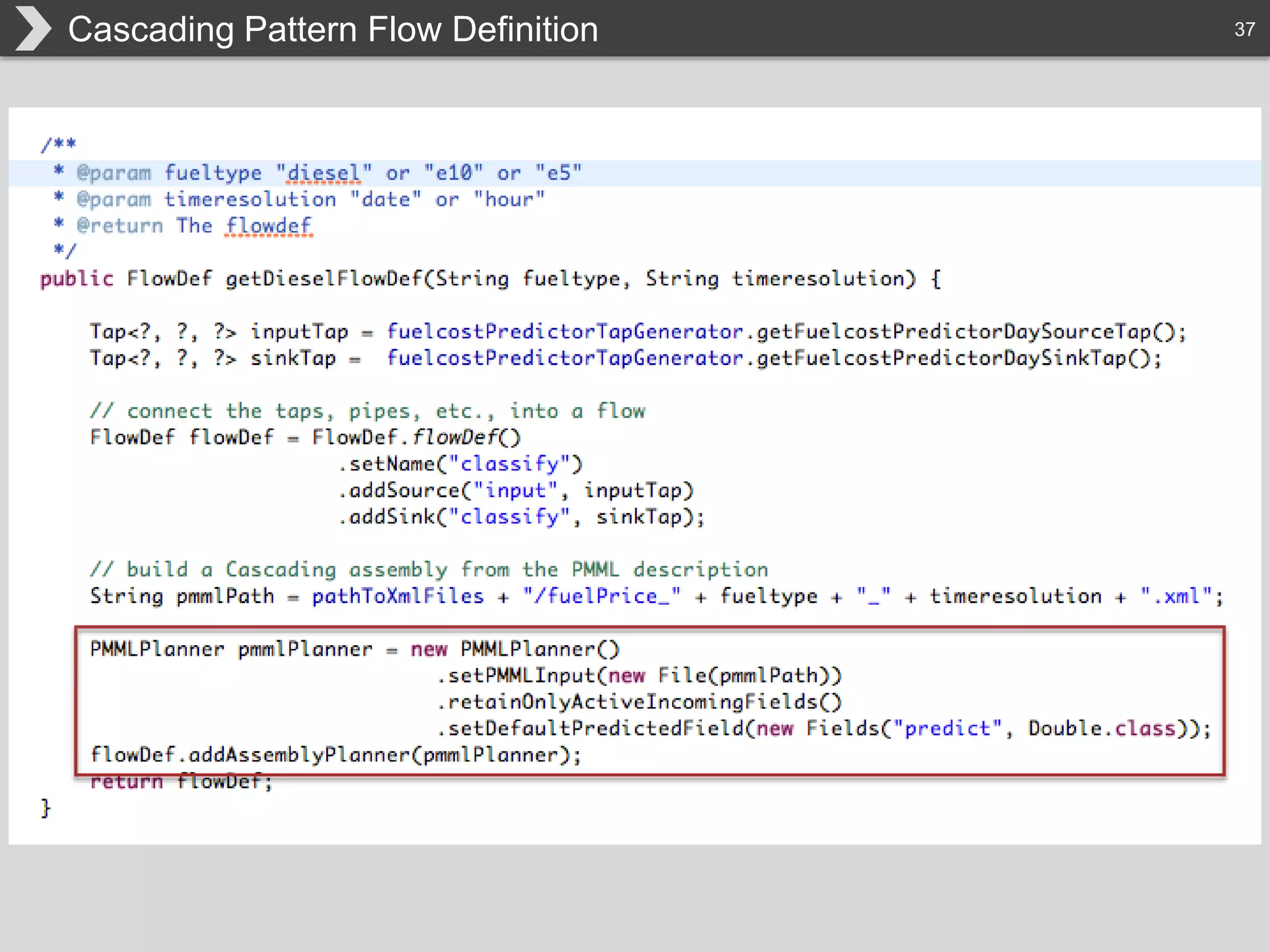
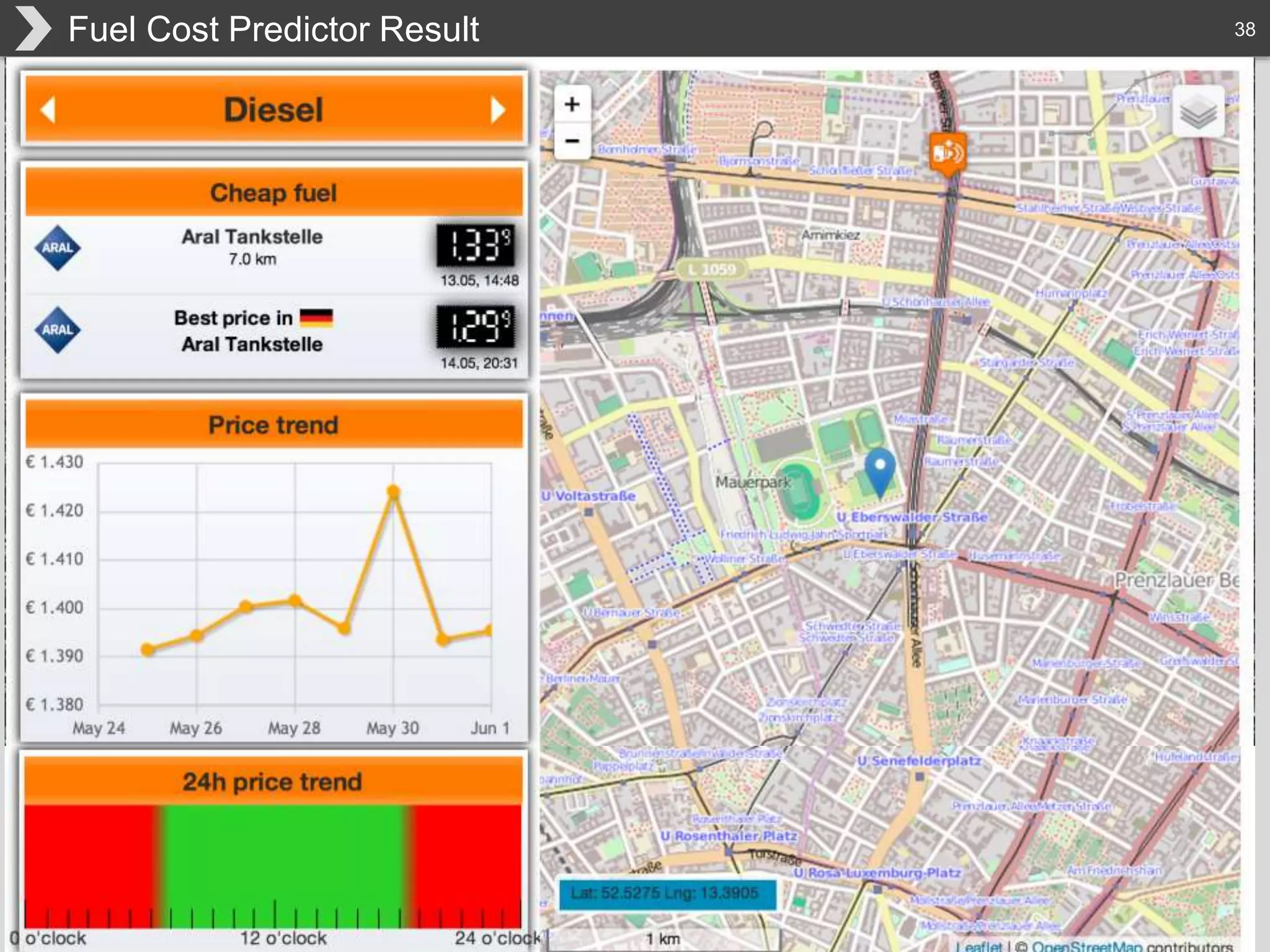
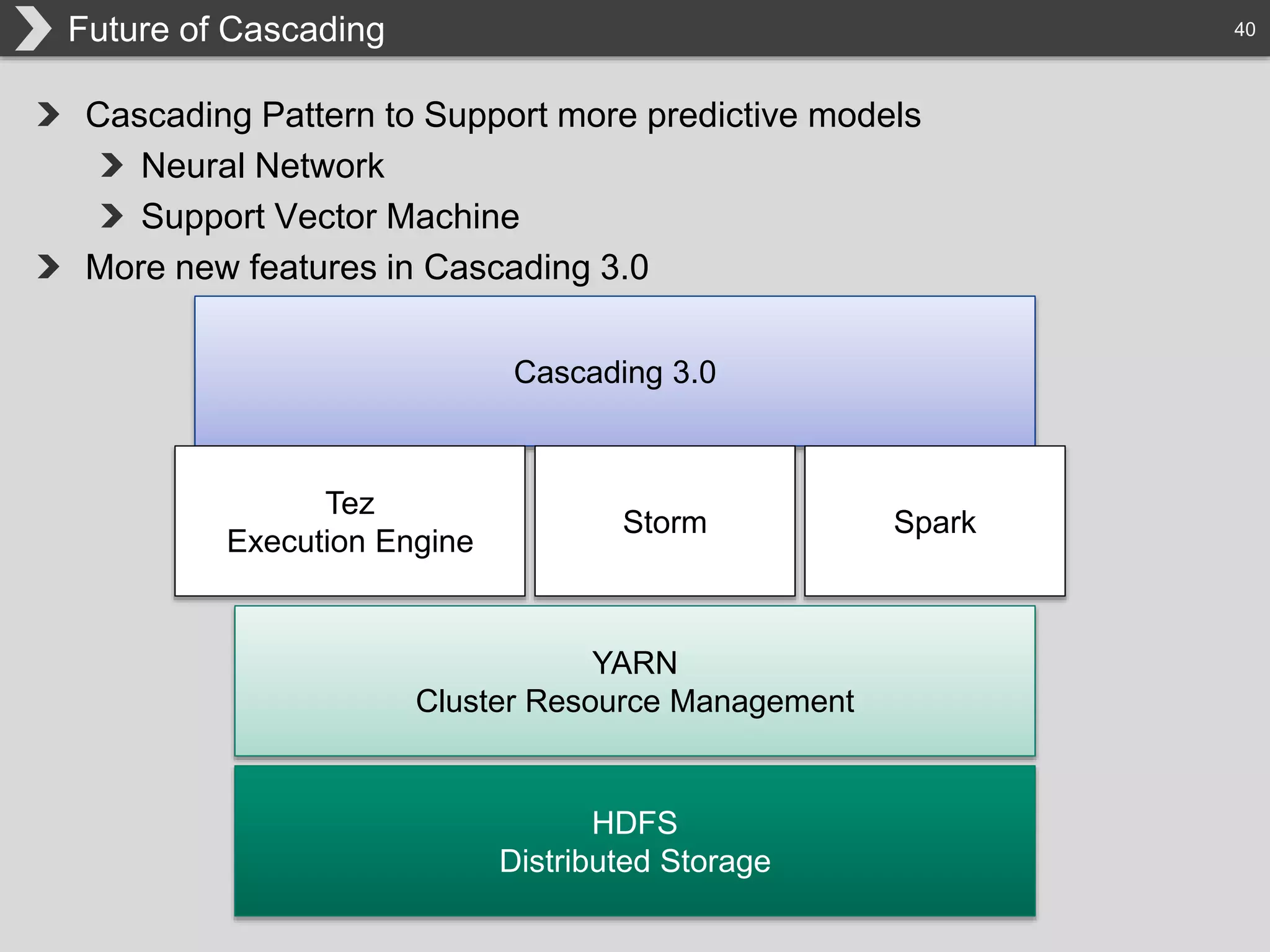
The document discusses Hadoop, an open-source framework designed for storage and processing of large datasets, highlighting its features like reliability, scalability, and cost-efficiency. It introduces Cascading, a Java framework for simplifying application development on Hadoop, facilitating a functional programming approach to map-reduce tasks. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of Hadoop application development and offers insights into predictive modeling using the Cascading framework.