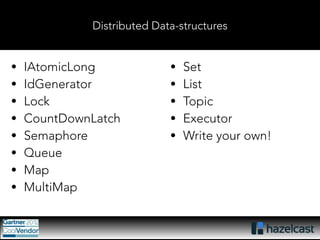
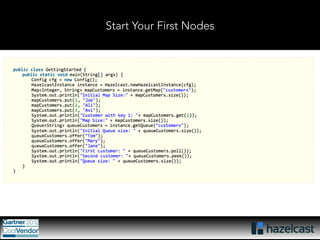
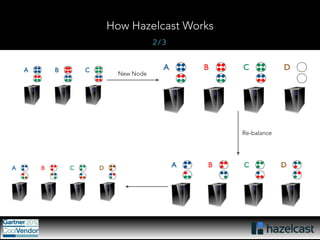
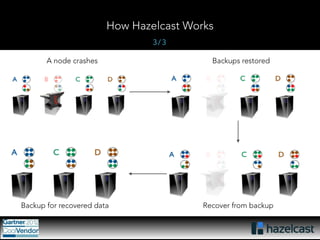
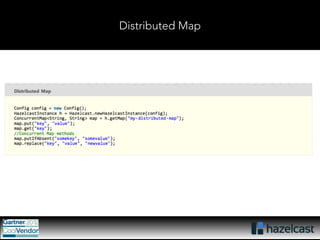
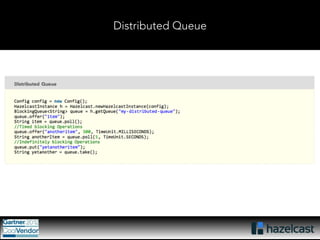
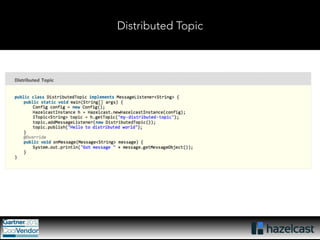
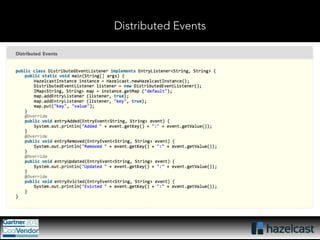
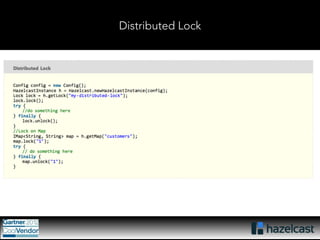
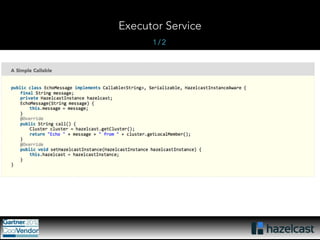
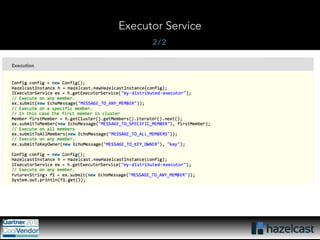
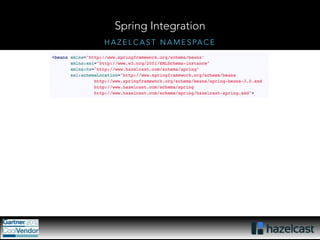
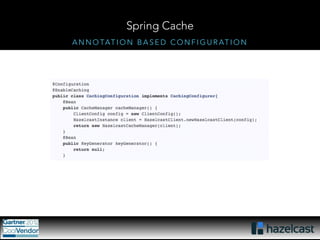
This document provides an overview of Hazelcast, a leading in-memory data grid solution. Hazelcast provides distributed data structures, execution services, and caching capabilities. It allows applications to scale linearly by adding additional nodes. Hazelcast can be configured via XML, API or Spring and supports features like transactions, custom serialization, and native client libraries. It integrates with Spring Framework for caching and can discover nodes via multicast or TCP/IP lists to form clusters across distributed systems.