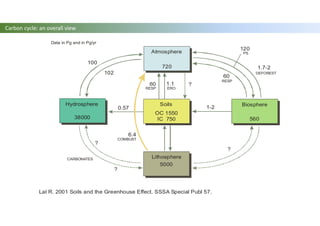
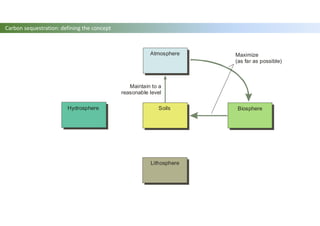
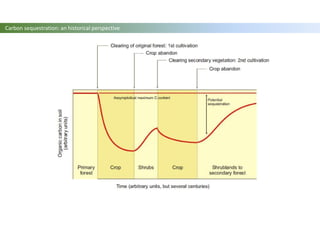
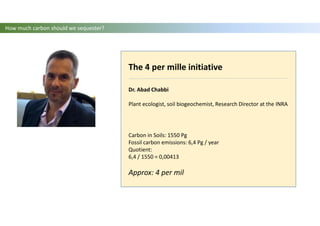
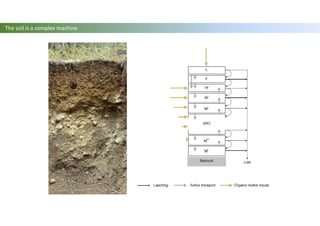
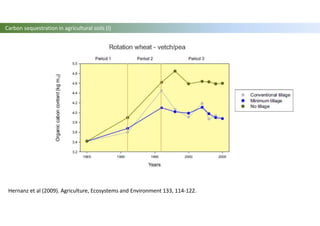
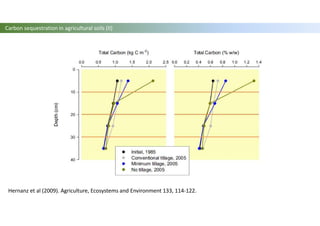
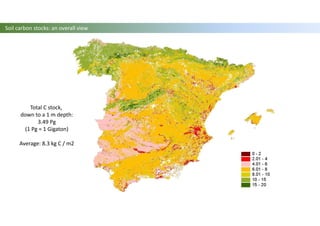
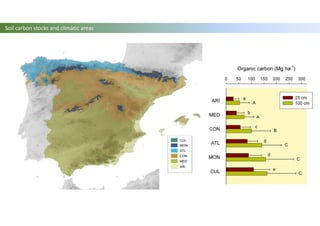
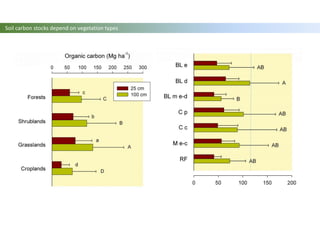
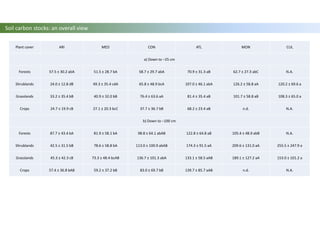
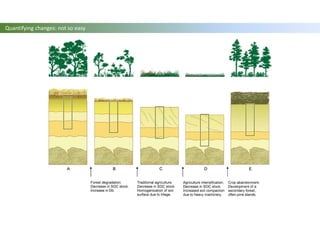
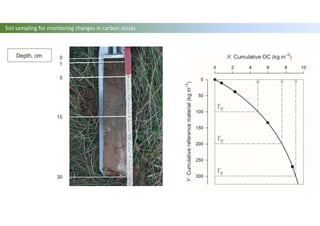
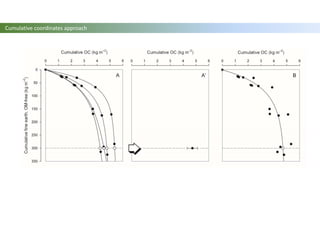
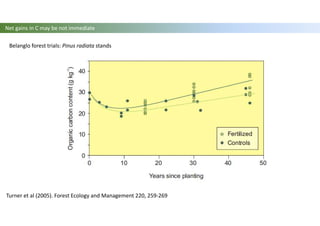
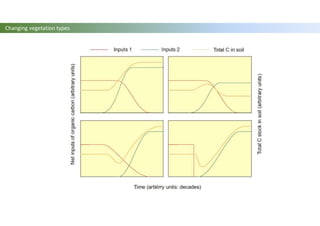
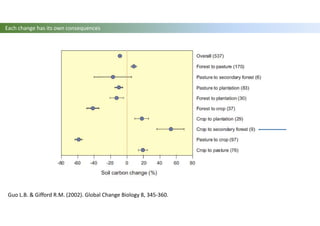
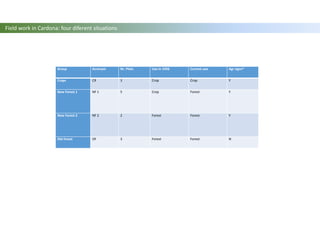
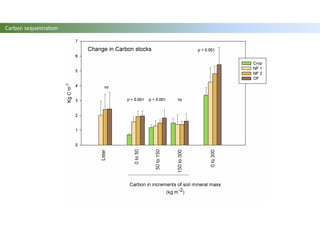
The document discusses carbon sequestration in soils, emphasizing the importance of maintaining and maximizing carbon levels across different ecological systems. It includes historical perspectives, estimates of carbon storage in various vegetation types, and the impact of land use changes on soil carbon stocks. Additionally, it highlights the complexities of quantifying these changes and suggests that managing soils for carbon sequestration is feasible.