The document discusses how to enhance application performance using JCache (JSR-107), a standardized caching mechanism for Java. It highlights the benefits of caching, common scenarios for use, challenges associated with cache implementation, and offers insights into Java caching features and standards. The presentation also outlines JCache's integration with various Java frameworks and discusses future developments in caching technologies.
























![© 2016 Hazelcast Inc. Confidential & Proprietary ‹#›
JCache: Entry Processors
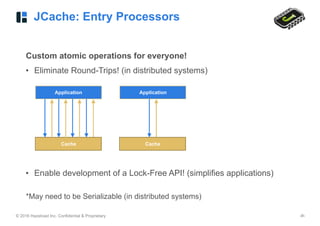
Custom atomic operations for everyone!
public class IncrementProcessor<K>
implements EntryProcessor<K, Integer, Integer>, Serializable {
@Override
public Integer process(MutableEntry<K, Integer> entry,
Object... arguments) {
if (entry.exists()) {
int amount =
arguments.length == 0 ? 1 :(Integer)arguments[0];
int current = entry.getValue();
entry.setValue(count + amount);
return current;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(“no entry exists”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcachemeetupljug18-160311134153/85/Caching-and-JCache-with-Greg-Luck-18-02-16-33-320.jpg)