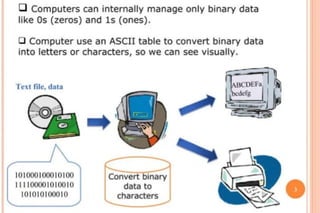
ASCII is a 7-bit code that assigns numeric values to letters, numbers, and other characters to allow computers to process text. It was developed in 1963 and most computers now use ASCII to represent text internally and allow data transfer between devices. The ASCII code table maps binary values to corresponding characters, allowing computers to convert between binary and visible text. While ASCII enabled basic text processing, it is limited to 127 or 255 characters and only supports the standard English language characters.




![ASCII T
1
able
AMERICAN STANDARD CODE FOR INFORI
MATI
ION
IINTERCHANGE(,
ASCIII)
~c ~ JC Oct Char DK t!ex Oo Char Dec ~ Dt-i CbA,r Dec. Hex D
el Char
0 0 n .Kl ~ 61 q ~ 60 ii10
J. 1 3 lil :u 411 I 6j "l gJ 61 li'I a
2 l' J M n :z • 11!',6" t!:tl 9! 61 ll-12 II
3 ) l :I~ 11 ;!:J • !ll :ill i9 lGJI U) C
. 4 ~ :u 2'1
'" $ ta "4 100 f=& 144 t:I
.,.
Si !$ c
... Ji 25 41 ,., i'i ~s JOI ~ l45 ~
6 ti n 1.fi 4!i
' 70 &ti P' Im ~ 'U I
.,
' ~ :i, 41
,. 'H 4:, {i !01 ~'1 U ,7 Q
~. 1B ii ~ a so
• )'} ill H 104 A J ,,
9 t n IG] 5 51 I l il cp I la! G9 lS1 i
HJ A llf tl :Z.li. 52 • 74 Q I 105 6.11 :tS2 J
1J !I u II) le. ,1 "'" l~ ill! E 101 16:a U3 ~r
11 c l,C
" lC ,. . Jfj ,c L 1"3. 6C 154 I
H I) u 111.!li :a 55 11
'° M ICl"l ~ 155
'"
21 E ll ~ :HJ 1£ 7! ,If;; ~ 110 61: lS6
"
a l C
J 1F
~· '
f'i '-f 0 111 Er: lSJ Q
]lfj, 10 ;ro ,=;~ so 0 BO !iO p l U 10 J(,g p
n H 21 :i n ii n 1!21 0 1111 11 161 (I
lB Ll so Jl 2 'S2 !21! R. tll n IQ r
u n 5'! I! ! 5l w s H5' "IJ t l 1,
10 u 9 J.; & !:I u, T U6 11 Ui4 l
ll il.5 53
" e 5 )5 m u 117 u l 5 u
:n t6 5,& J5 i:;5 ~ ,. l 111! 116 I & ~
:JJ, ~; !H n 6l , S1 n 'i"J JILi 'U a 1 ..
2• 2 ll i8 Si X 110 JI na ..
25 ' 5iJ "l 9 ~t y 1a ,:o i l .,
26 511 1,1, ~ t m 1A a,: ,
~
, U!i s lfl JI lil I 1ll ~ UJ [
ZS, lC c:, I!' ,. < !H '5C 114 IC n, I
19 ffll J5 61 1D ~ 9.J ~ I Ia TI) u )
30 15. E2 J! l .. 91 !¥ - !16, Ji!; u
:
u IF f cl F 11 ~ ff U7 i1if n1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cao-ppt-230401044112-9444c89c/85/CAO-ppt-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![An example of ASCII code of character''$"
~ ~~-:::.] 64 32
~ '.
Blna~--o o1 o
Decimal-·
- - -32
16
I
+
8 4
0100
I
2
I
I
!
4 - 36
1
I
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cao-ppt-230401044112-9444c89c/85/CAO-ppt-pdf-7-320.jpg)