Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times






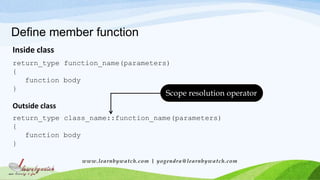


This document discusses the basics of creating a C++ class, including defining the class with public and private members, creating objects of the class type, and accessing class members both inside and outside the class. It explains that a class creates a user-defined data type and describes the general form of a C++ class with sections for private and public data and functions. It also covers defining member functions inside and outside the class and using the dot operator and scope resolution operator to access class members and functions.







