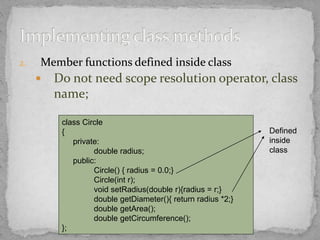
The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts like classes, objects, encapsulation, and inheritance. Some key points:
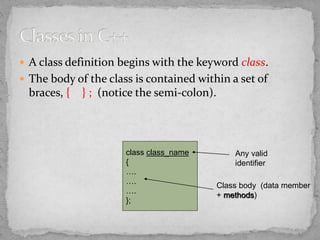
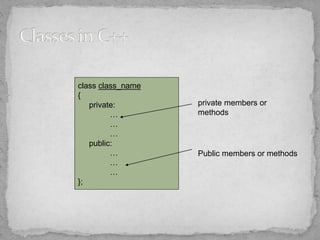
- Classes group together data (attributes) and functions (behaviors) into user-defined types. They encapsulate these within public and private sections.
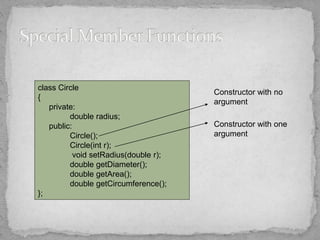
- Objects are instances of classes that reserve memory at runtime. Constructors initialize objects, while destructors handle memory cleanup.
- Member functions defined within classes can access private members directly, while outside functions require the class scope resolution operator.
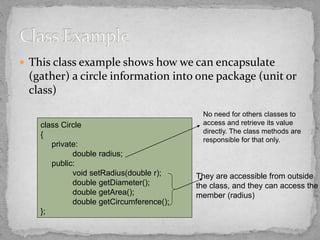
- Classes provide templates for creating multiple similar objects, hiding implementation details behind public interfaces. This is a more modular approach than procedural programming.