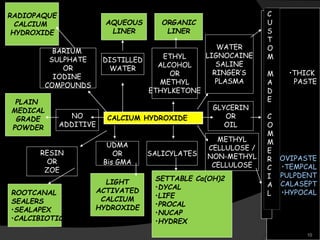
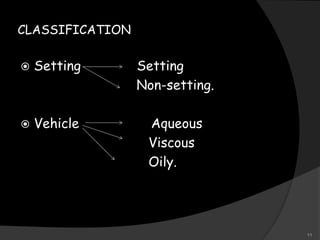
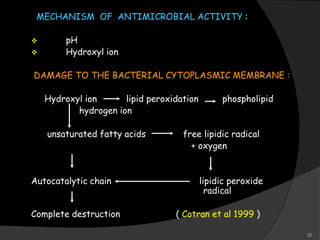
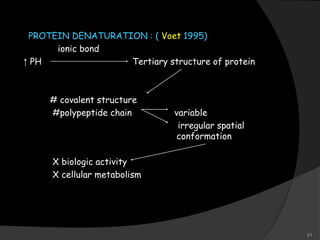
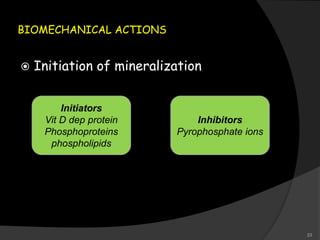
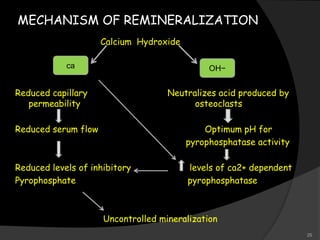
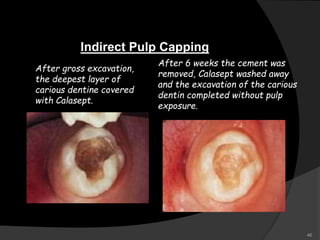
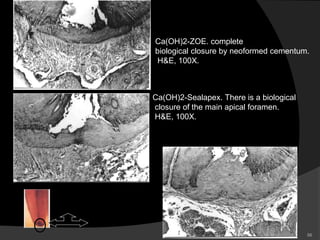
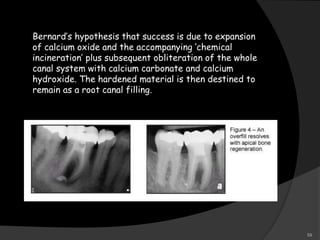
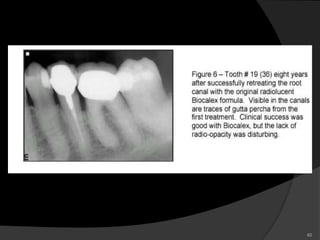
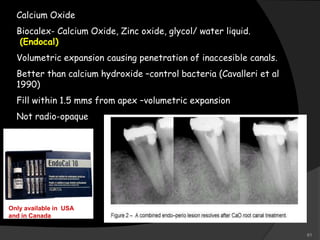
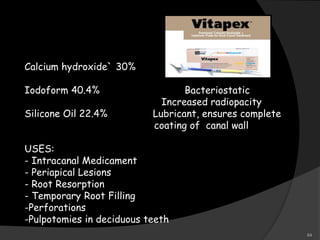
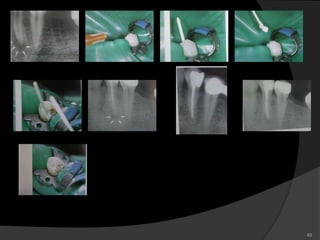
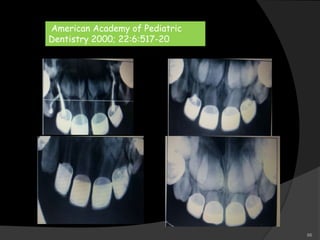
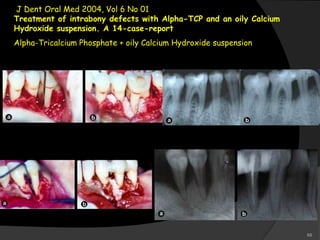
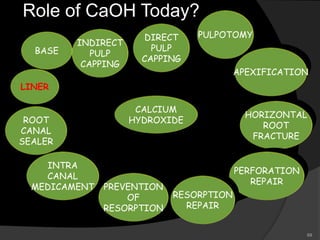
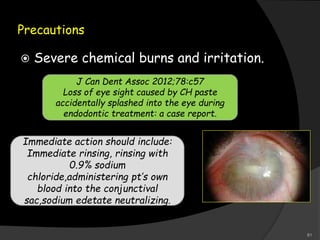
This document provides an overview of calcium hydroxide, including its history of use in dentistry, properties, classifications, mechanisms of action, and clinical applications. Calcium hydroxide has been used since the 1920s as a pulp capping agent and to promote healing. It is classified based on its setting properties and vehicle. As an alkaline substance, calcium hydroxide has antimicrobial effects through its high pH and induces mineralization. It can form a dentine bridge and dissolve necrotic material. Current uses include as a root canal sealer, liner, intracanal medicament, and for pulp capping, pulpotomy, and repair of root fractures or perforations.