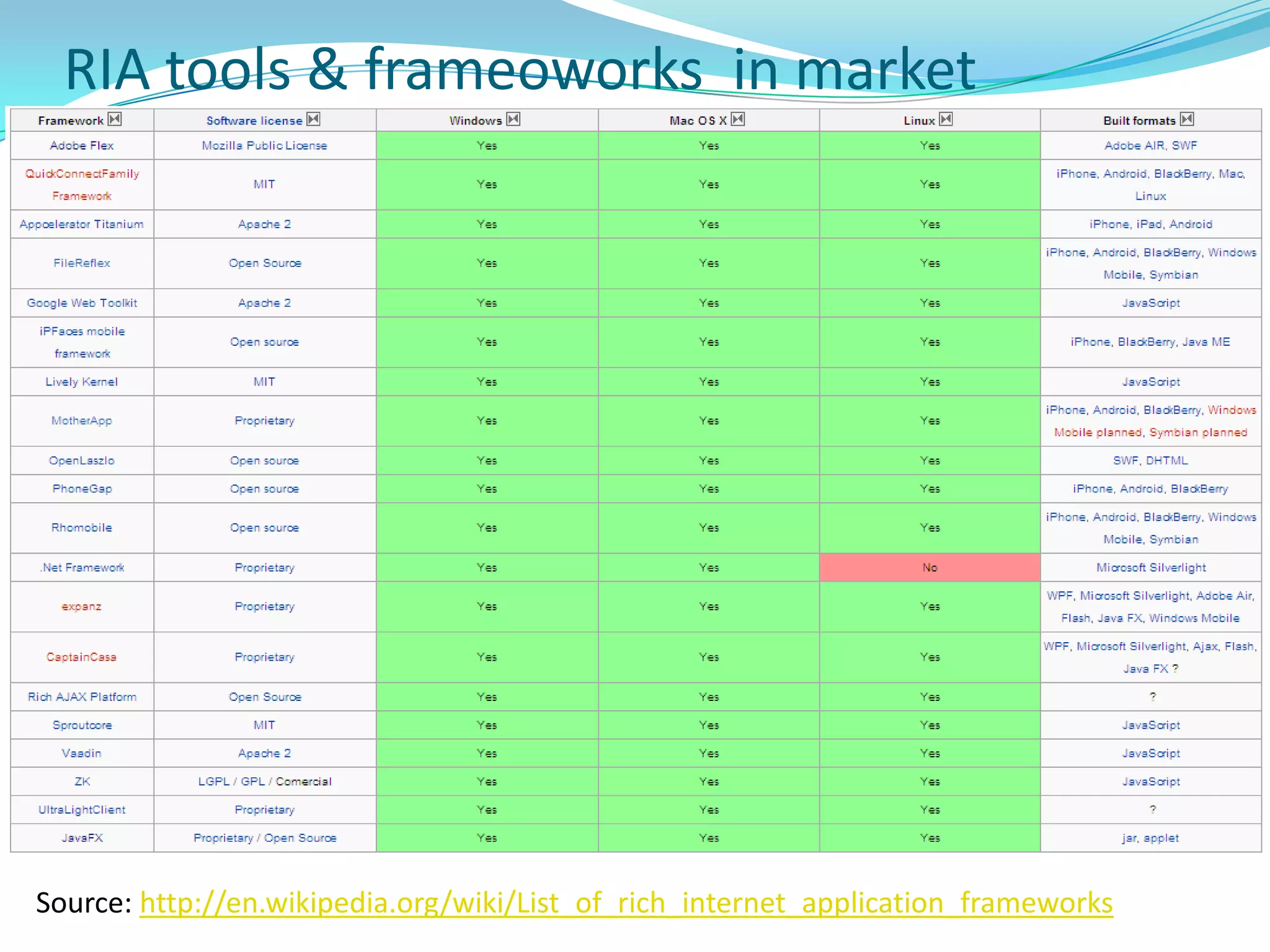
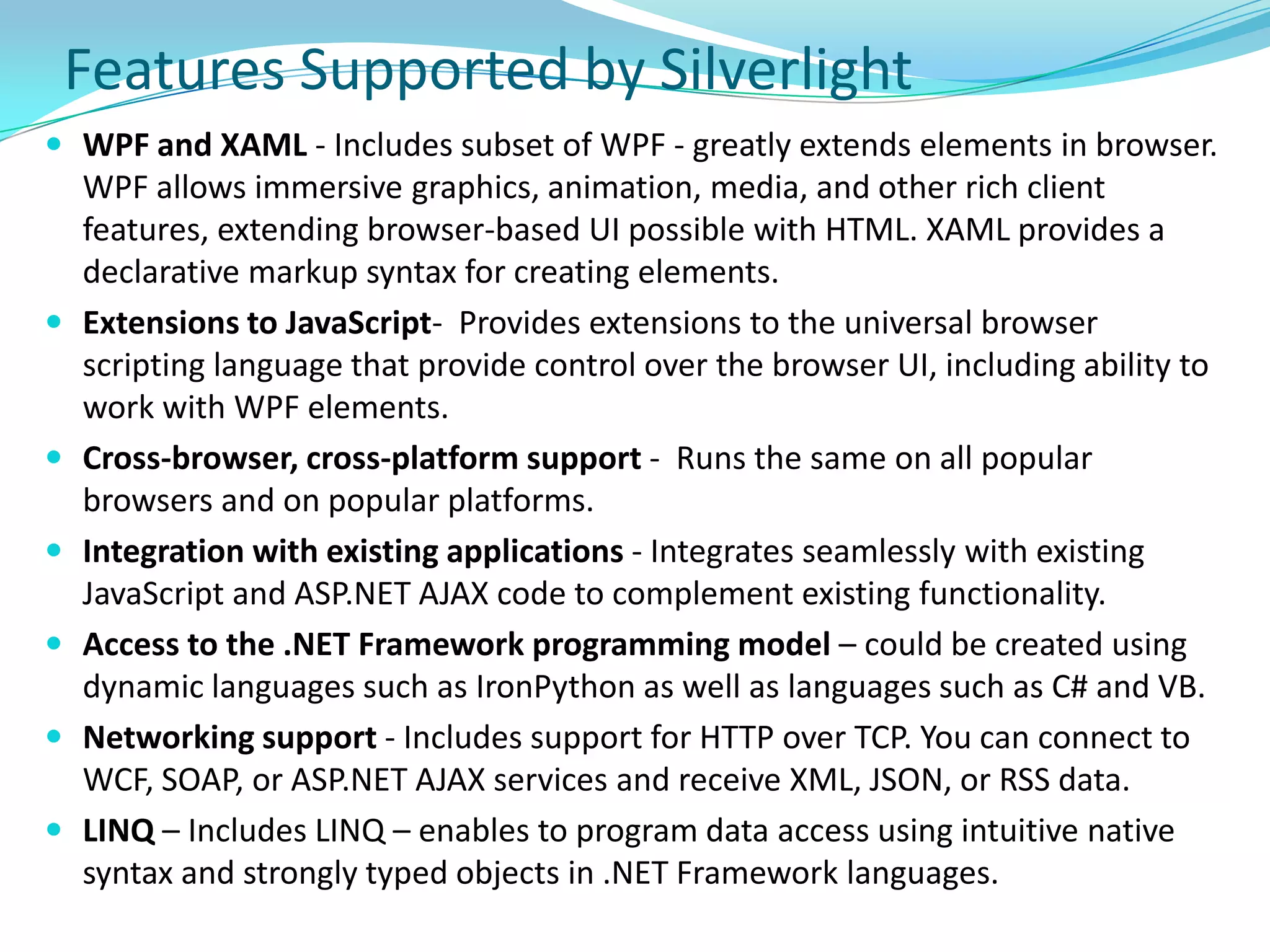
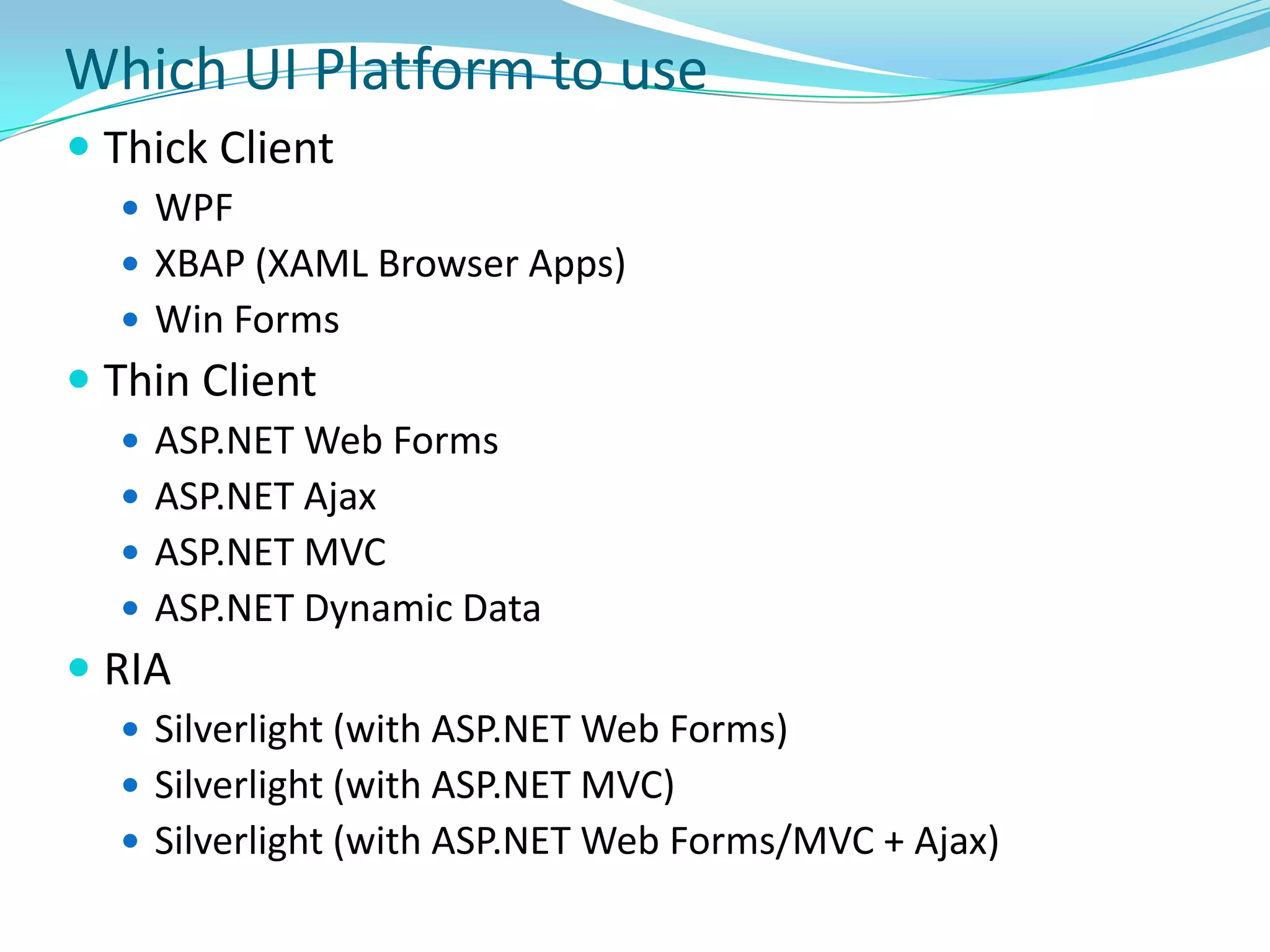
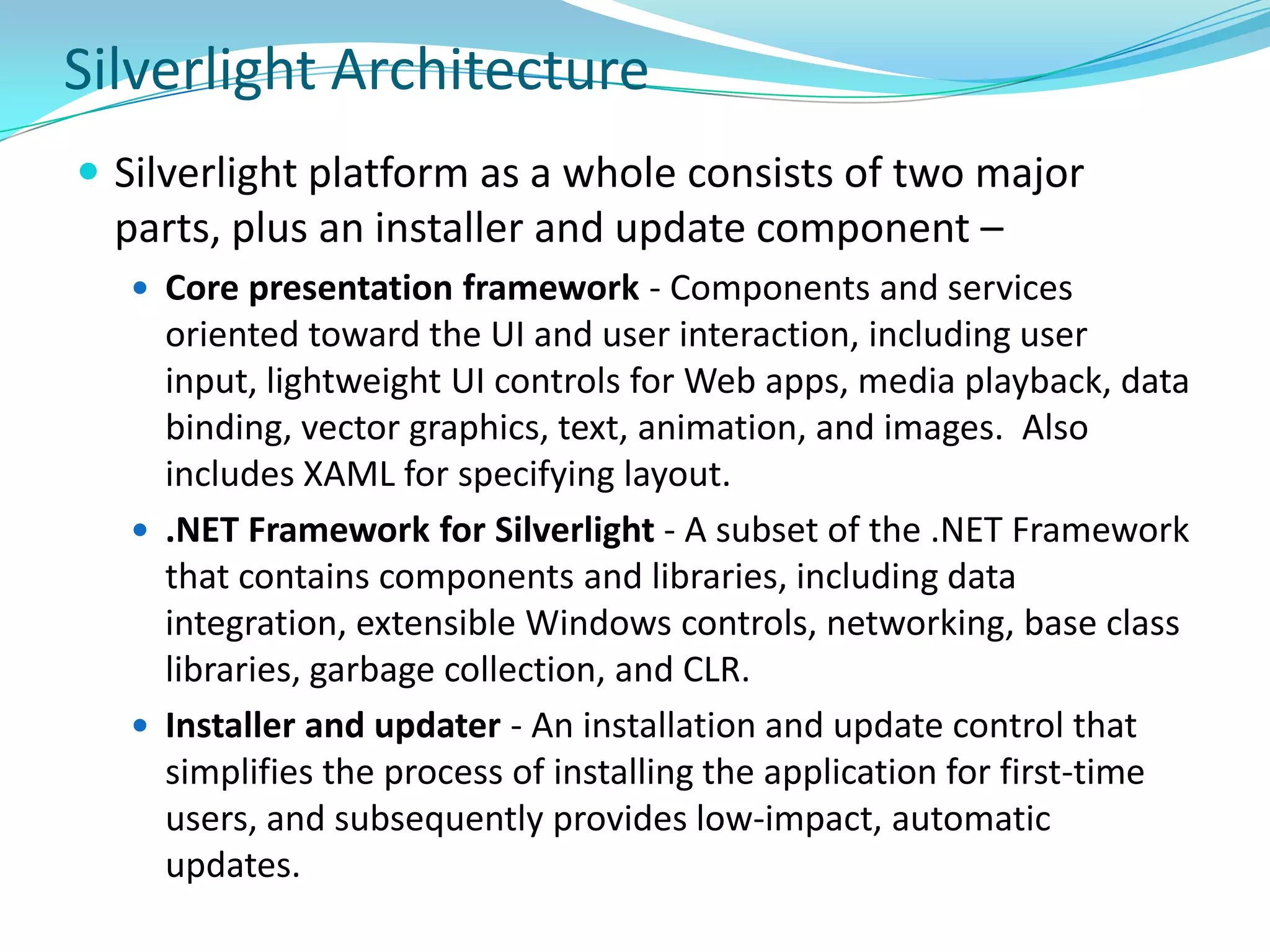
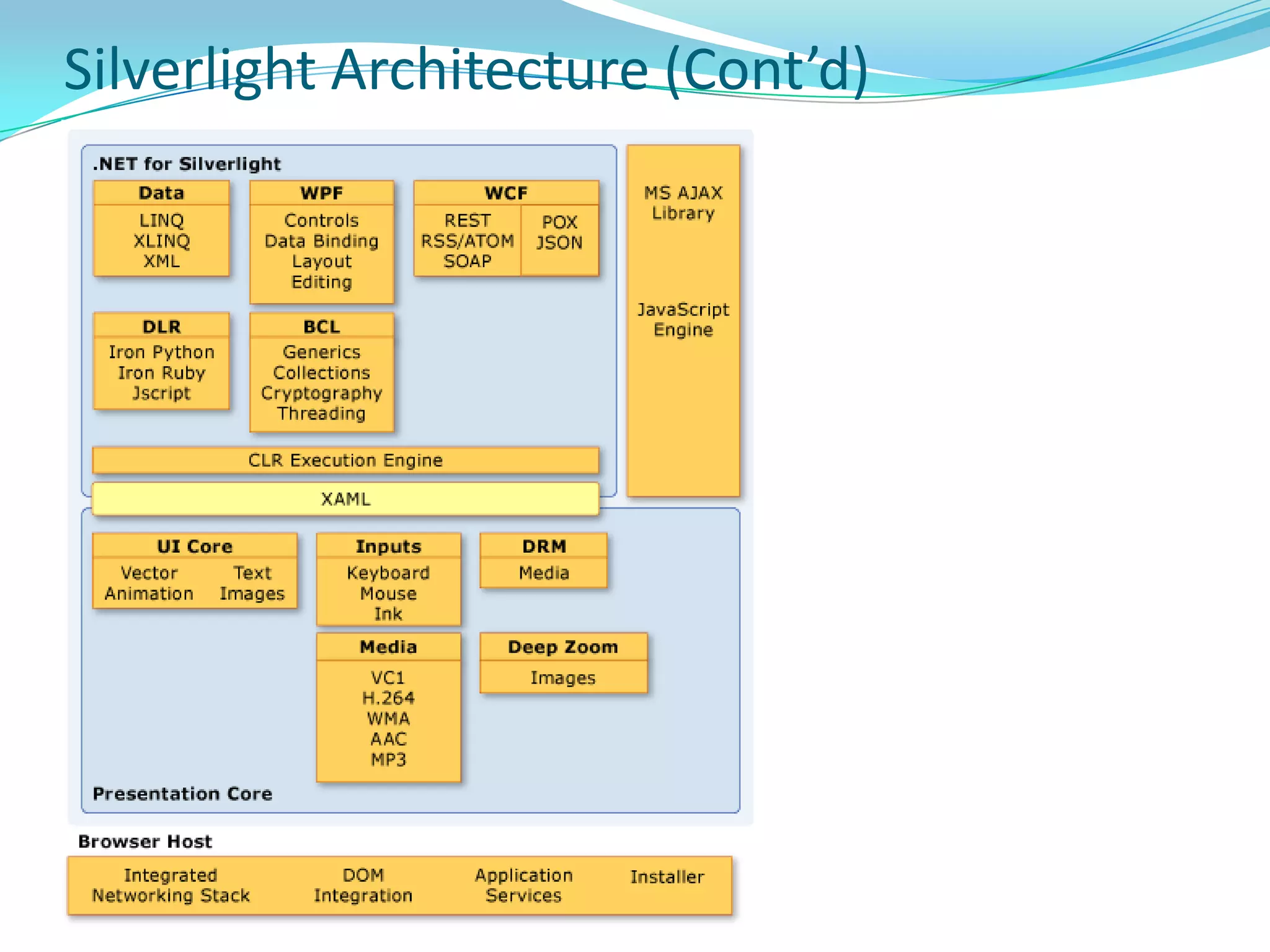
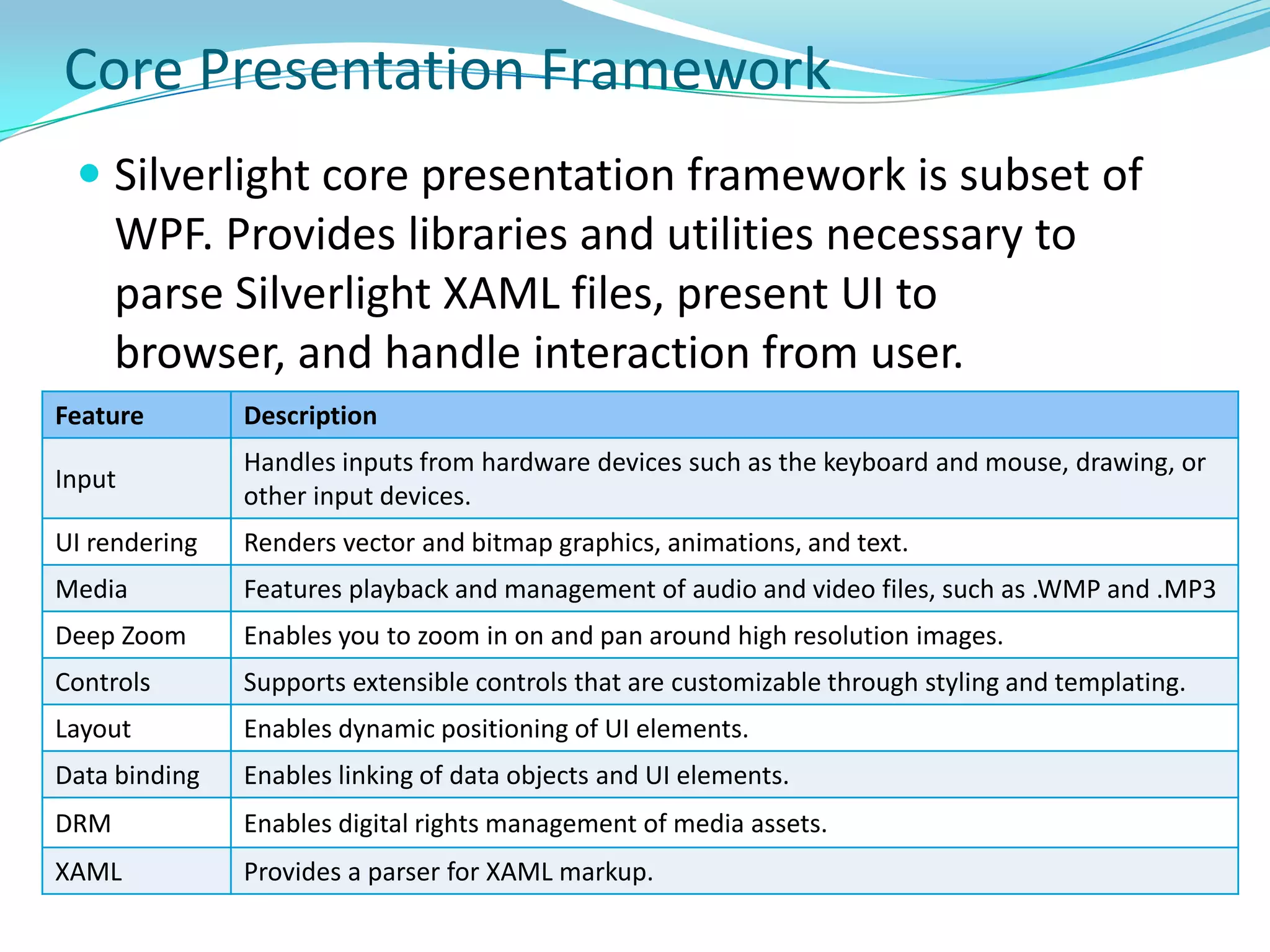
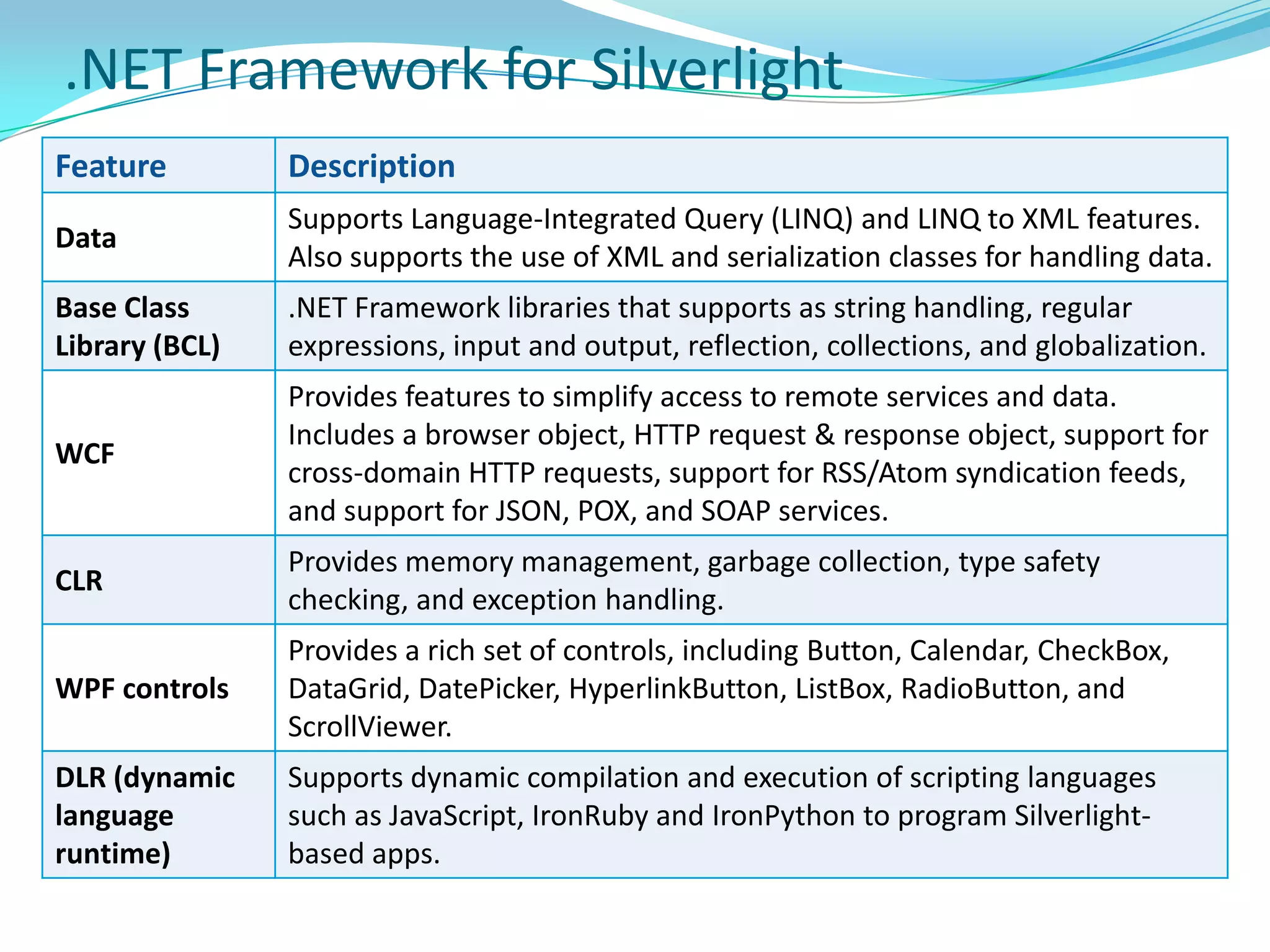
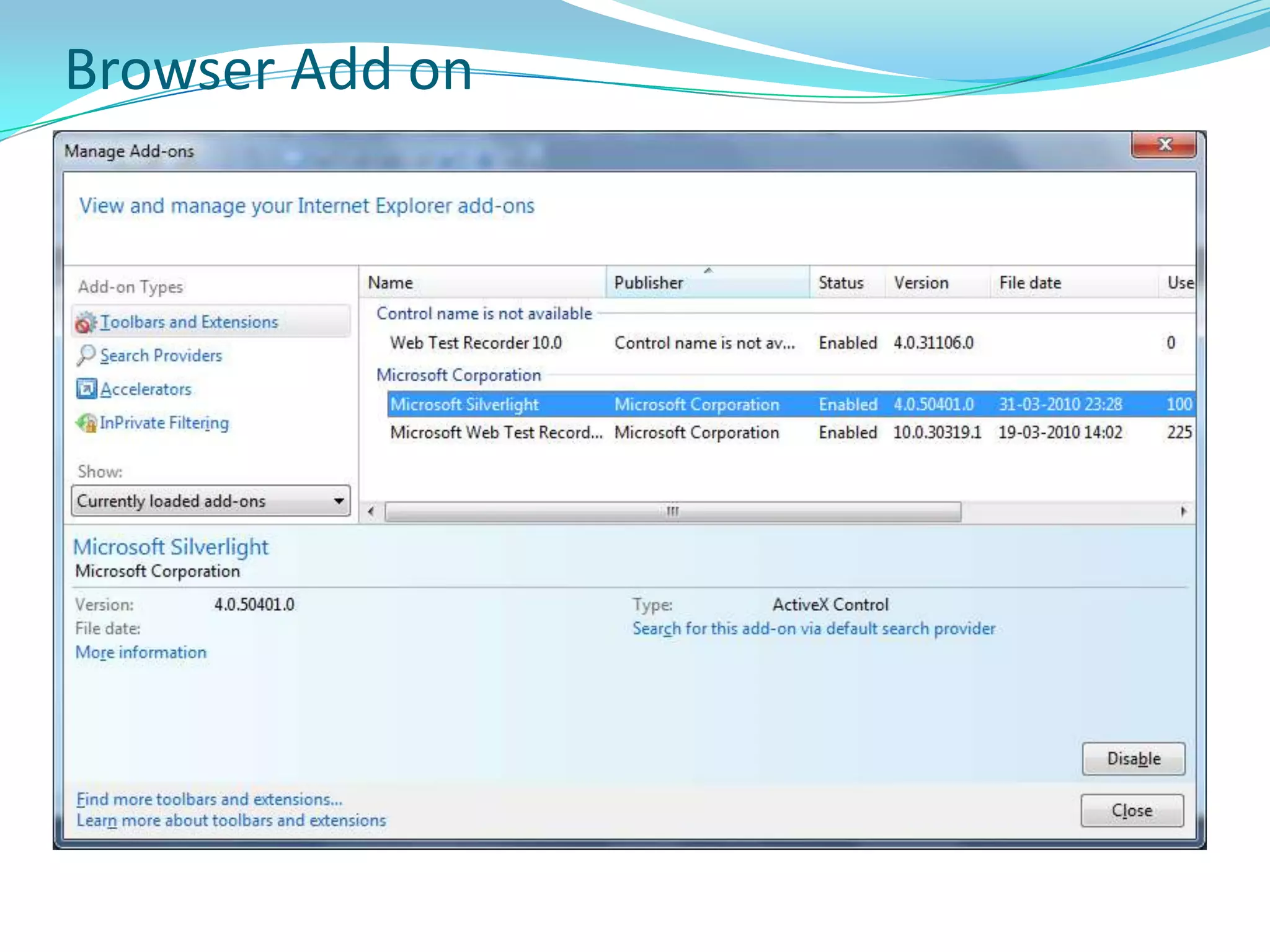
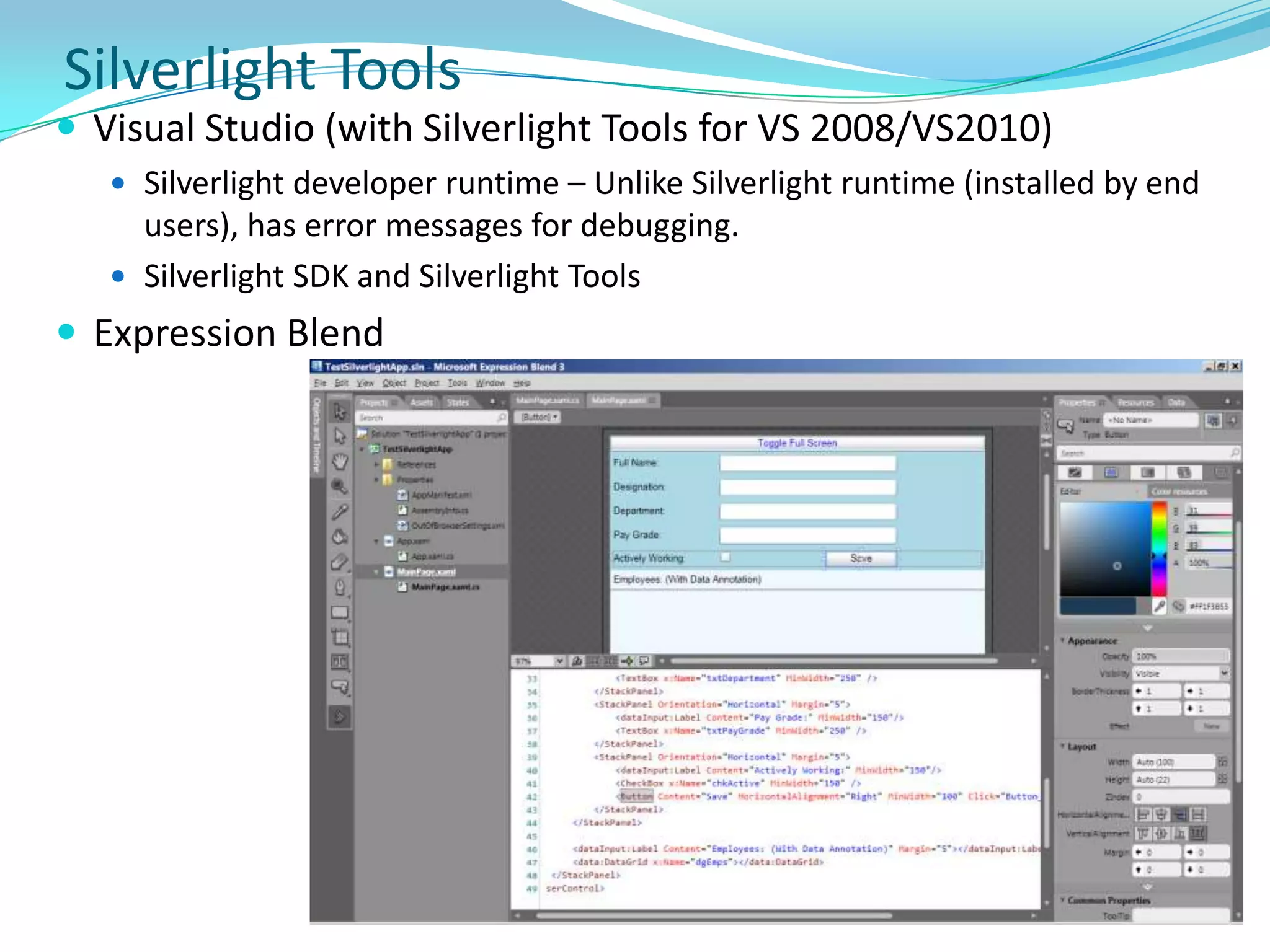
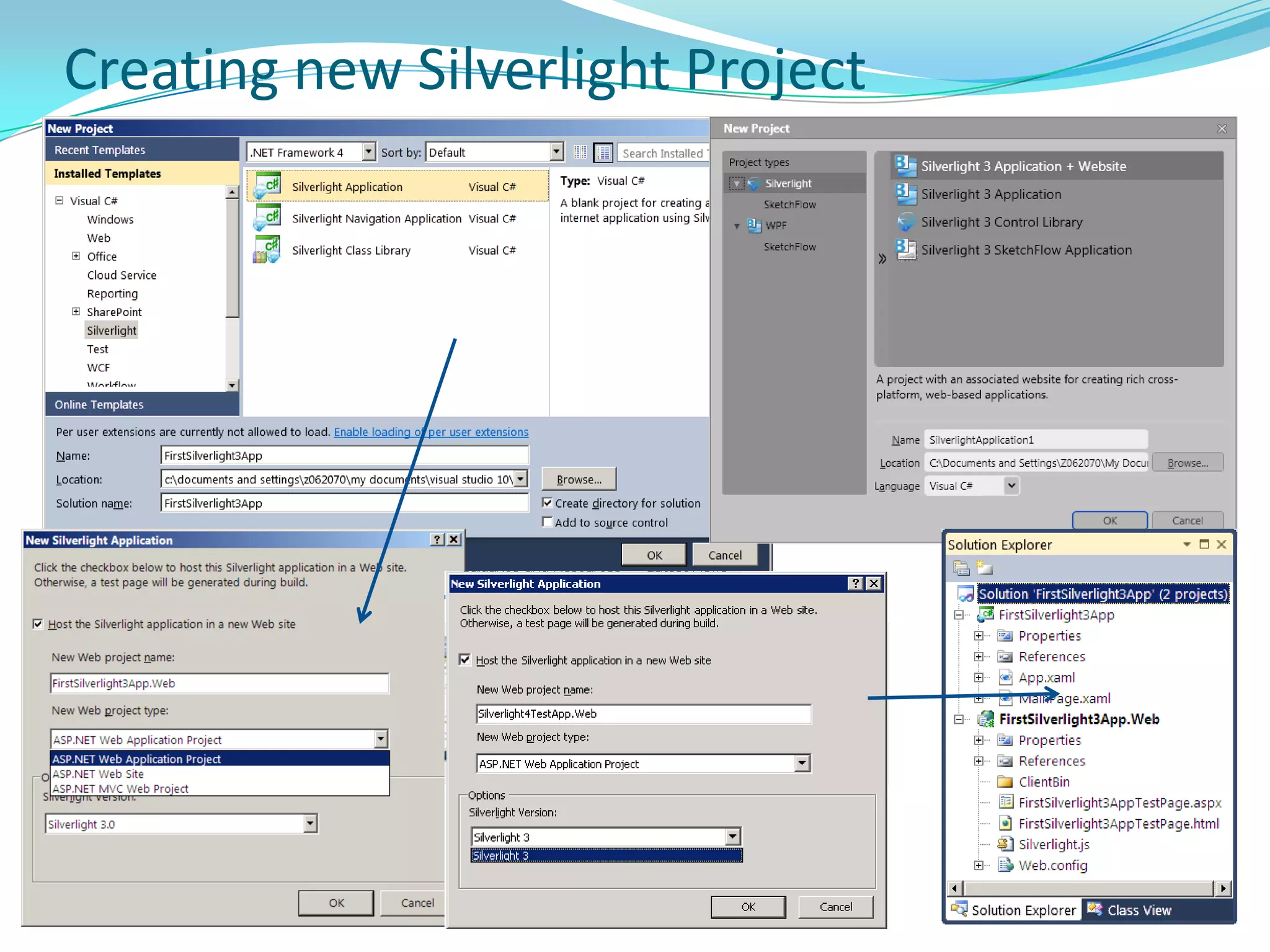
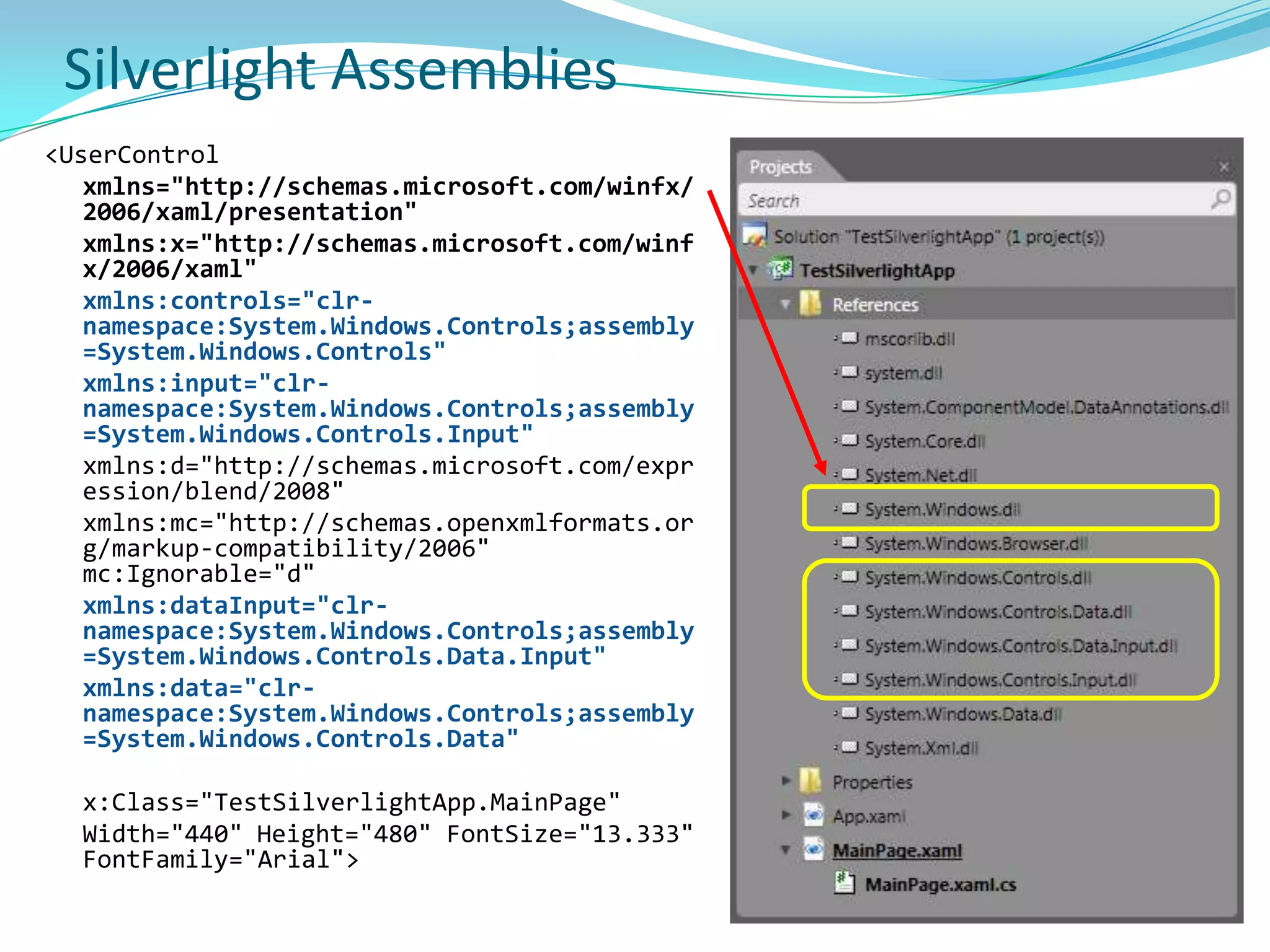
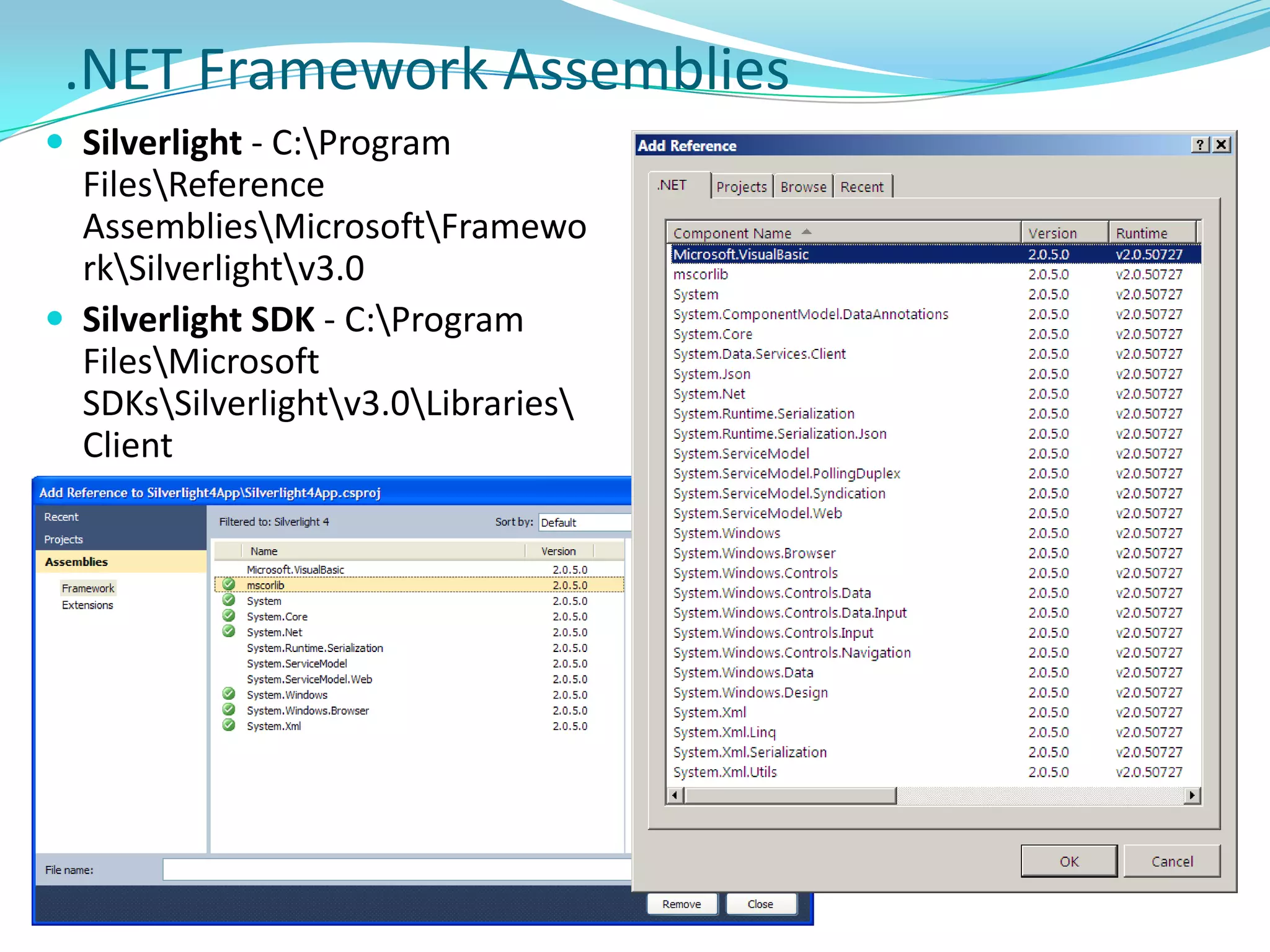
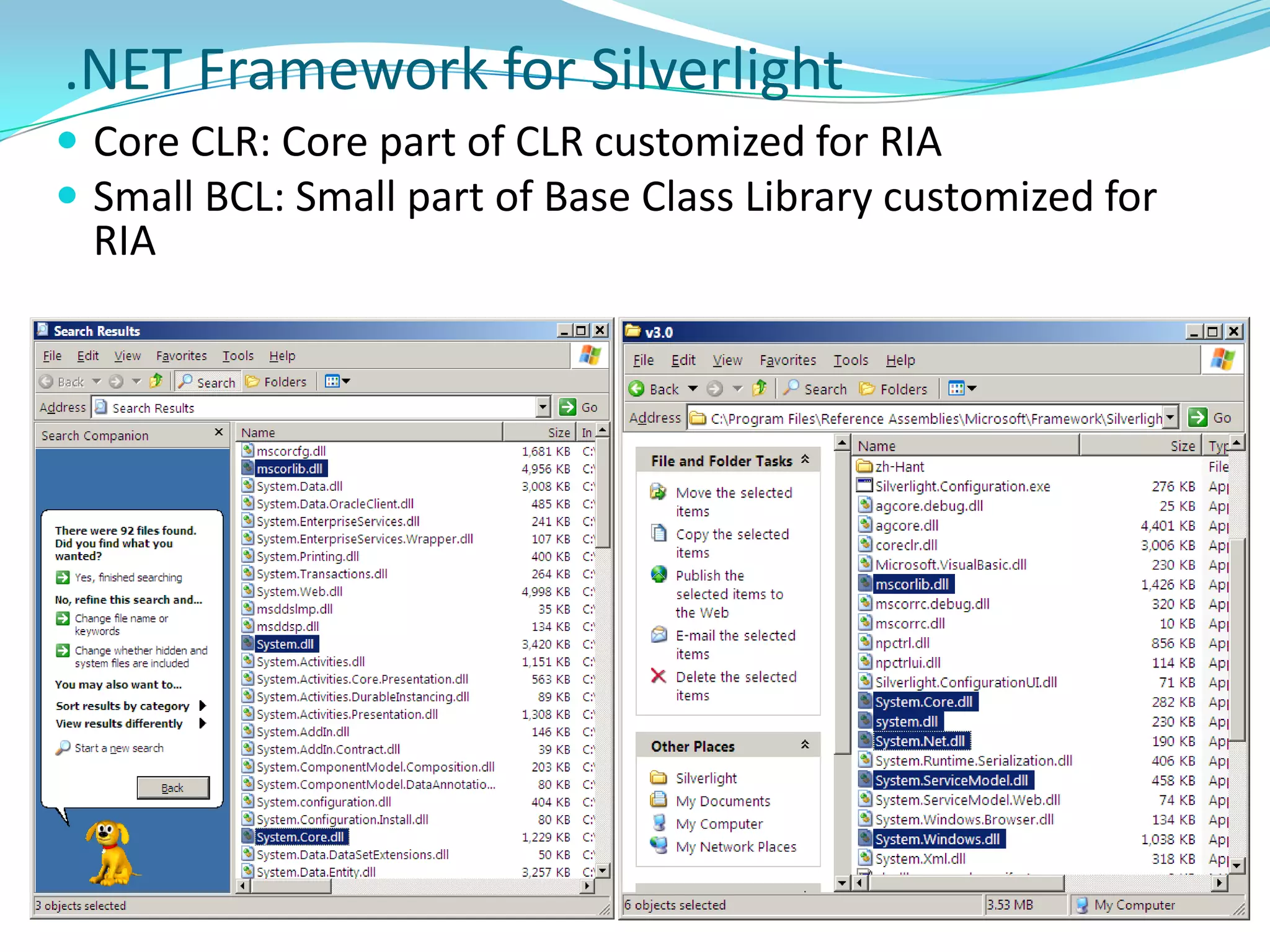
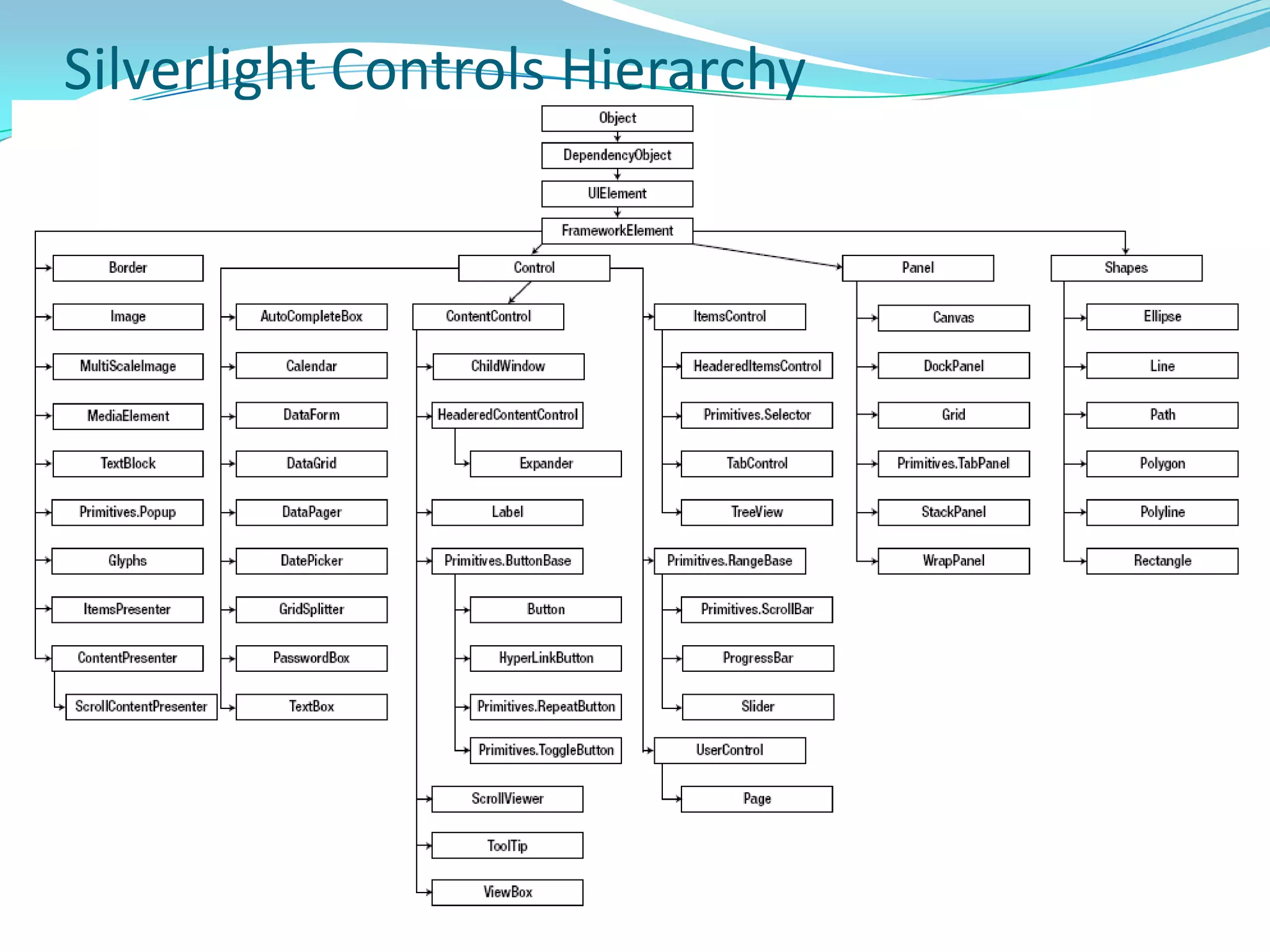
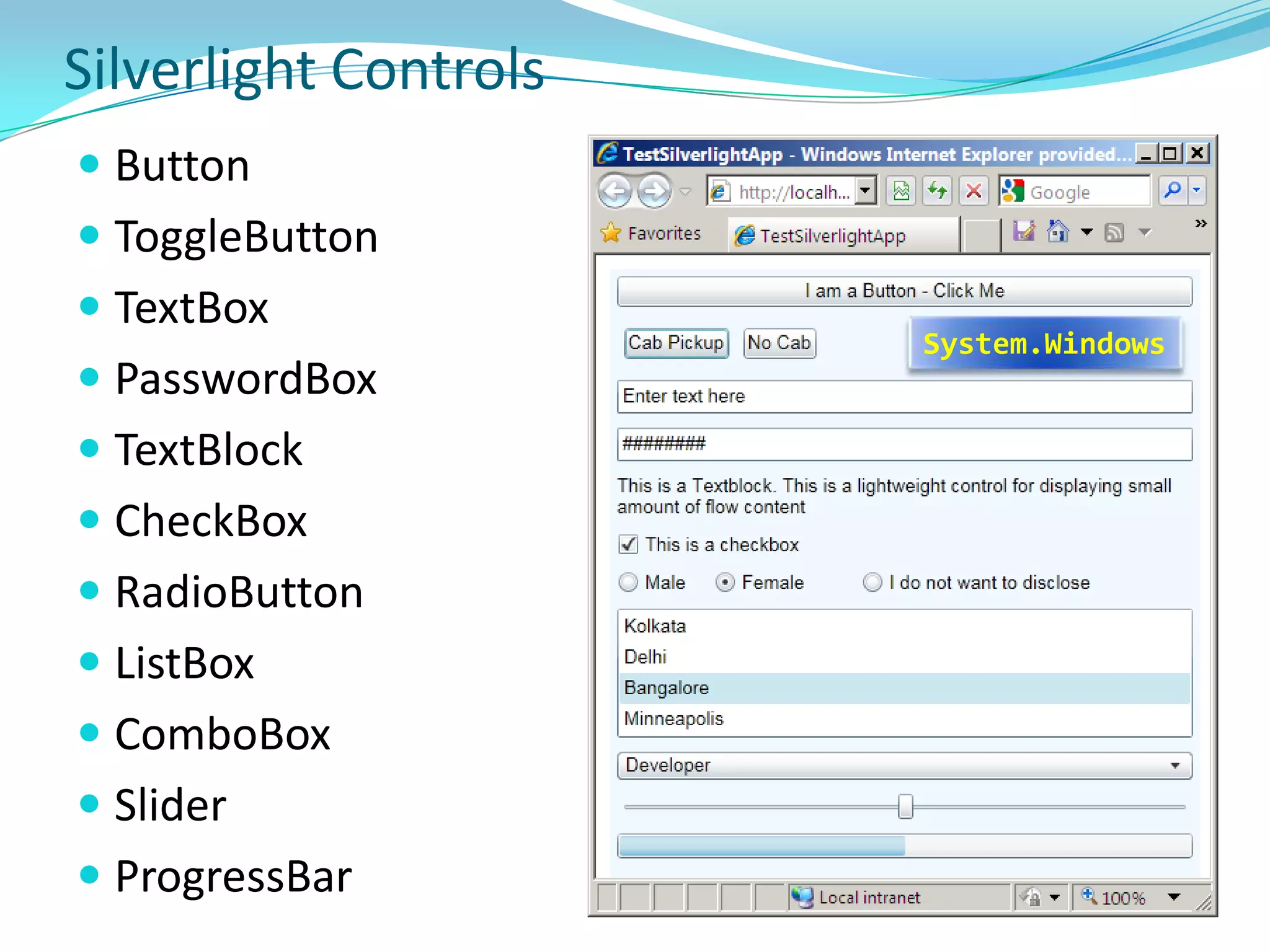
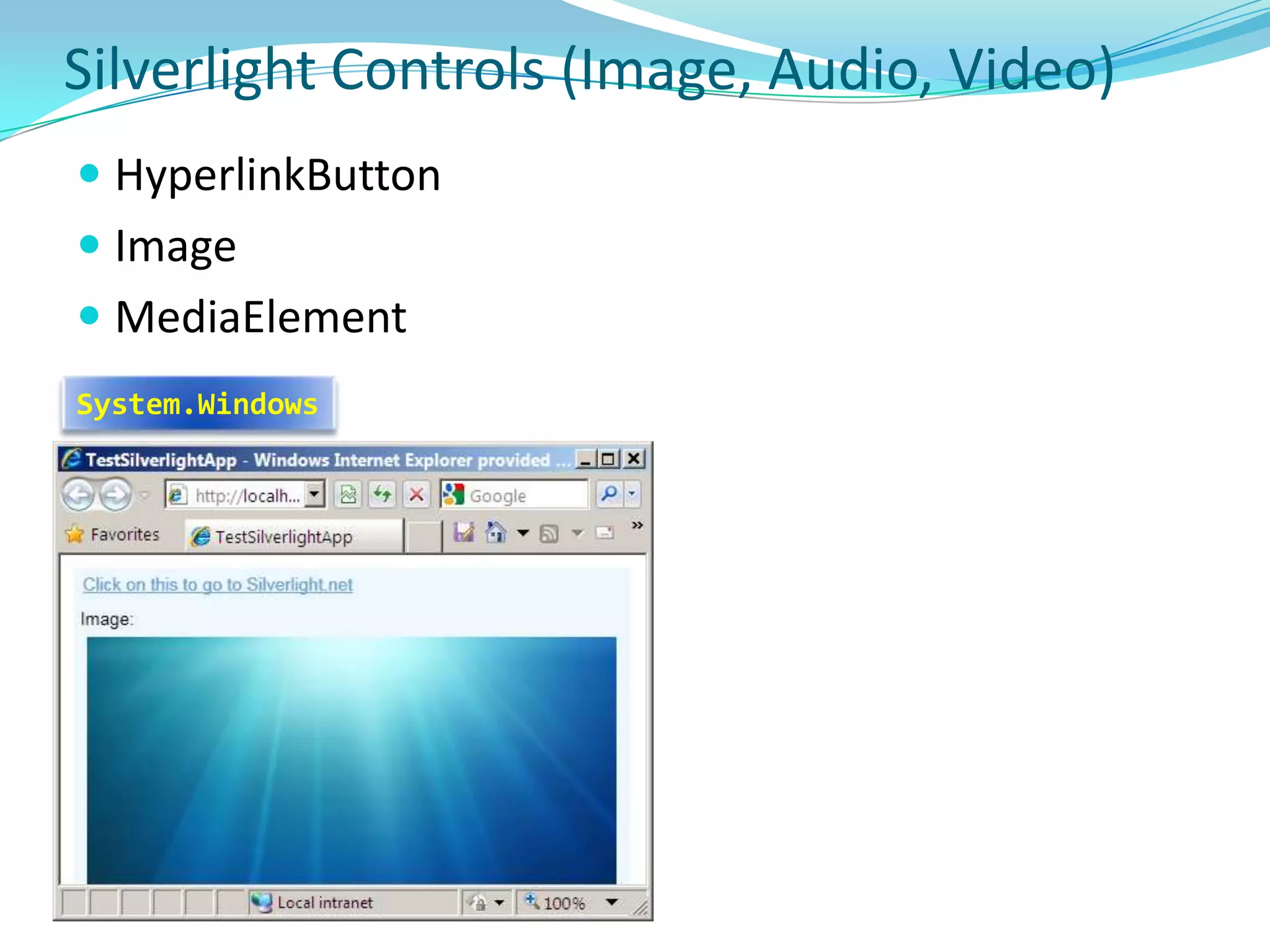
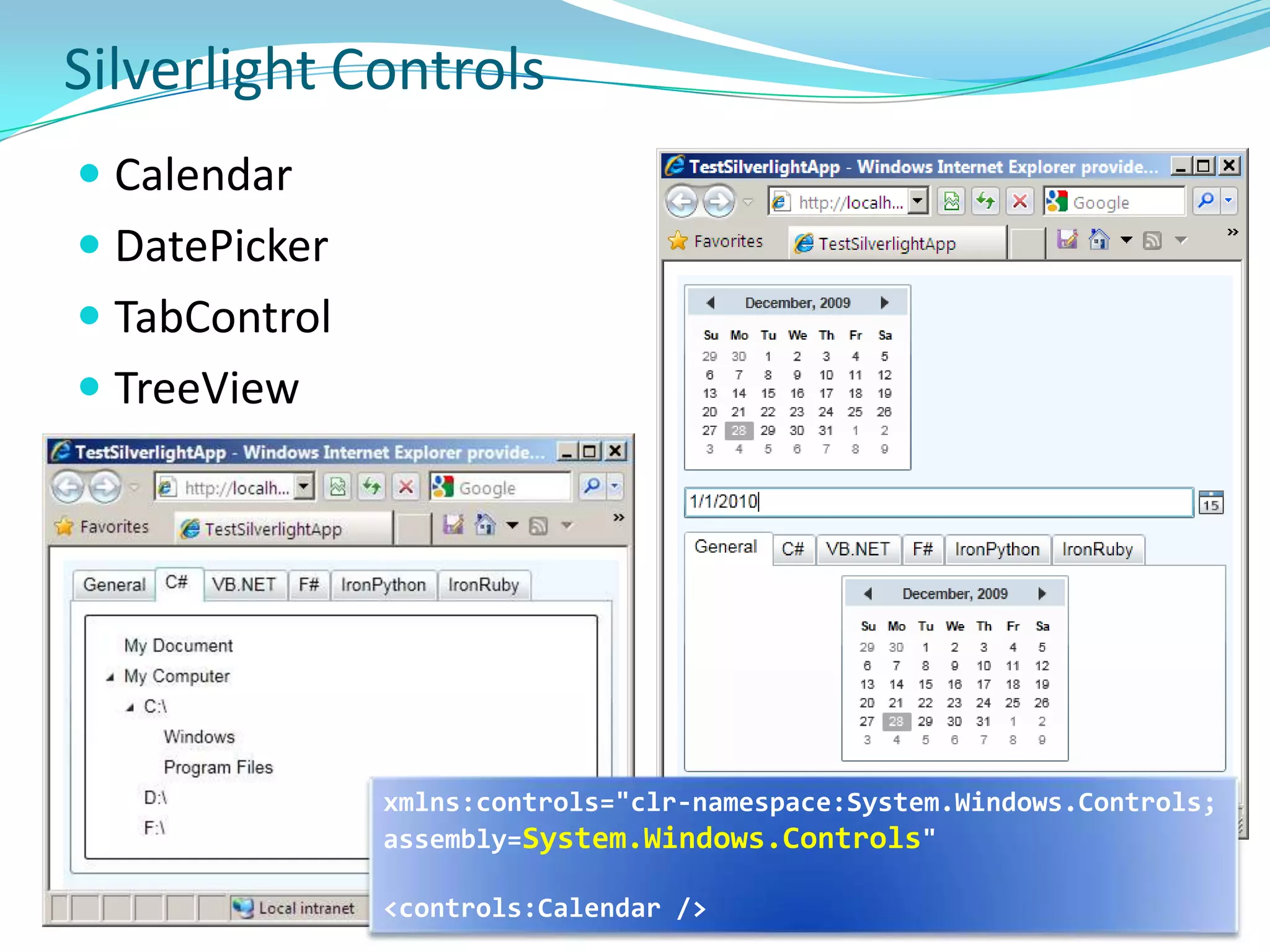
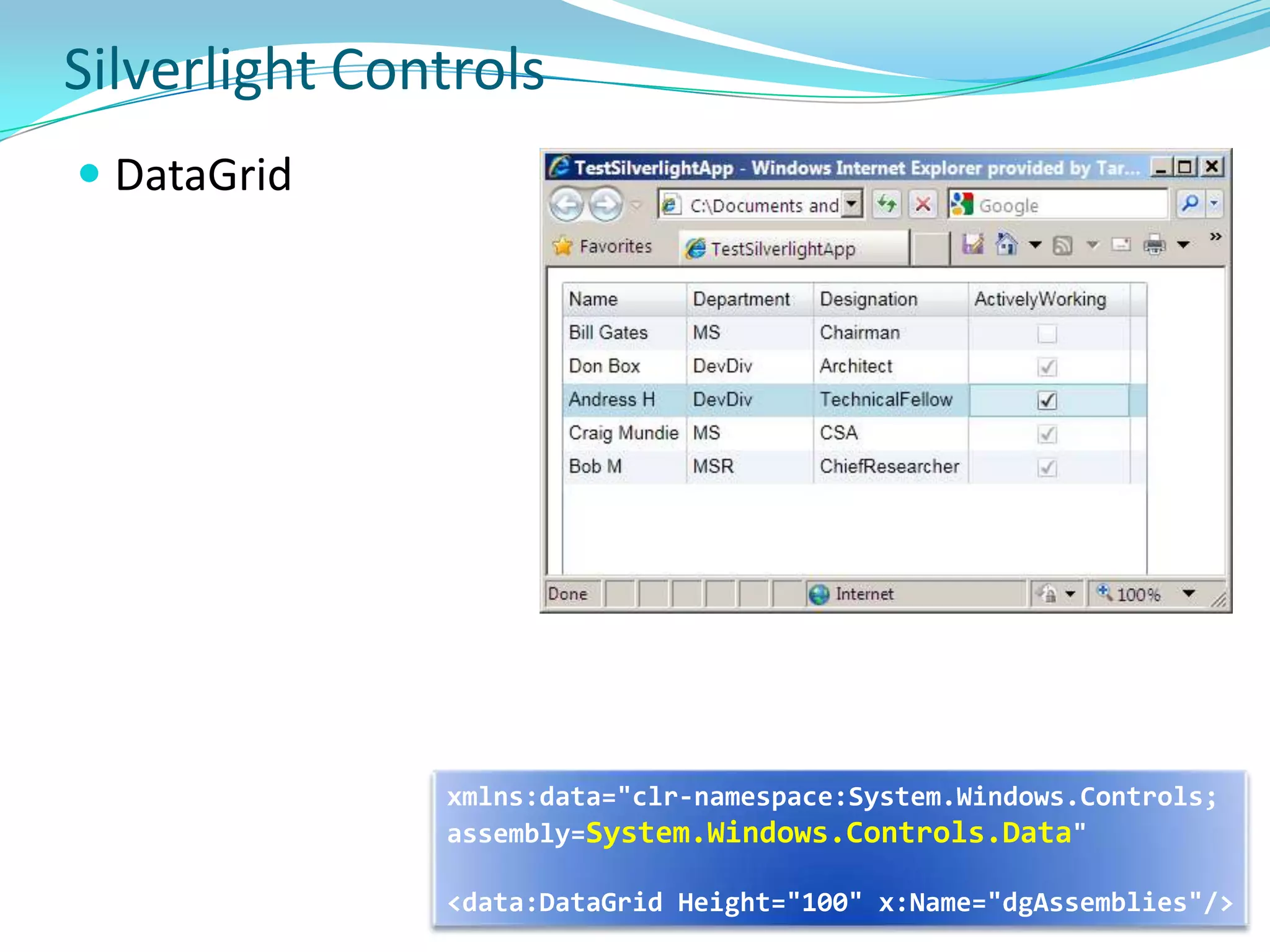
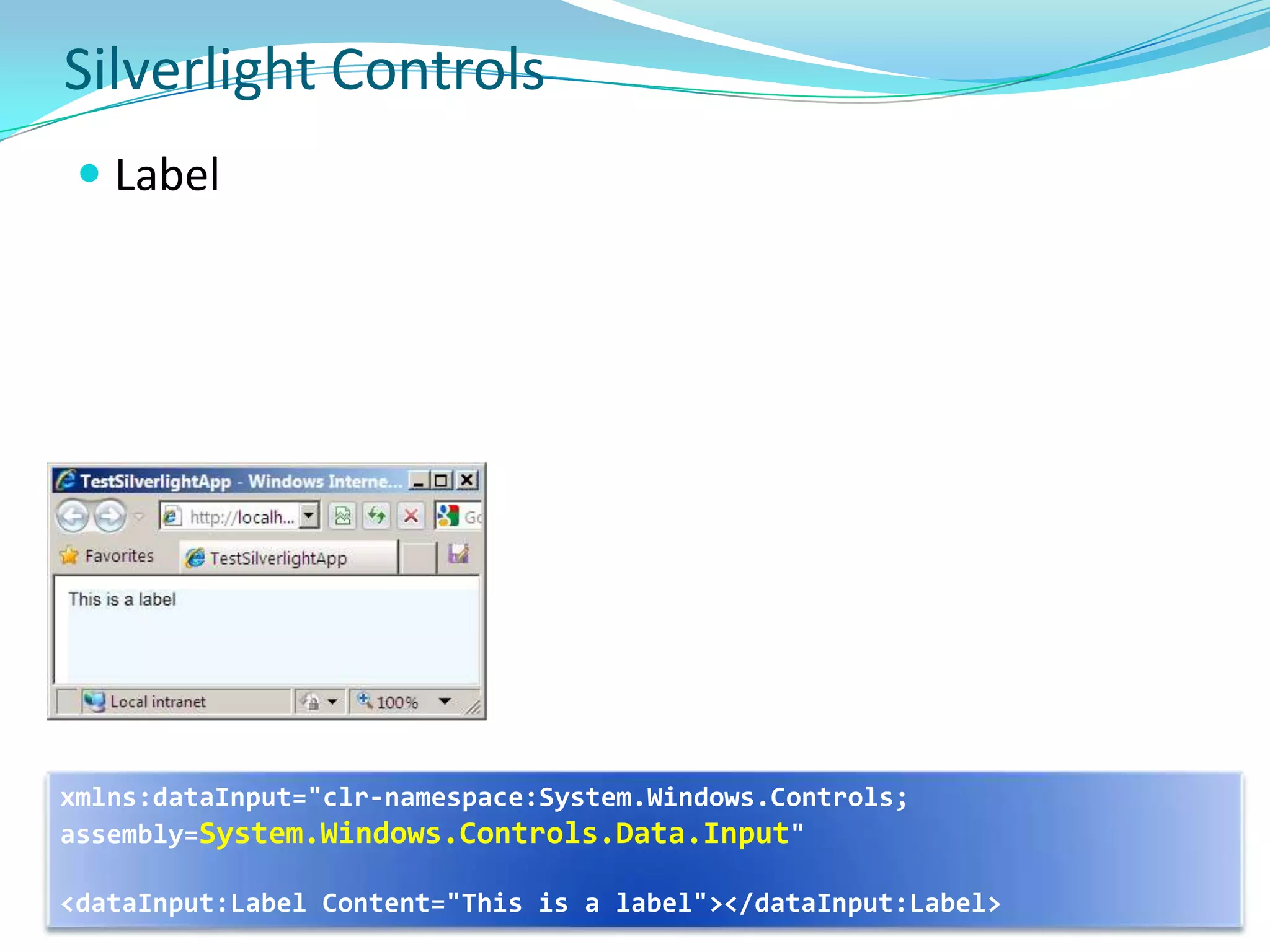
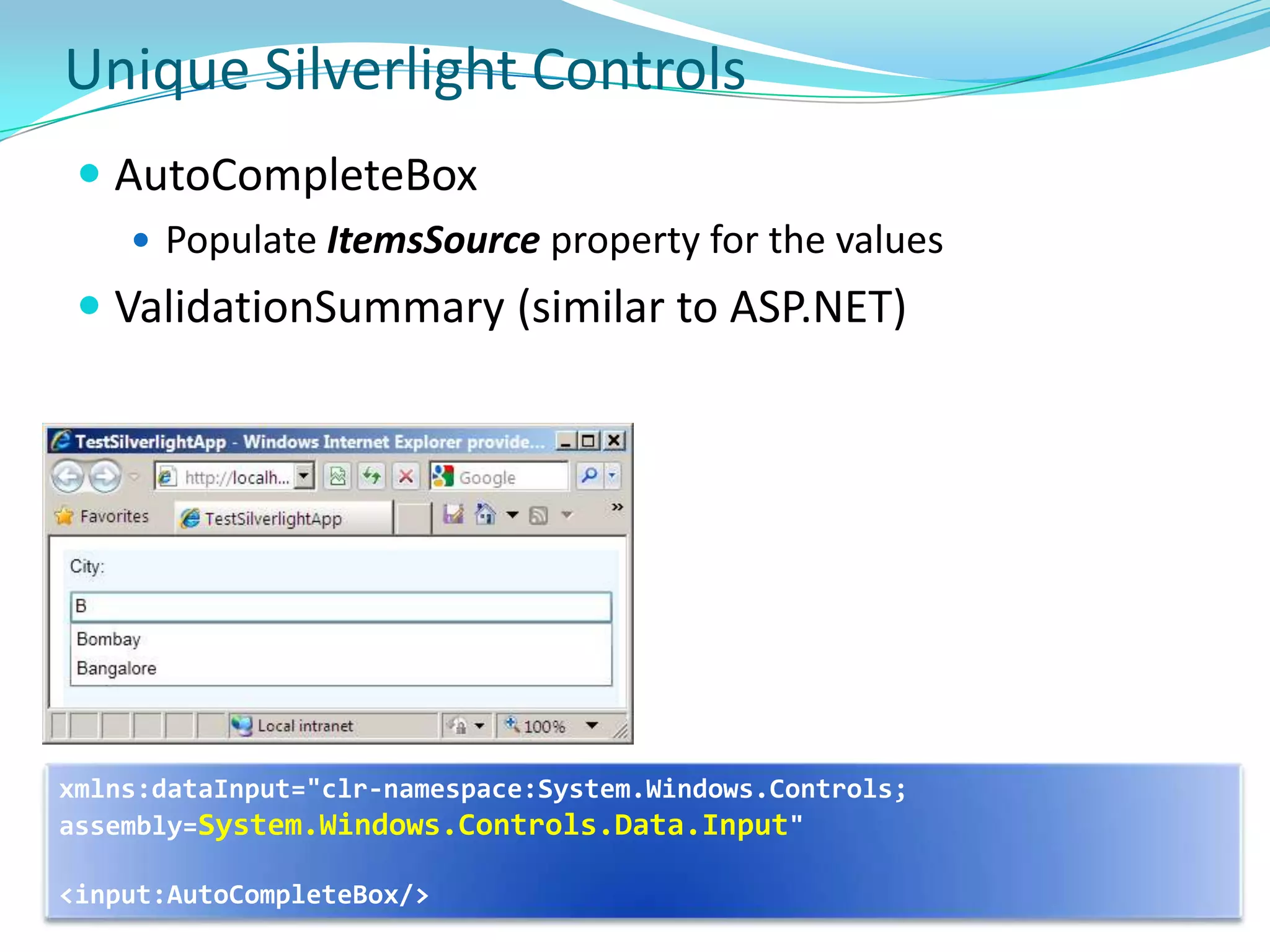
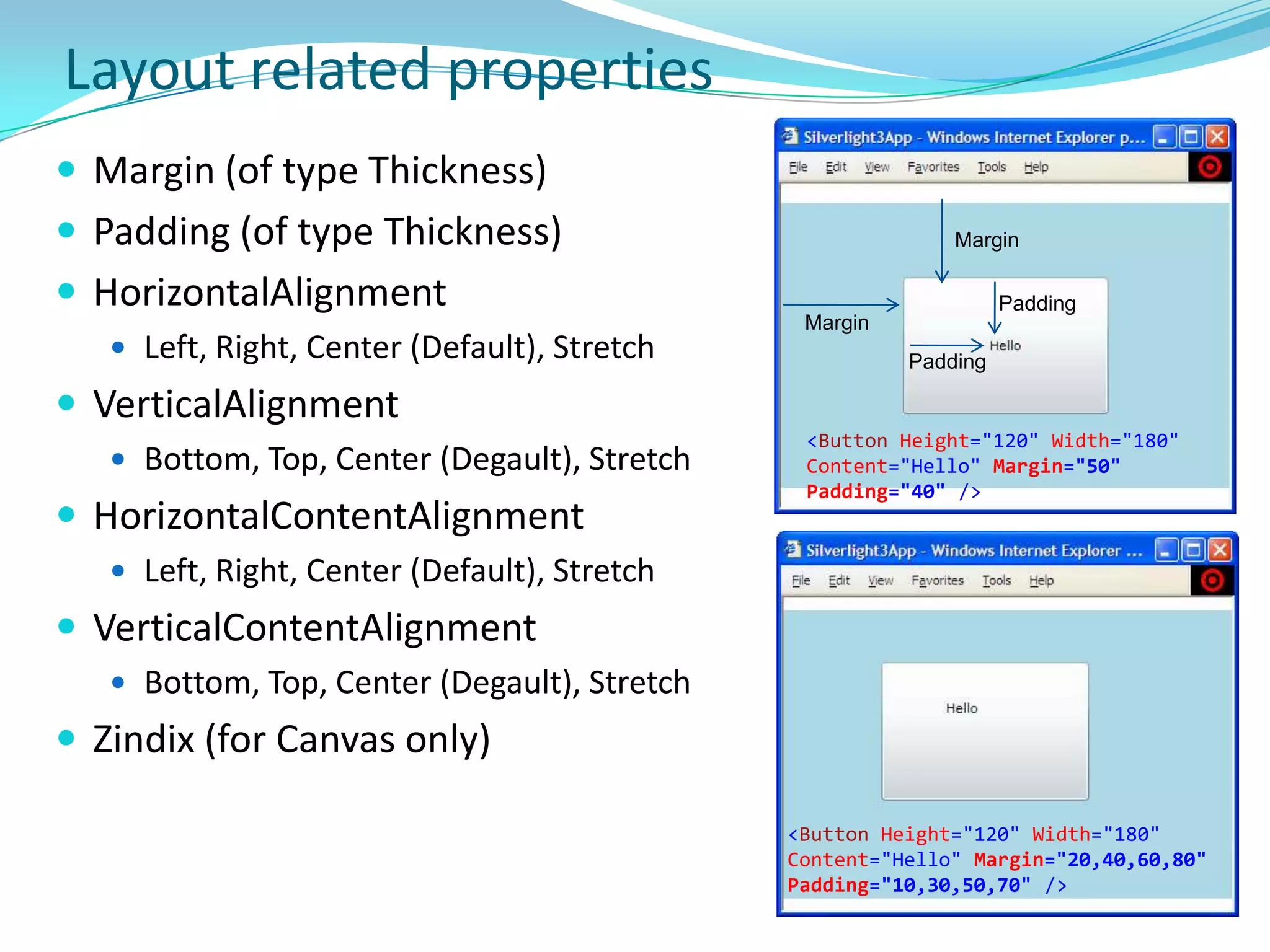
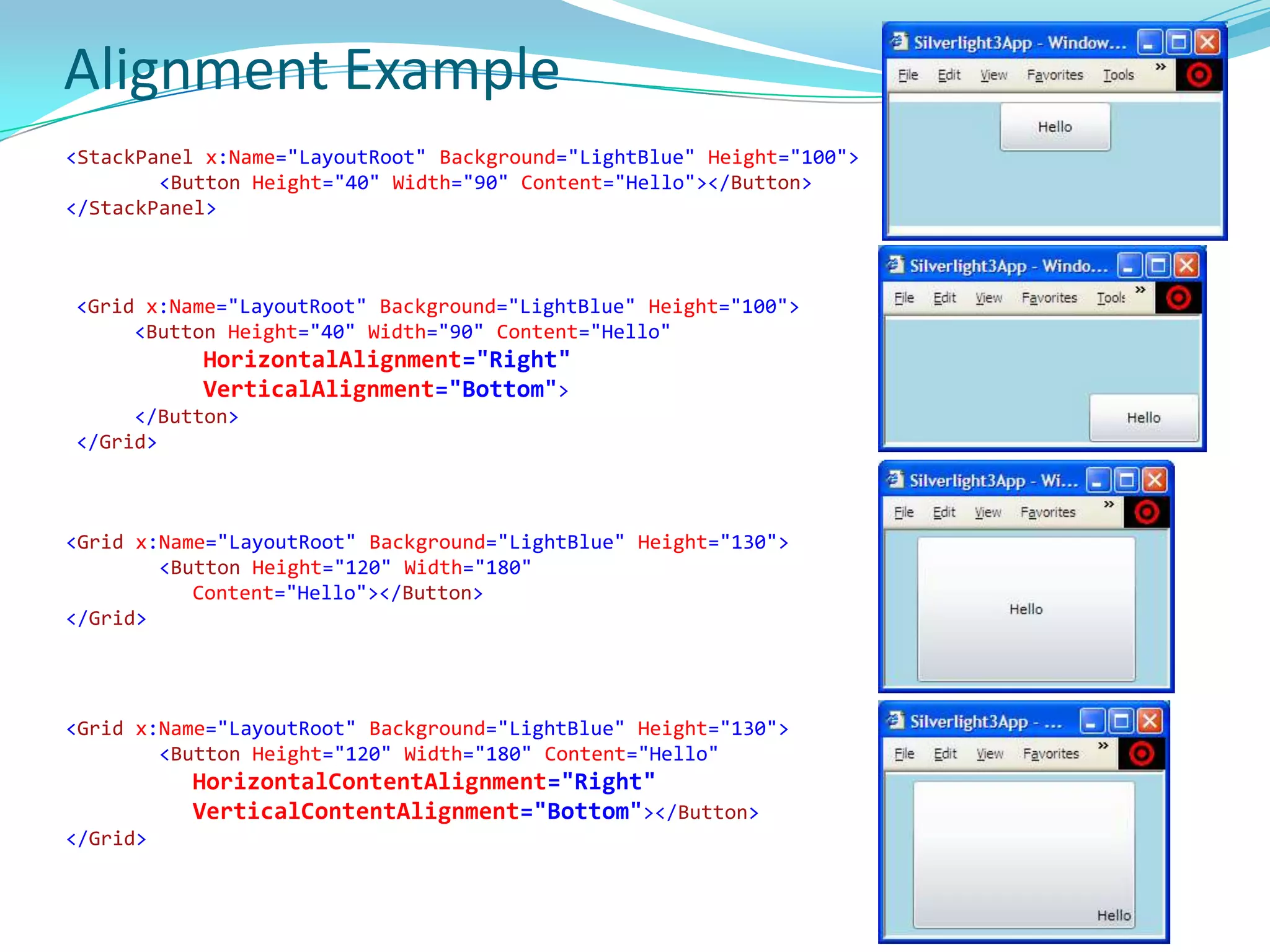
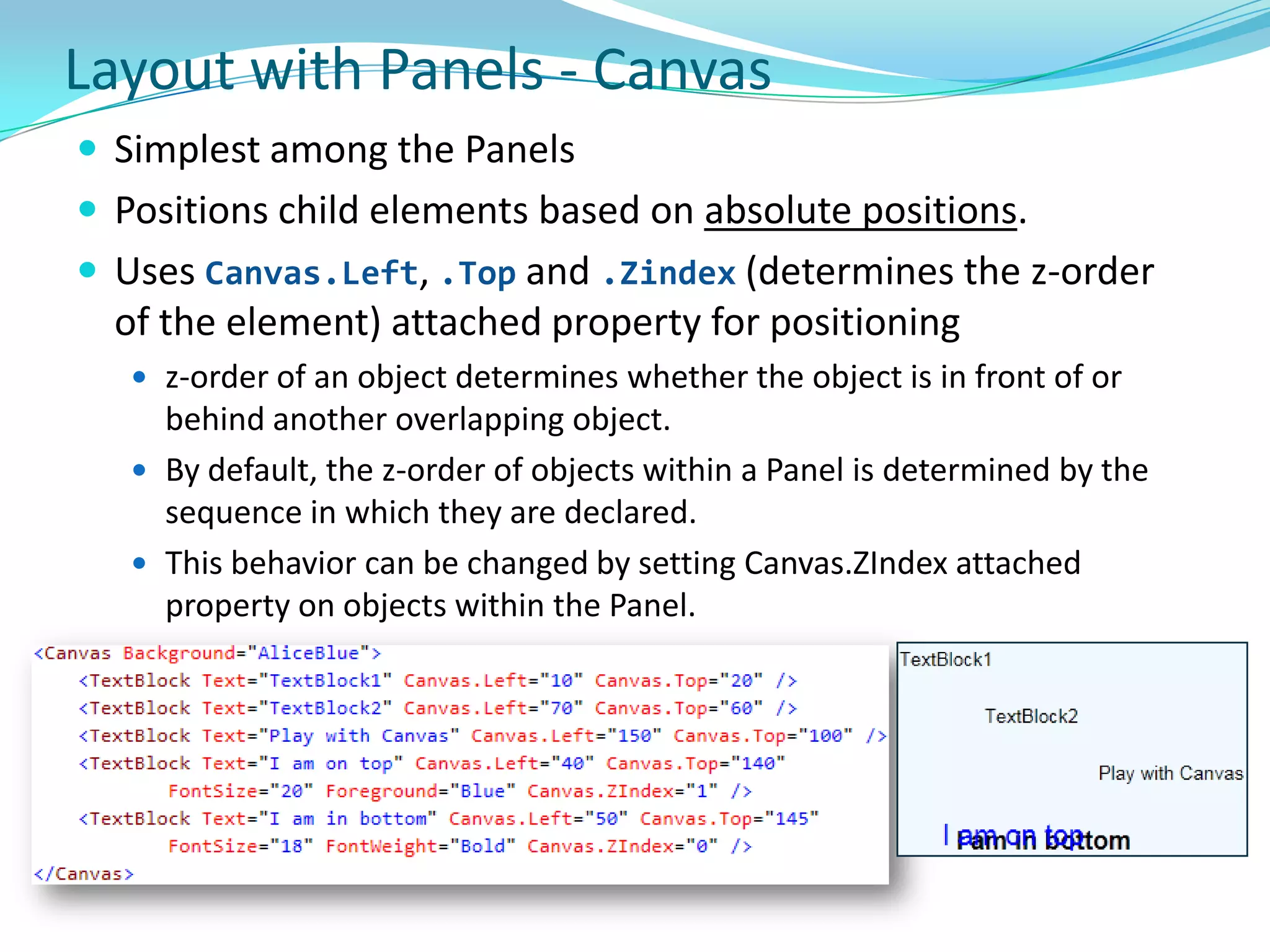
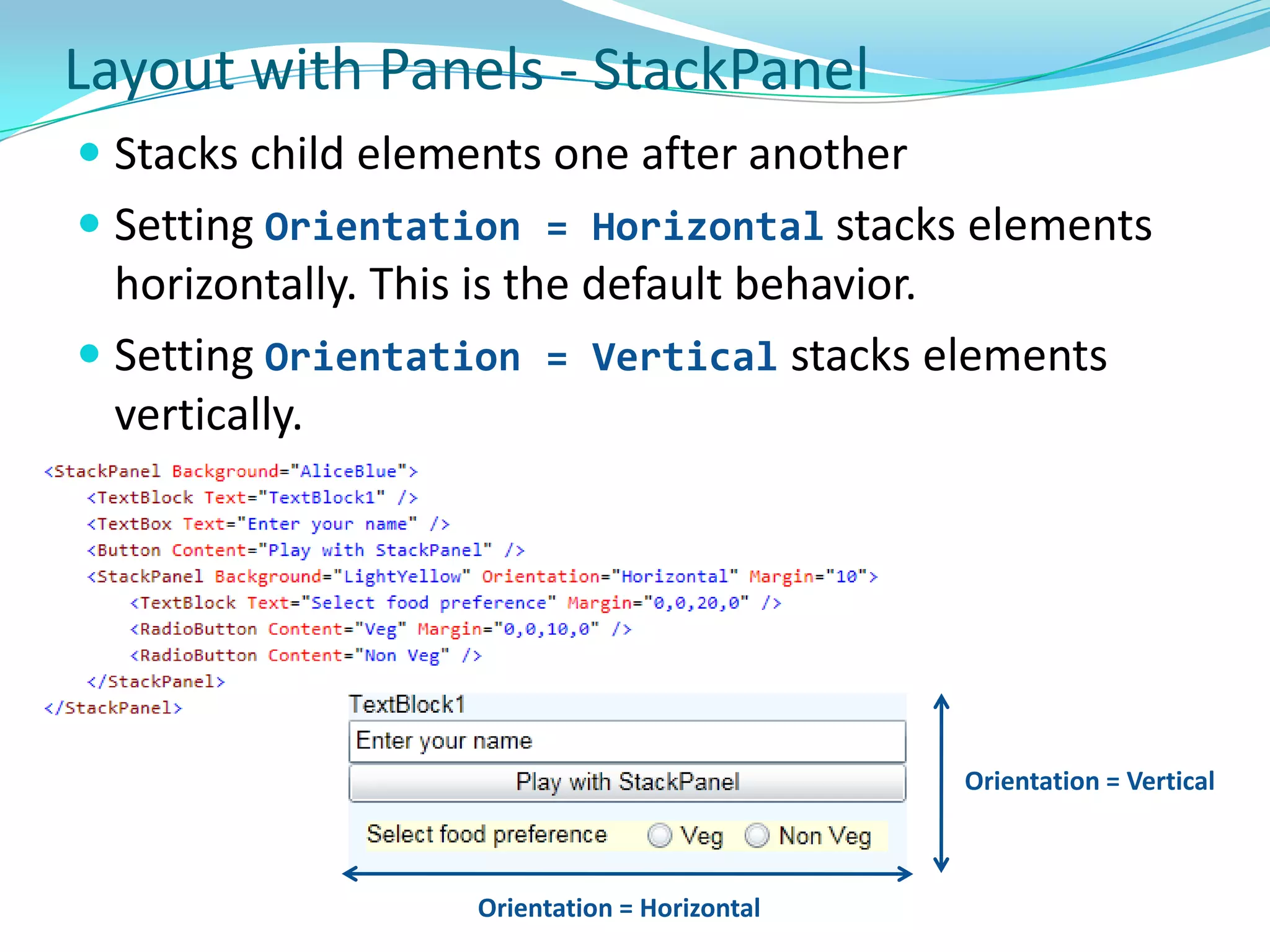
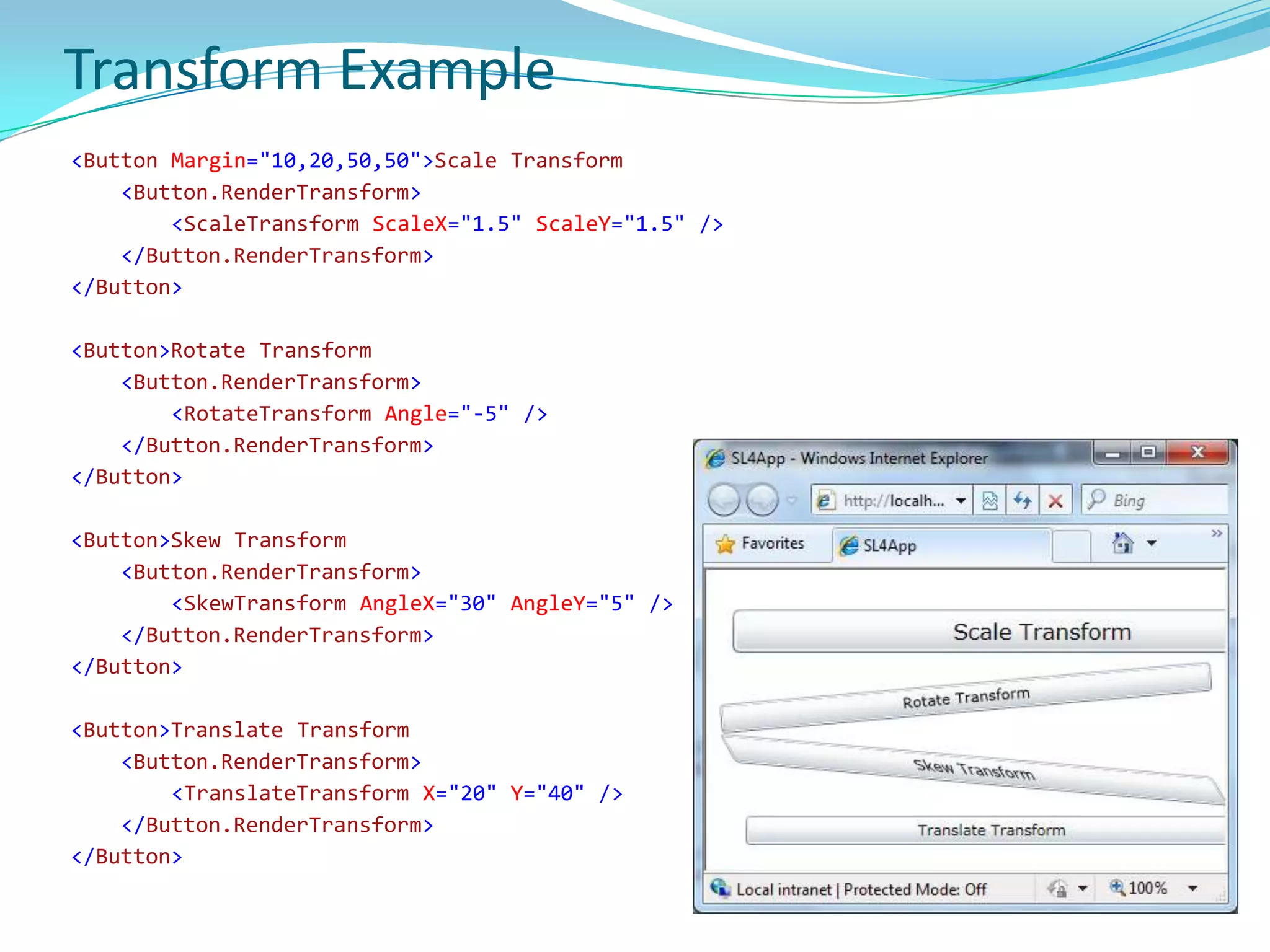
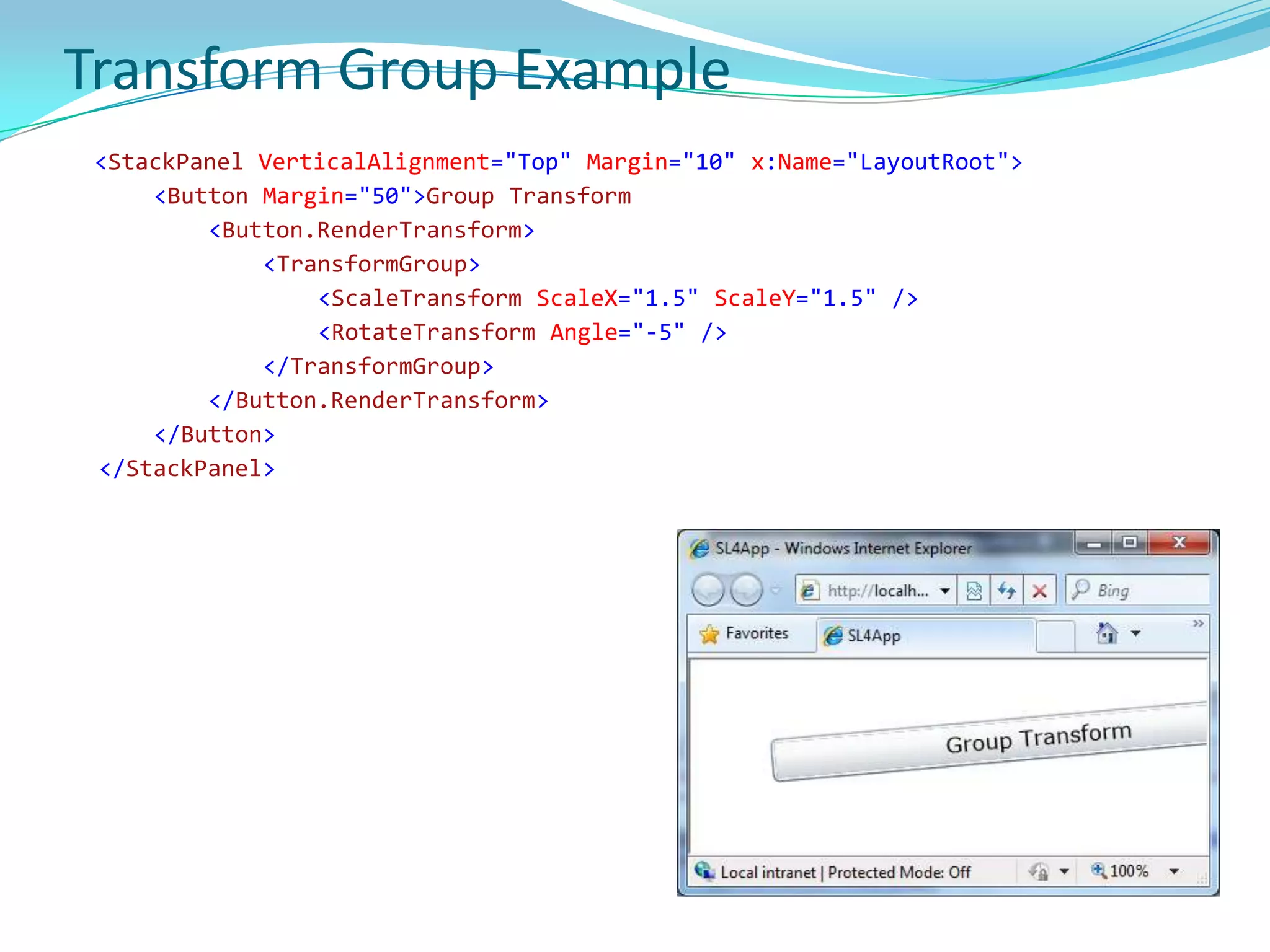
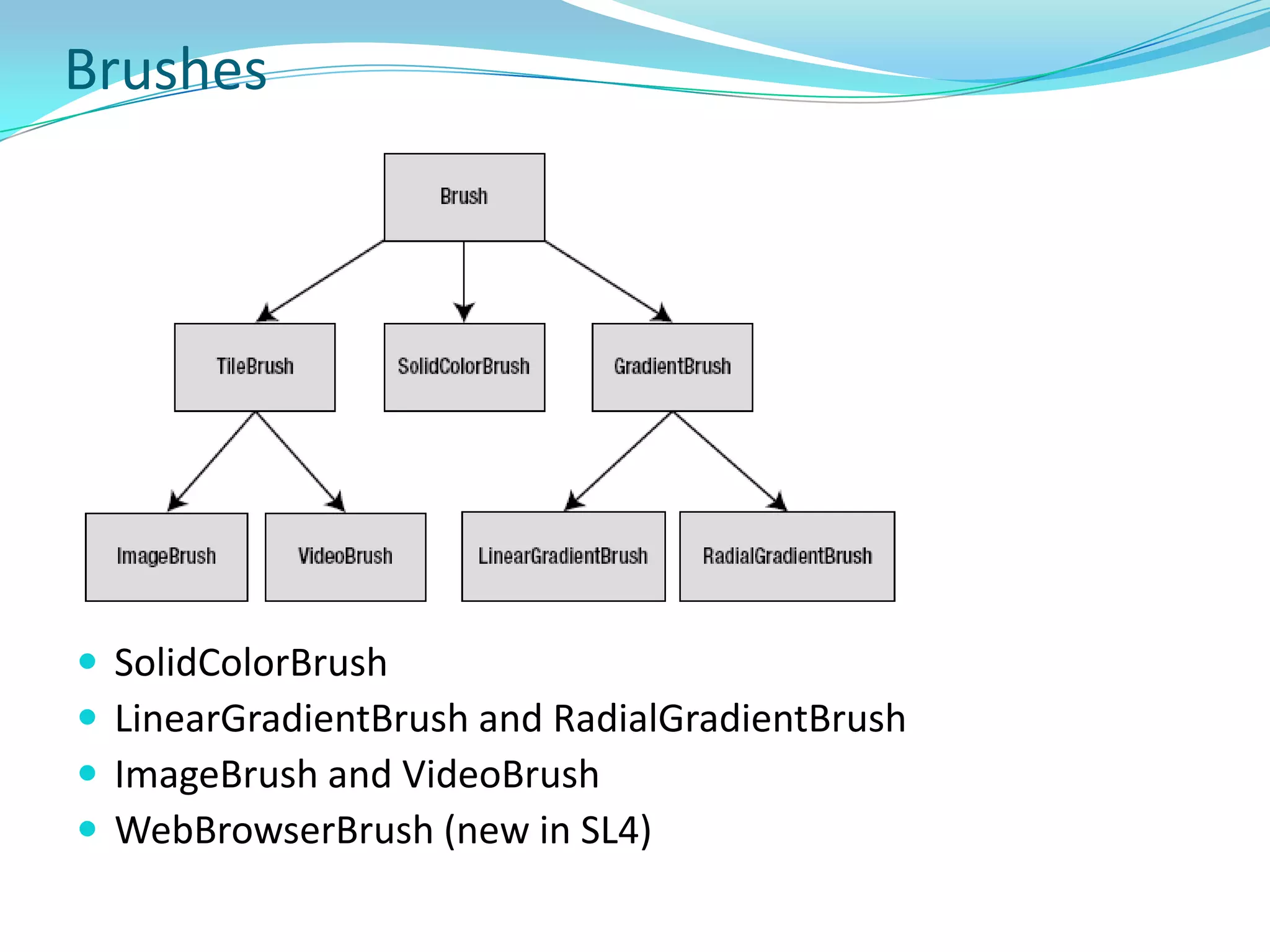
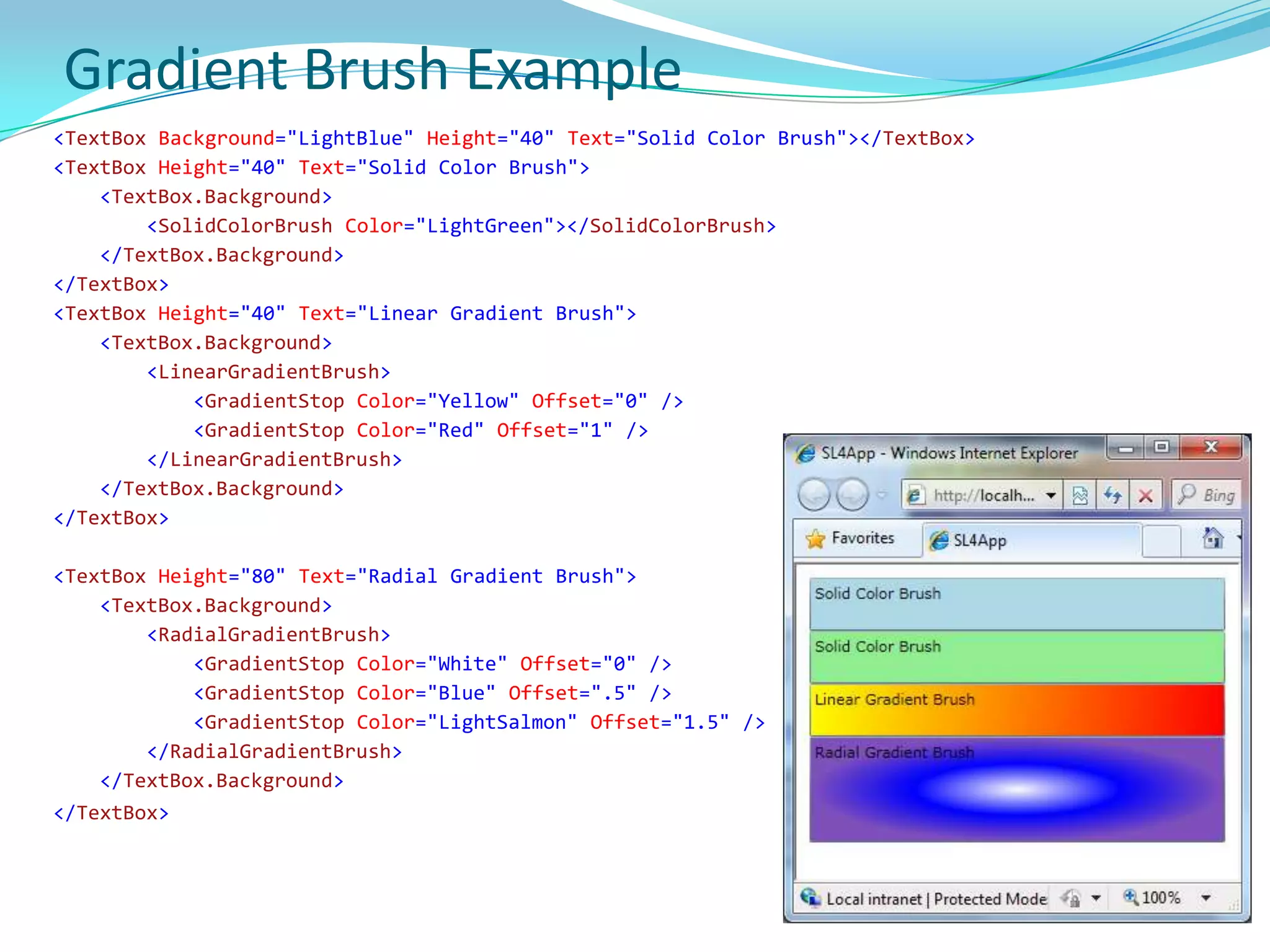
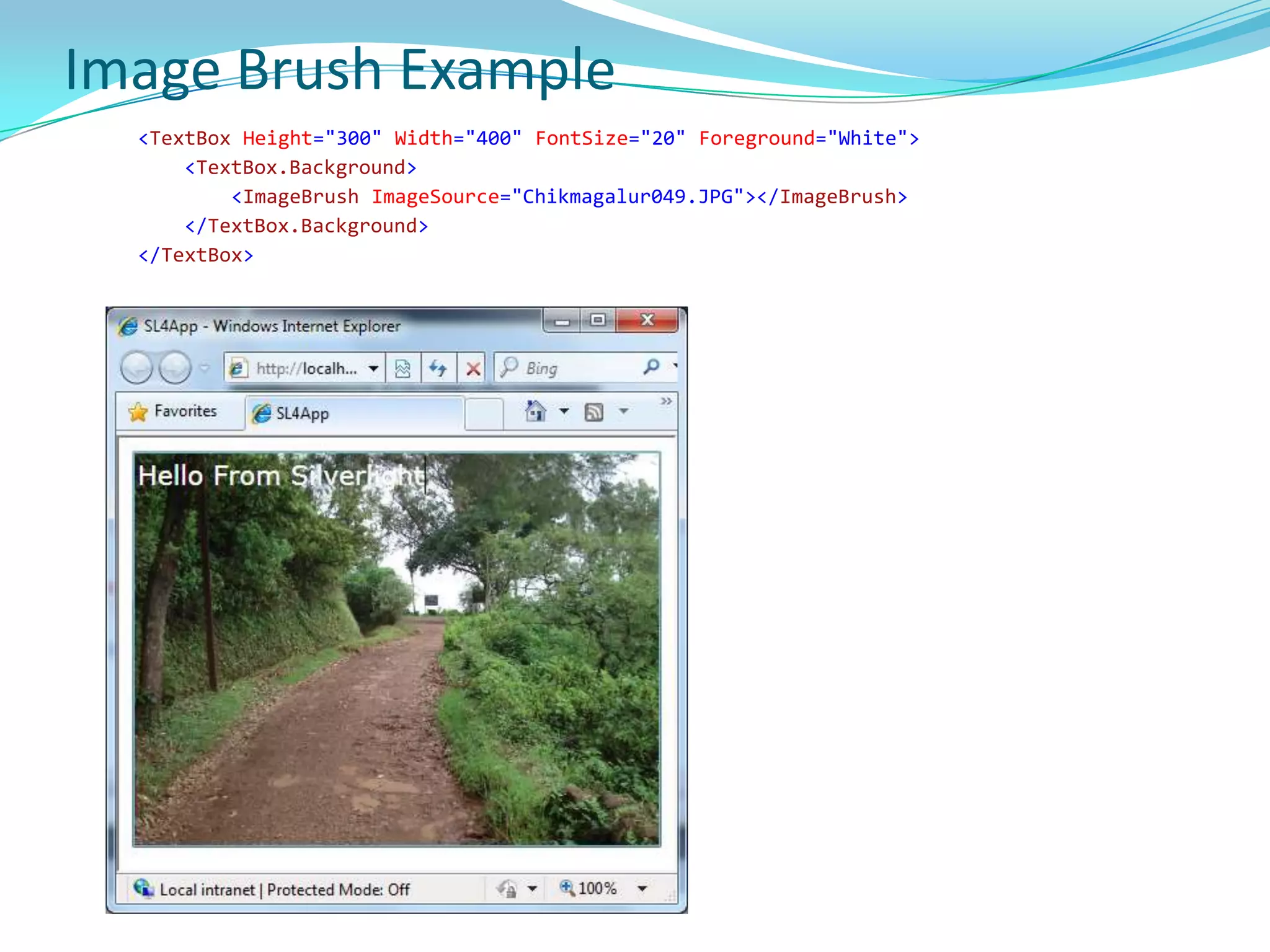
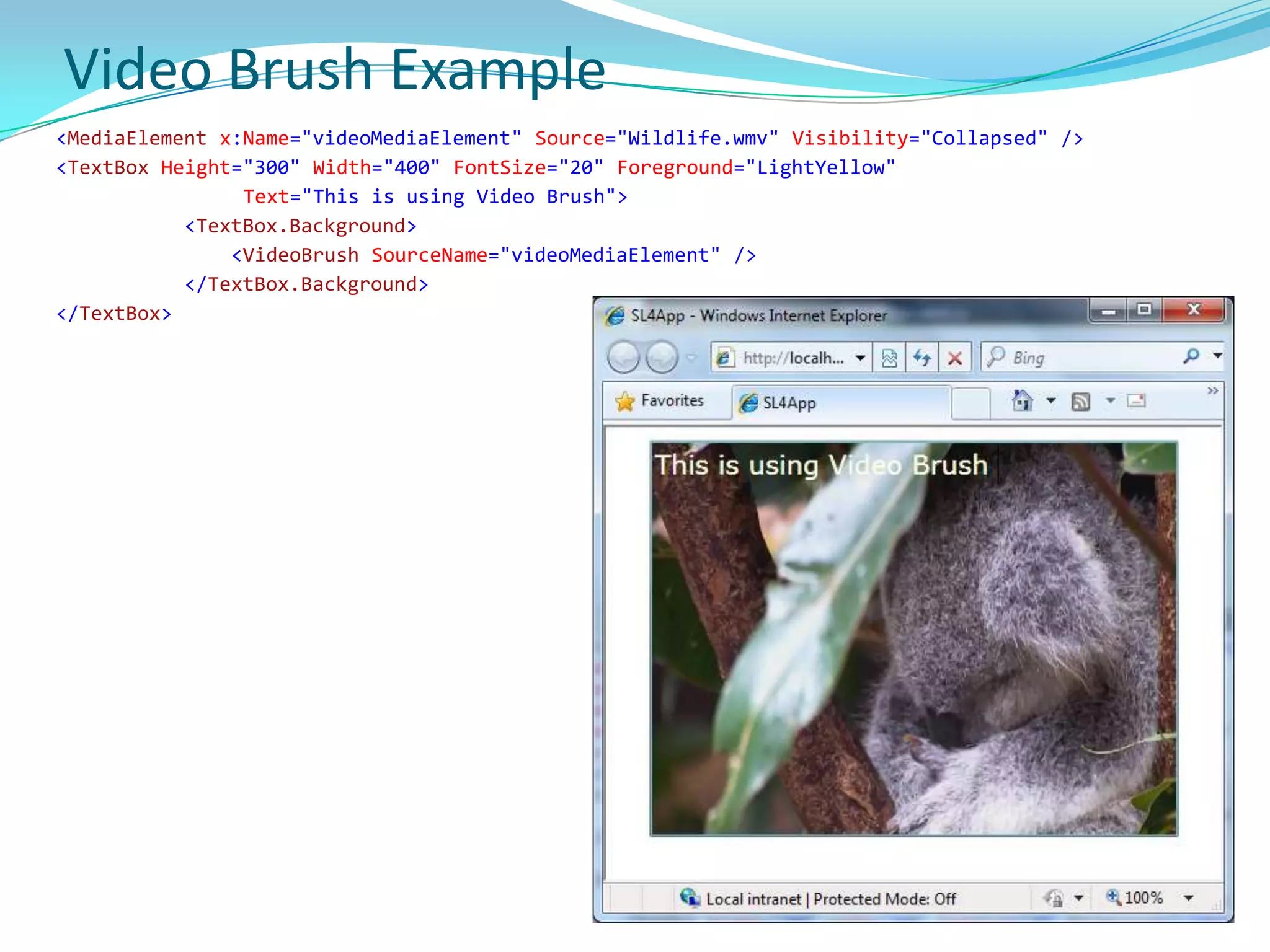
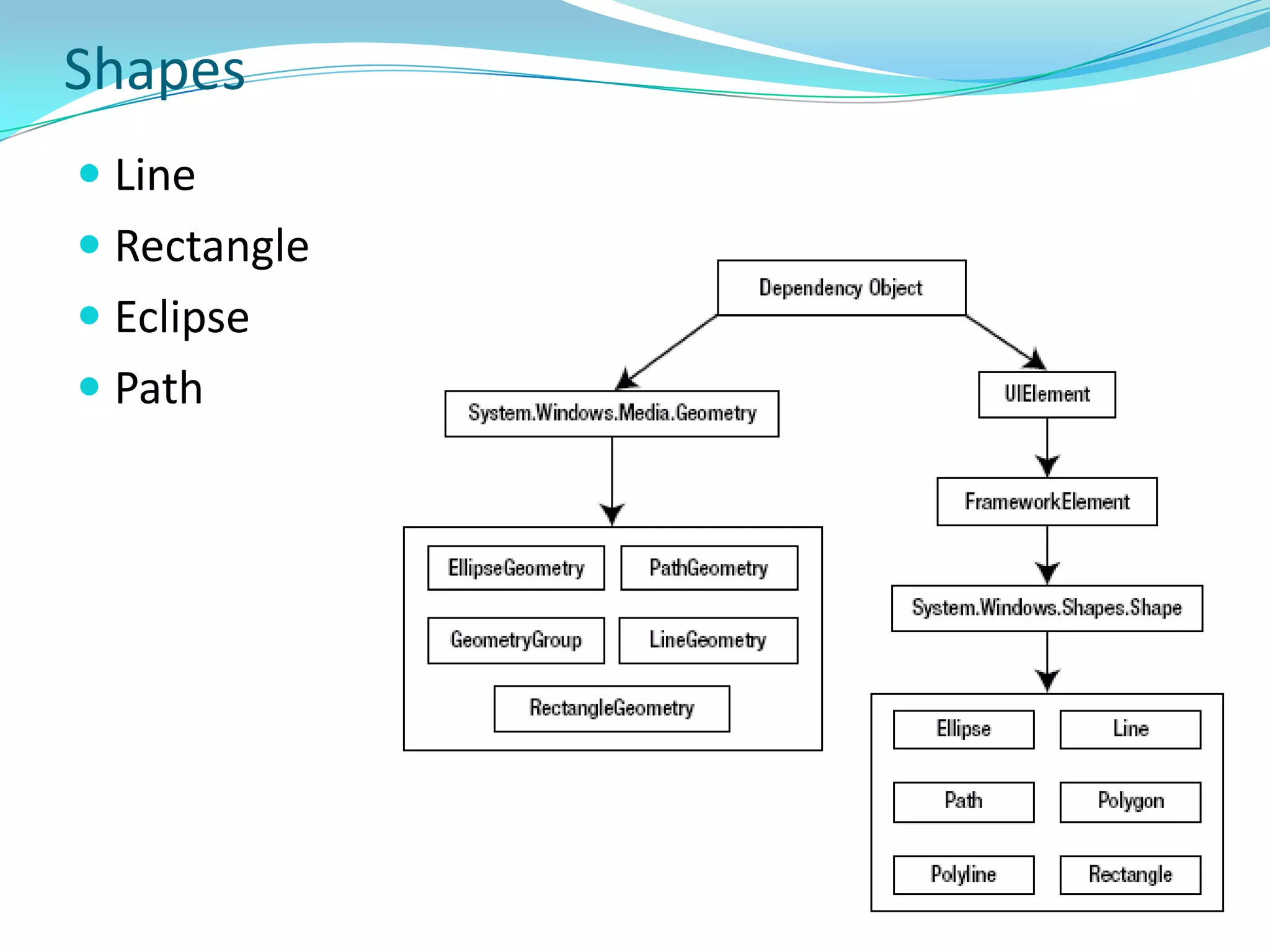
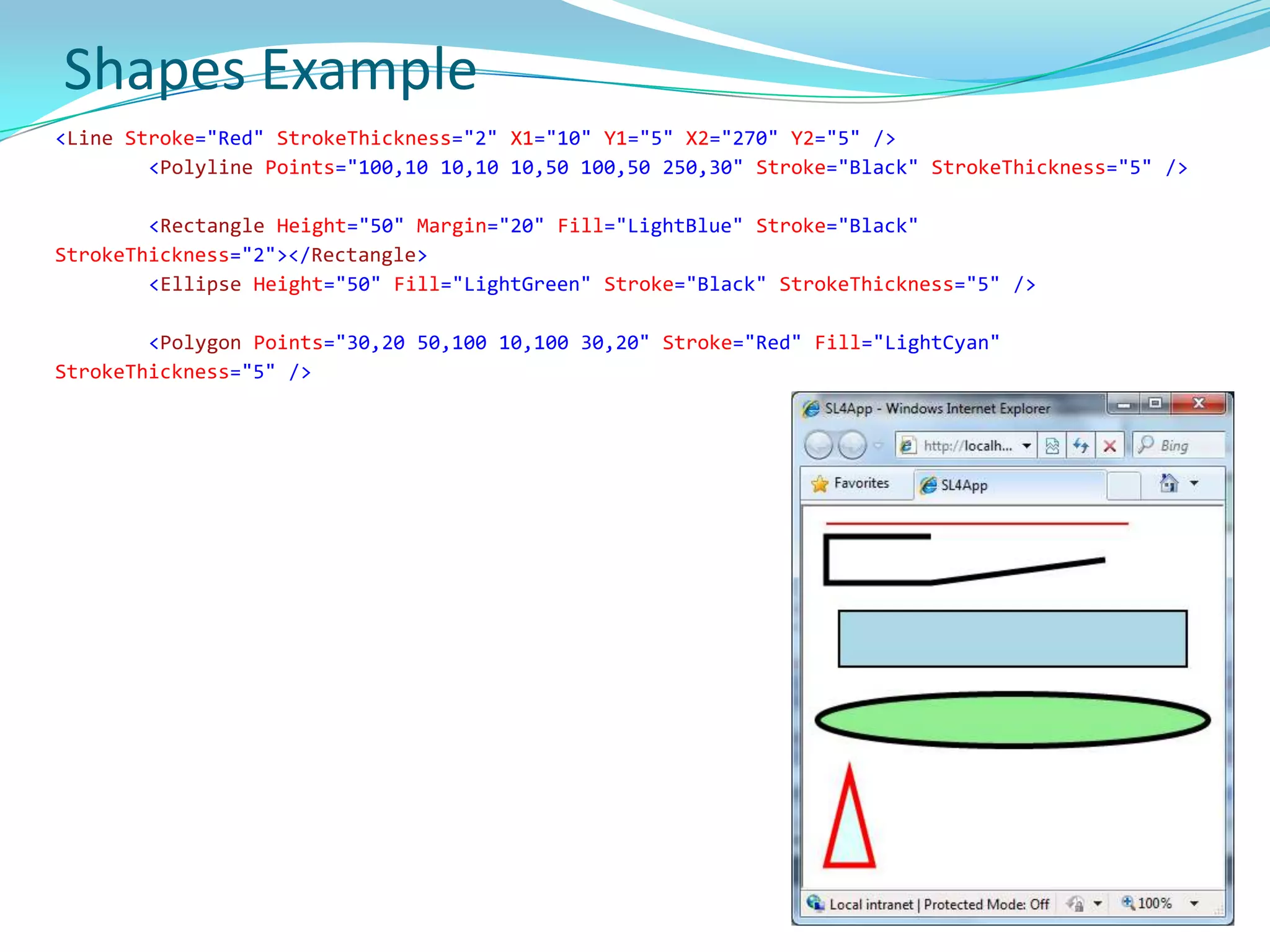
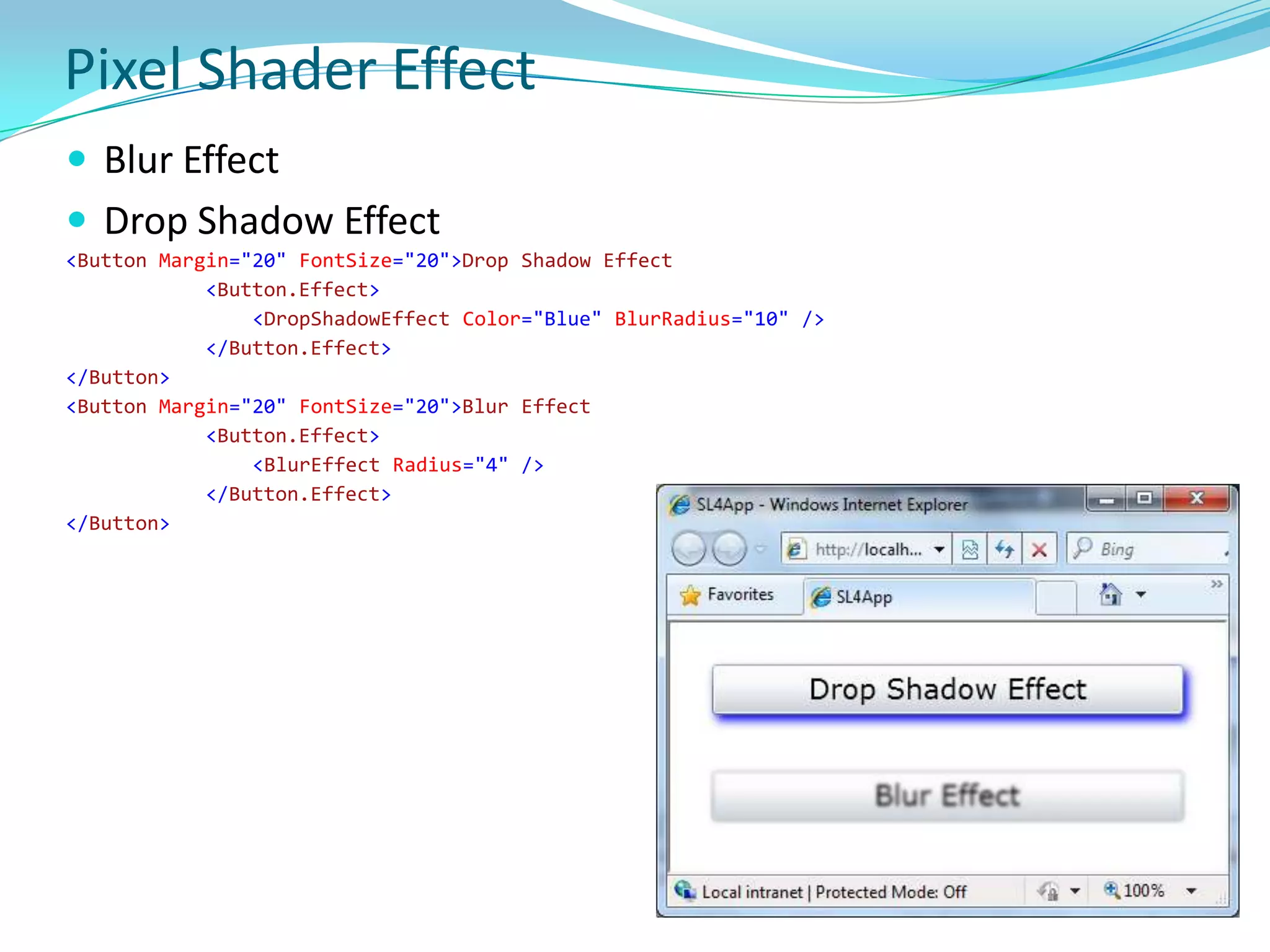
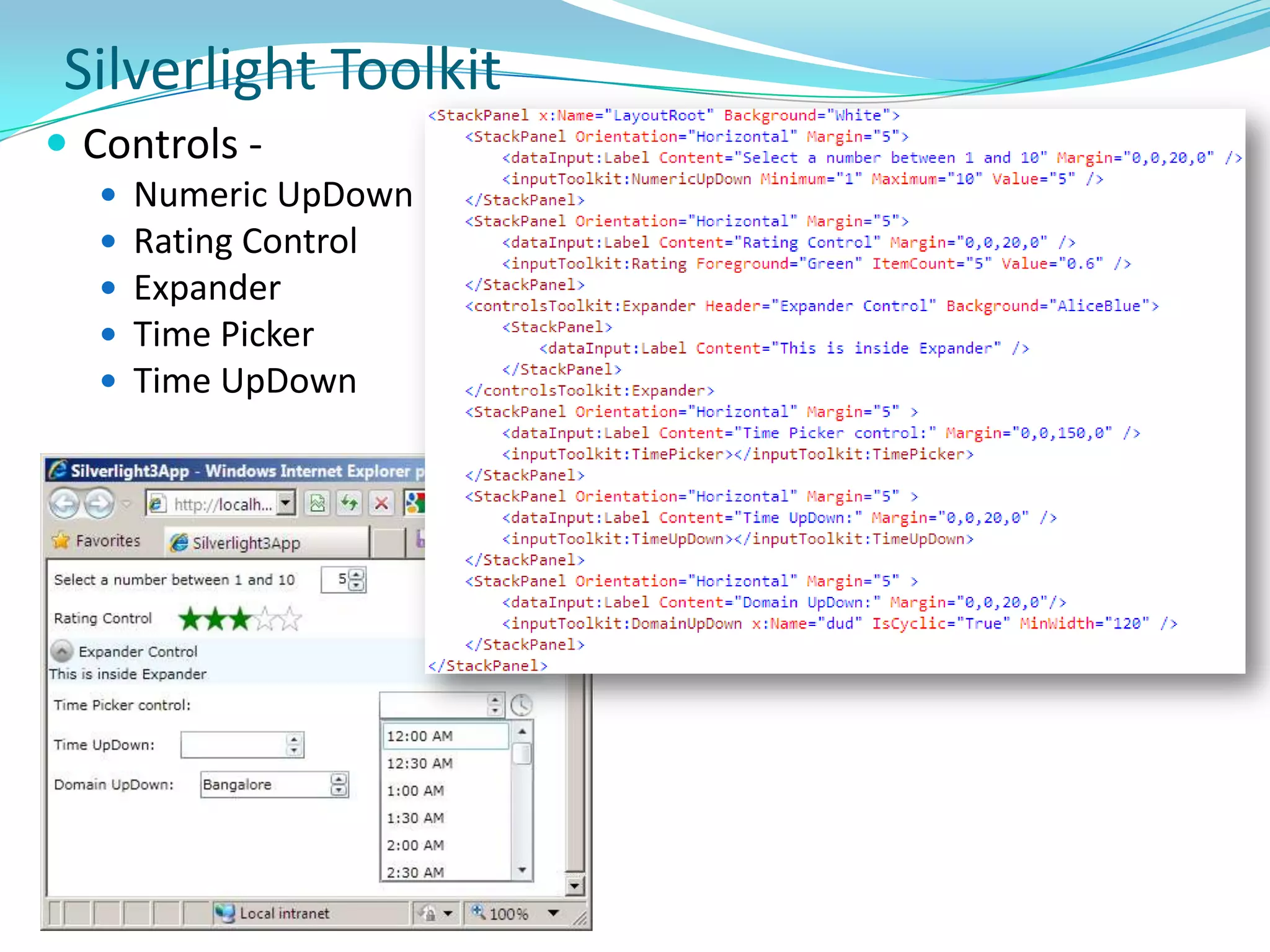
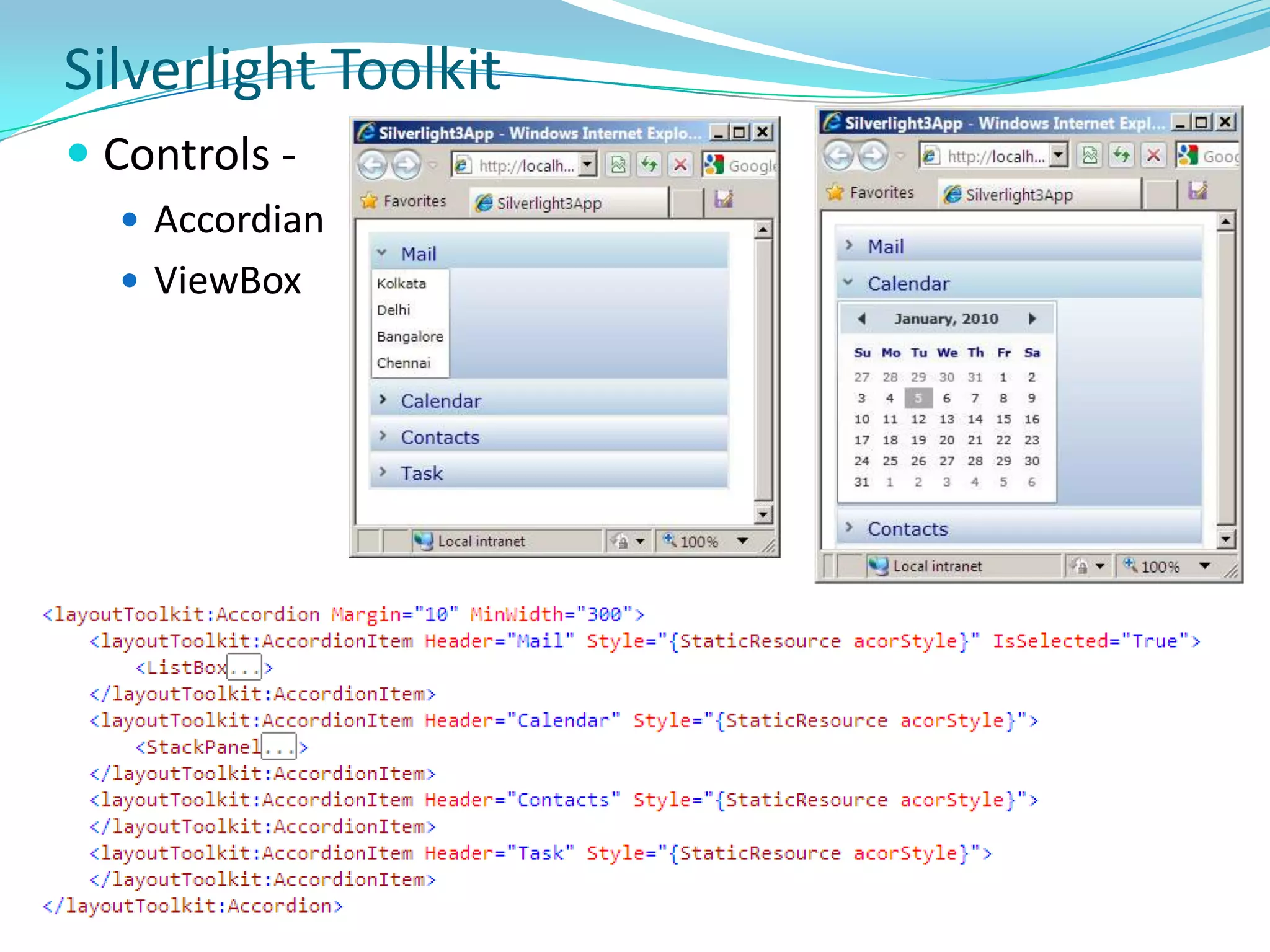
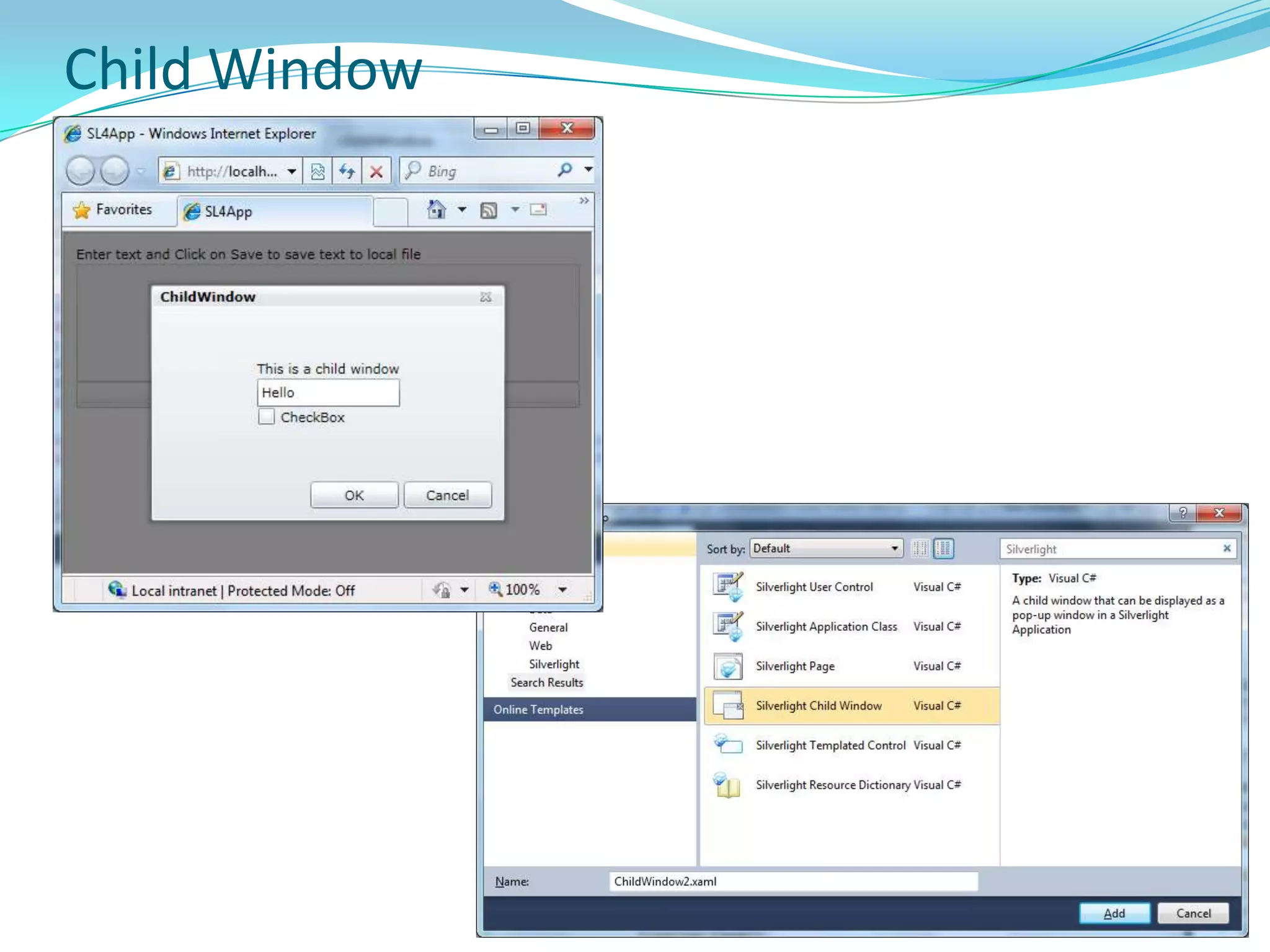
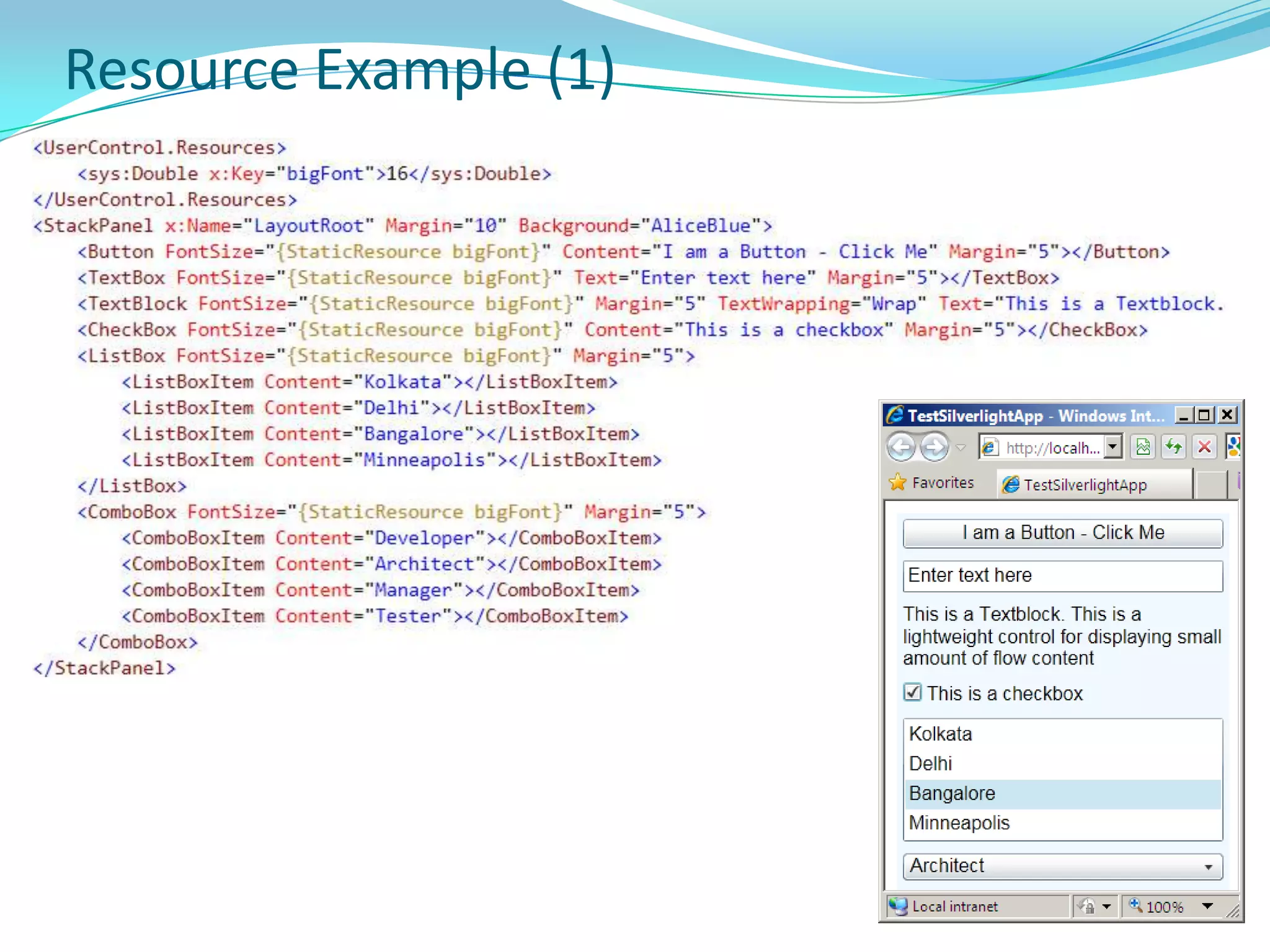
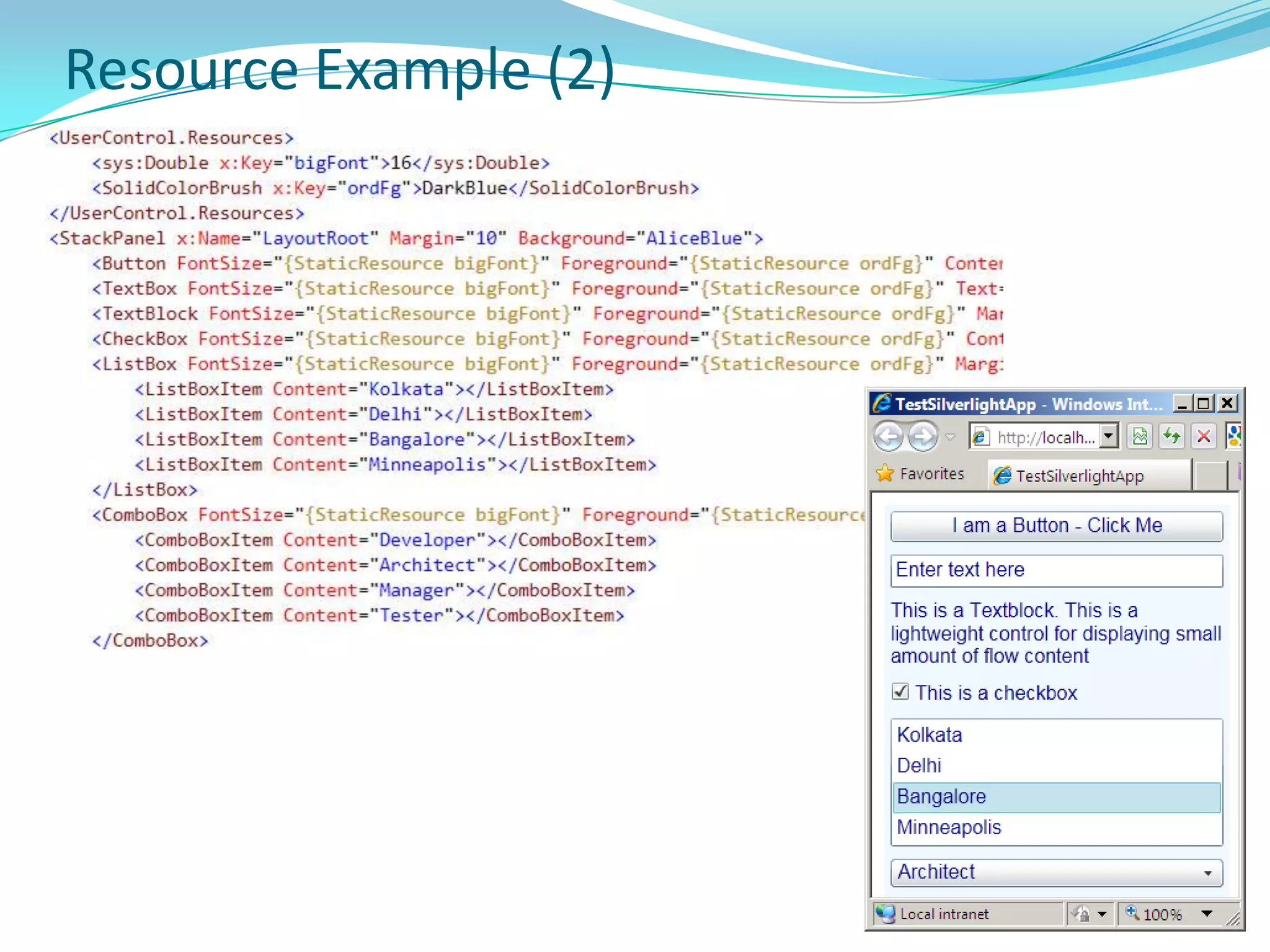
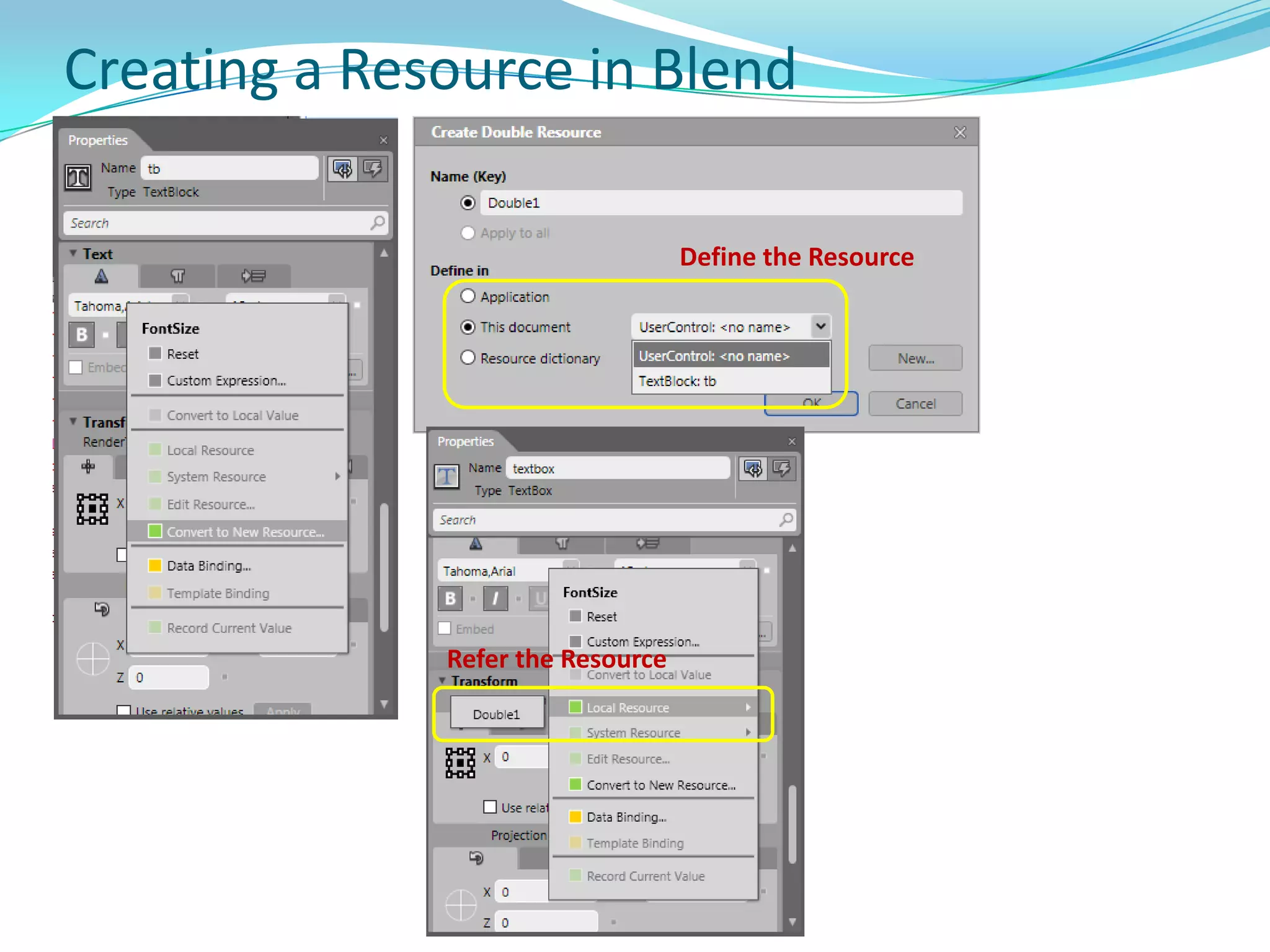
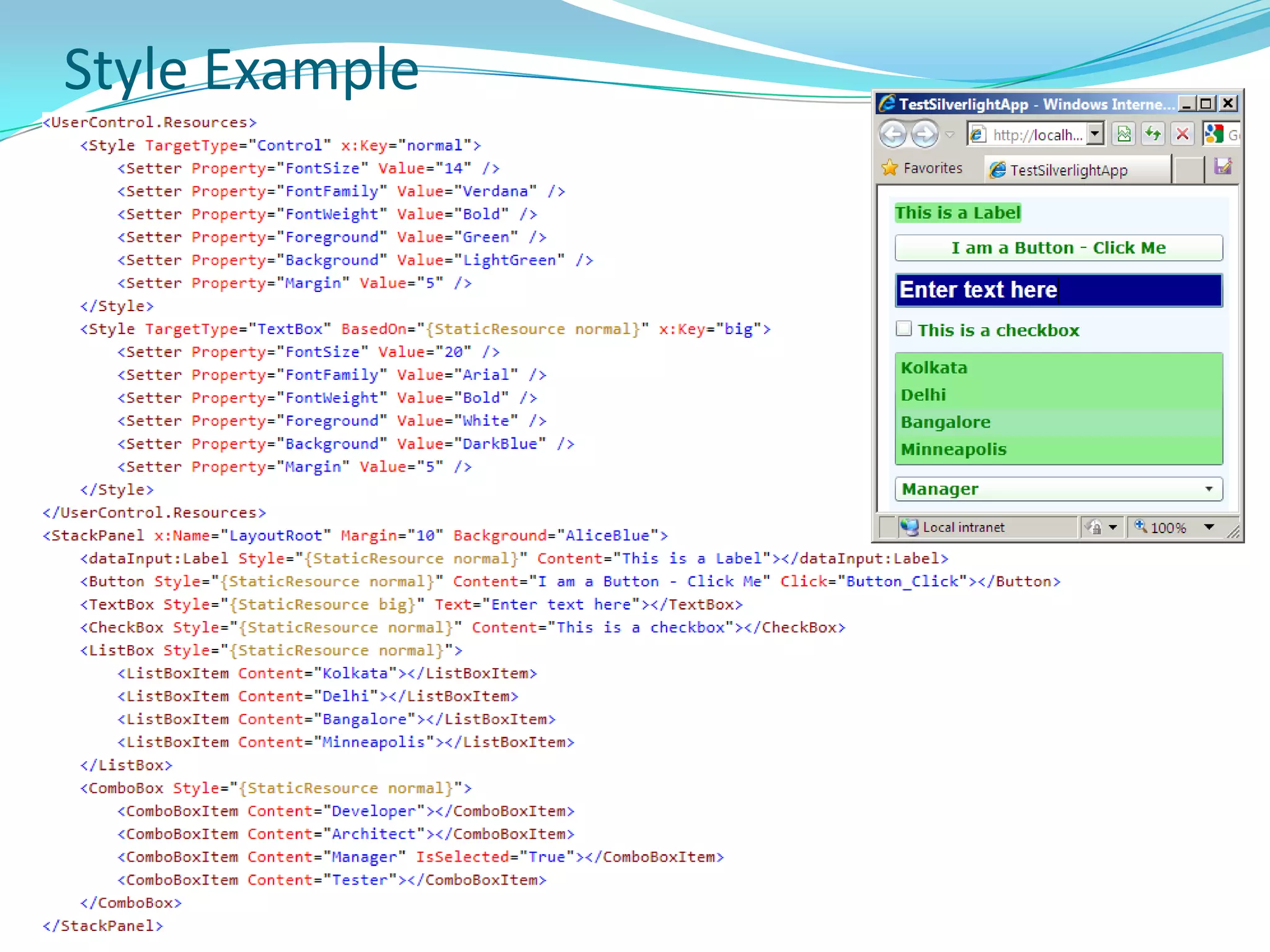
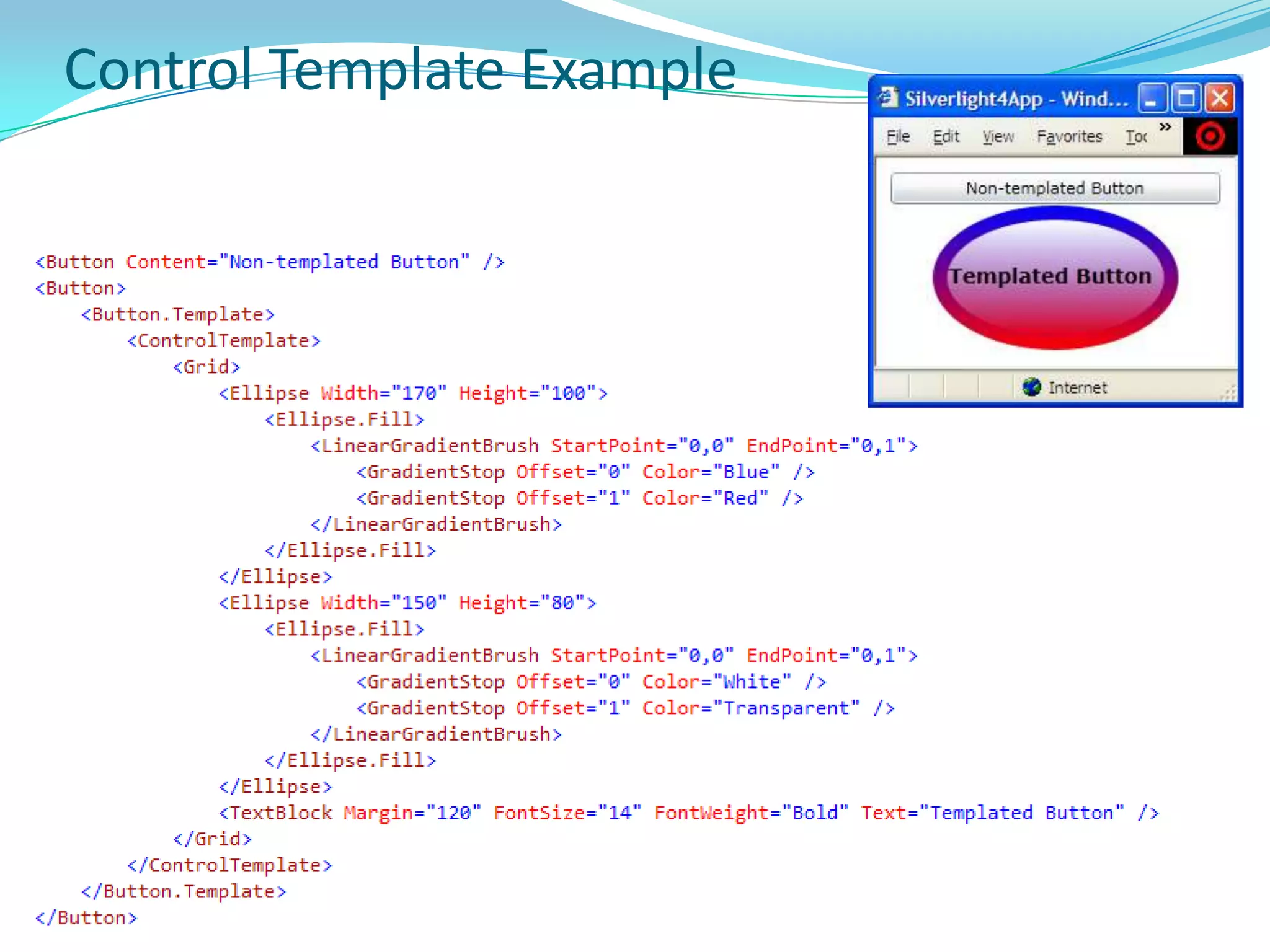
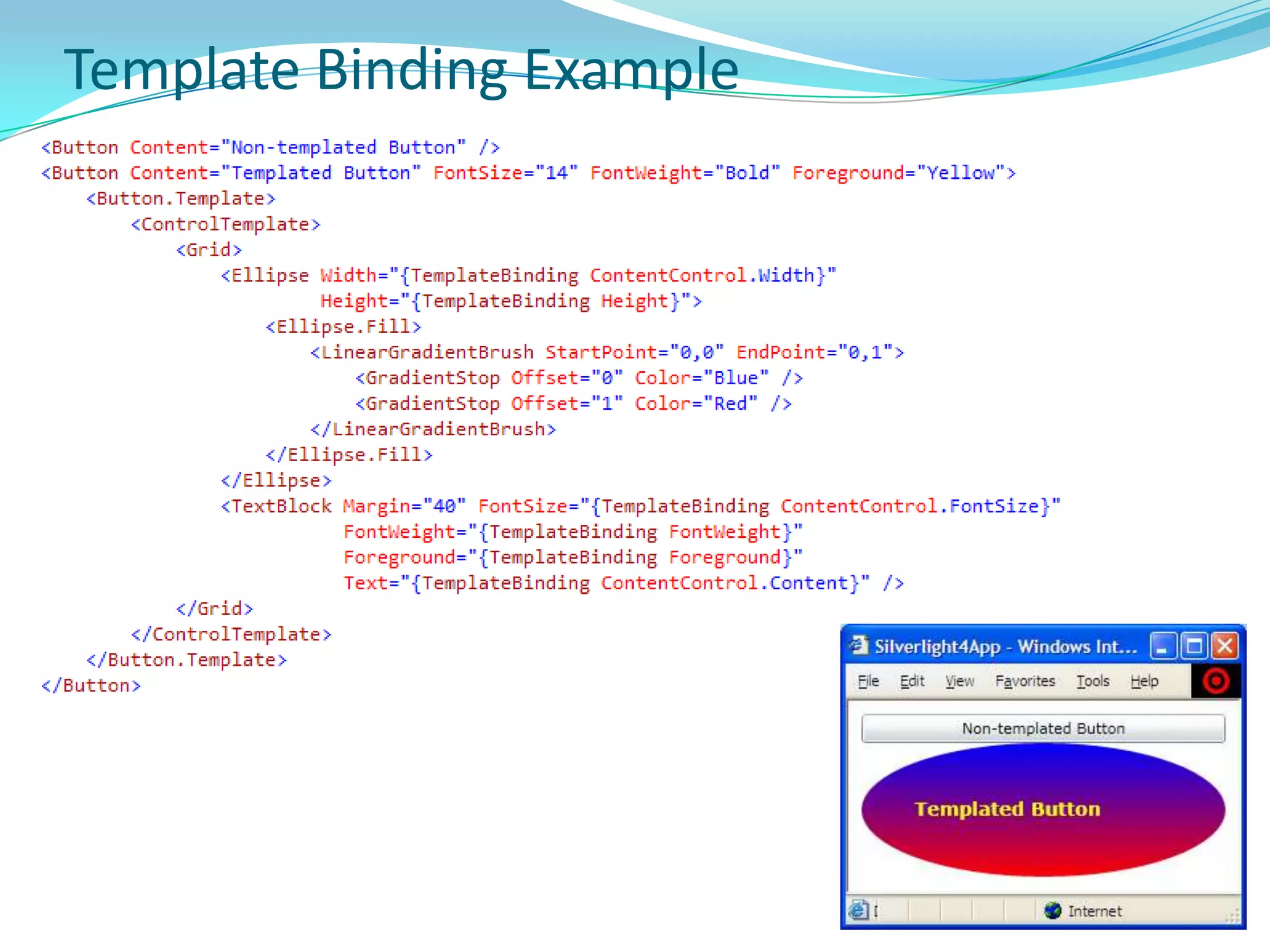
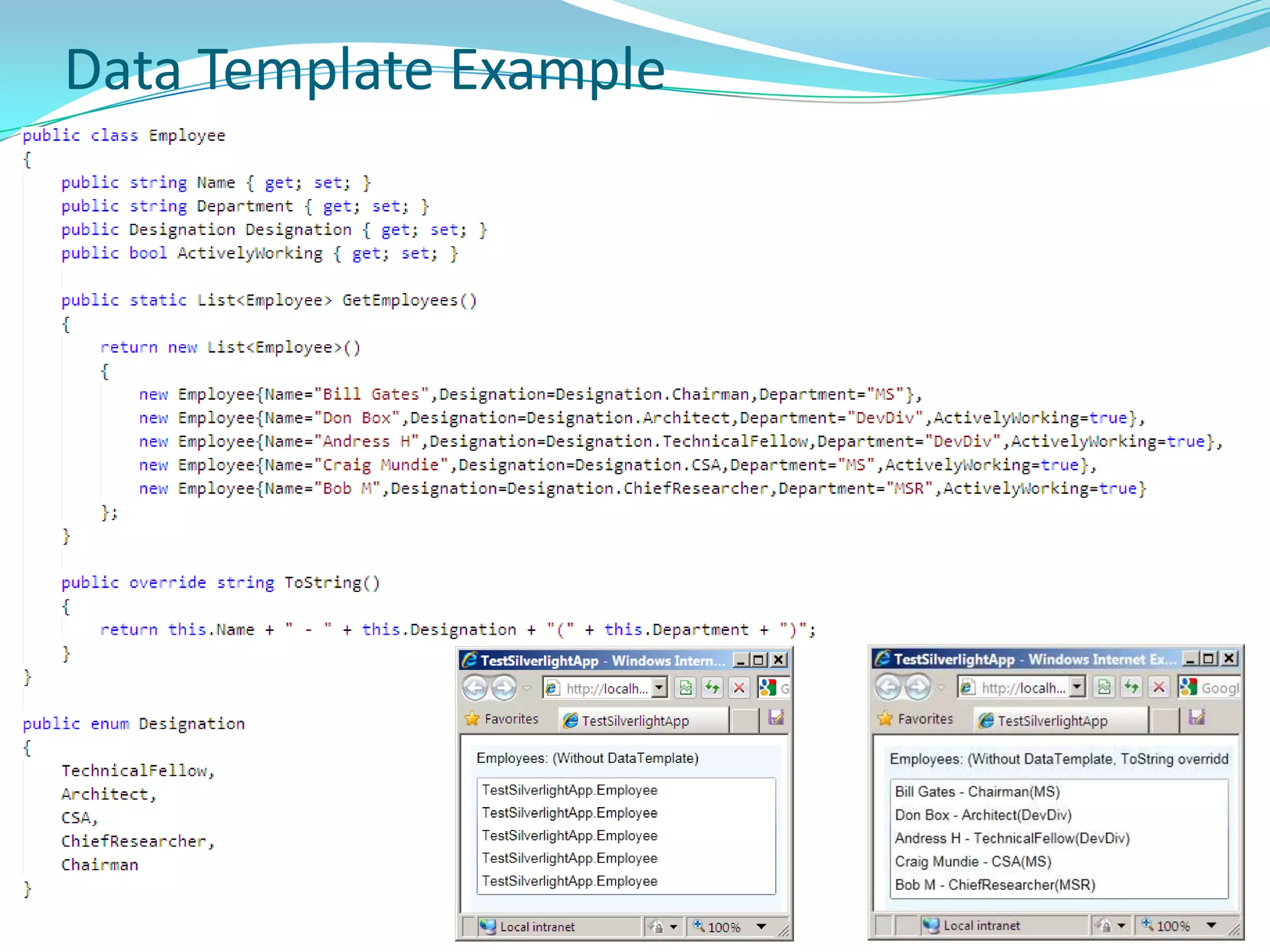
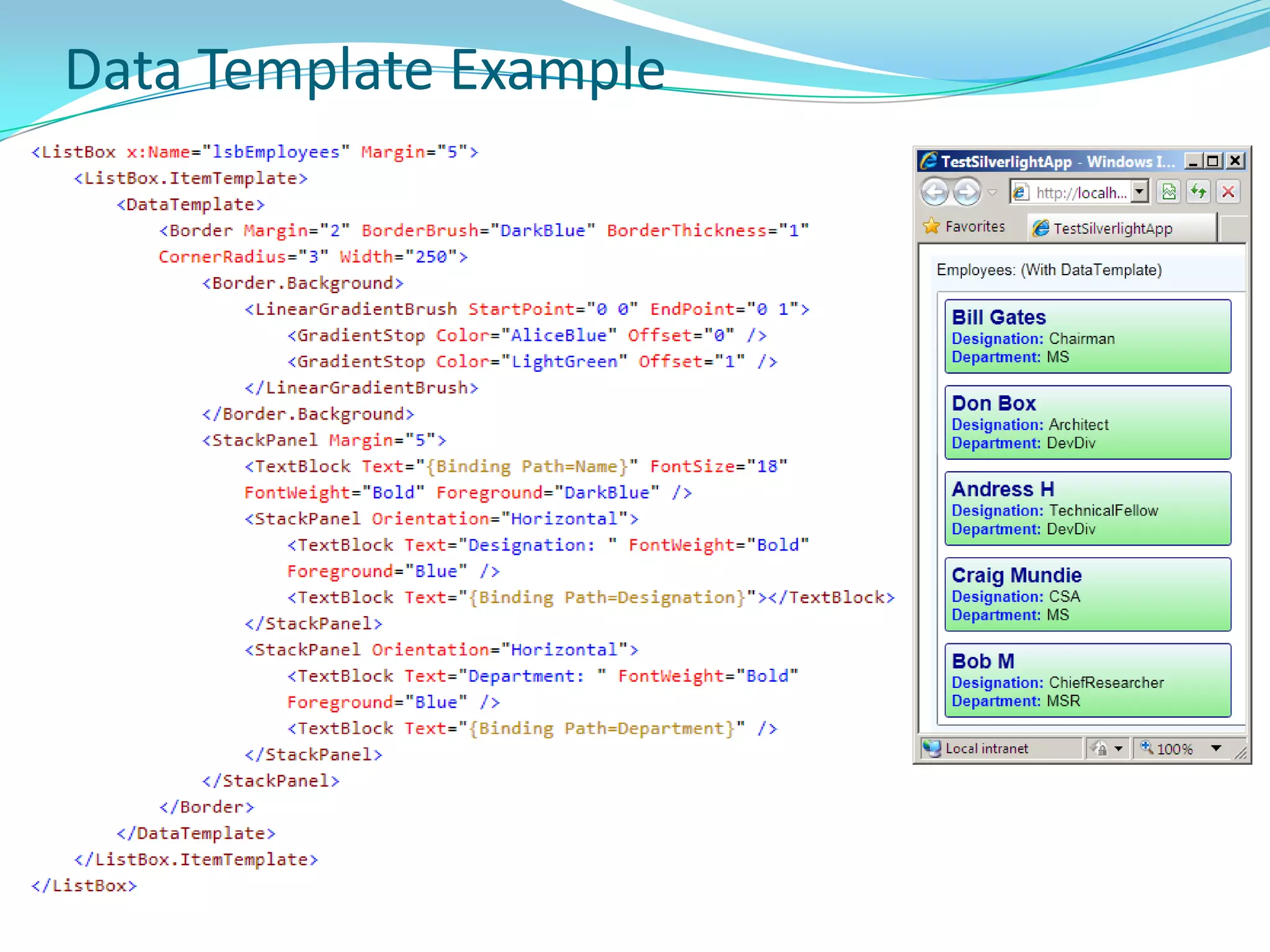
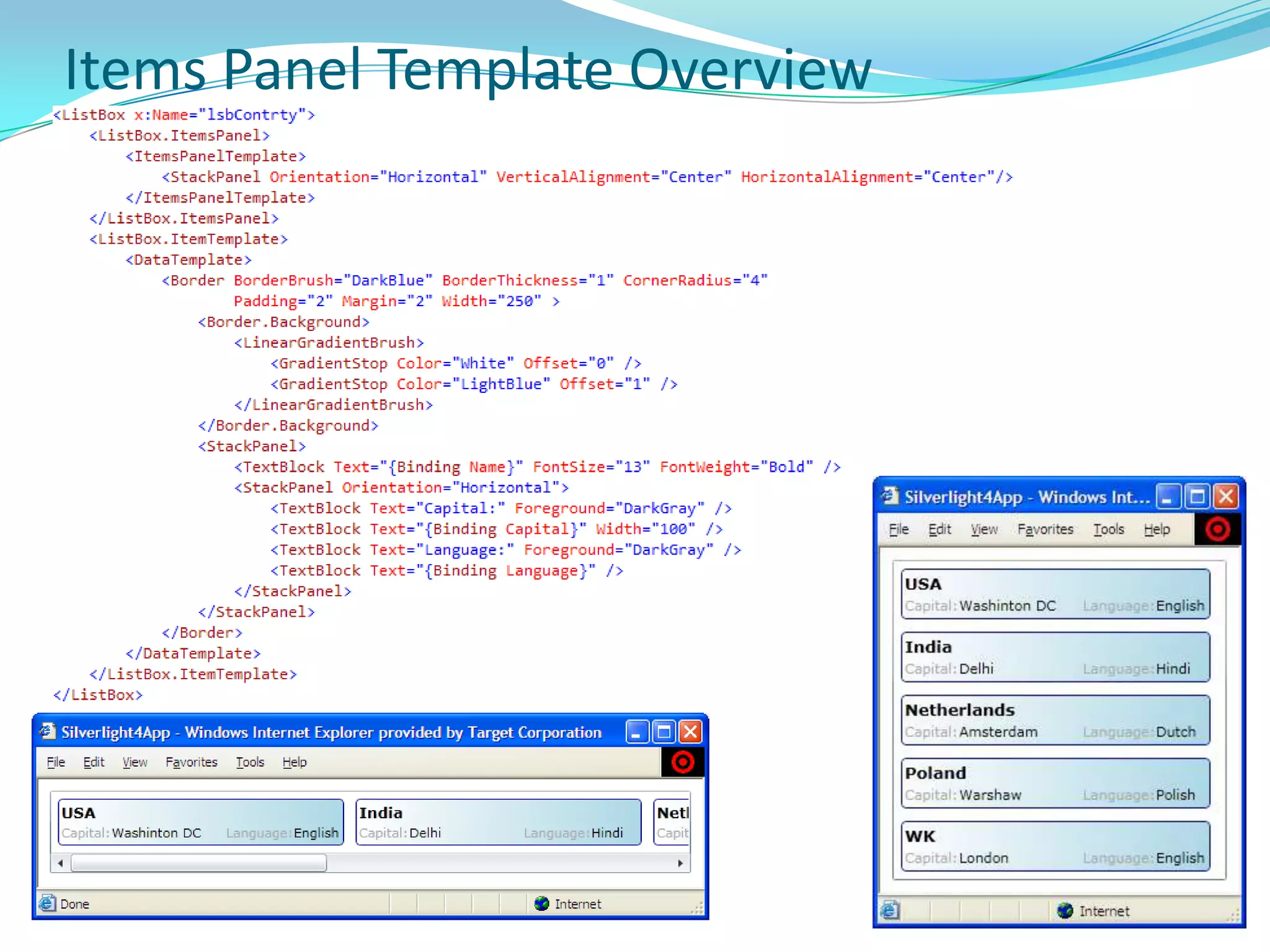
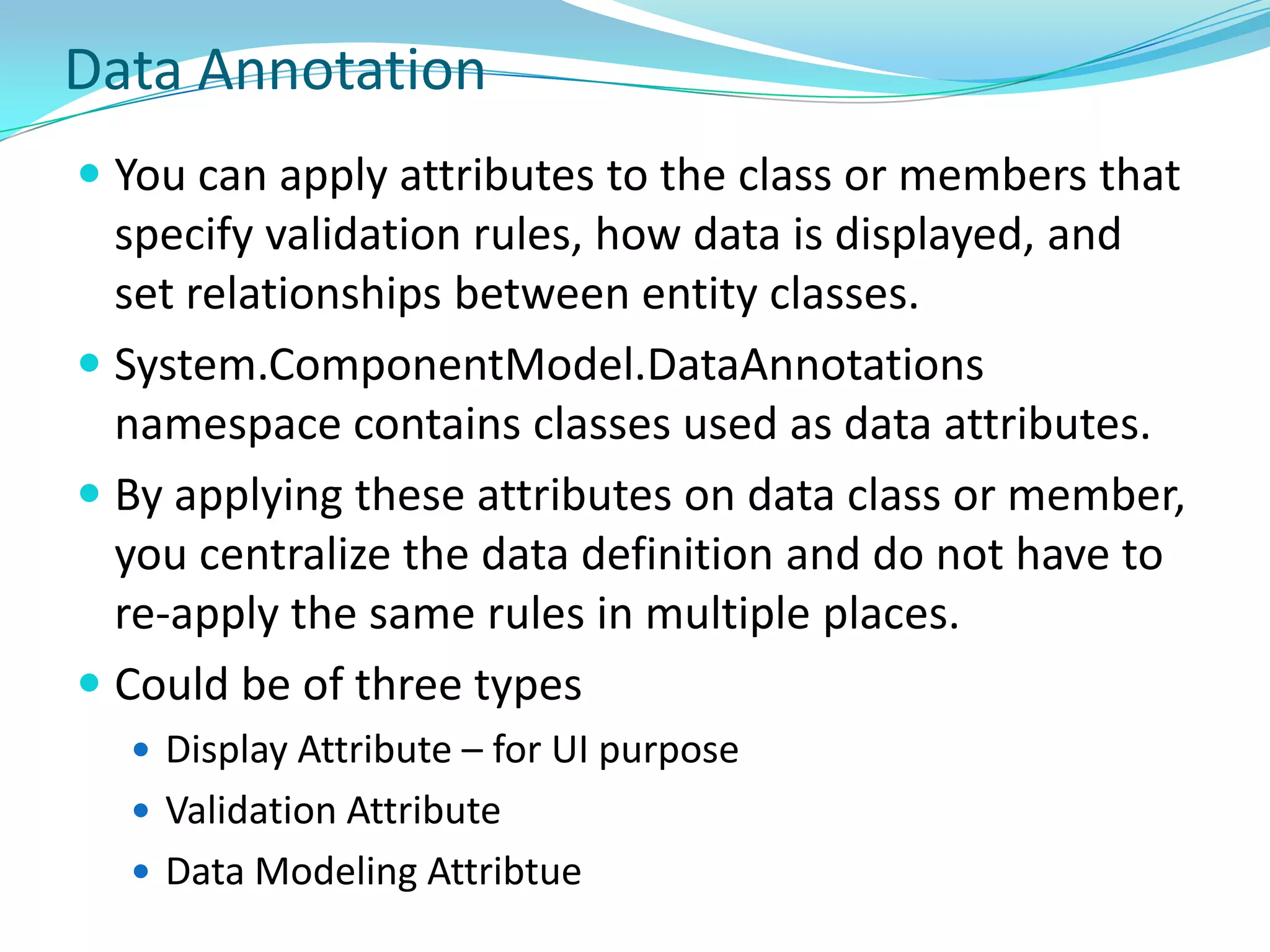
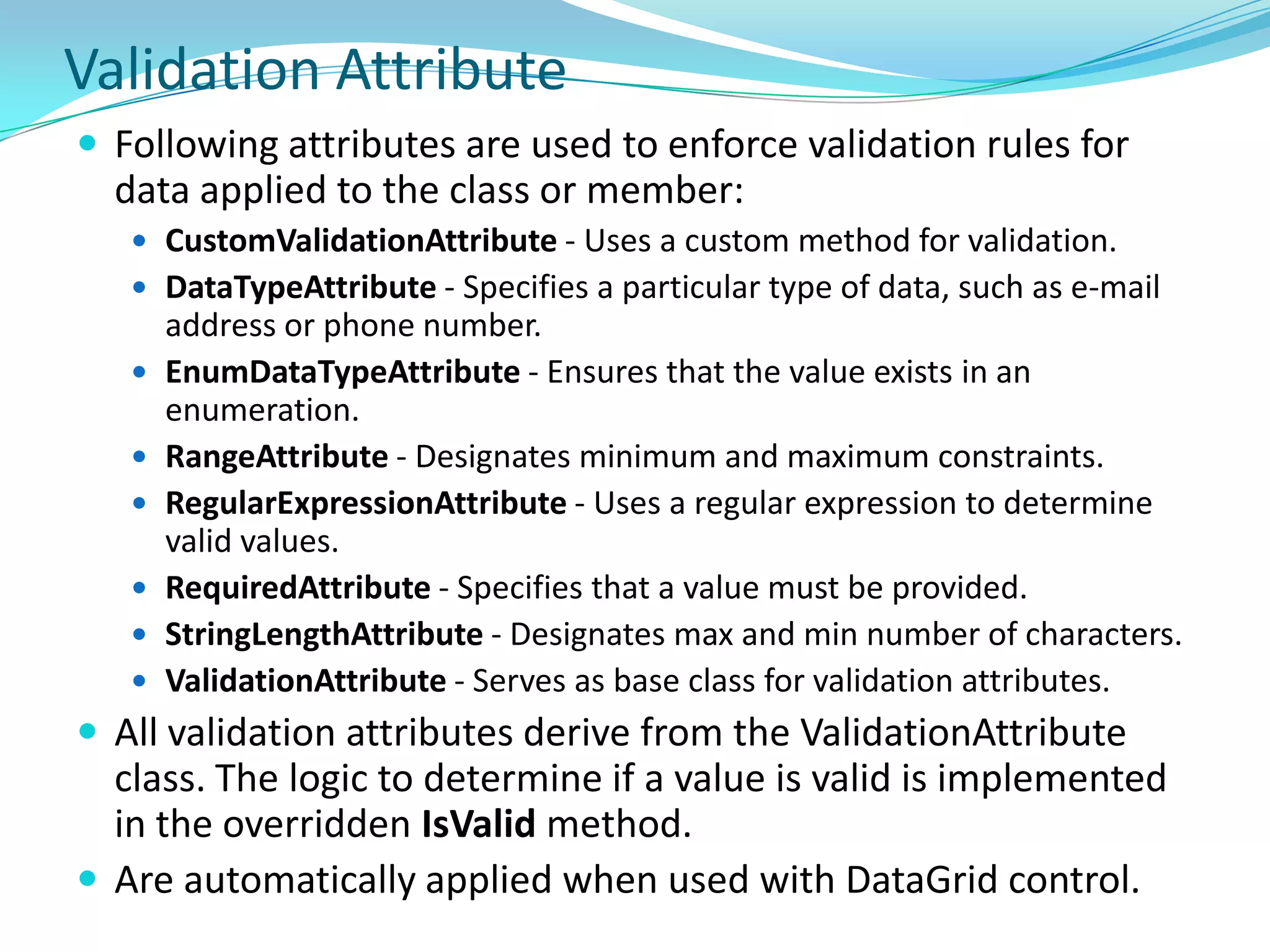
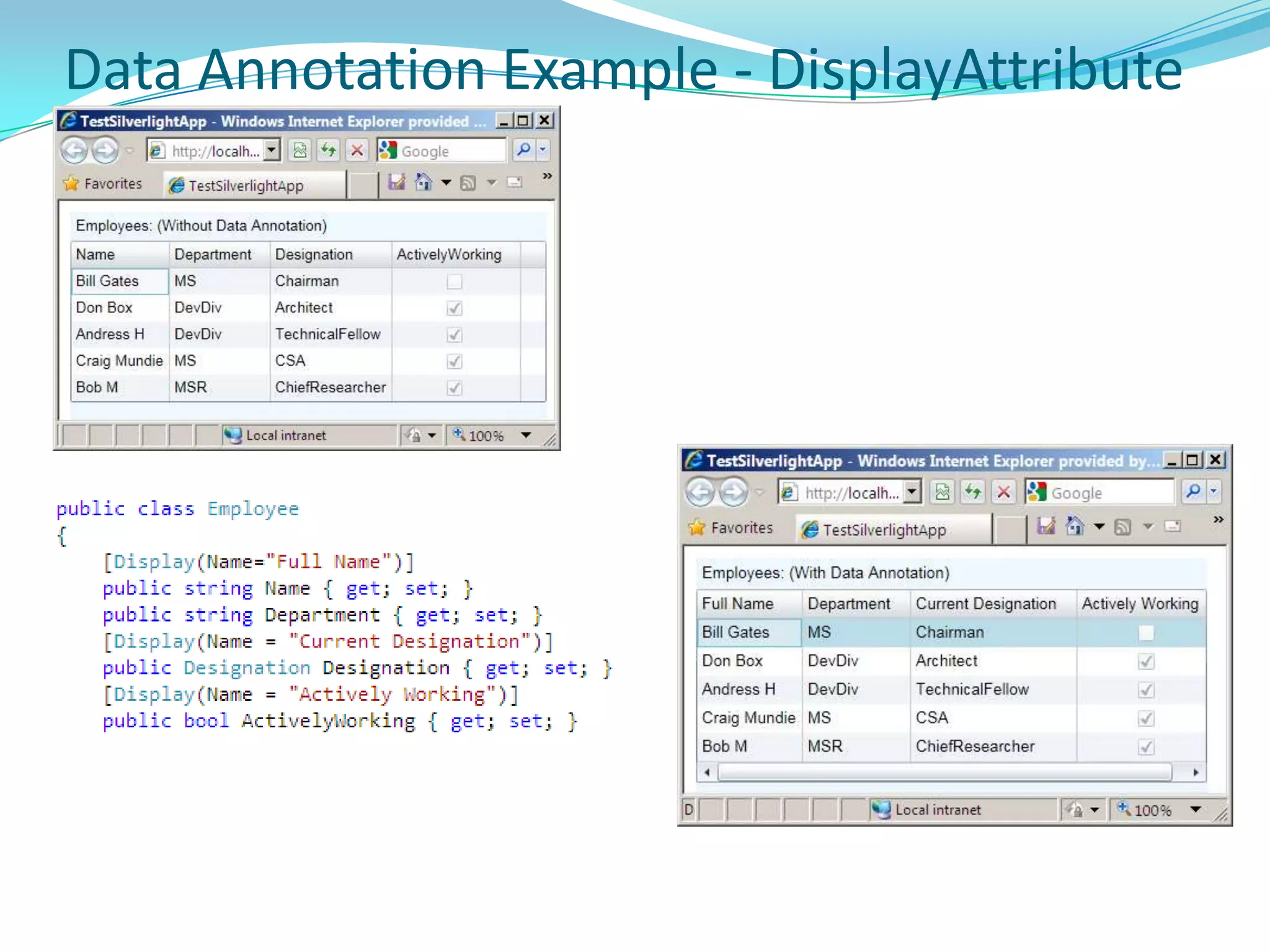
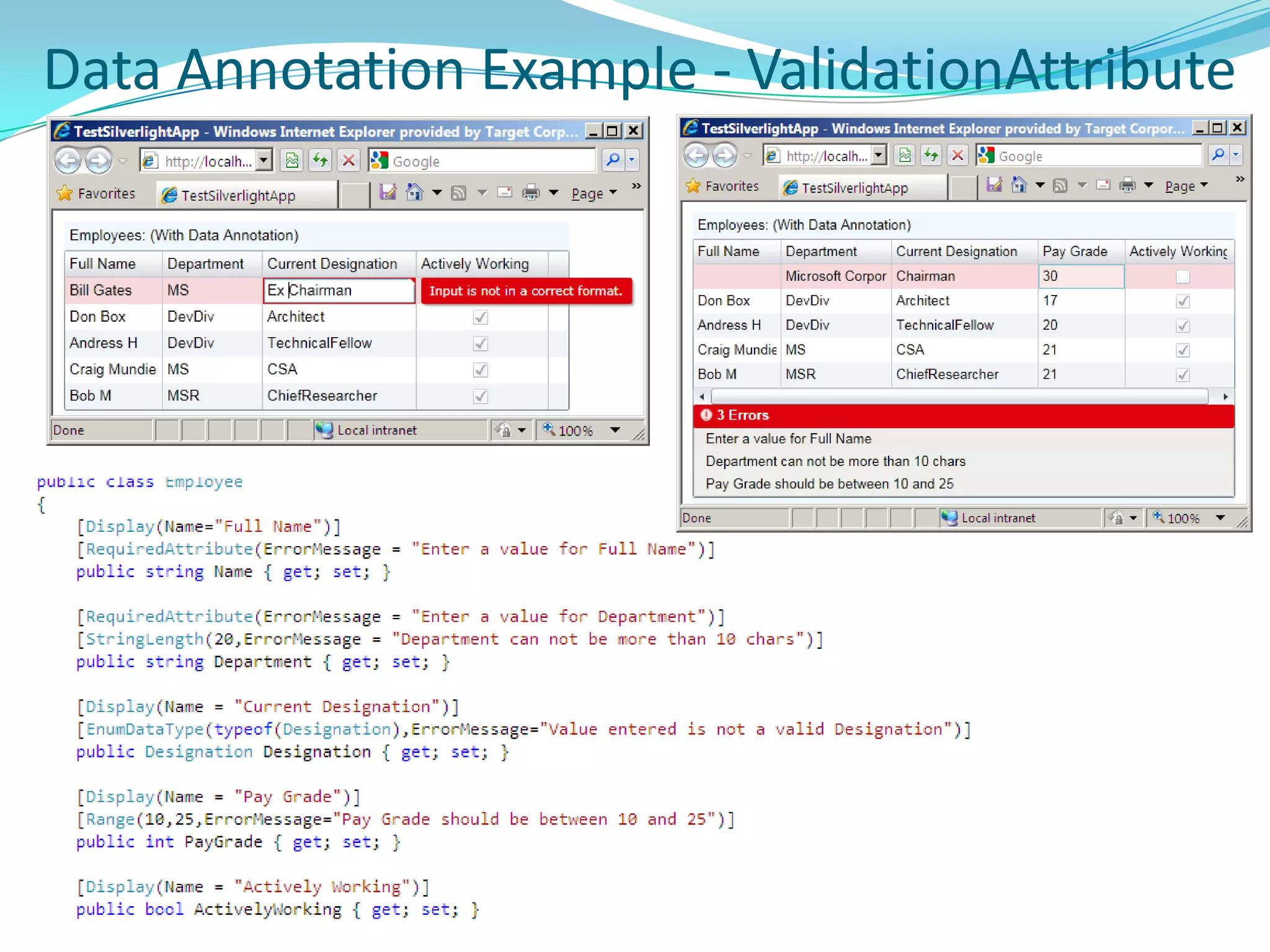
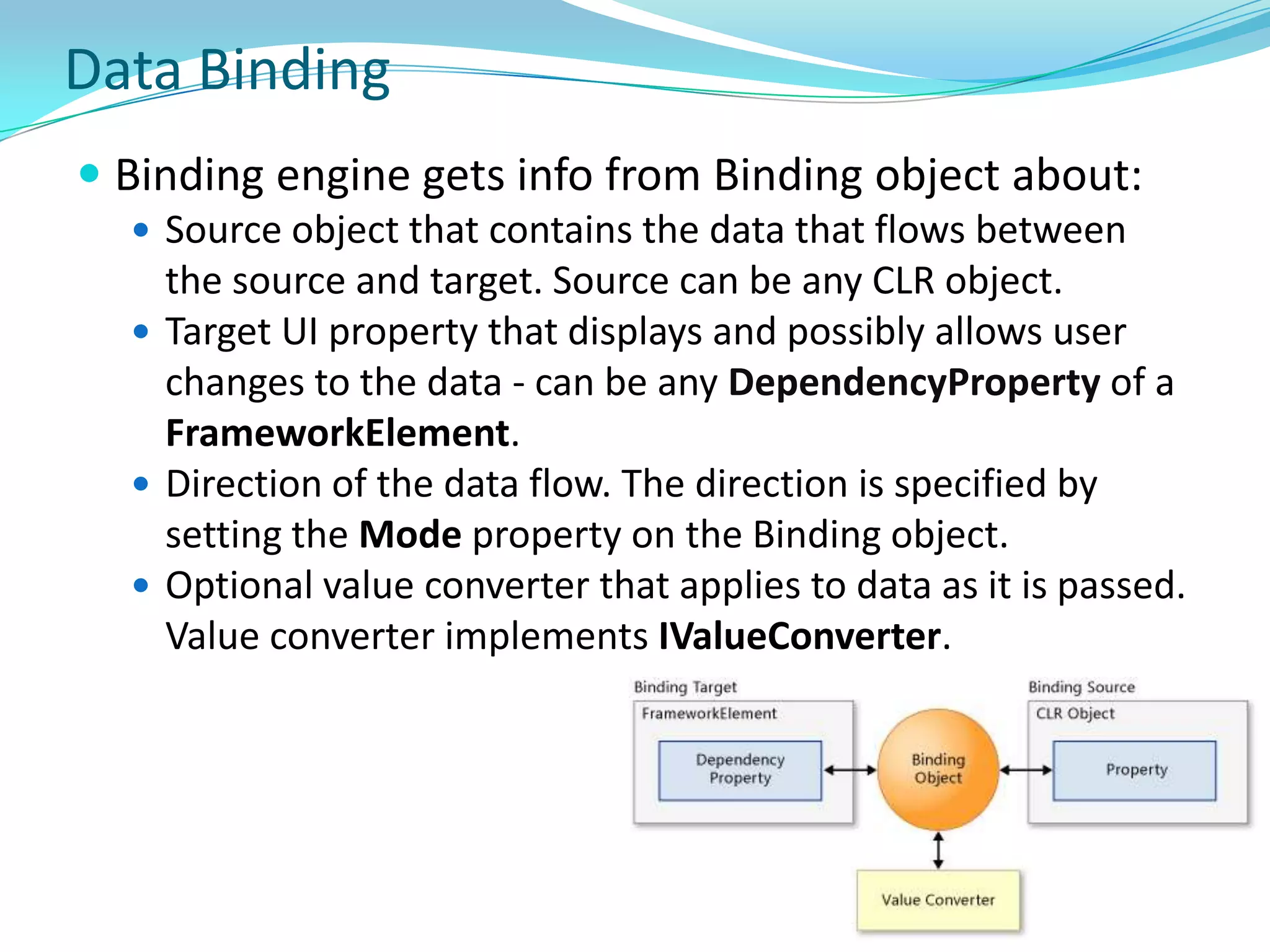
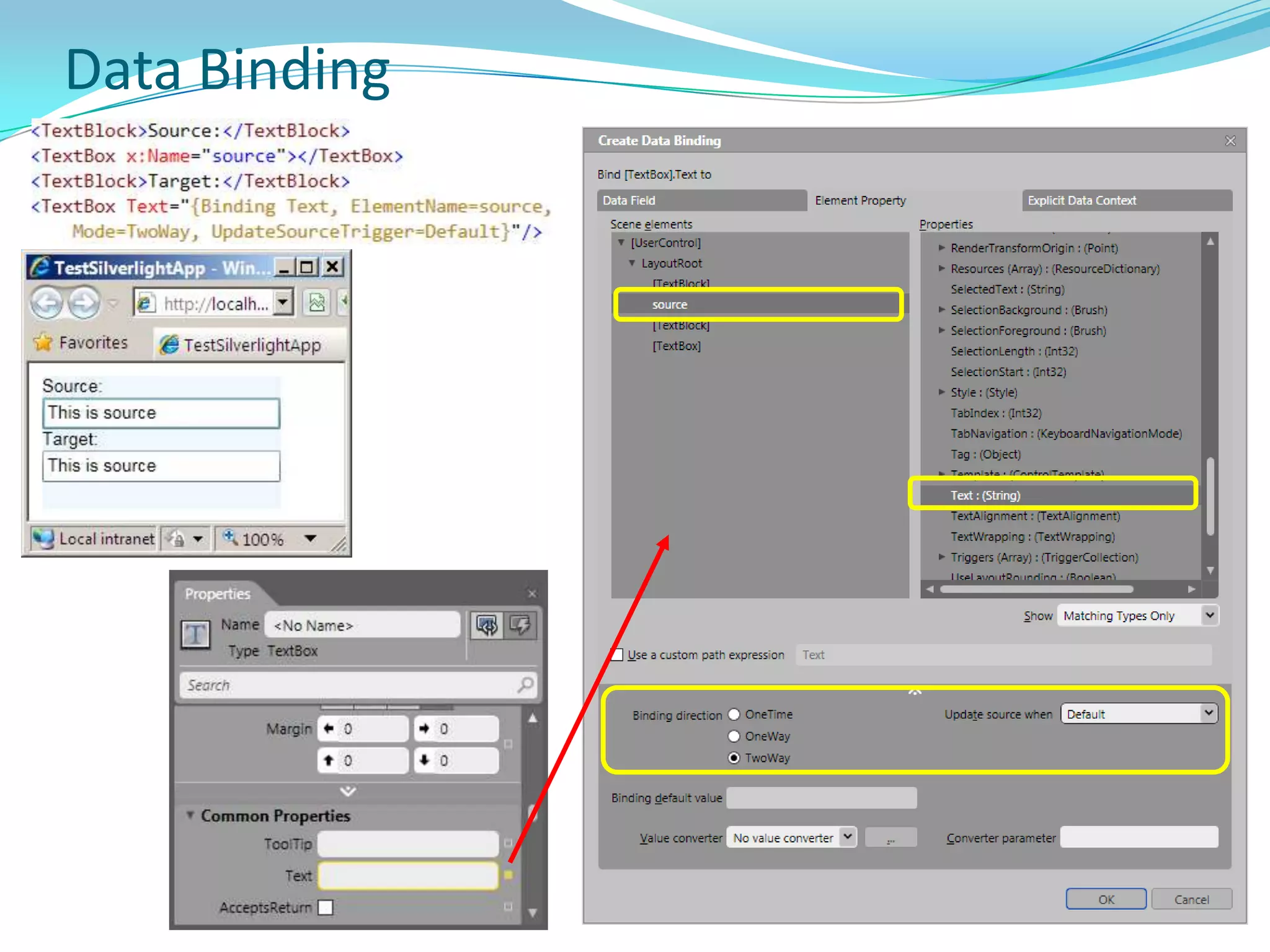
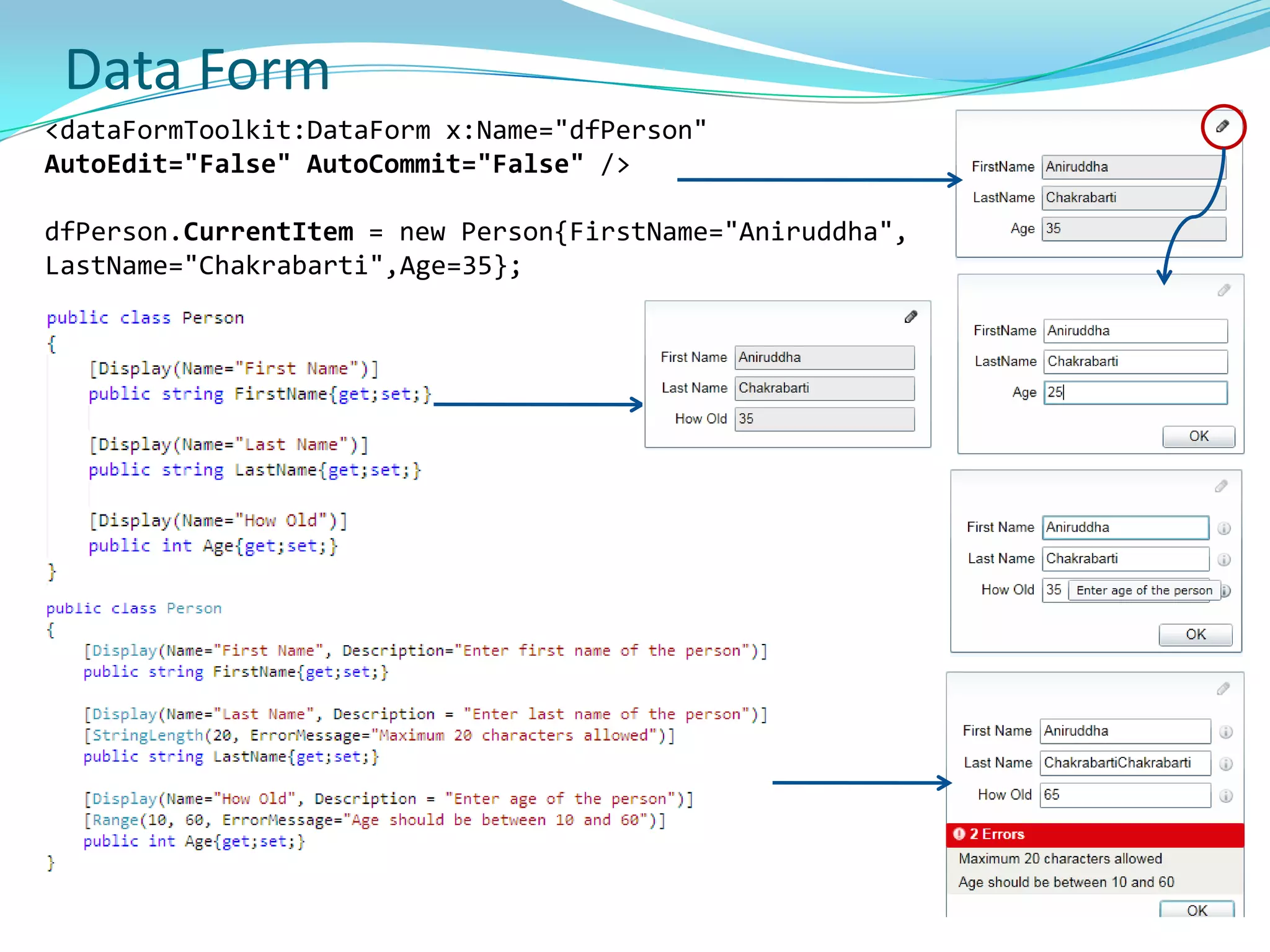
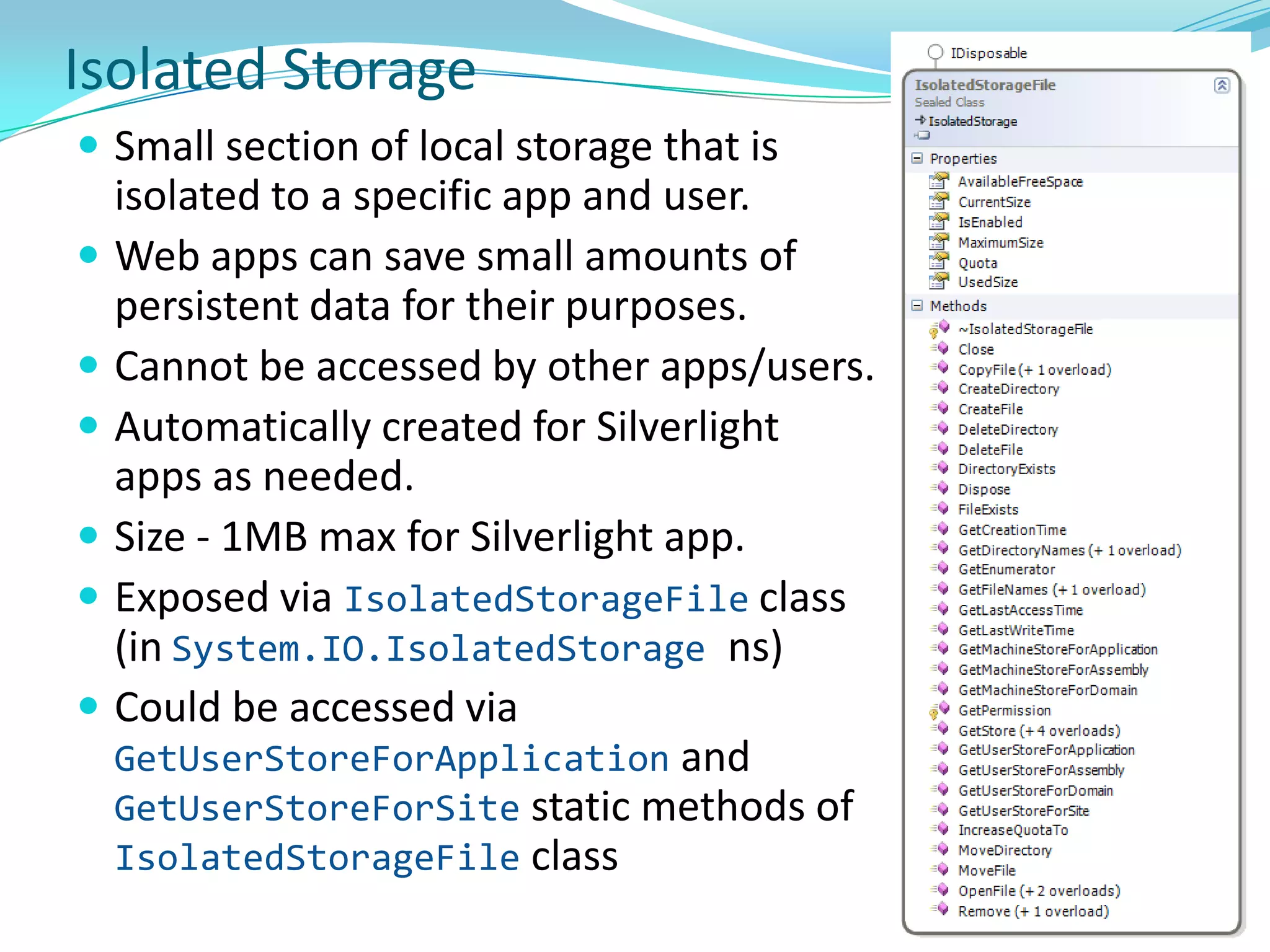
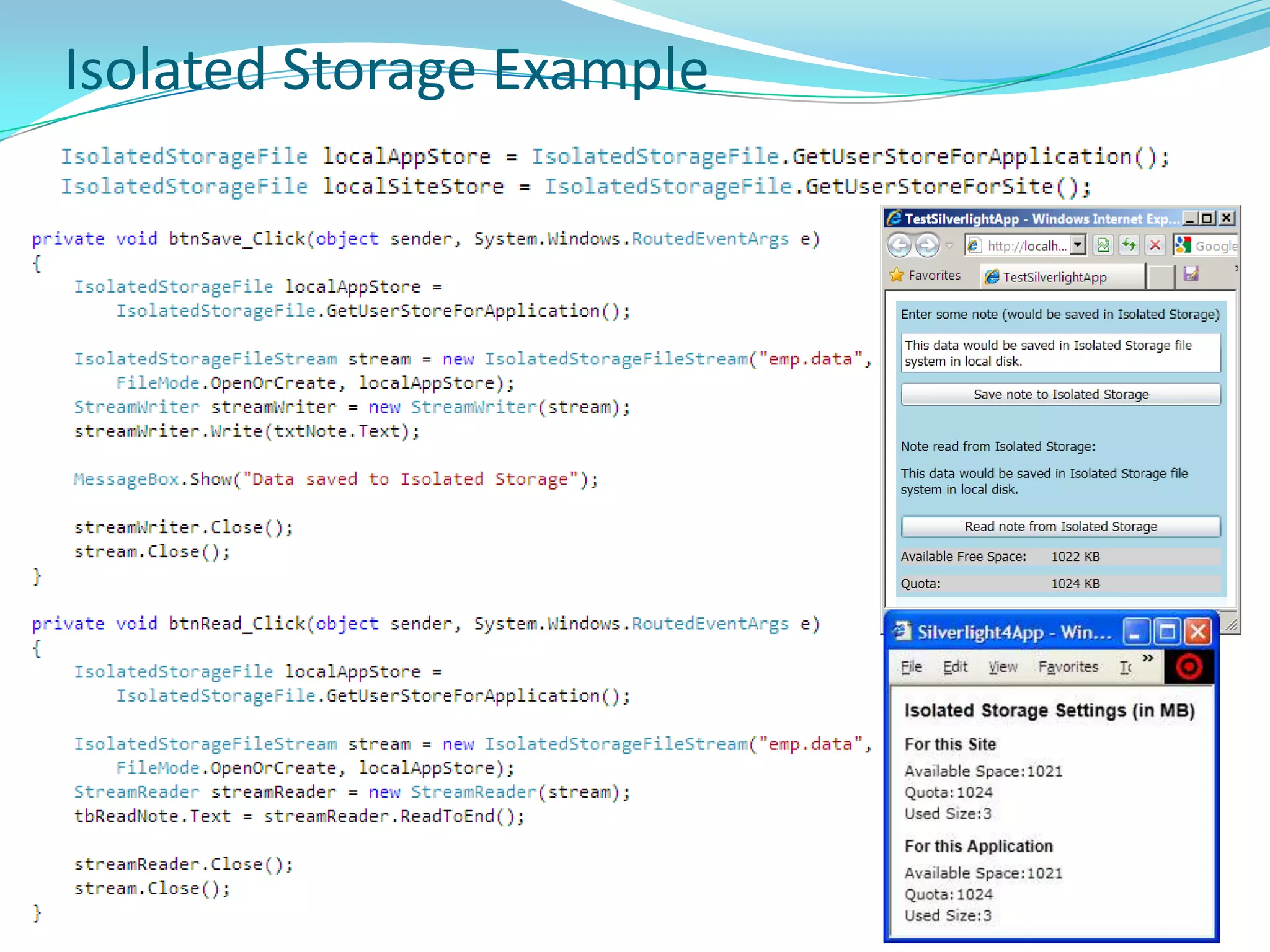
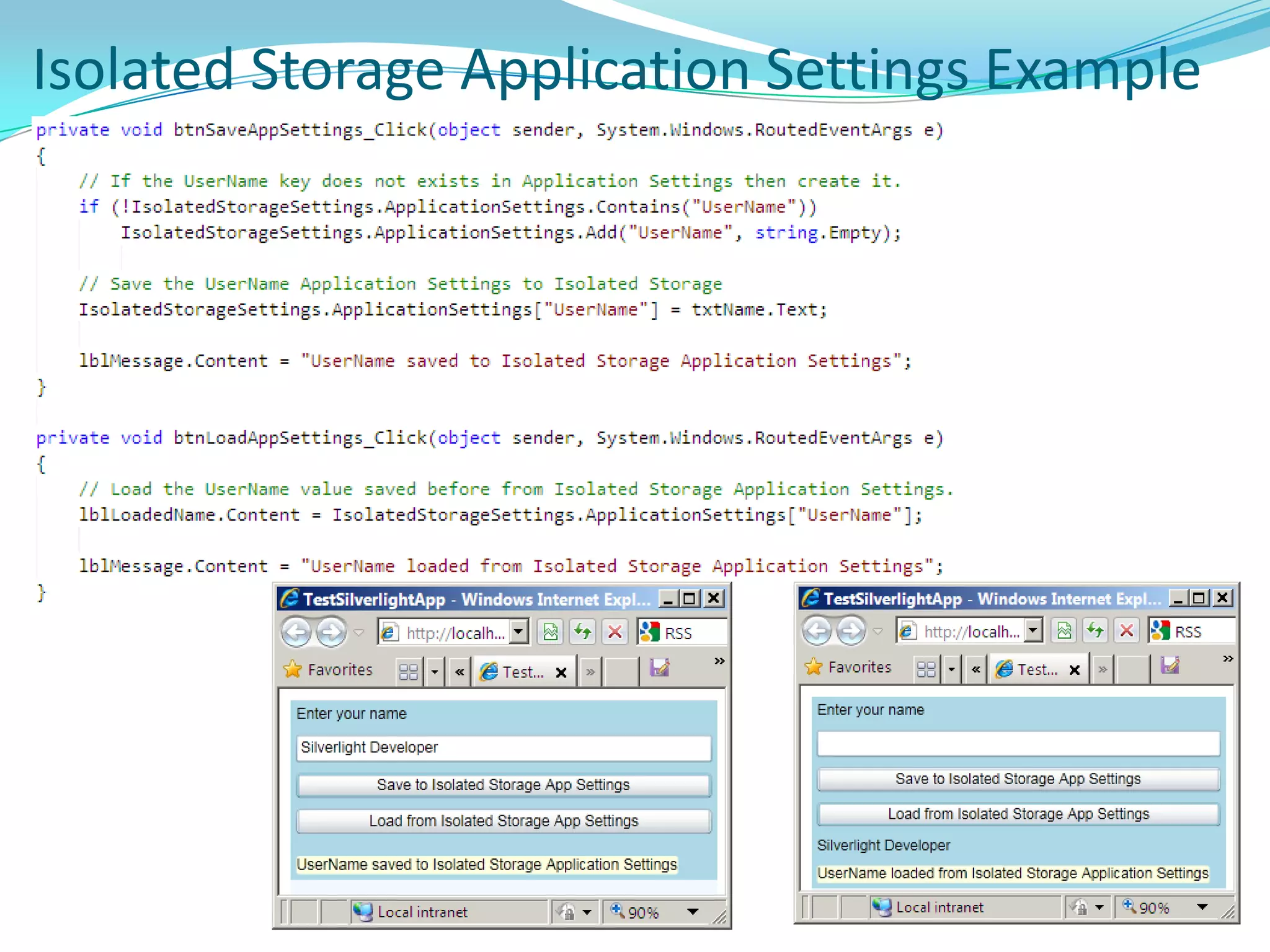
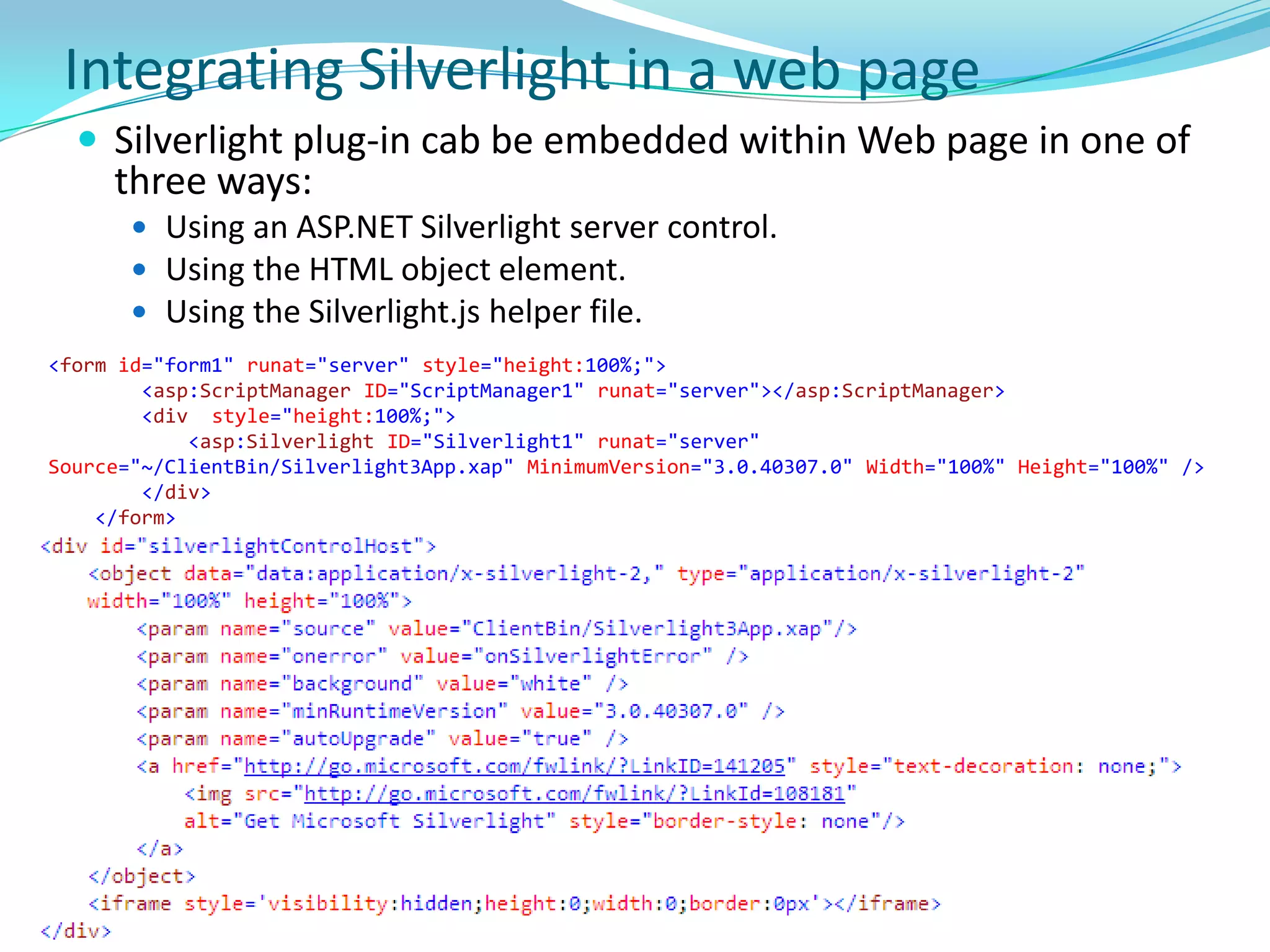
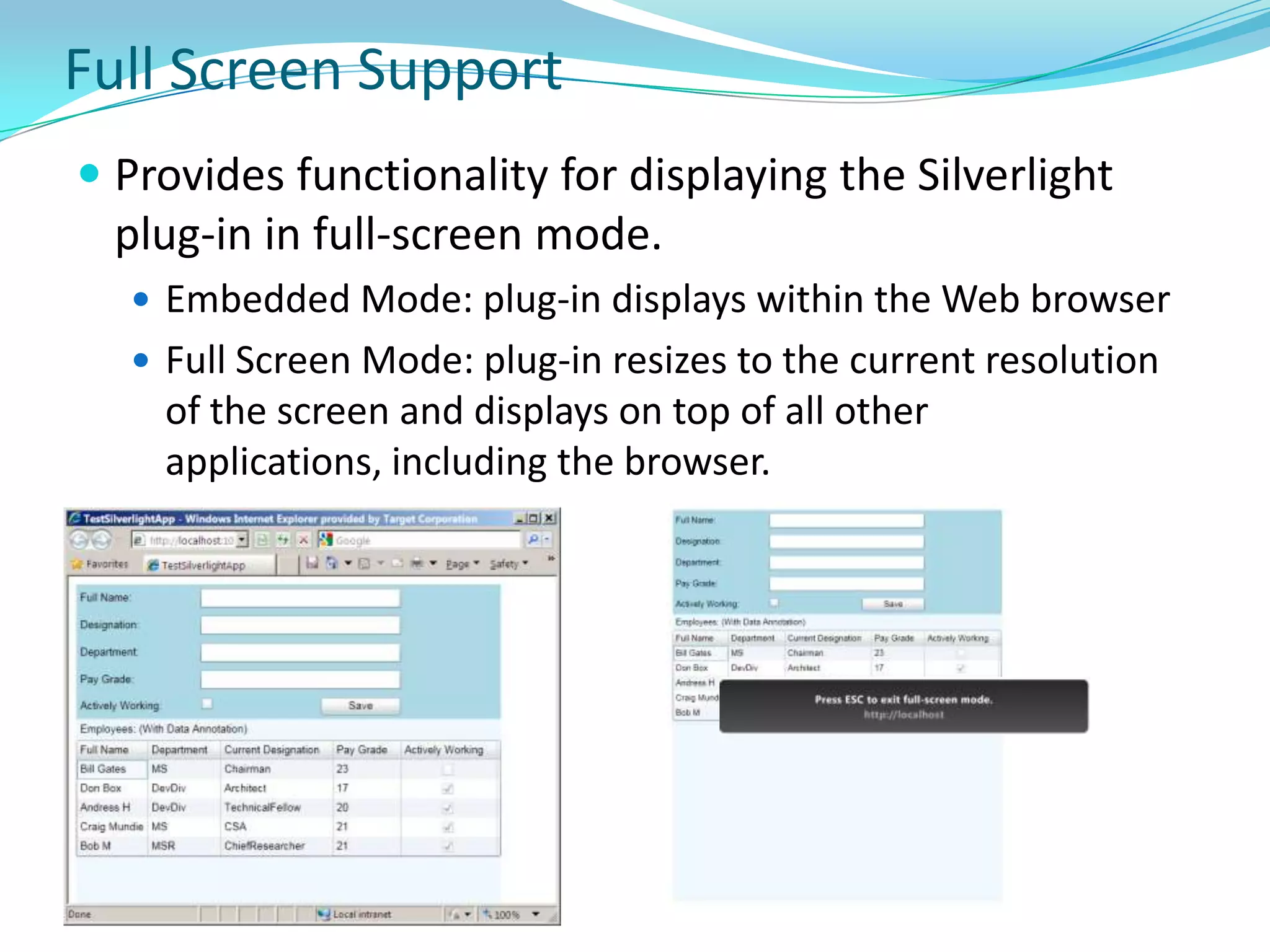
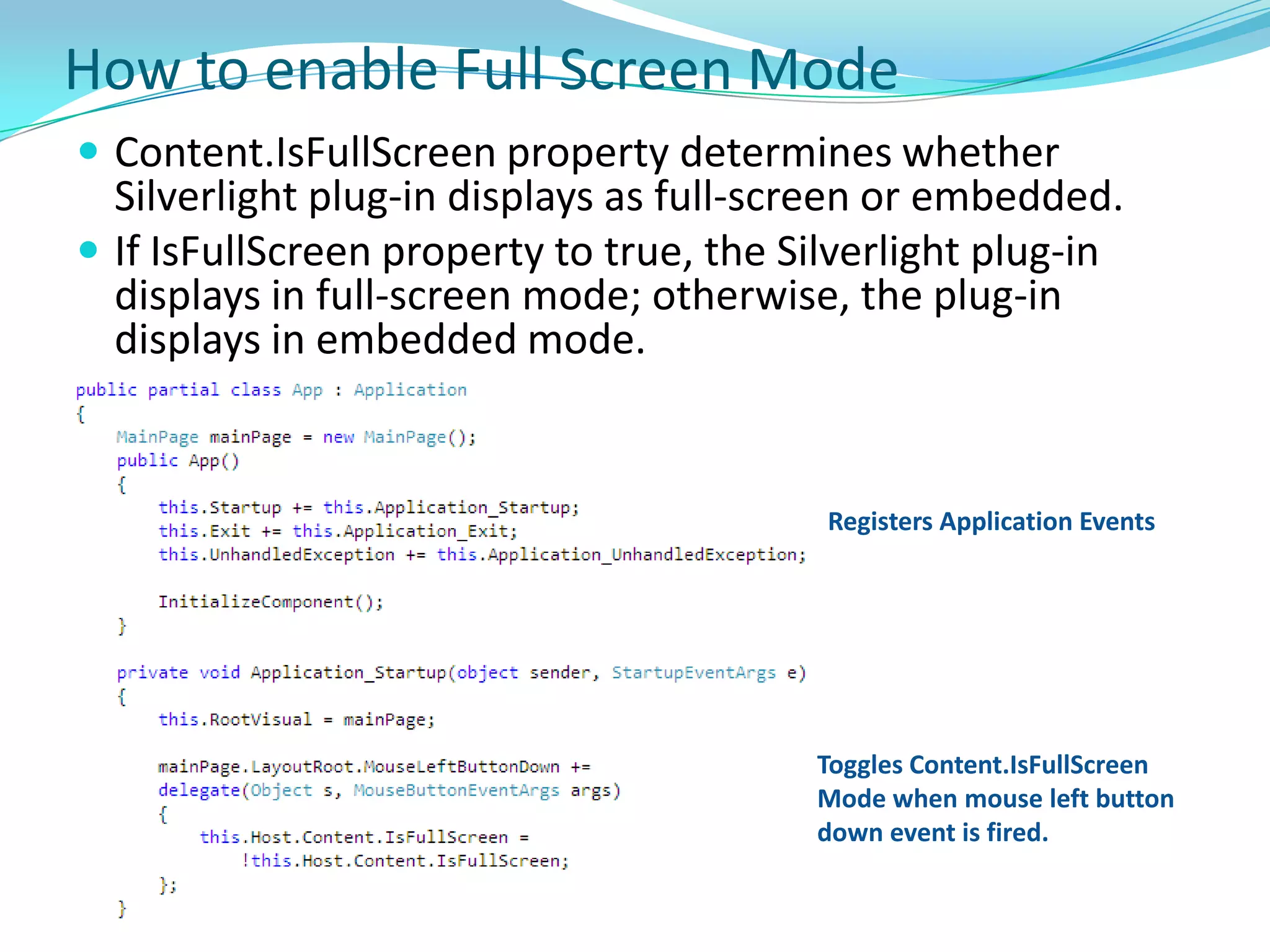
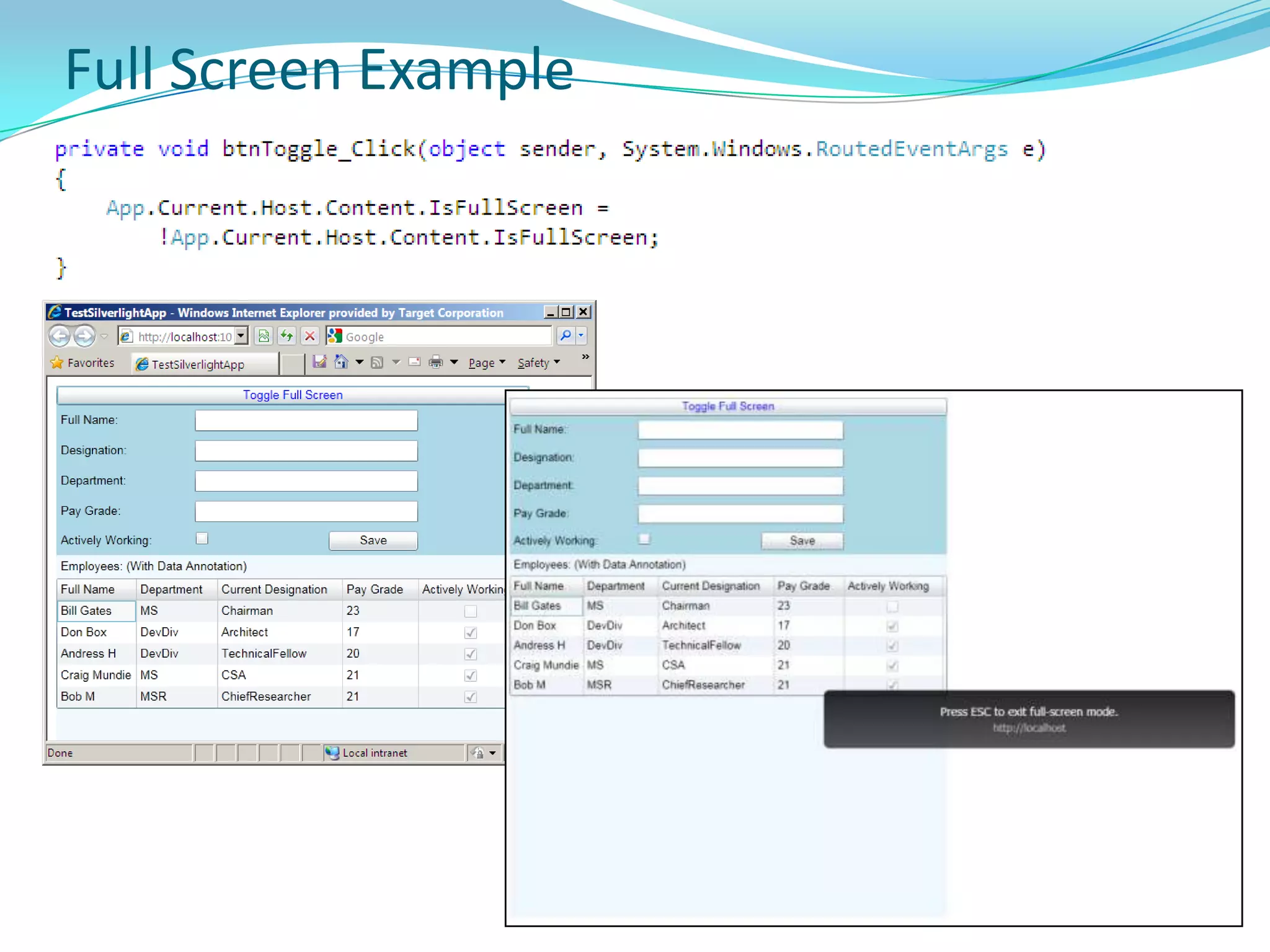
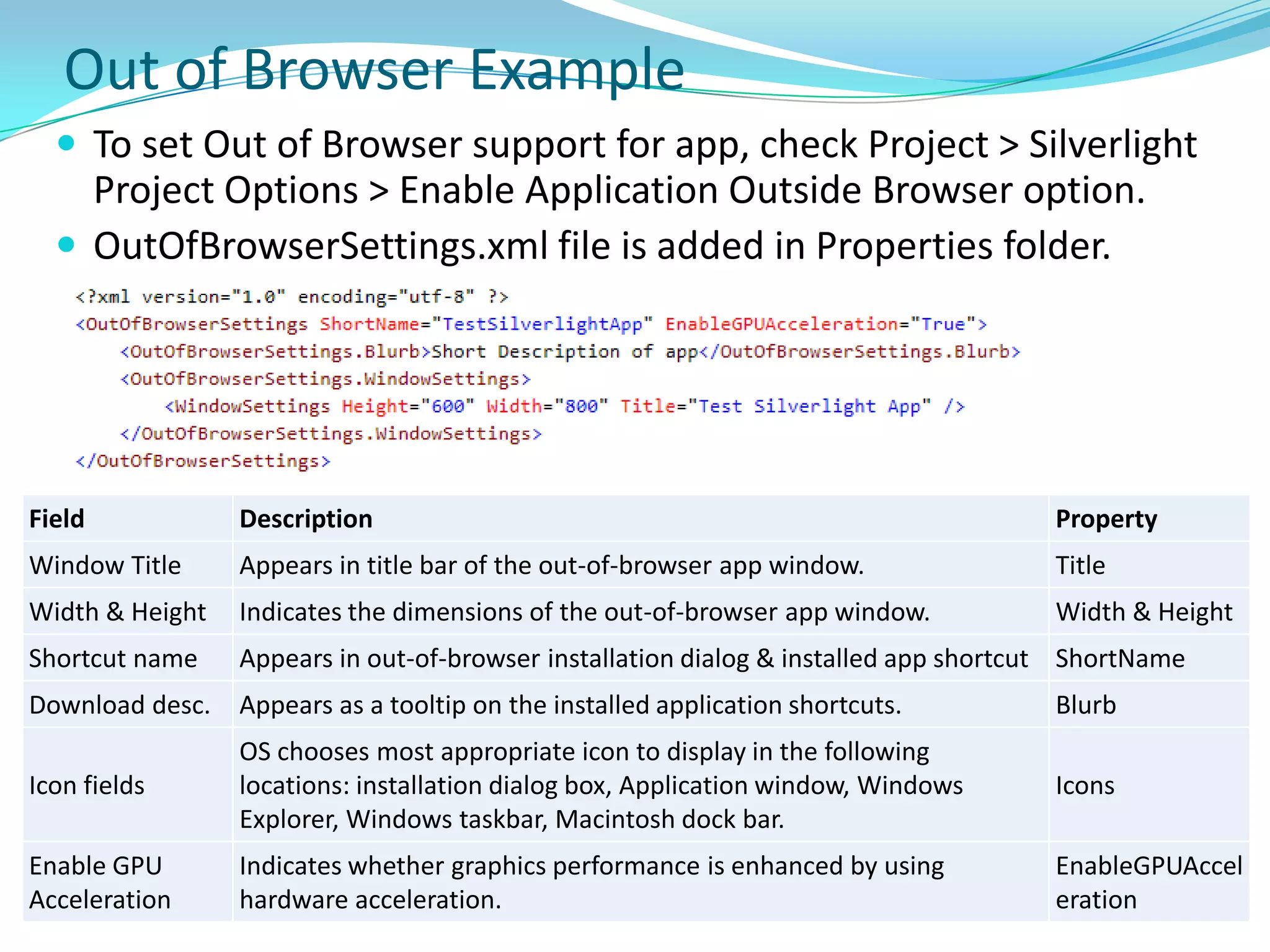
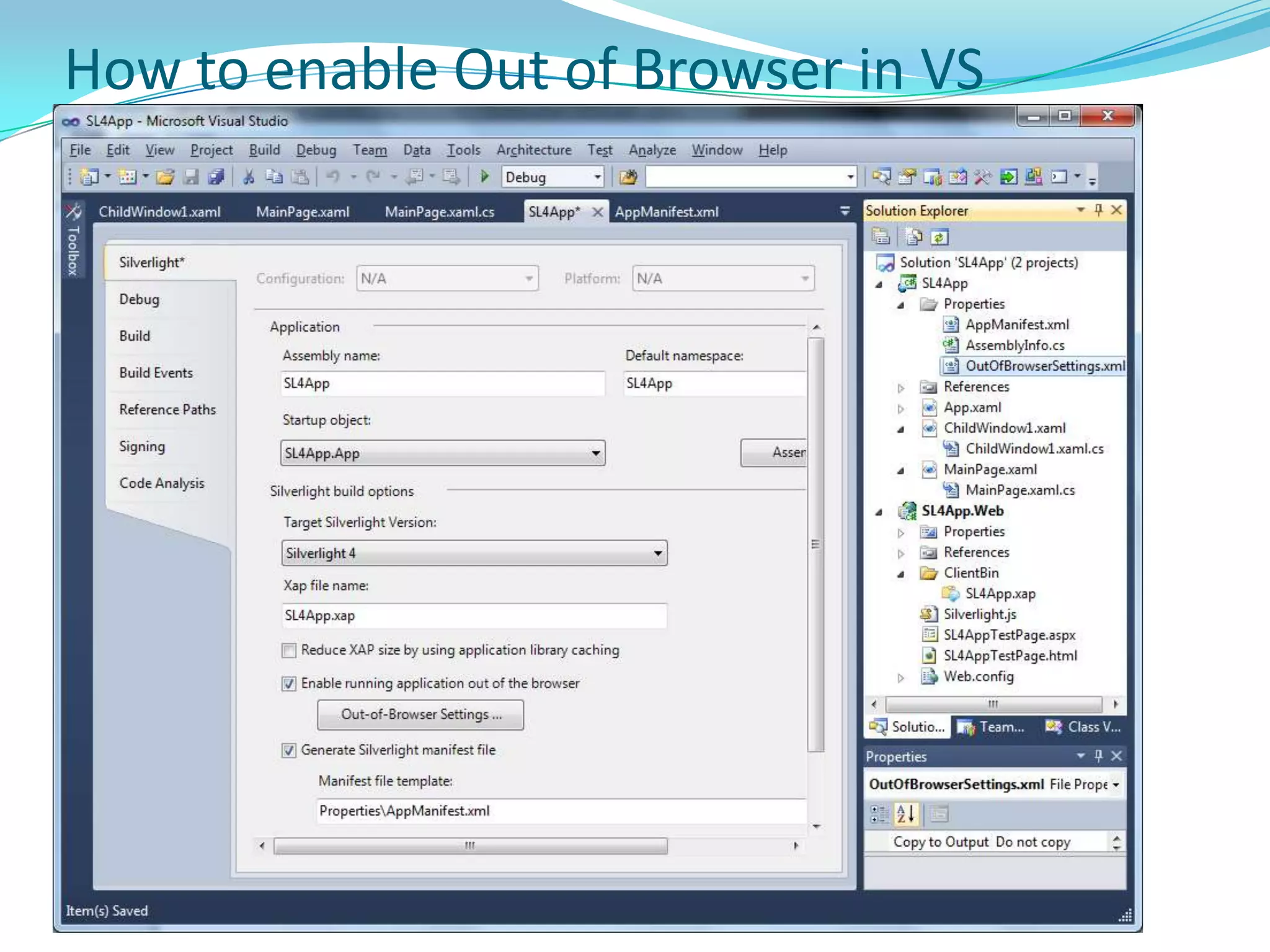
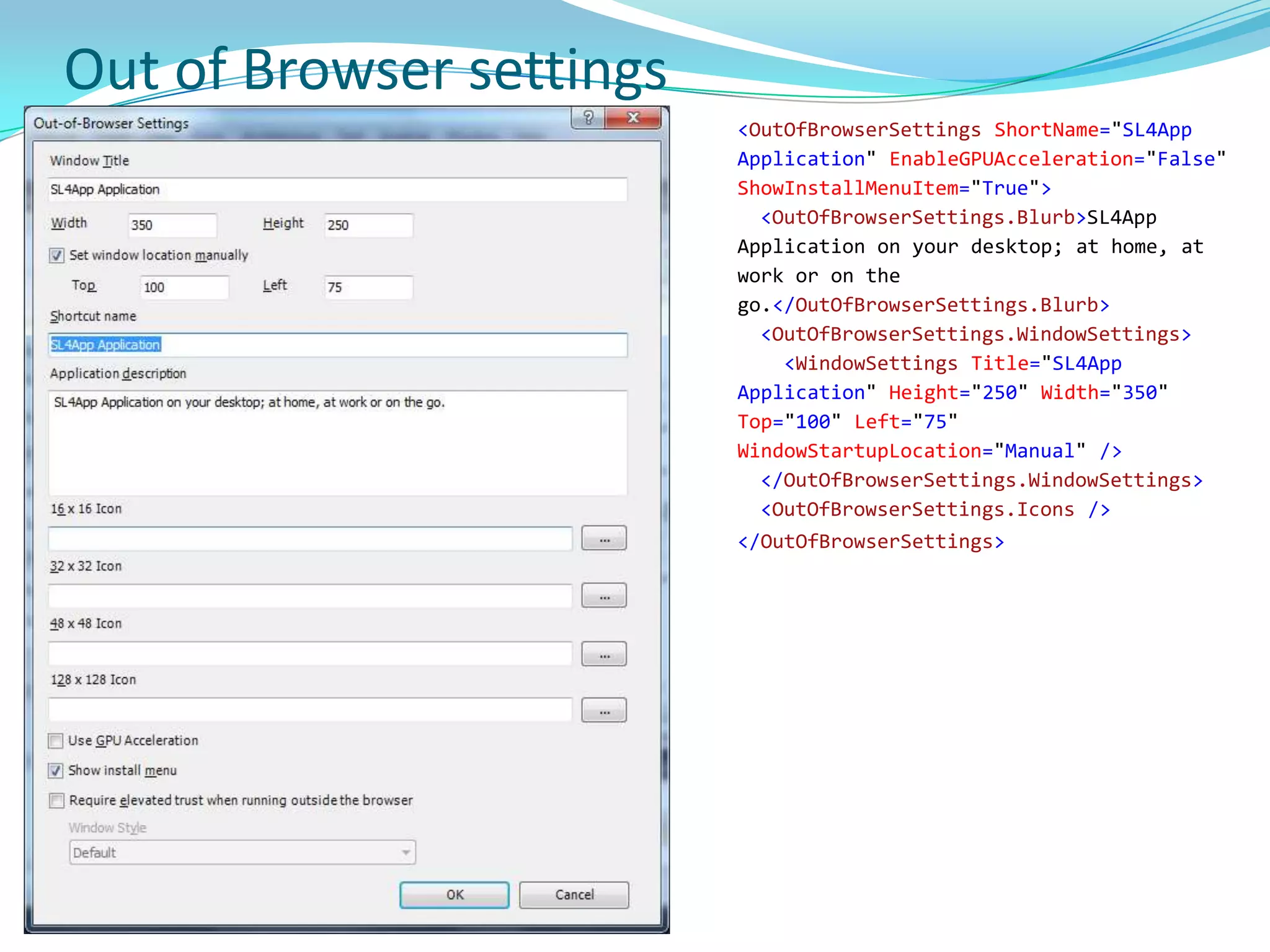
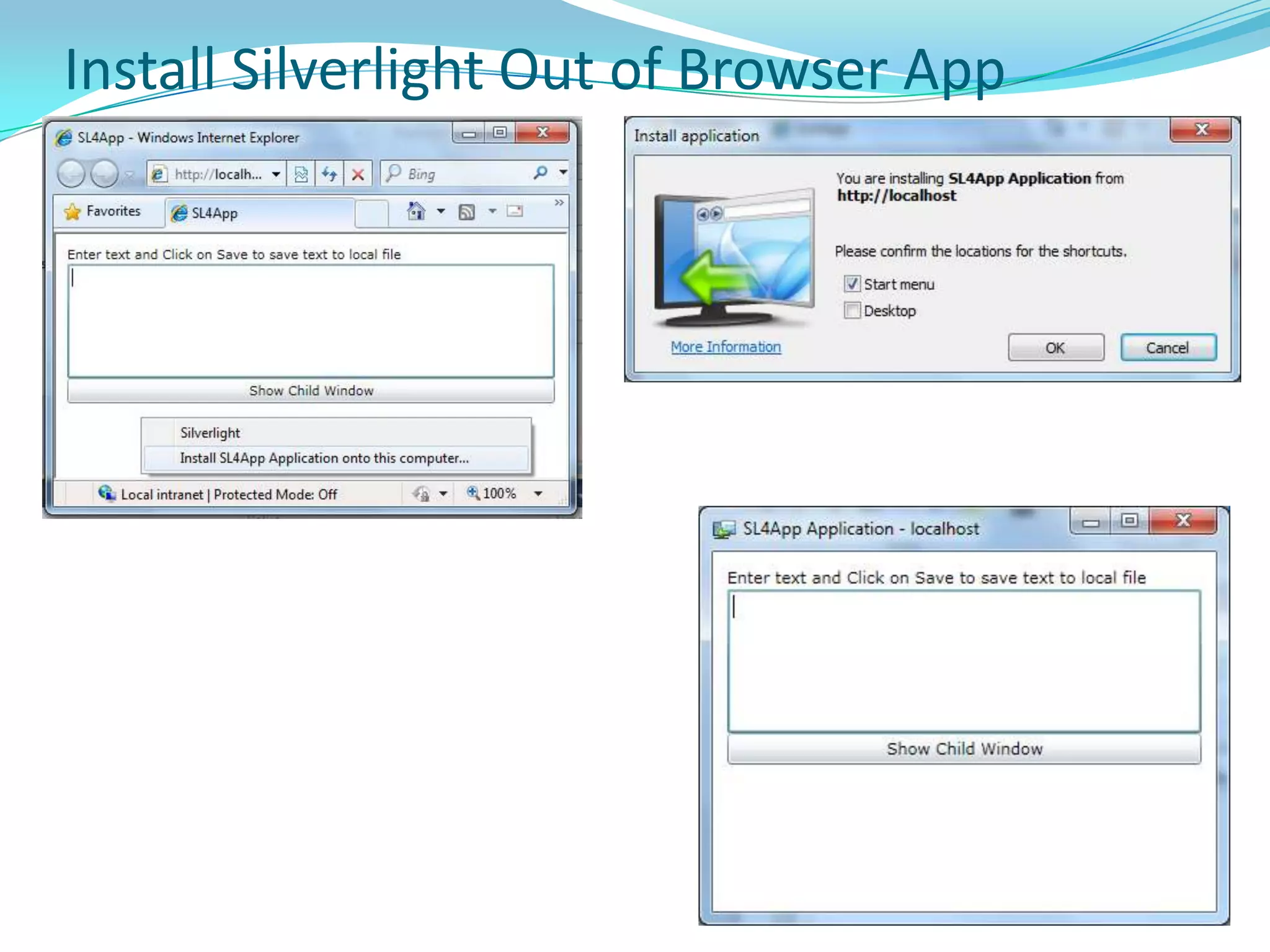
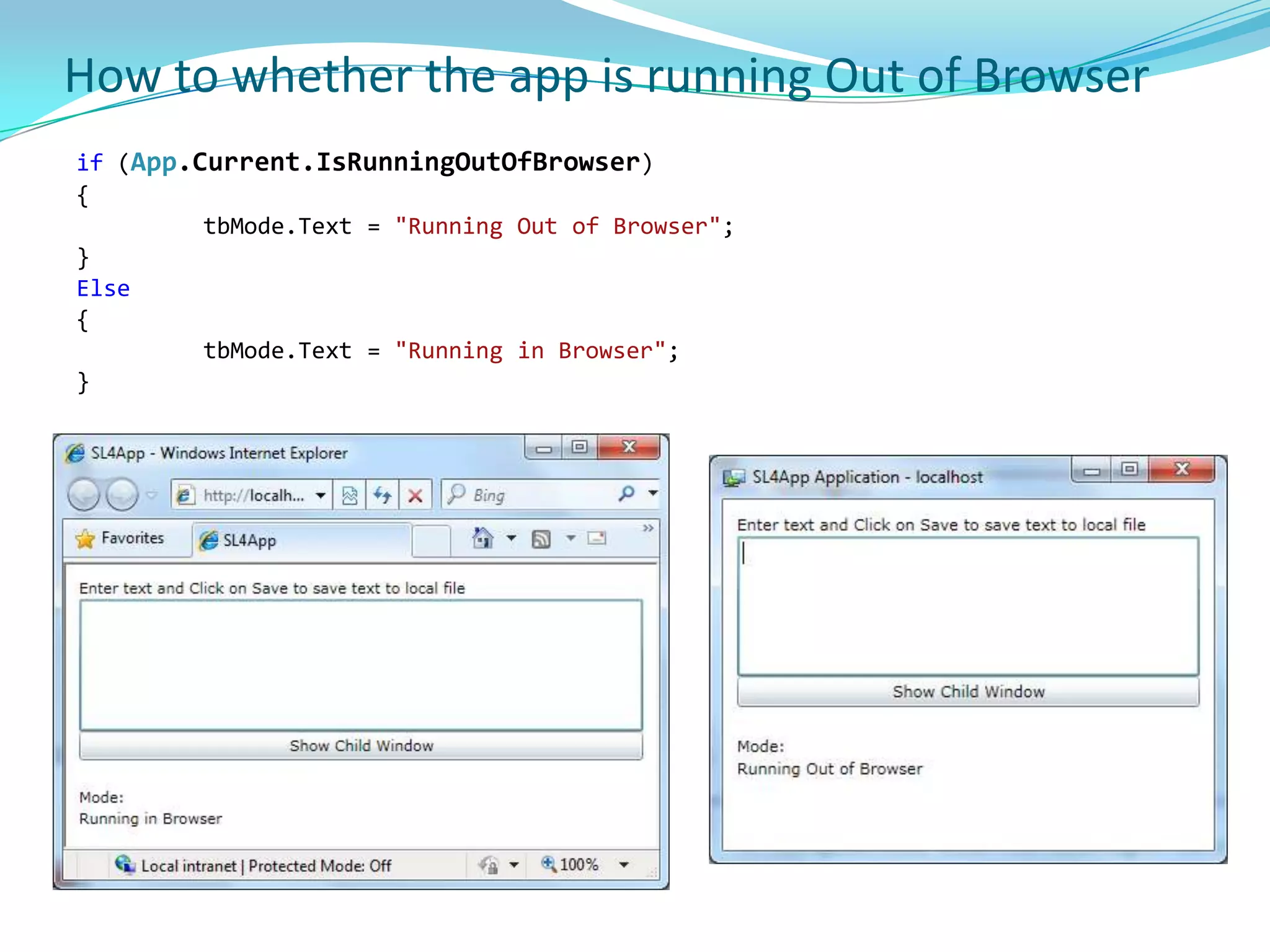
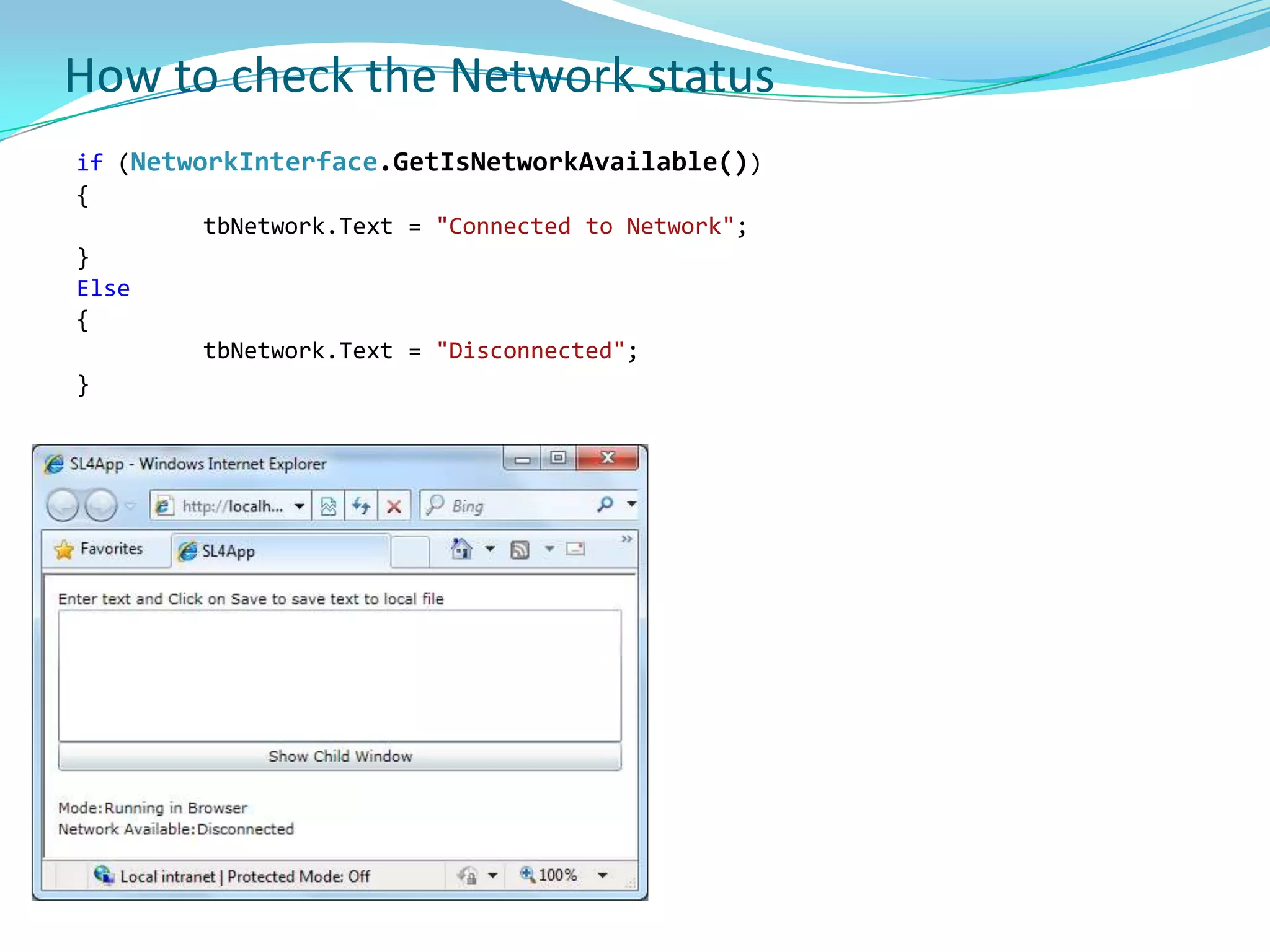
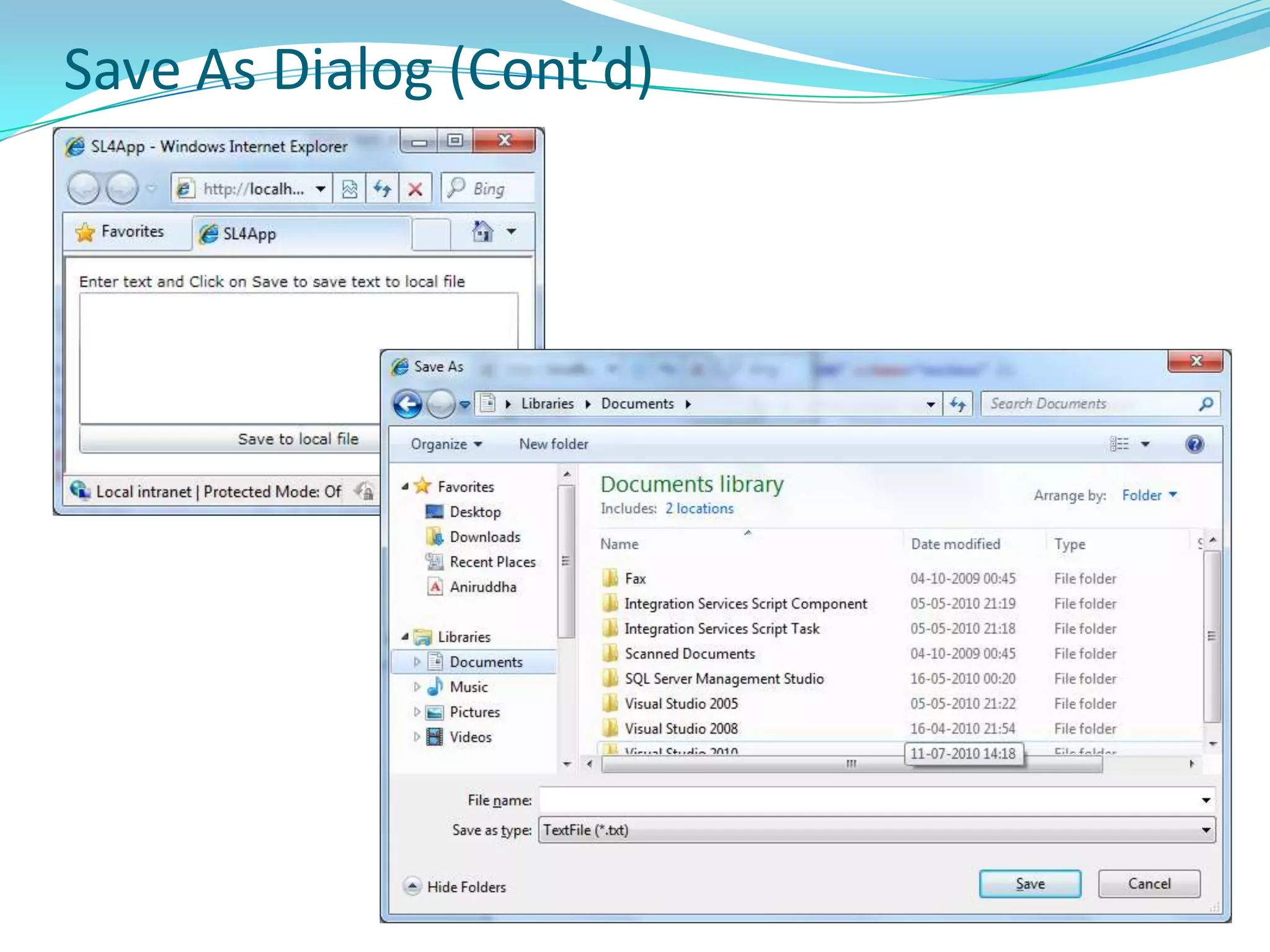
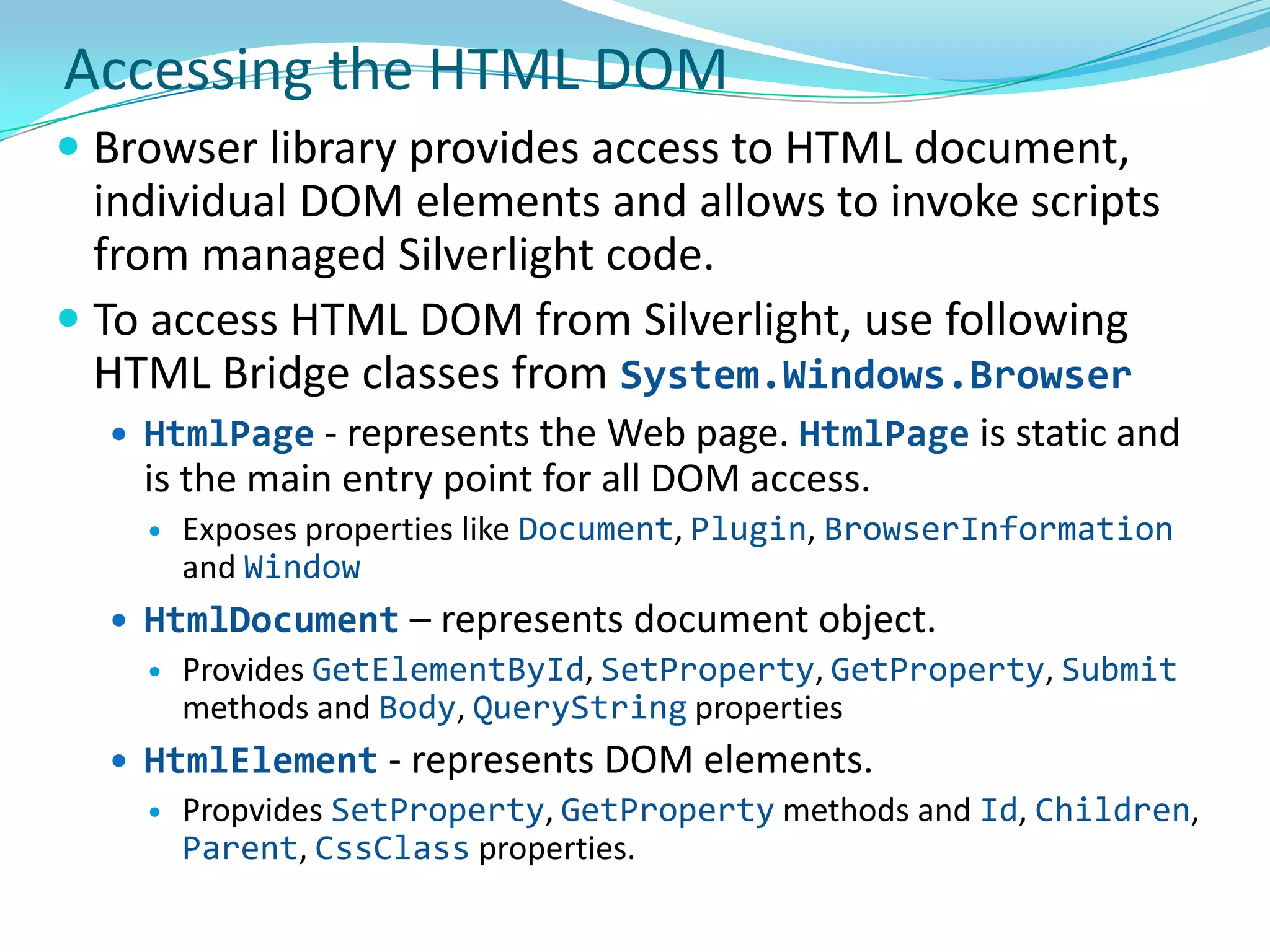
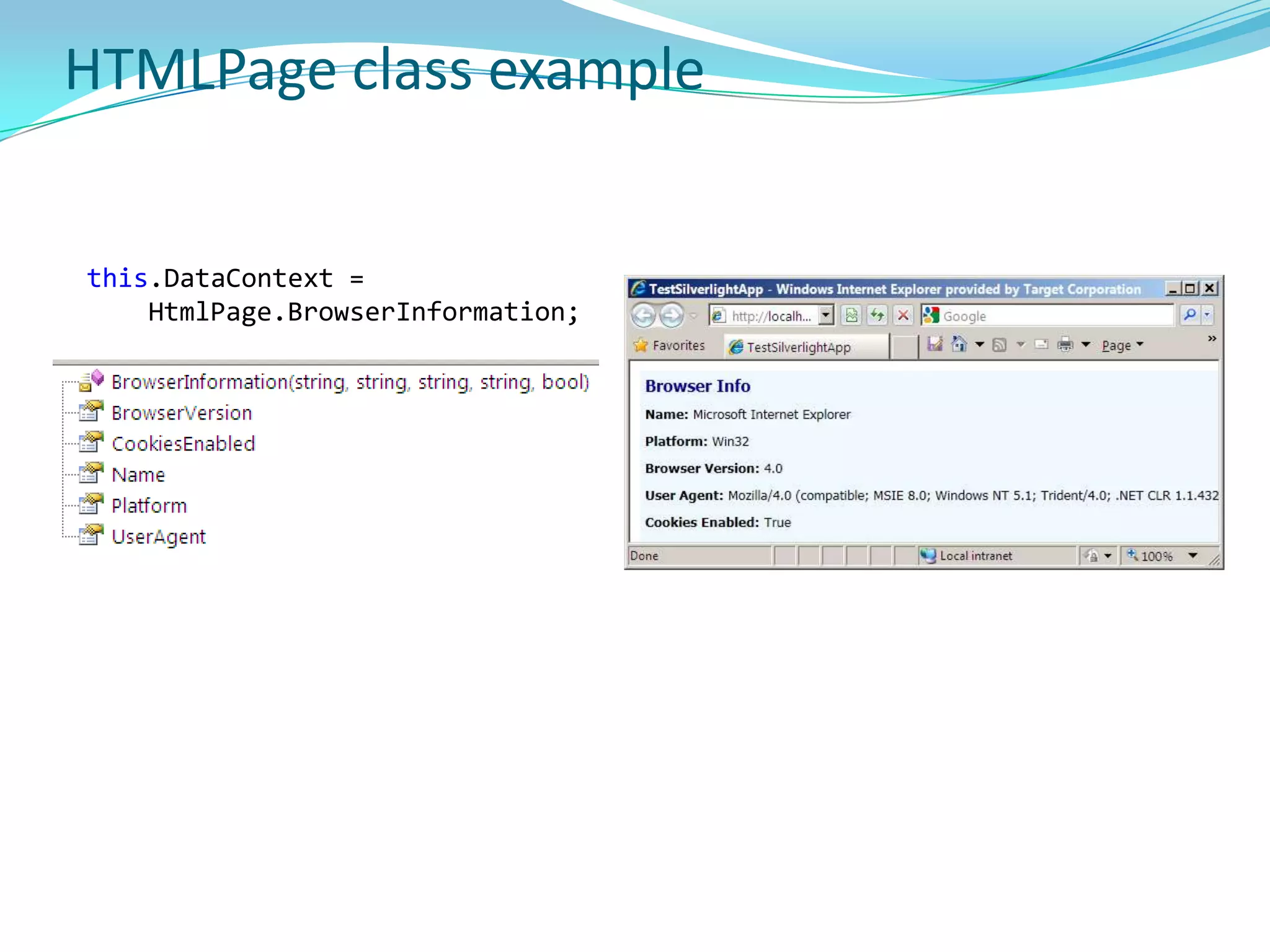
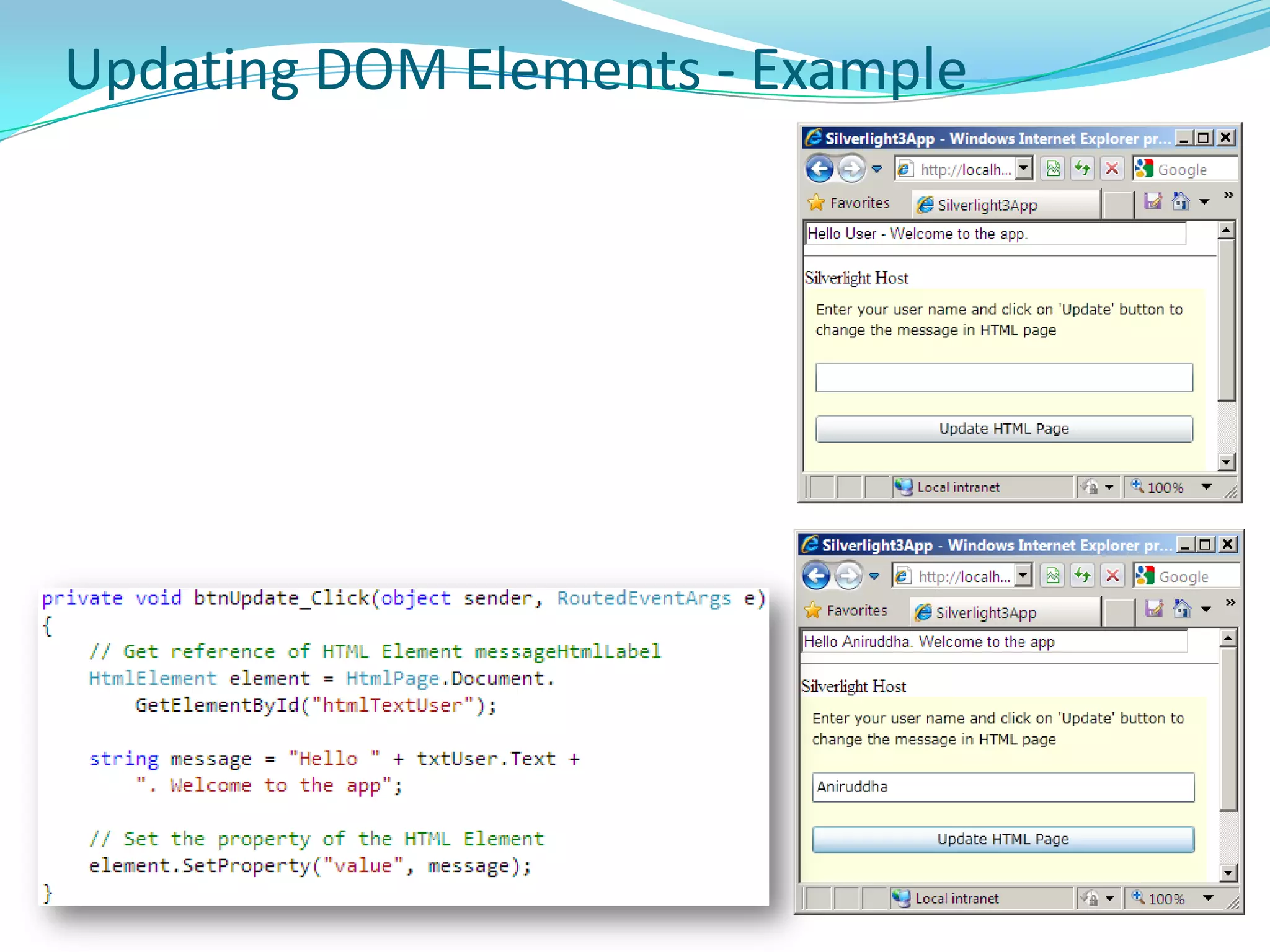
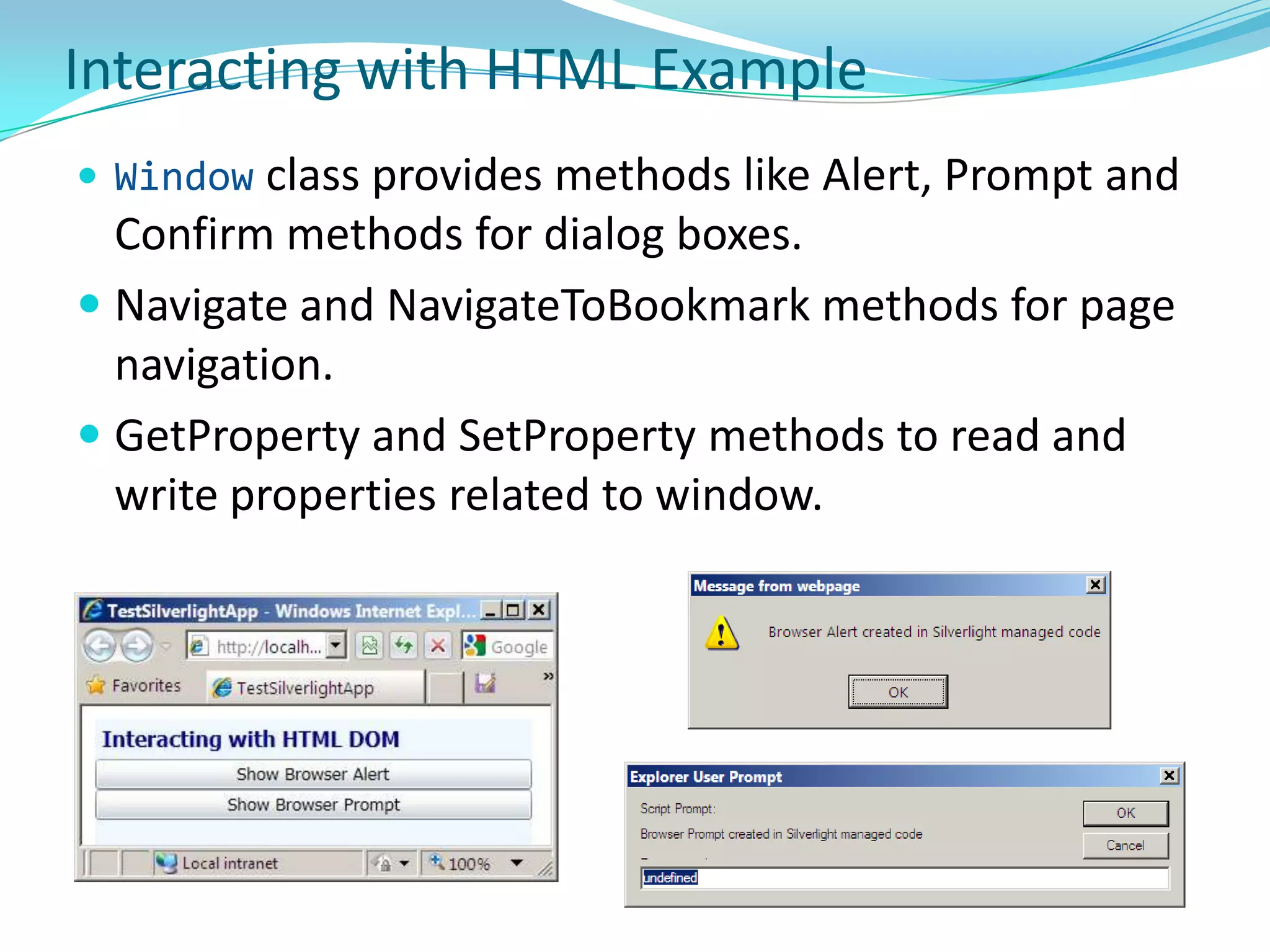
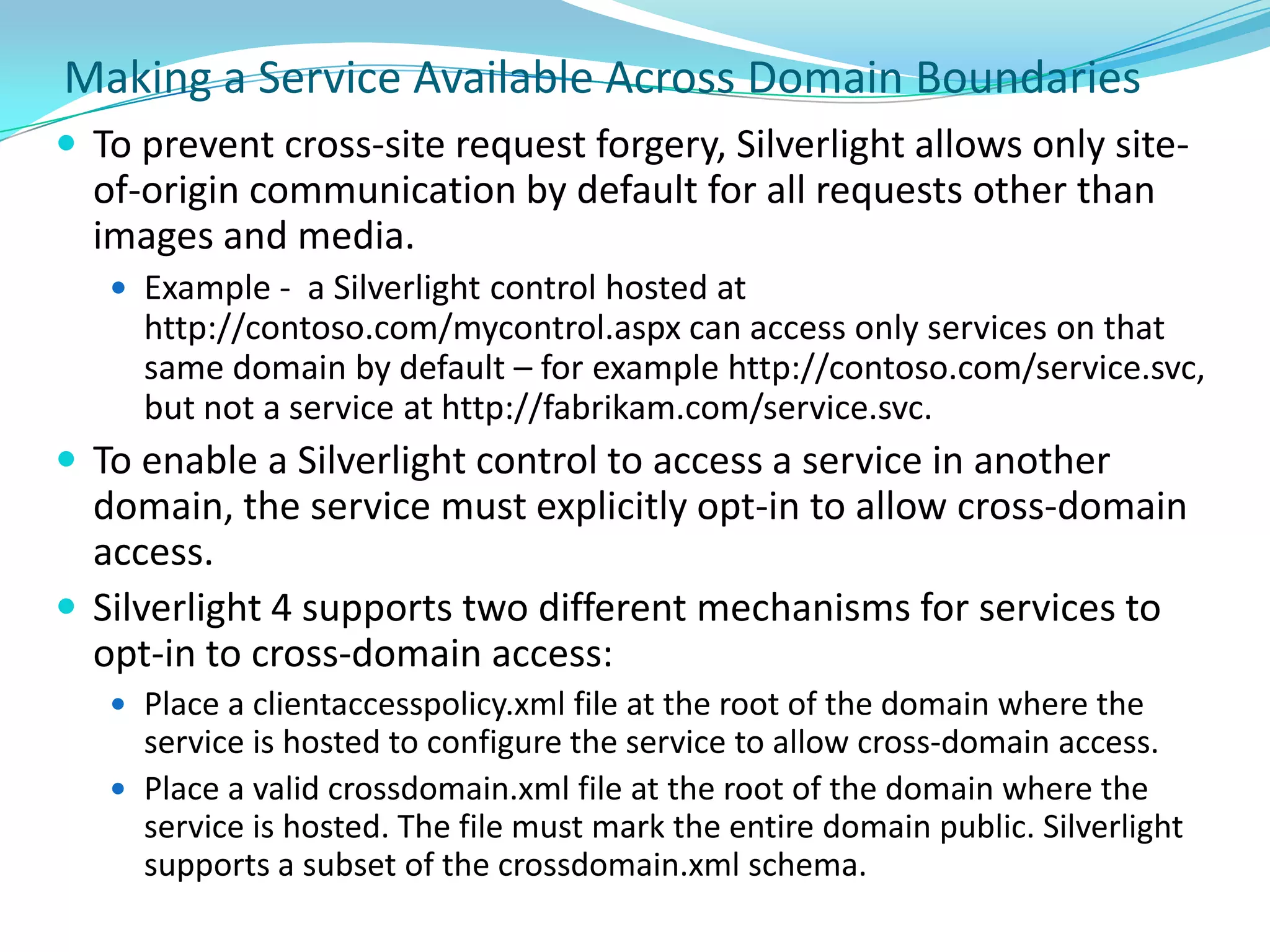
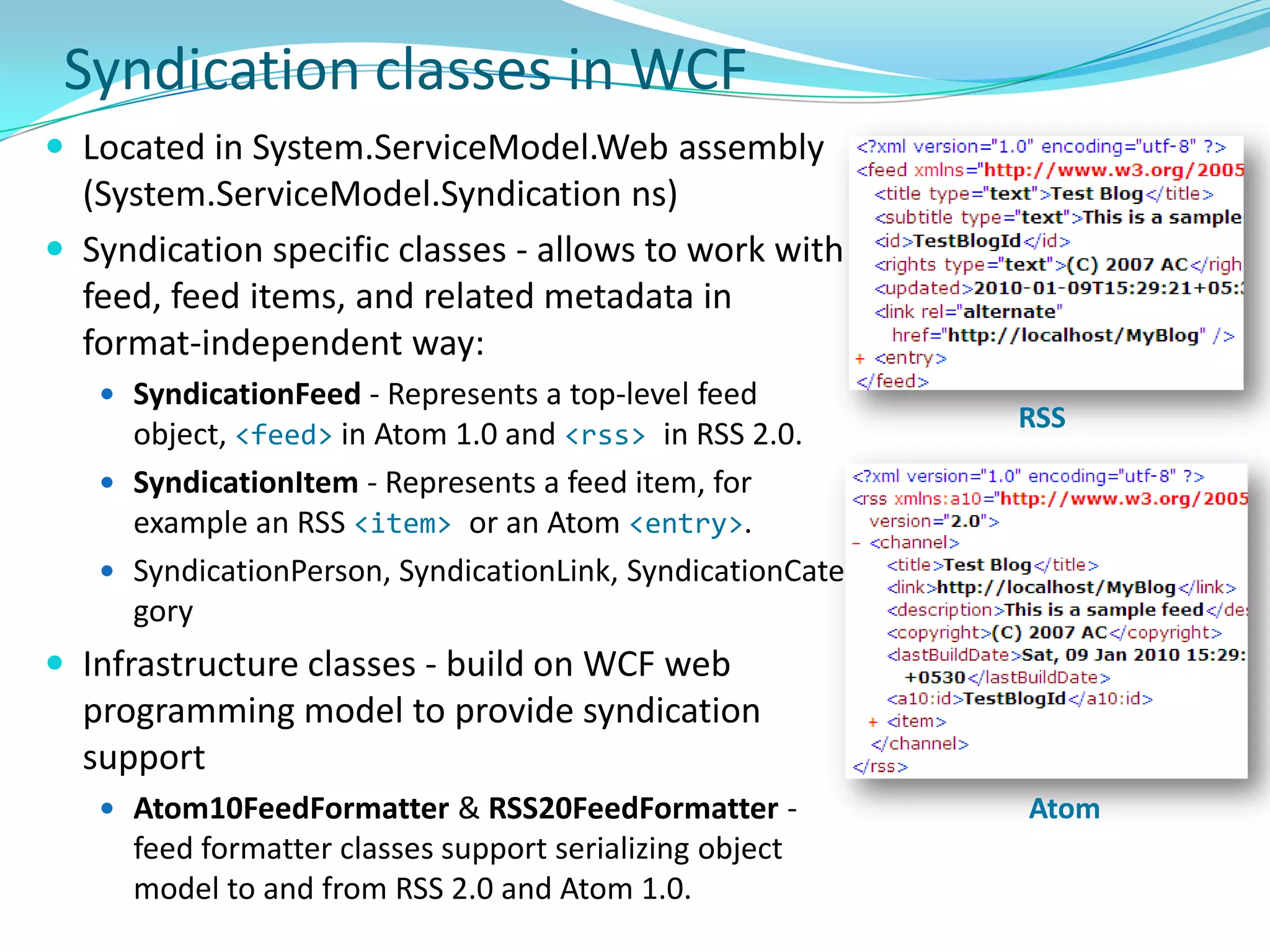
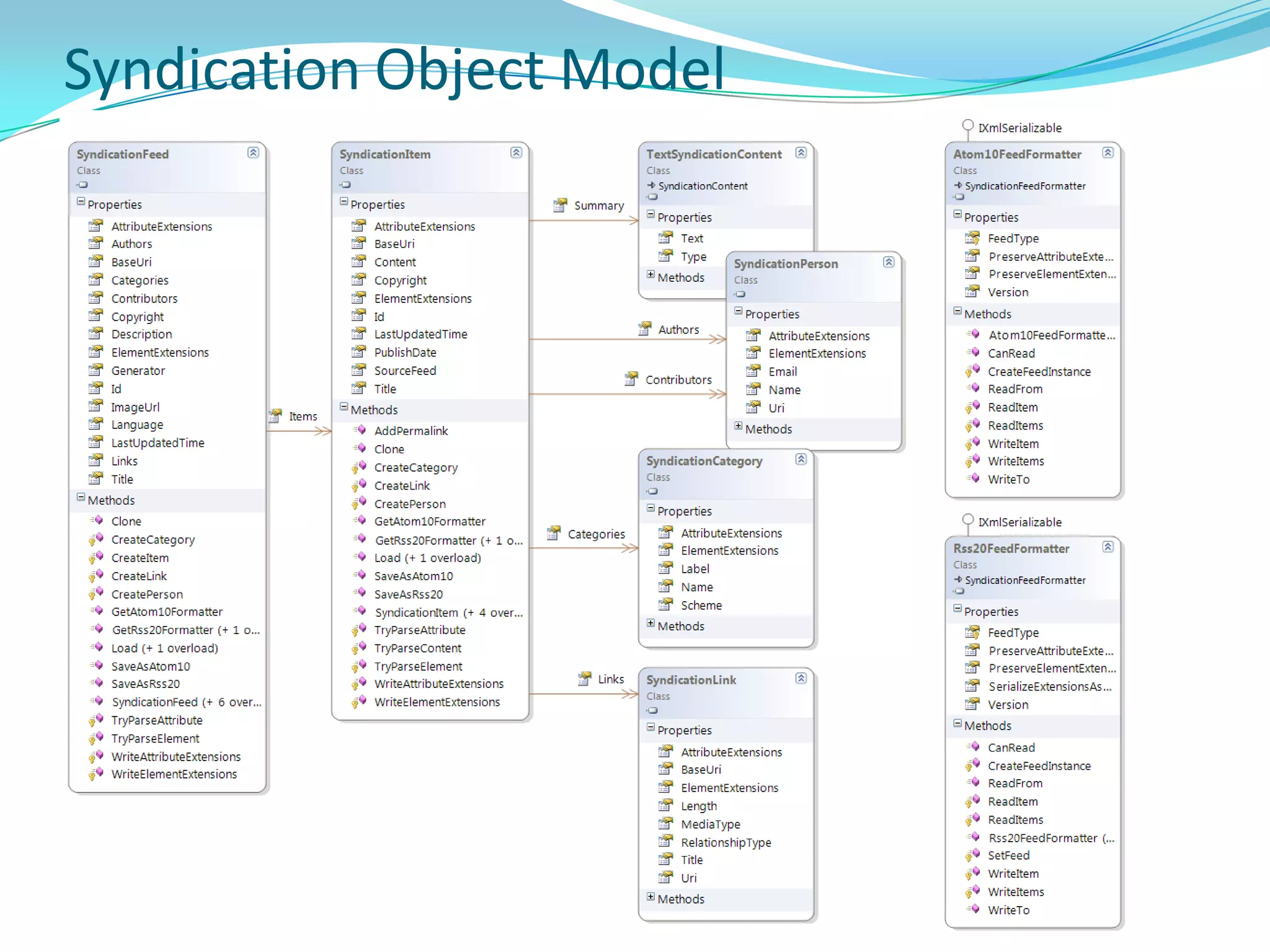
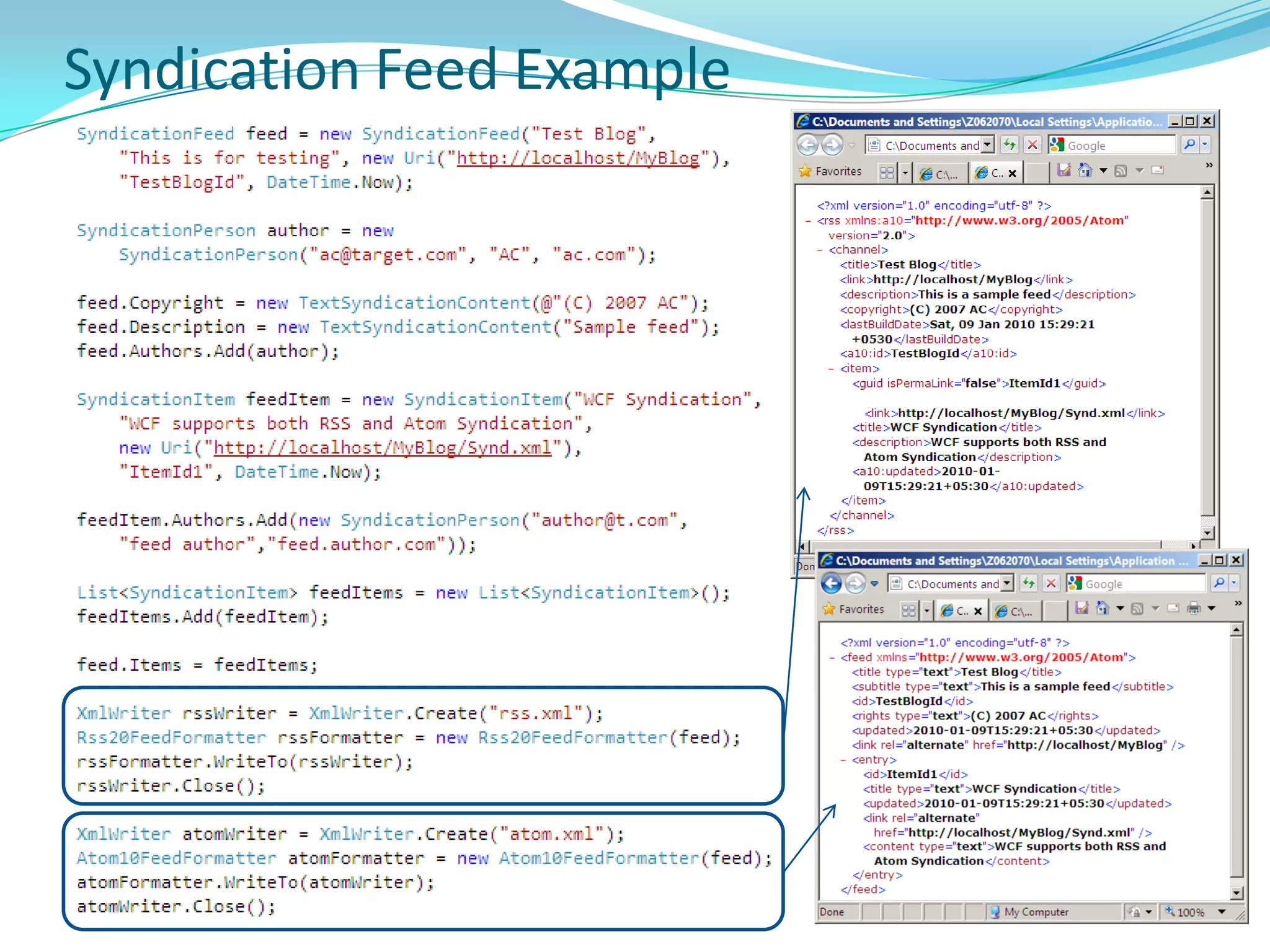
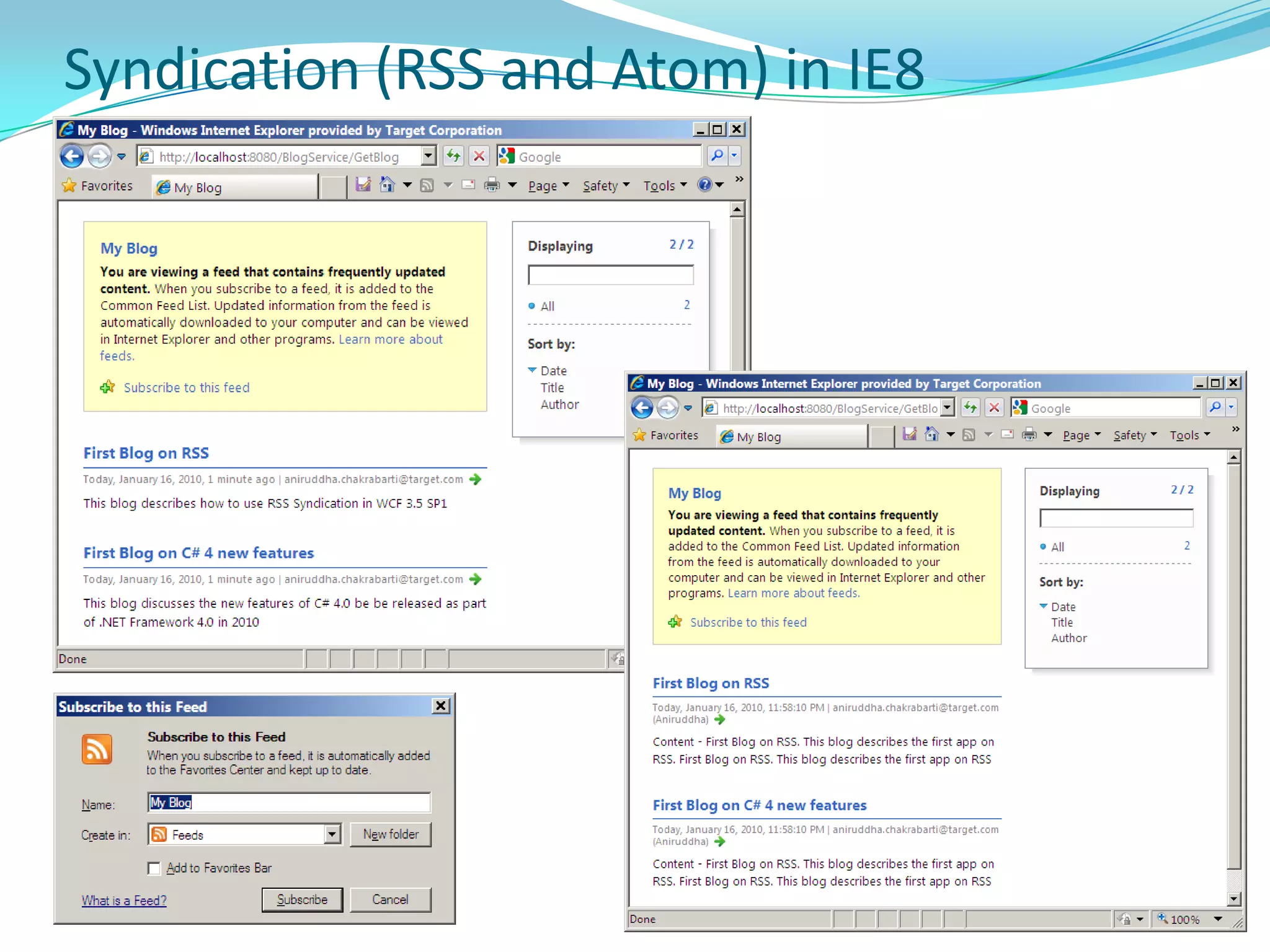
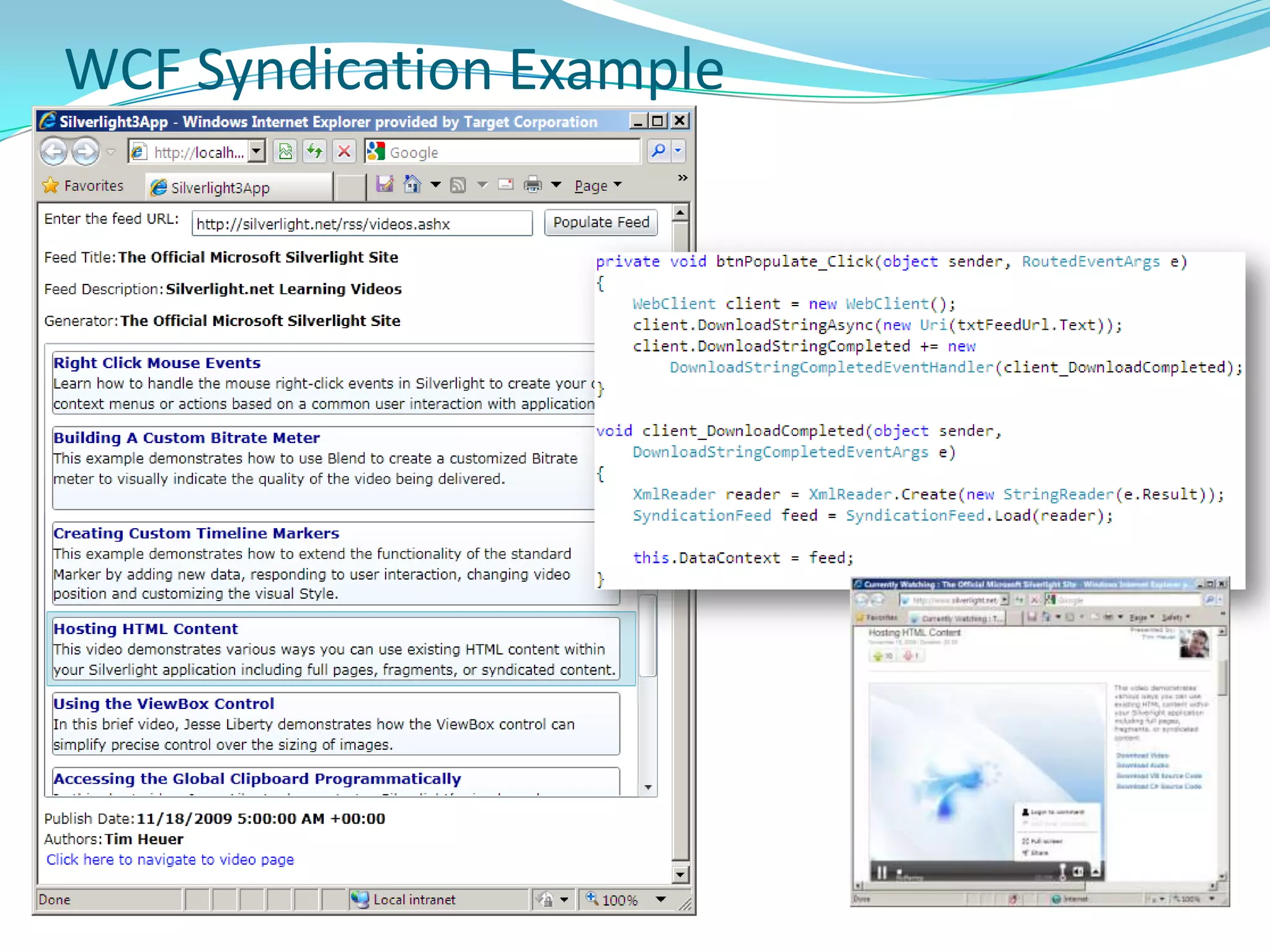
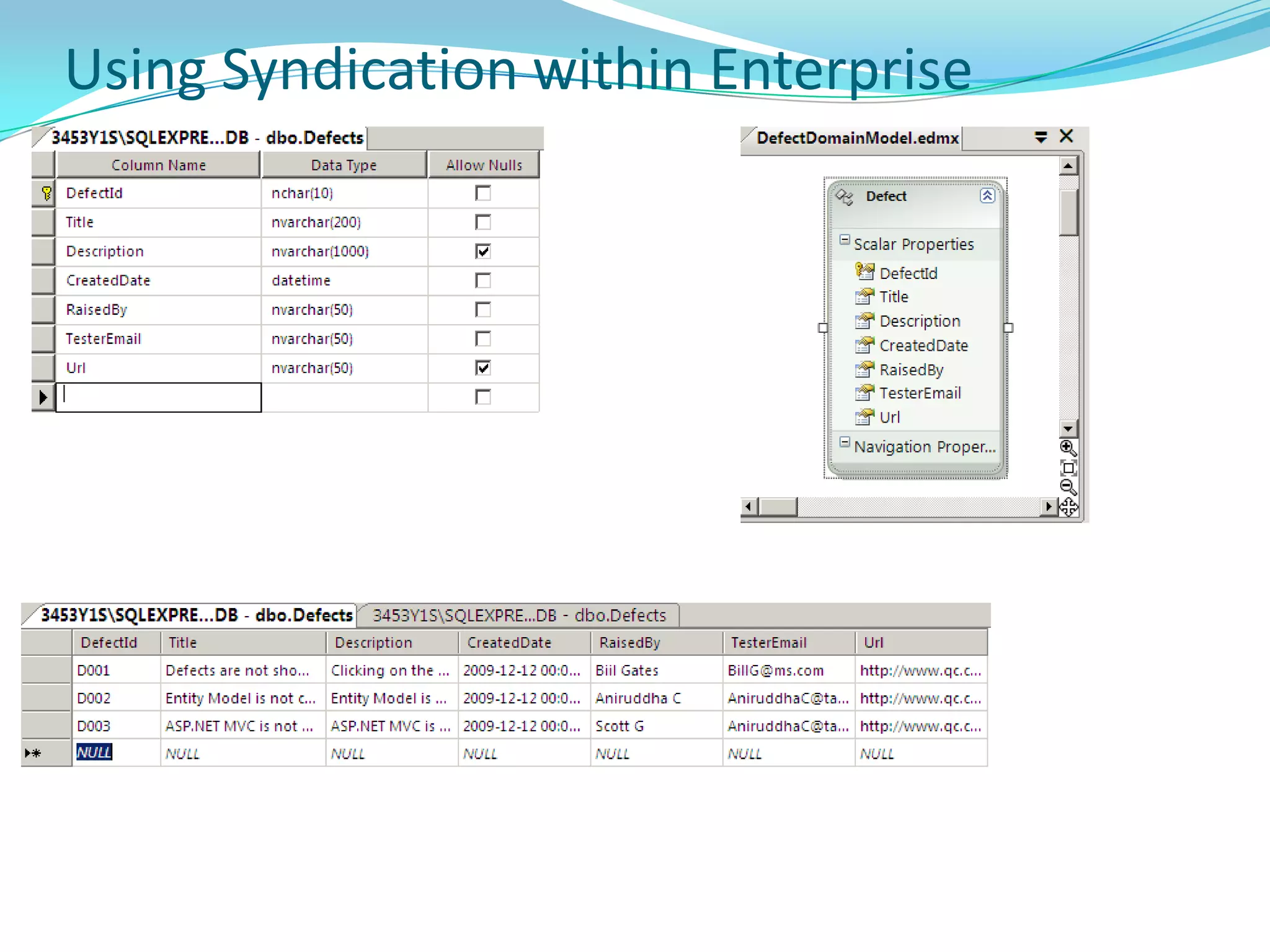
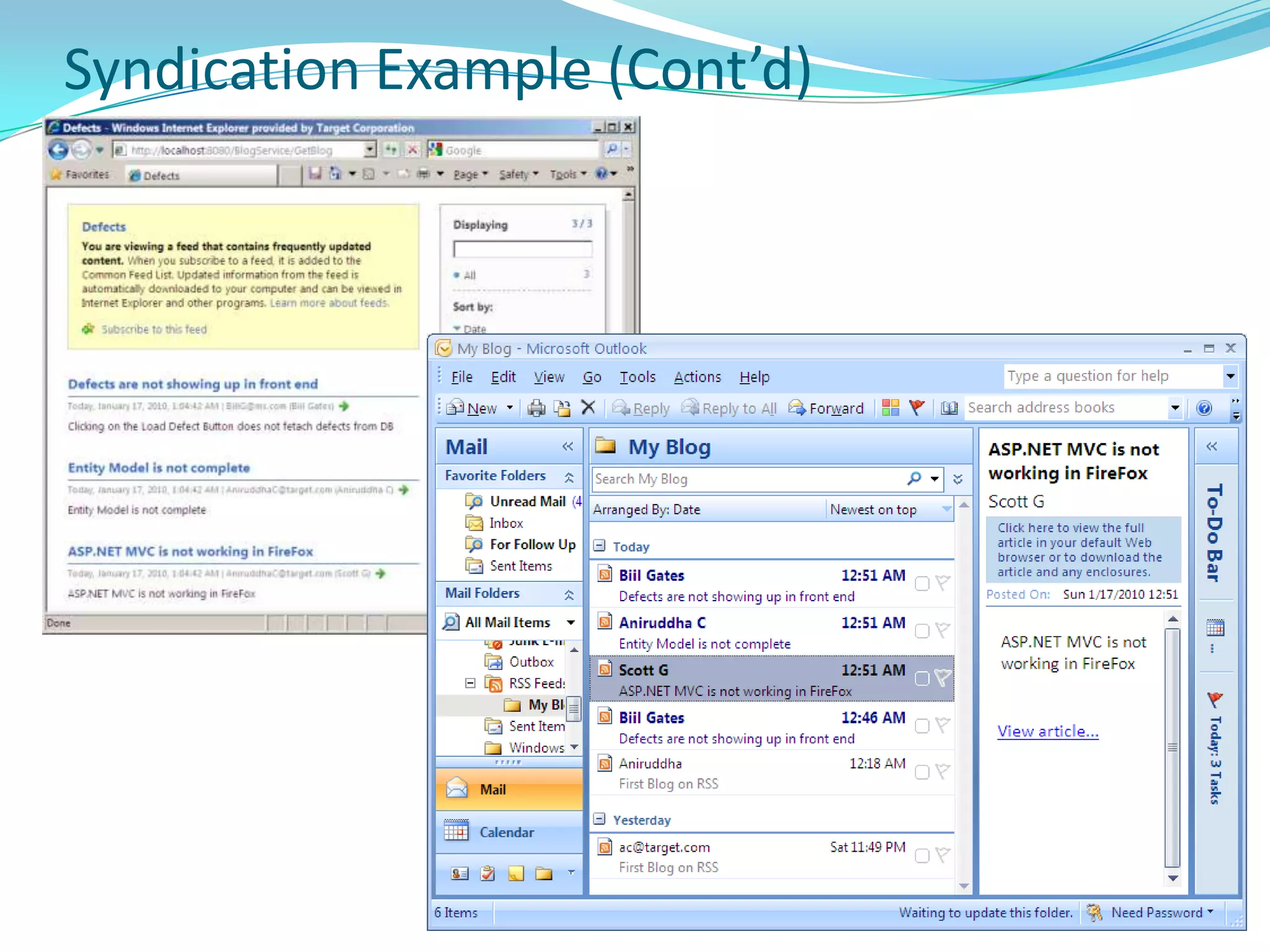
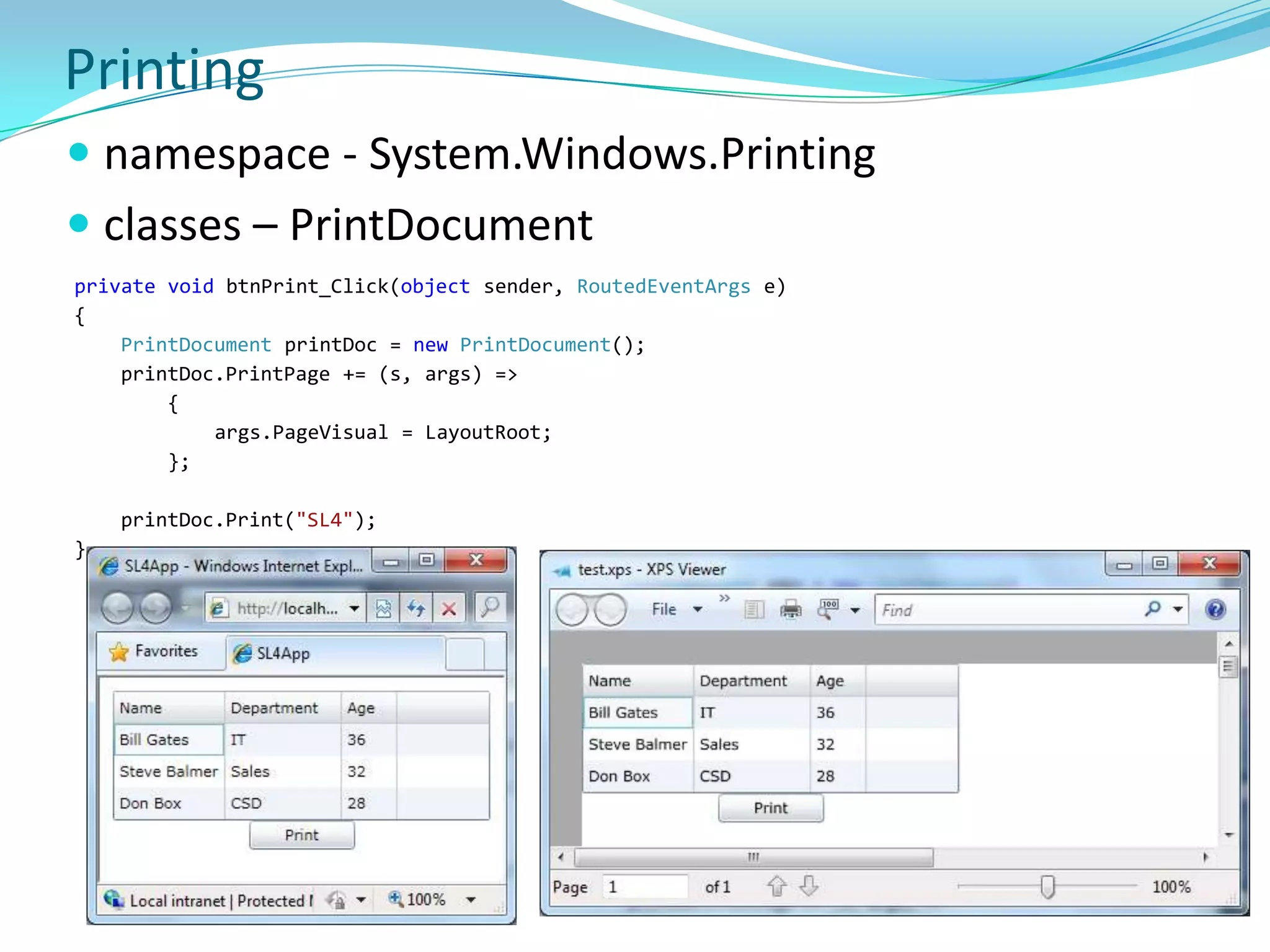
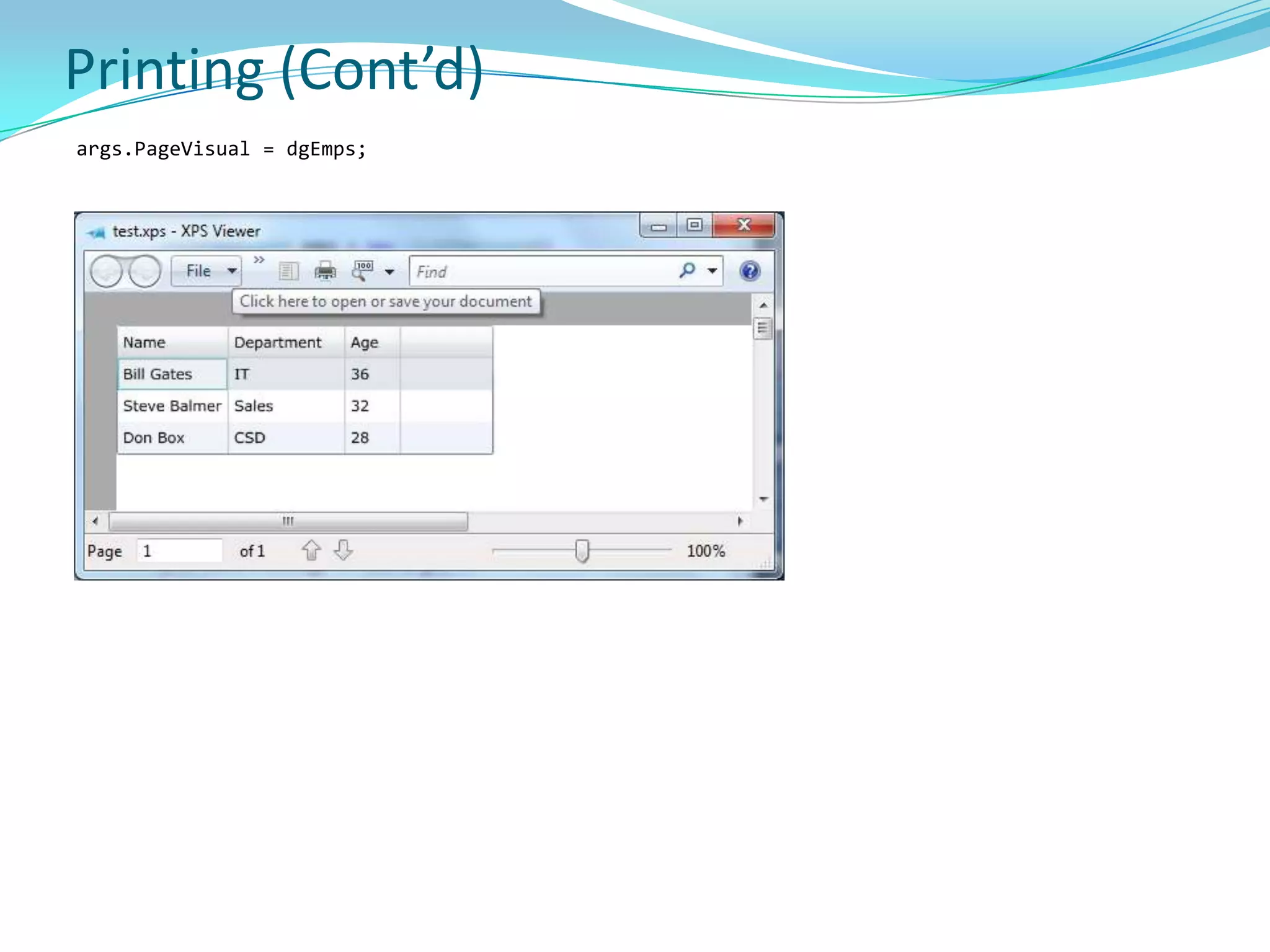
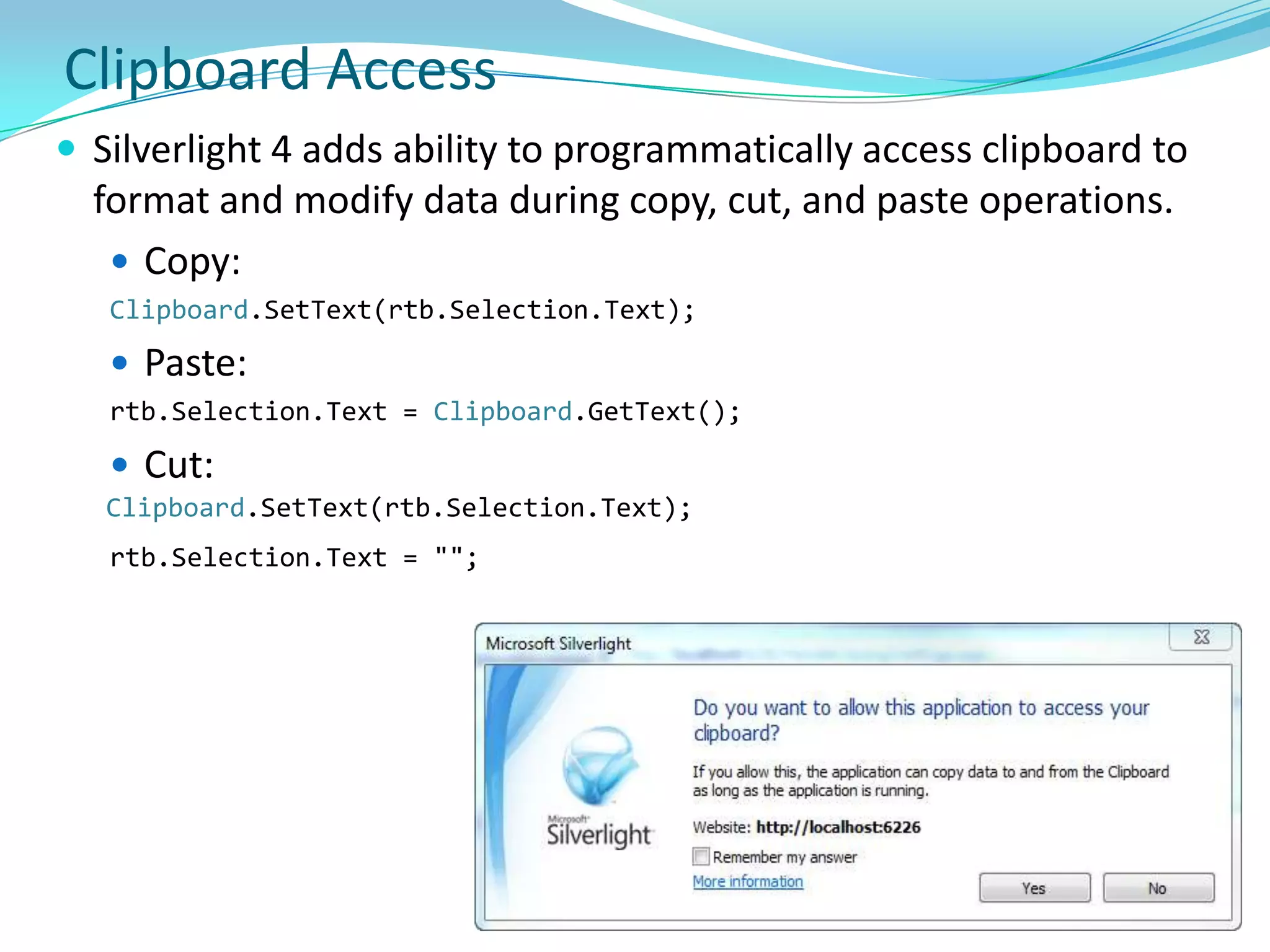
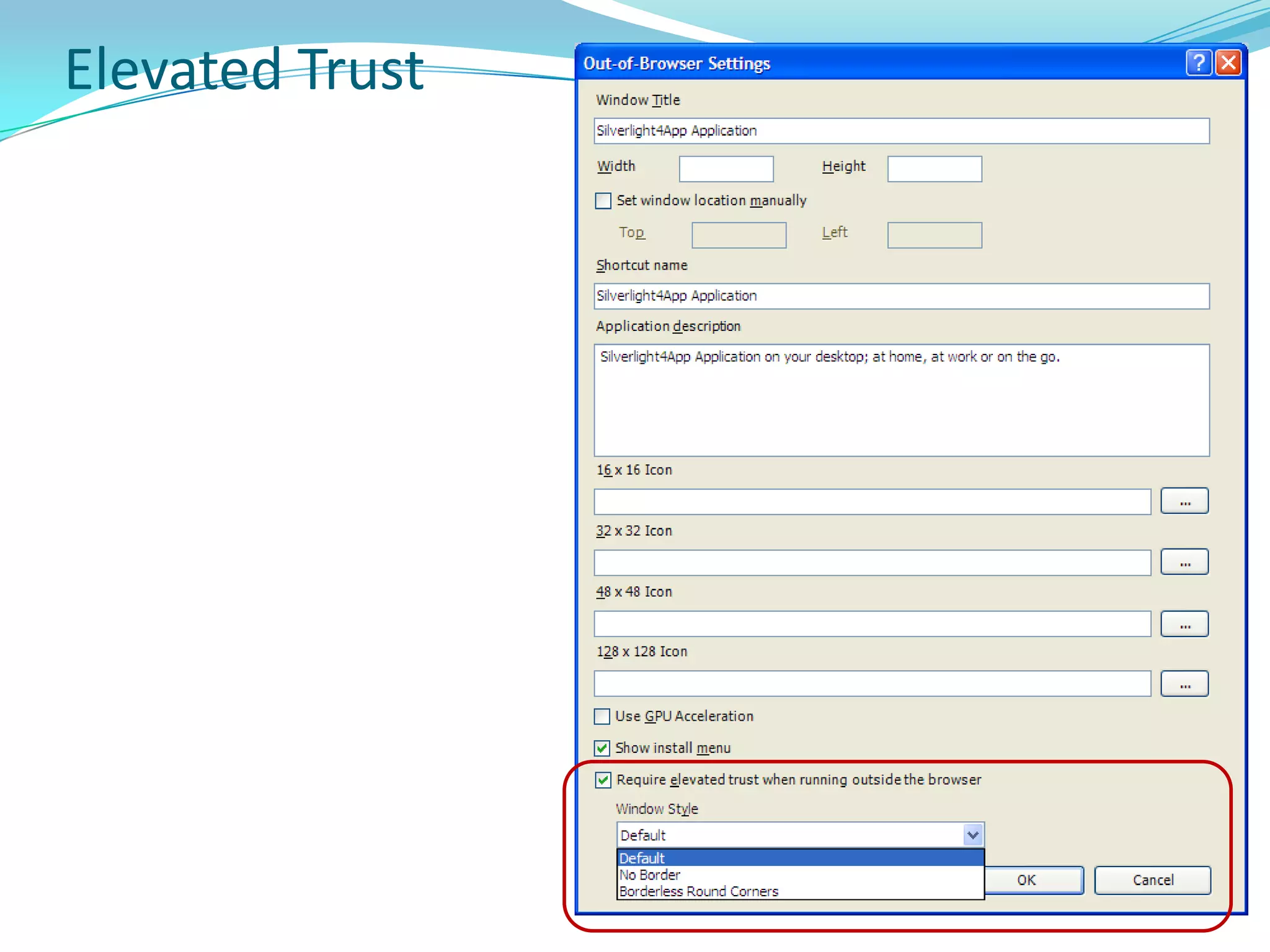
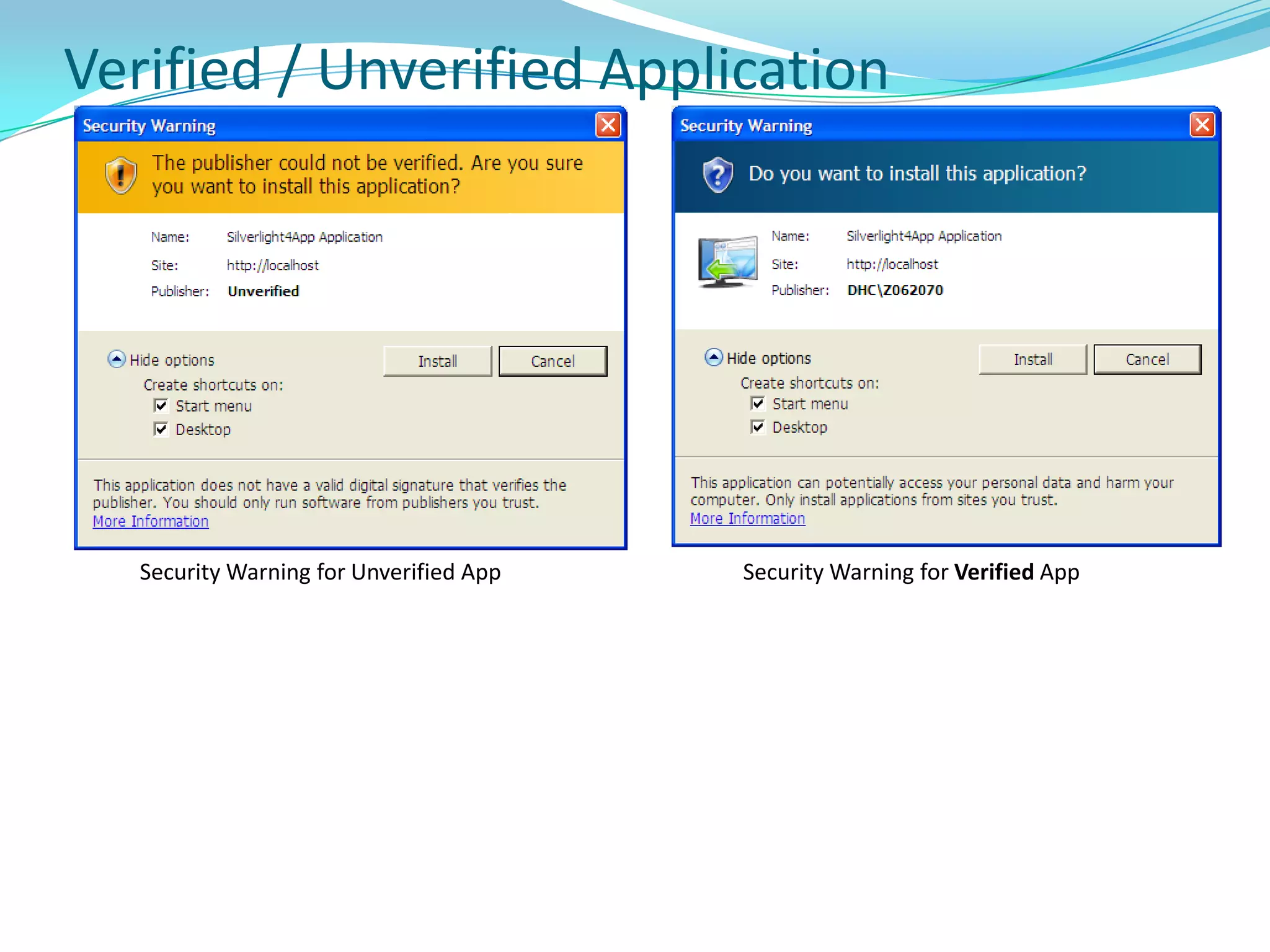
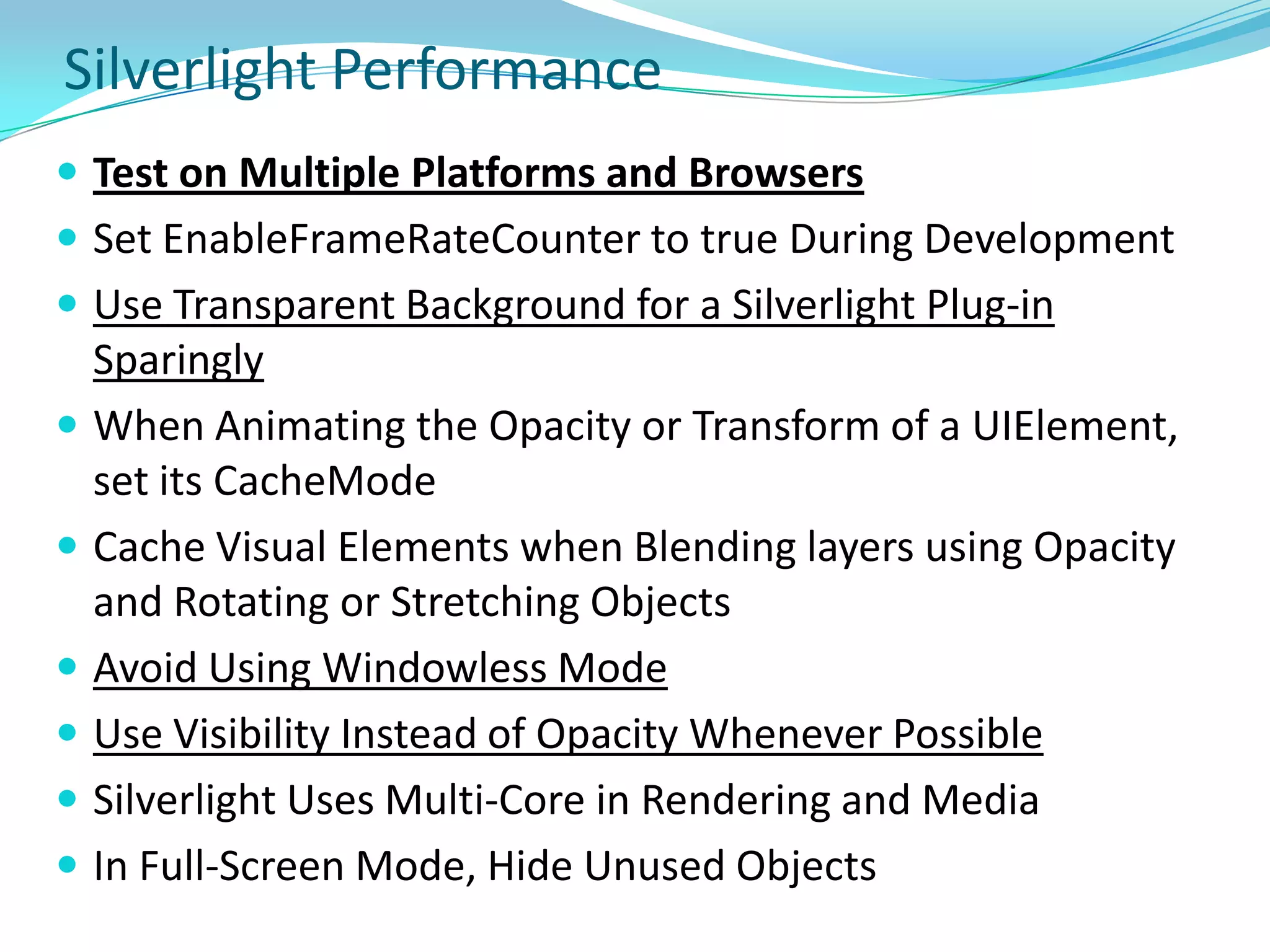
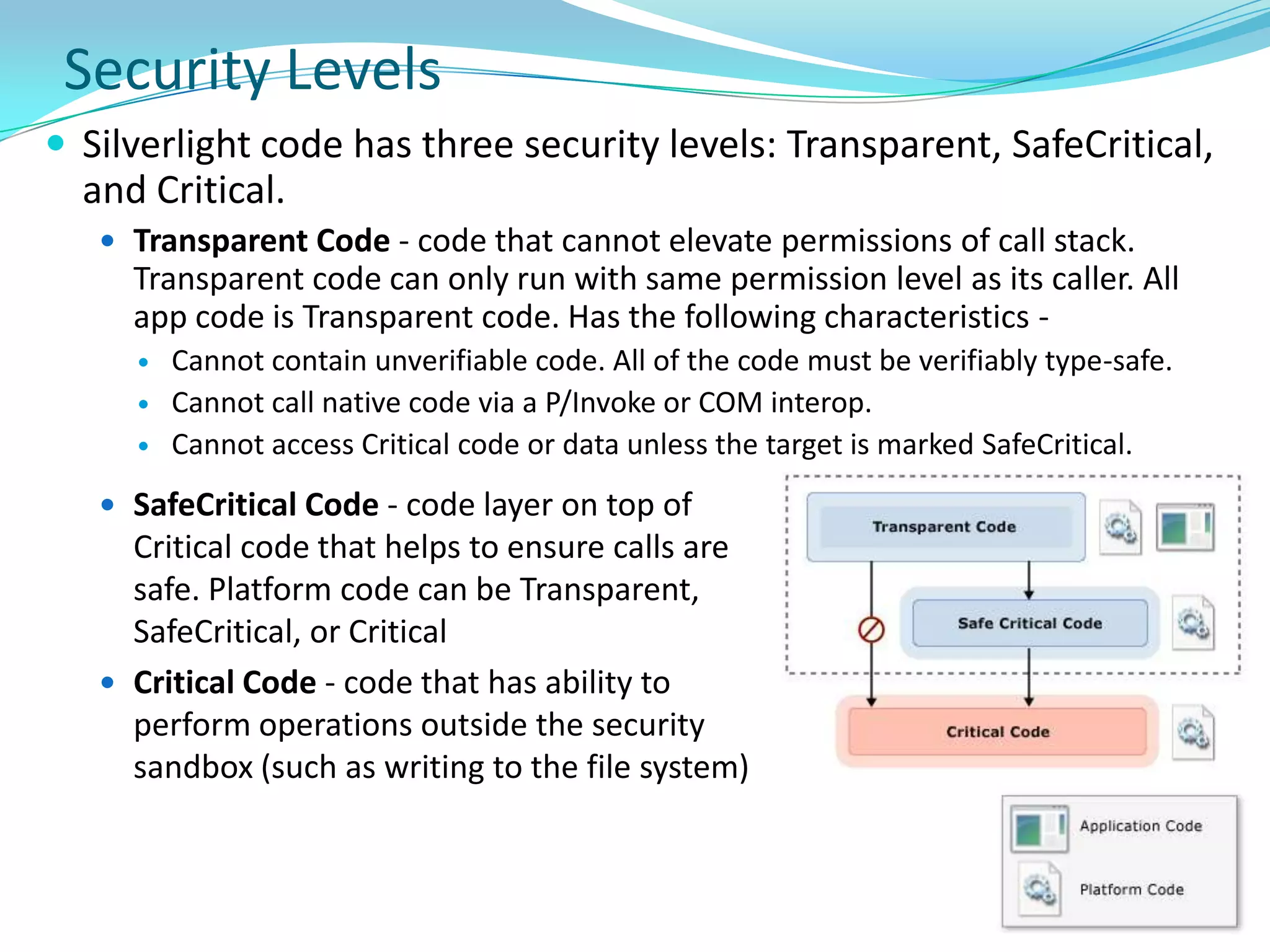
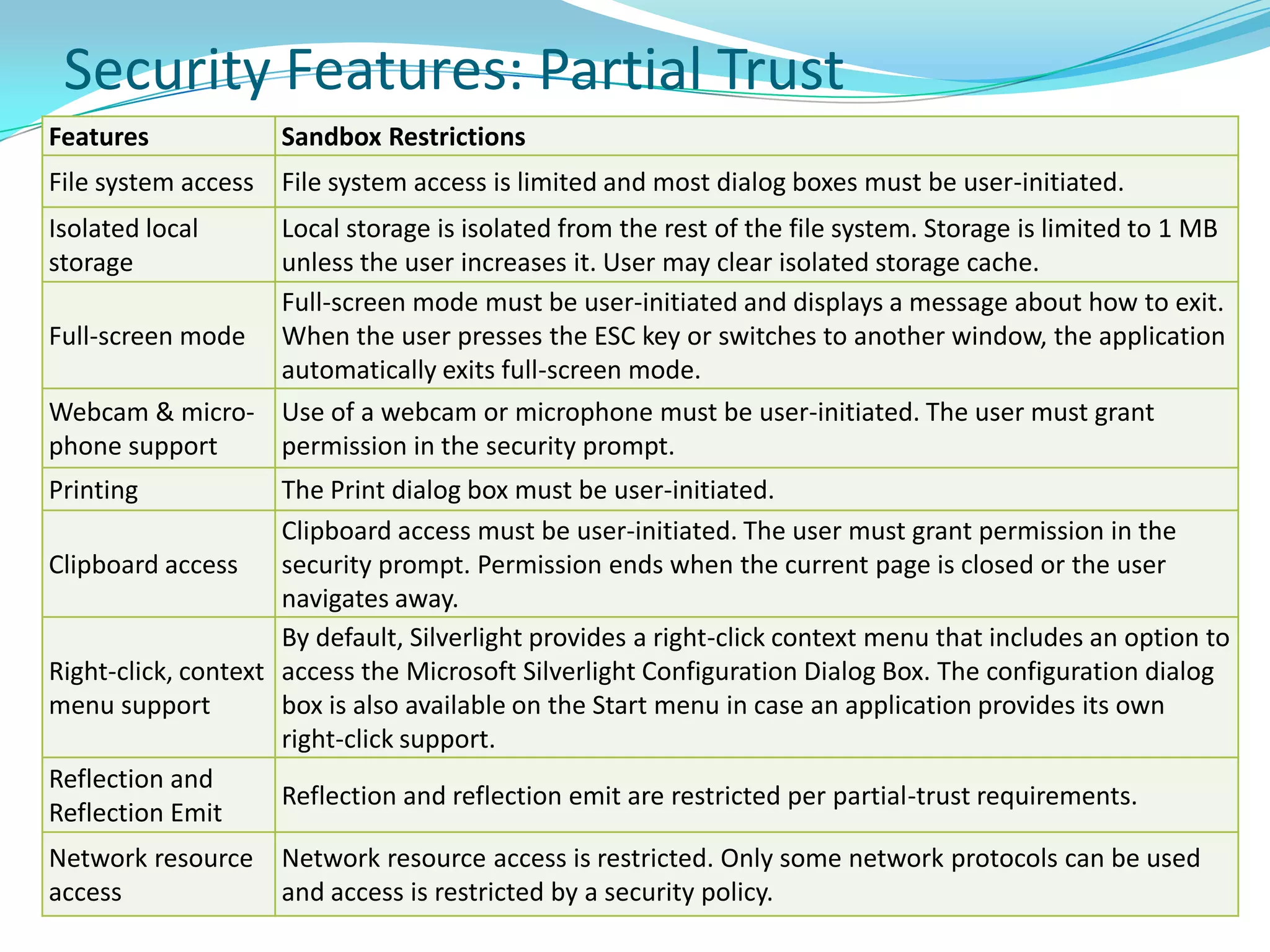
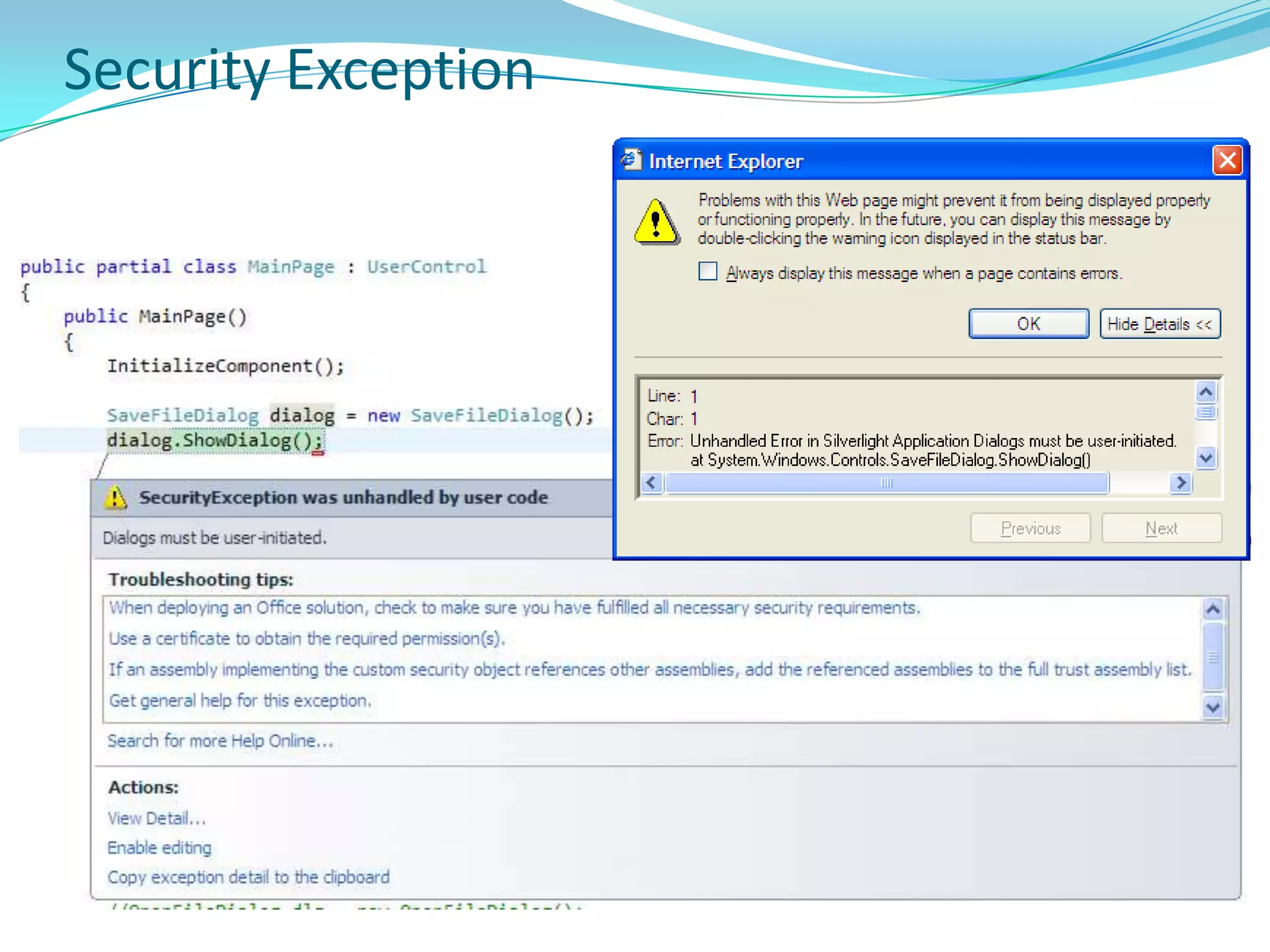
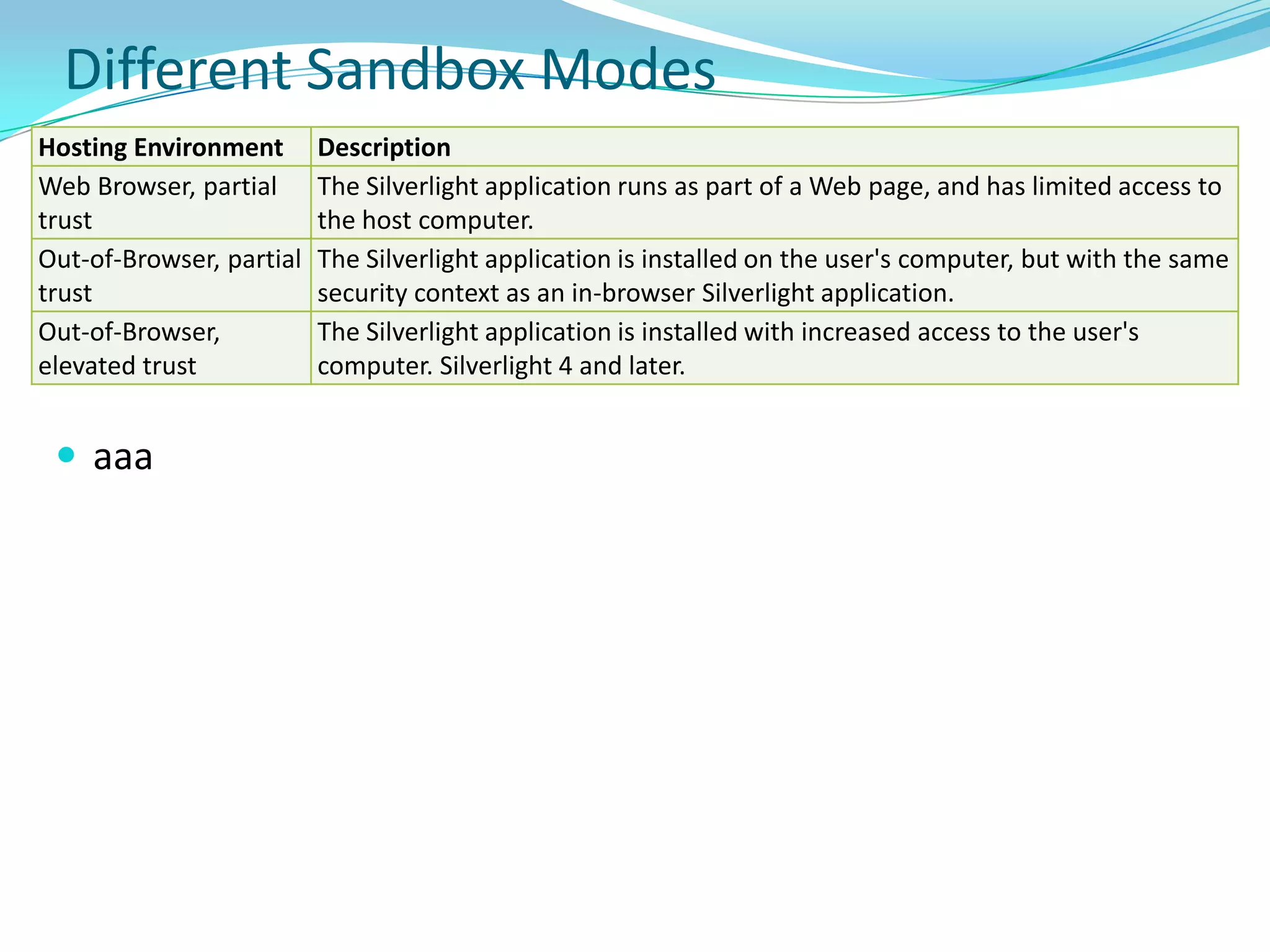
This document provides an overview and summary of the Silverlight Intermediate course. It discusses Rich Internet Applications and various RIA tools, provides a history and overview of Silverlight architecture, and covers key Silverlight concepts like controls, data binding, and the managed and JavaScript application programming models. The document also outlines the course agenda, which includes discussions of Silverlight controls, resources, templates, services, and new features in Silverlight 4.