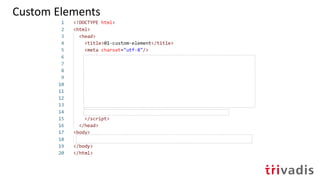
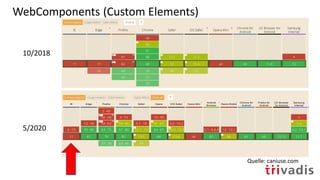
The document discusses micro-frontends, which view web applications as a composition of features developed independently by cross-functional teams, allowing for end-to-end ownership of each feature. It outlines various methods for implementing micro-frontends, such as server-side template composition and the use of web components. The document also highlights the challenges of using Angular in this context and provides references for further exploration of the topic.


![Was sind MicroFrontends?
Definitionsversuche
– The idea behind Micro Frontends is to think about a website or web app as a composition of
features which are owned by independent teams. Each team has a distinct area of
business or mission it cares about and specialises in. A team is cross functional and develops its
features end-to-end, from database to user interface. – [1]
– In this approach, a web application is broken up by its pages and features, with each feature being
owned end-to-end by a single team. Multiple techniques exist to bring the application features—some
old and some new—together as a cohesive user experience, but the goal remains to allow each feature
to be developed, tested and deployed independently from others. – [2]
[1] Michael Geers: https://micro-frontends.org/
[2] ThoughtWorks: https://www.thoughtworks.com/radar/techniques/micro-frontends
Unabhängigkeit End-To-Endfeature-basierte Modularisierung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-3-320.jpg)


![Angular?
• „[…] but is quite challenging to use in scenarios that
don‘t fit that specific Single Page application model.“
• Rob Wormald, Angular Team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-6-320.jpg)
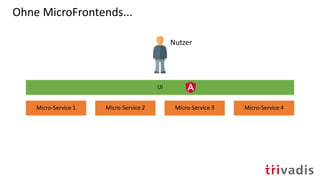
![Welche Möglichkeiten zur technischen Umsetzung von
MicroFrontends gibt es?
[1] https://martinfowler.com/articles/micro-frontends.html
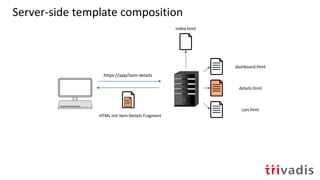
Server-seitige
Komposition via
Templates
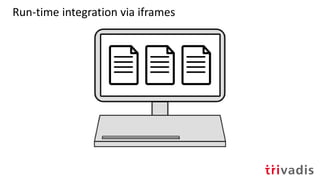
Integration zum
Build-Zeitpunkt
via iframes
via JavaScript
via Web Components
Laufzeit-
integration
Kombinationen
der Ansätze](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-8-320.jpg)

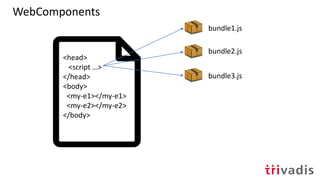

![Web components are a set of web platform APIs that allow you to create
new custom, reusable, encapsulated HTML tags to use in web pages and
web apps. Custom components and widgets build on the Web Component
standards, will work across modern browsers, and can be used with any
JavaScript library or framework that works with HTML.
Web components are based on existing web standards. Features to support
web components are currently being added to the HTML and DOM specs,
letting web developers easily extend HTML with new elements with
encapsulated styling and custom behavior. – [1]
[1] webcomponents.org: https://www.webcomponents.org/introduction
Definition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-14-320.jpg)







![Angular?
• „[…] but is quite challenging to use in scenarios that
don‘t fit that specific Single Page application model.“
Rob Wormald, Angular Team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-26-320.jpg)
![Wie kann ein MicroFrontend mit AngularElements umgesetzt werden?
[1] https://www.webcomponents.org/introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microfrontends-fuer-microservices-201001105426/85/MicroFrontends-fur-Microservices-27-320.jpg)




