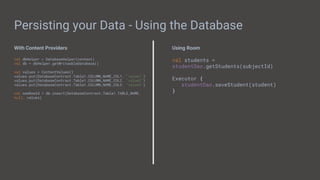
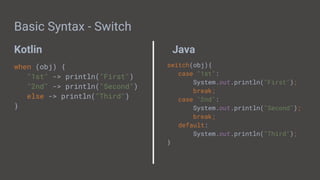
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Android app development, covering its history, essential components, and the Kotlin programming language. Key topics include setting up Kotlin for Android, basic syntax comparisons with Java, Android components like activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers, as well as database management using Room and Content Providers. Additionally, it discusses architectural patterns (MVC, MVP, MVVM) and testing strategies for Android applications.













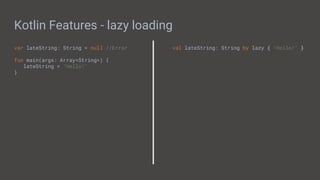
![Kotlin Java
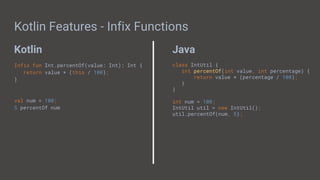
Basic Syntax - Functions
fun main(args: Array<String>){
}
fun getInt(): Int{
}
public static void main(String[] args){
}
int getInt(){
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingmobileappswithandroid-190614010133/85/Building-Mobile-Apps-with-Android-16-320.jpg)






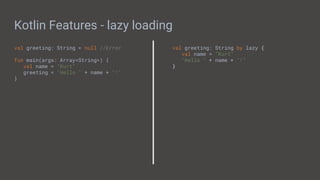
![Kotlin Java
Kotlin Features - Null Safety
var notNullable: String
var nullable: String?
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
notNullable = null //Error
notNullable = "Hi" //OK
nullable = null //OK
nullable = "Hi" //OK
}
String nullable;
public static void main(String[] args){
nullable = null; //OK
nullable = "HI"; //OK
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingmobileappswithandroid-190614010133/85/Building-Mobile-Apps-with-Android-23-320.jpg)
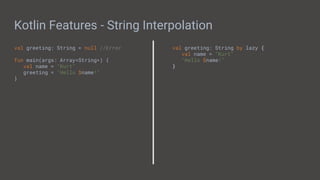
![Kotlin Java
Kotlin Features - Null Safety
var nullable: String?
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var length = nullable?.length
var forceLength = nullable!!.length
length = nullable.length ?: 0
}
String nullable;
public static void main(String[] args){
int length;
if(nullable != null) {
length = nullable.length();
}
length = nullable != null ?
nullable.length() : 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingmobileappswithandroid-190614010133/85/Building-Mobile-Apps-with-Android-24-320.jpg)