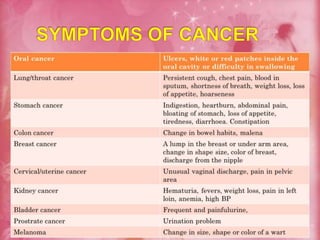
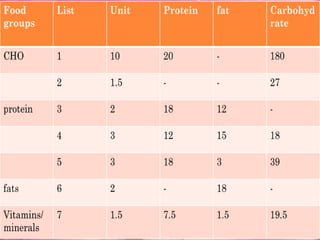
This document discusses cancer, its types and symptoms, and dietary management for cancer patients. It outlines several common types of cancer and lists the key objectives of nutritional therapy as meeting increased metabolic demands, preventing weight loss, and alleviating symptoms. It provides recommendations for calorie, protein, vitamin, and mineral intake for cancer patients and examples of nutrient distributions and daily meal plans that emphasize high calorie, moderate protein, and high fiber intake.