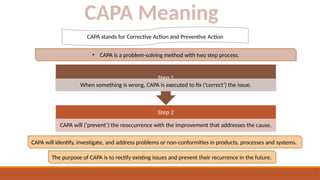
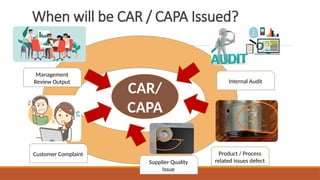
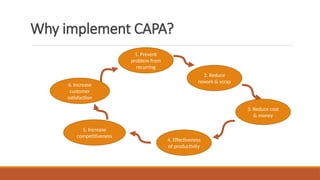
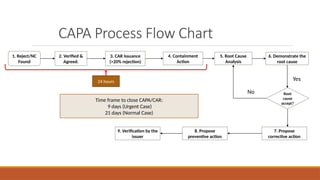
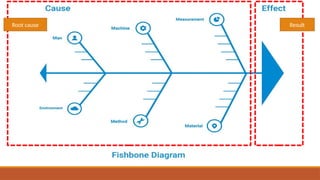
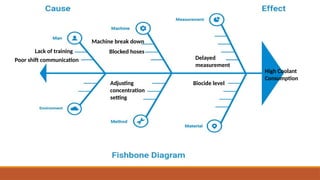
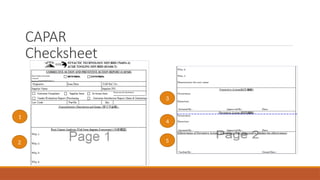
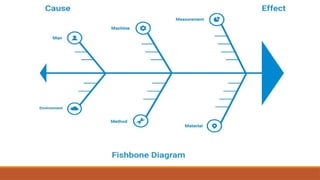
The document outlines the Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA) process, which aims to resolve existing issues and prevent their recurrence in products, processes, and systems. CAPA involves identifying problems, conducting root cause analysis, and implementing corrective and preventive measures within specified timeframes. The document also highlights the importance of containing issues during the investigation phase and provides a structured approach for documenting problems and their resolutions.