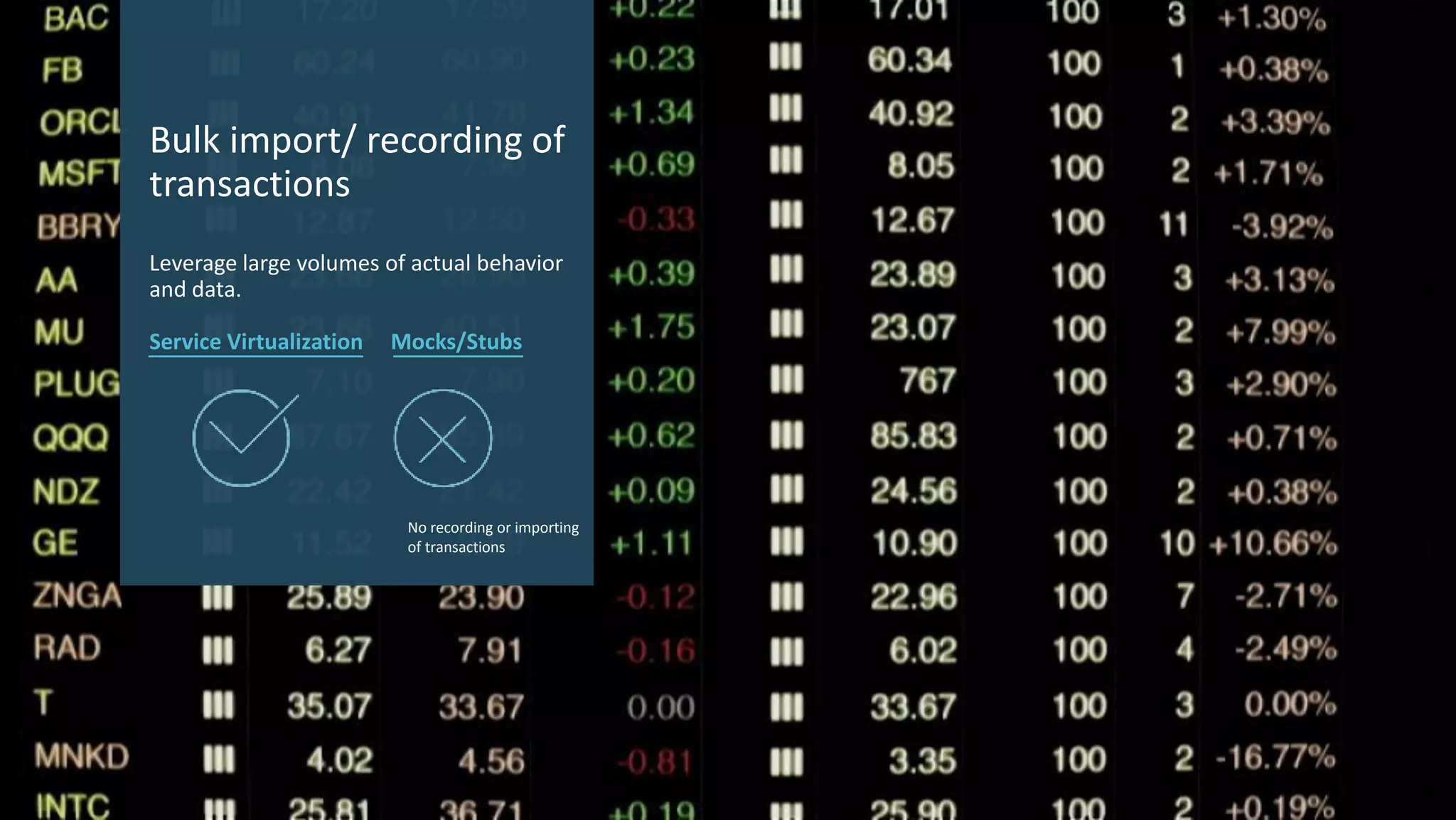
Service virtualization provides more robust testing capabilities than traditional mocks and stubs by simulating real services and enabling reuse across teams. It virtualizes services to reduce dependencies, support comprehensive testing including performance and integration testing, and improve the development process through earlier defect detection and shorter release cycles. In contrast, mocks and stubs are limited to the development environment and require code modifications for each application.