Embed presentation










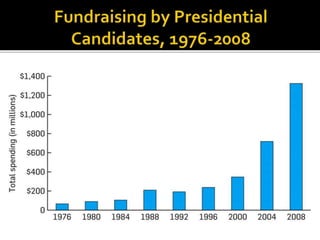
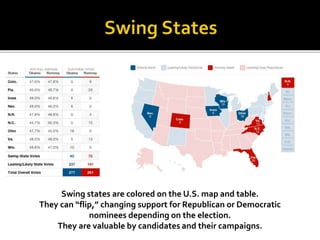








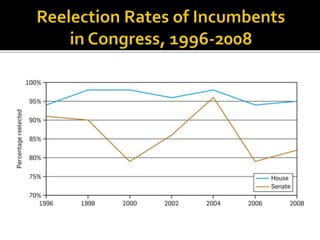


This document contains summaries of key concepts in political science: - It describes the original design of the US presidency and differences between the House and Senate. The House represents proportional population, sits for 2 years. The Senate gives 2 seats to each state, terms are staggered. - It defines types of campaign funding: direct "hard money" donations and less regulated "soft money". - It explains swing states that can support either party, and microtargeting of specific demographic ads. - It outlines valence, position, and wedge issues that candidates emphasize. - It lists key factors that influence elections: the economy, presidential popularity, time in office of the incumbent party. - It defines party identification and the coat






















