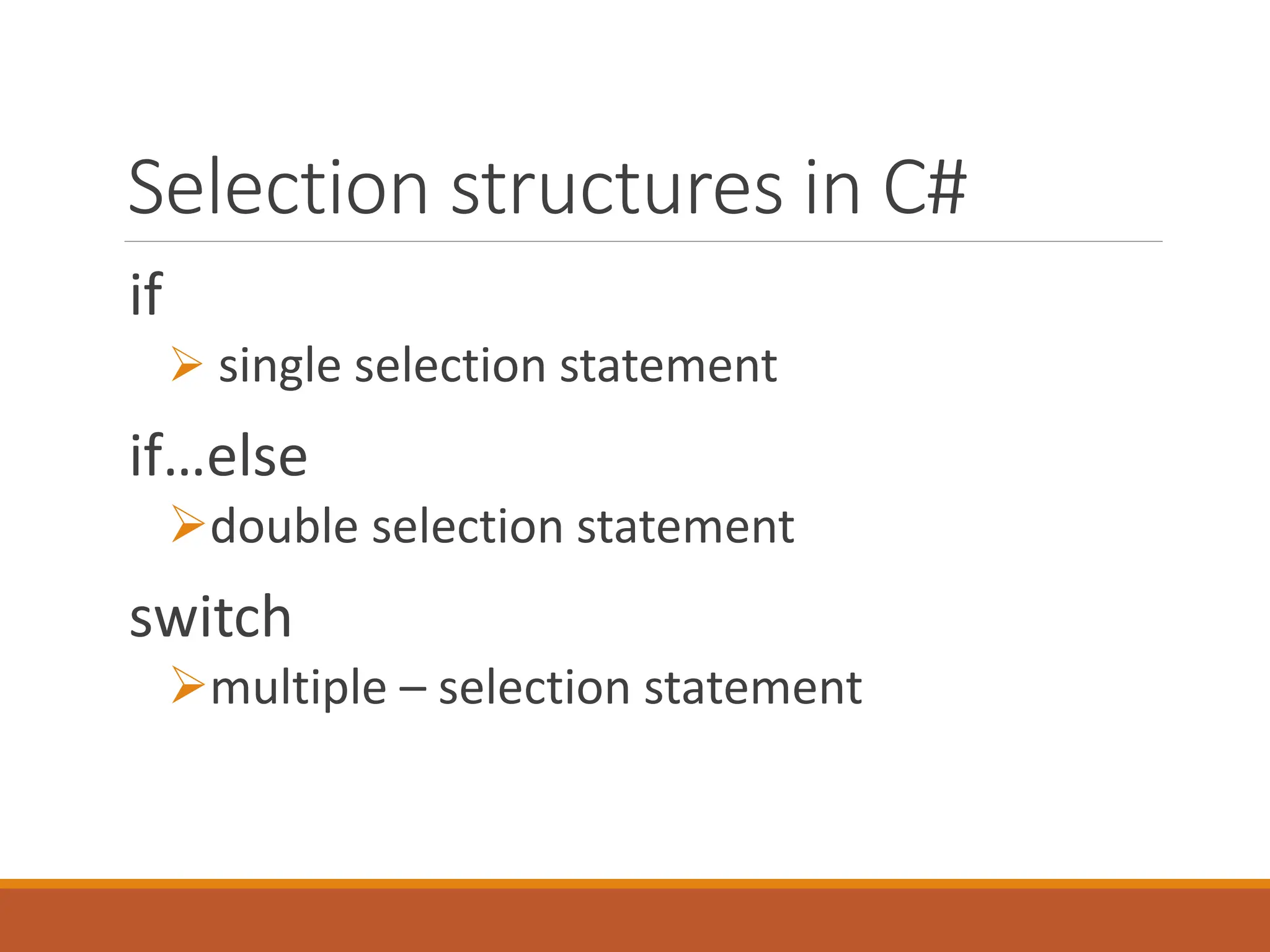
The document provides an overview of control statements in C#, including selection structures like if and switch, as well as repetition structures like while loops. It explains various programming techniques such as controlled entry and exit from modules, avoiding goto statements, and using nested ifs for conditional logic. Additionally, it covers type conversion, particularly in arithmetic operations, and offers examples for implementing these concepts in C#.









![Nested control statements
See example of a multiplication table generation
class MultiplicationTable{
static void Main(string[] args){
int i=2, j, k;
while (i <= 12){
for (j = 1; j <= 10; j++){
Console.WriteLine(i + " x " + j + " = " + i * j );
}
Console.WriteLine("n");
i++;
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccontrolstatements-240419035014-caedf438/75/C-Control-Statements-For-loop-Do-While-ppt-11-2048.jpg)
