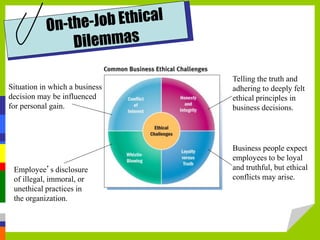
Business ethics refer to standards of conduct governing how businesses and employees should behave. This involves balancing profitability with moral responsibilities to customers, employees, shareholders, and society. Unethical practices can harm stakeholders and damage a company's reputation. Common issues include conflicts of interest, dishonesty, privacy violations, and environmental/social impacts. Developing strong ethics codes, training, and leadership can help guide ethical decision-making and mitigate risks to businesses.