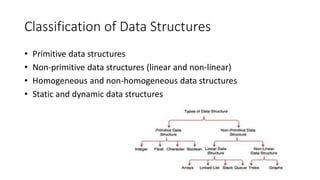
The document classifies data structures into primitive and non-primitive types, further categorizing non-primitive structures into linear and non-linear, as well as homogeneous and non-homogeneous varieties. It explains static versus dynamic data structures, detailing typical operations such as create, destroy, selection, updation, searching, sorting, merging, splitting, and traversal. Essential examples are provided, such as arrays, linked lists, trees, and graphs.
![1. Primitive data structures
These are the basic data structures and are directly operated upon by the
machine instructions.
They are integers, floating point numbers, characters, string constants,
pointers etc.
Like: int a =10;
The corresponding machine level code will be like:
store the int value in so and so location.
But if I write: int arr[10]=20;
The machine instruction doesn’t know array index 10! So, intermediate steps
will be there to convert this particular instruction to machine level.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classificationofdatastructures-240430074313-a7a1dadc/85/Data-Structures-Classification-of-Data-Structures-3-320.jpg)