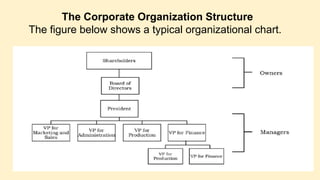
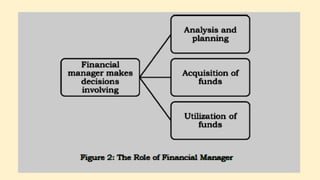
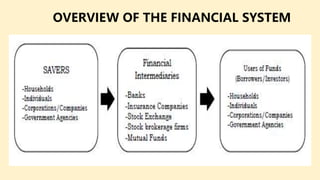
The document defines finance and describes who is responsible for financial management within an organization. It states that financial management deals with decisions that are meant to maximize shareholder wealth. Financial managers make planning, acquisition, and utilization of funds decisions that involve risk-return tradeoffs and can impact share prices. The roles of the finance manager include investing, financing, operating, and dividend decisions.