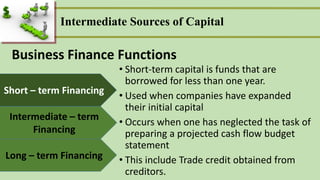
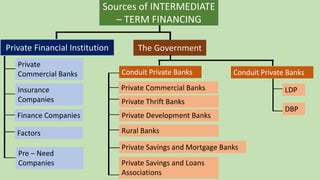
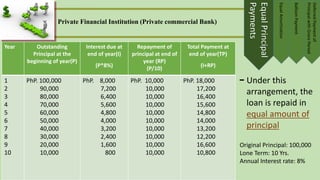
The document discusses different types and sources of intermediate-term financing or capital. It defines intermediate-term financing as borrowings with a repayment schedule of more than one year but less than ten years. Some key points made in the document include:
- Intermediate-term financing is used for small business expansions and typically comes from commercial banks and insurance companies. Common uses include machinery purchases and facility upgrades.
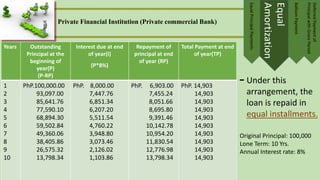
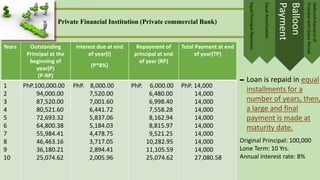
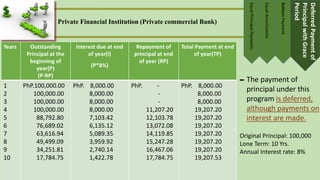
- Repayment is usually done through installment plans over 1-5 years. Options include equal principal payments, equal amortization, balloon payments, and deferred principal payments.
- Sources mentioned are private financial institutions like commercial banks, insurance companies, and finance companies, as well as government-backed banks