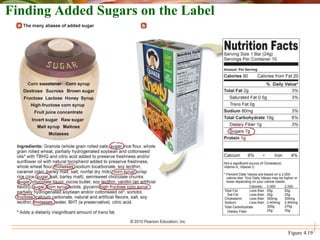
This document discusses carbohydrates and their classification. Carbohydrates are produced by plants through photosynthesis and are converted into glucose for human energy. Carbohydrates are classified as simple or complex, with simple carbohydrates being monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose or disaccharides like sucrose, lactose, and maltose composed of two monosaccharides. Complex carbohydrates are polysaccharides like starch stored in plants and glycogen stored in animal liver and muscle. The document also distinguishes between naturally occurring sugars in foods and added sugars in processed foods and sweets.