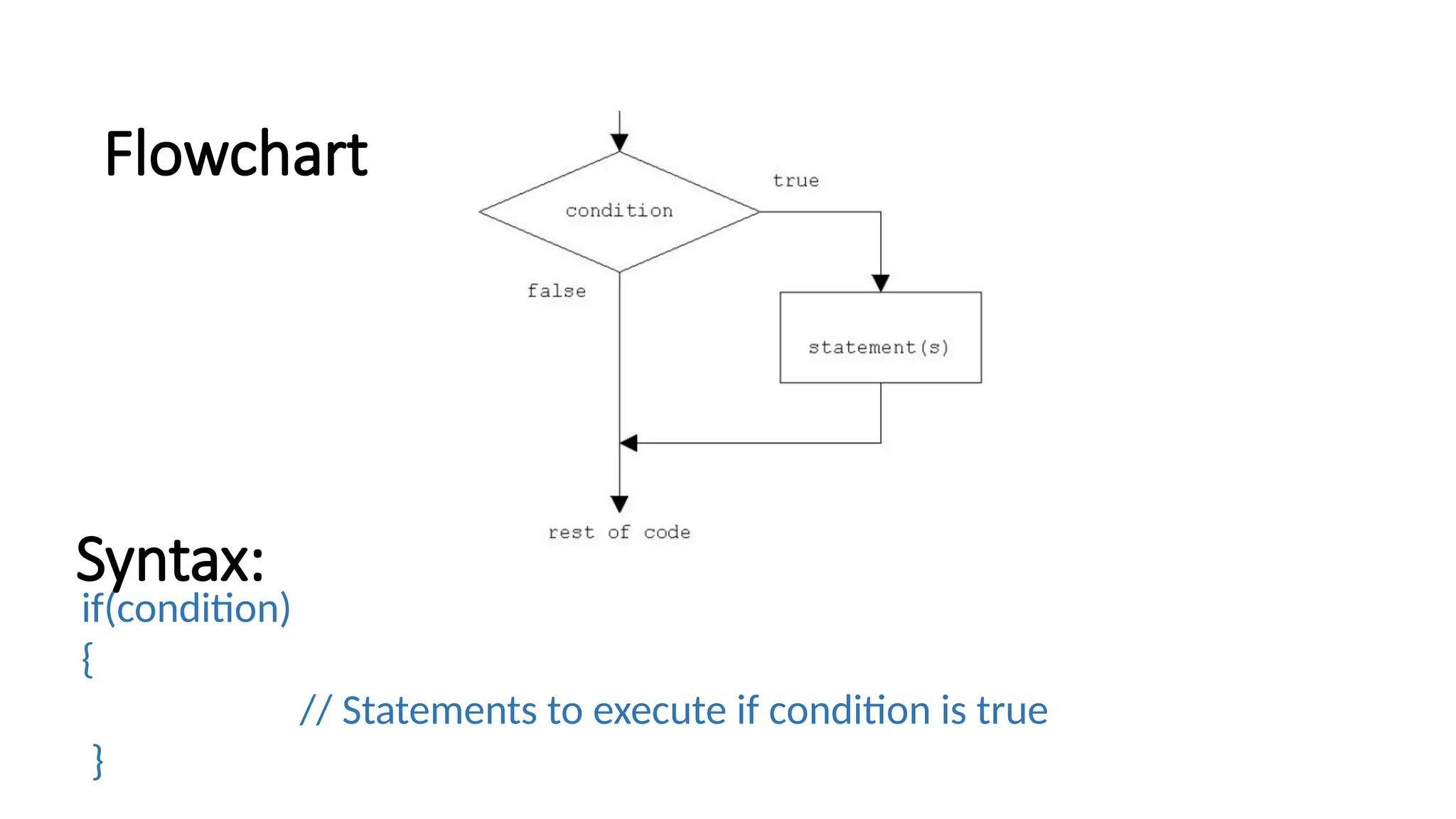
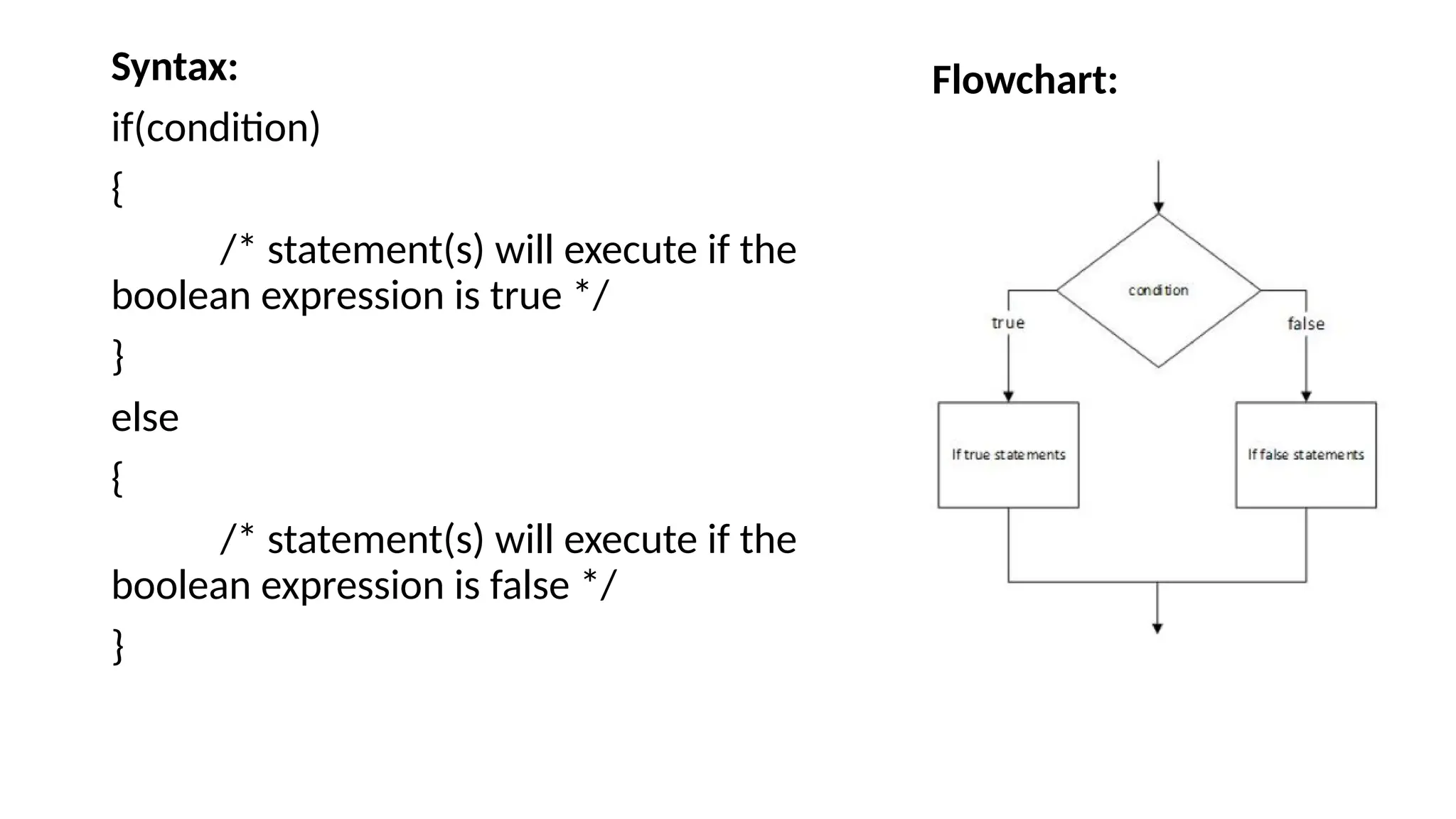
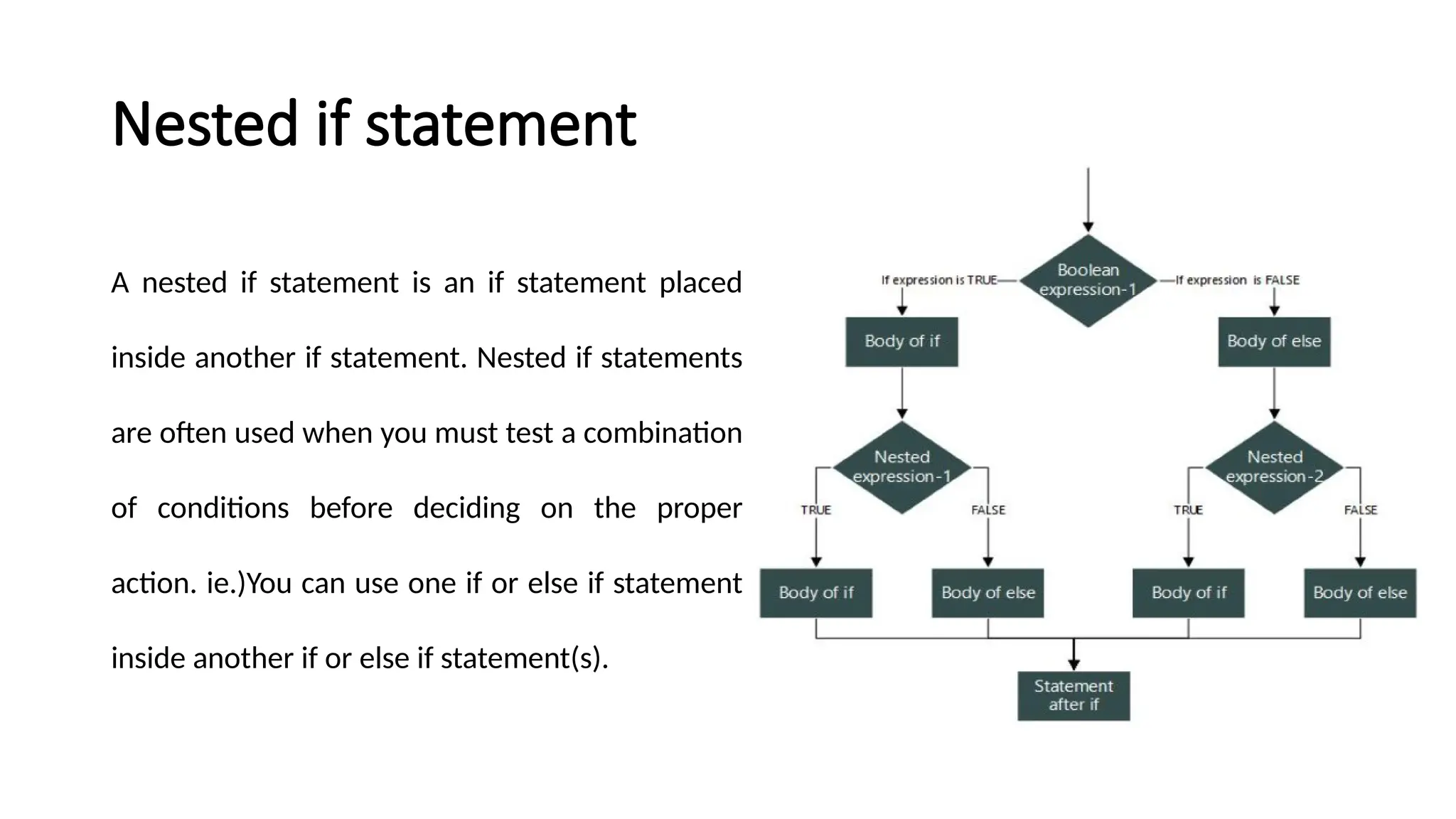
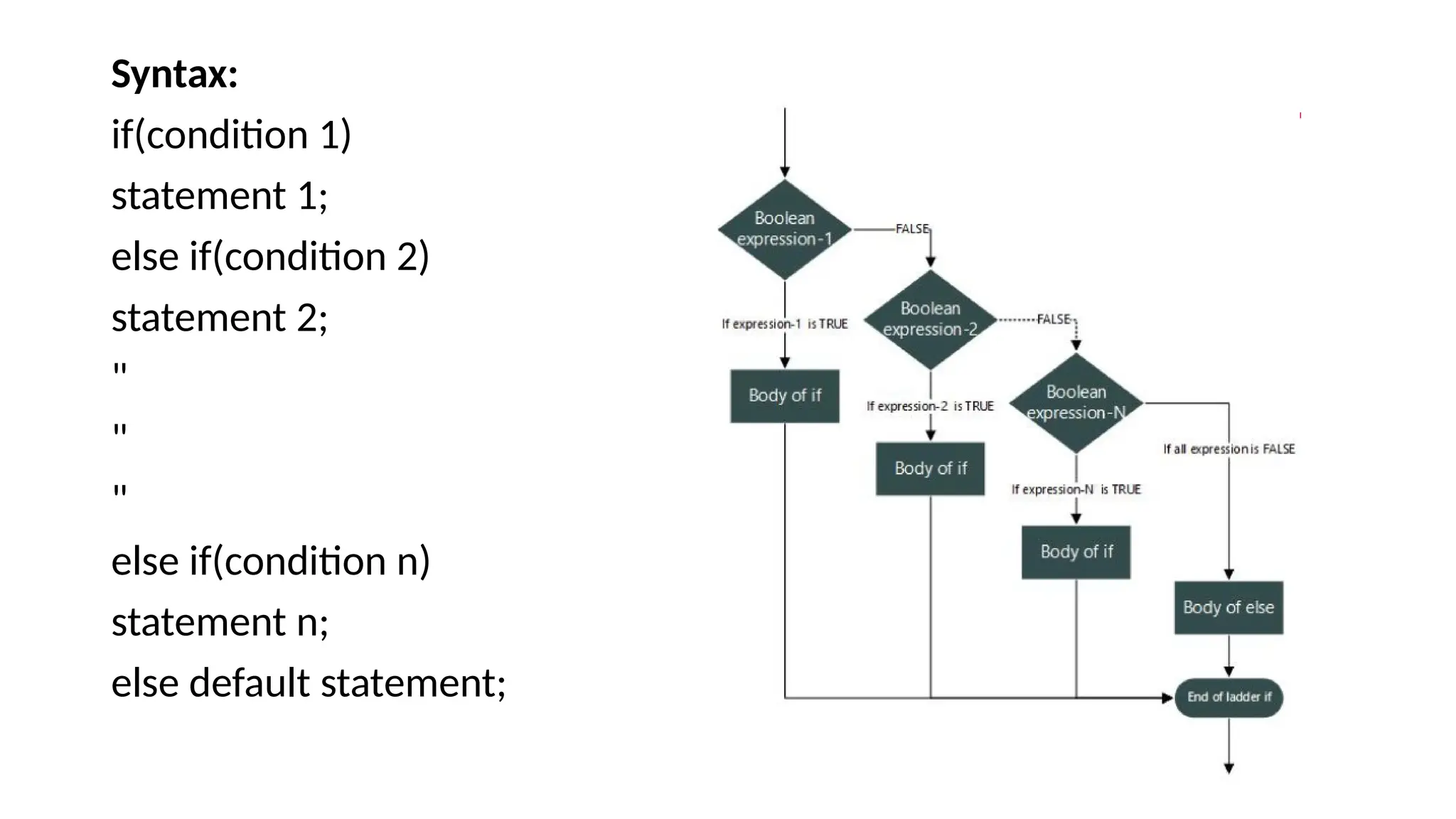
The document explains control statements in C and C++, which determine the flow of program execution through decision-making structures. It covers various types of conditional statements such as if, if-else, nested if, if-else ladder, switch statement, and jump statements like break and continue. Examples illustrate how these statements function, enabling programmers to write conditional code effectively.