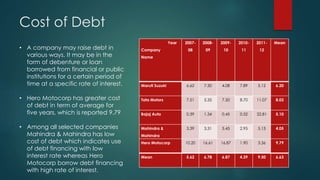
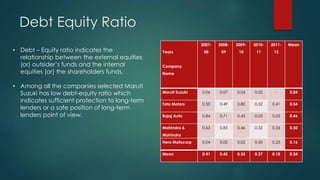
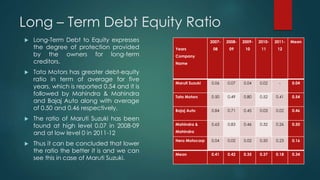
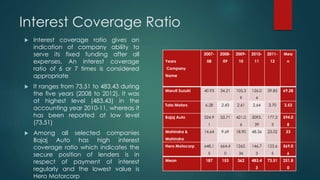
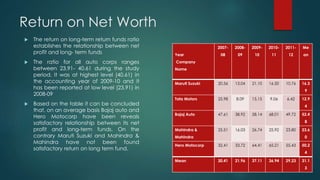
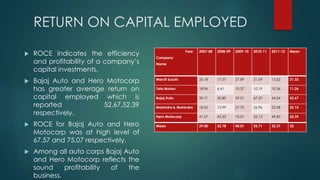
The document analyzes the capital structure of major automobile companies in India over a five year period from 2007-2008 to 2011-2012. It examines the leverage, cost of capital, and financial ratios of companies like Maruti Suzuki, Tata Motors, Bajaj Auto, Mahindra & Mahindra, and Hero MotoCorp. The analysis finds that Tata Motors has the highest financial leverage and debt ratios on average, while Maruti Suzuki has the lowest. Bajaj Auto has the highest interest coverage and fixed asset turnover ratios, indicating efficient use of assets. The return on net worth is highest for Bajaj Auto and Hero MotoCorp, showing a satisfactory relationship between profits and funds employed.