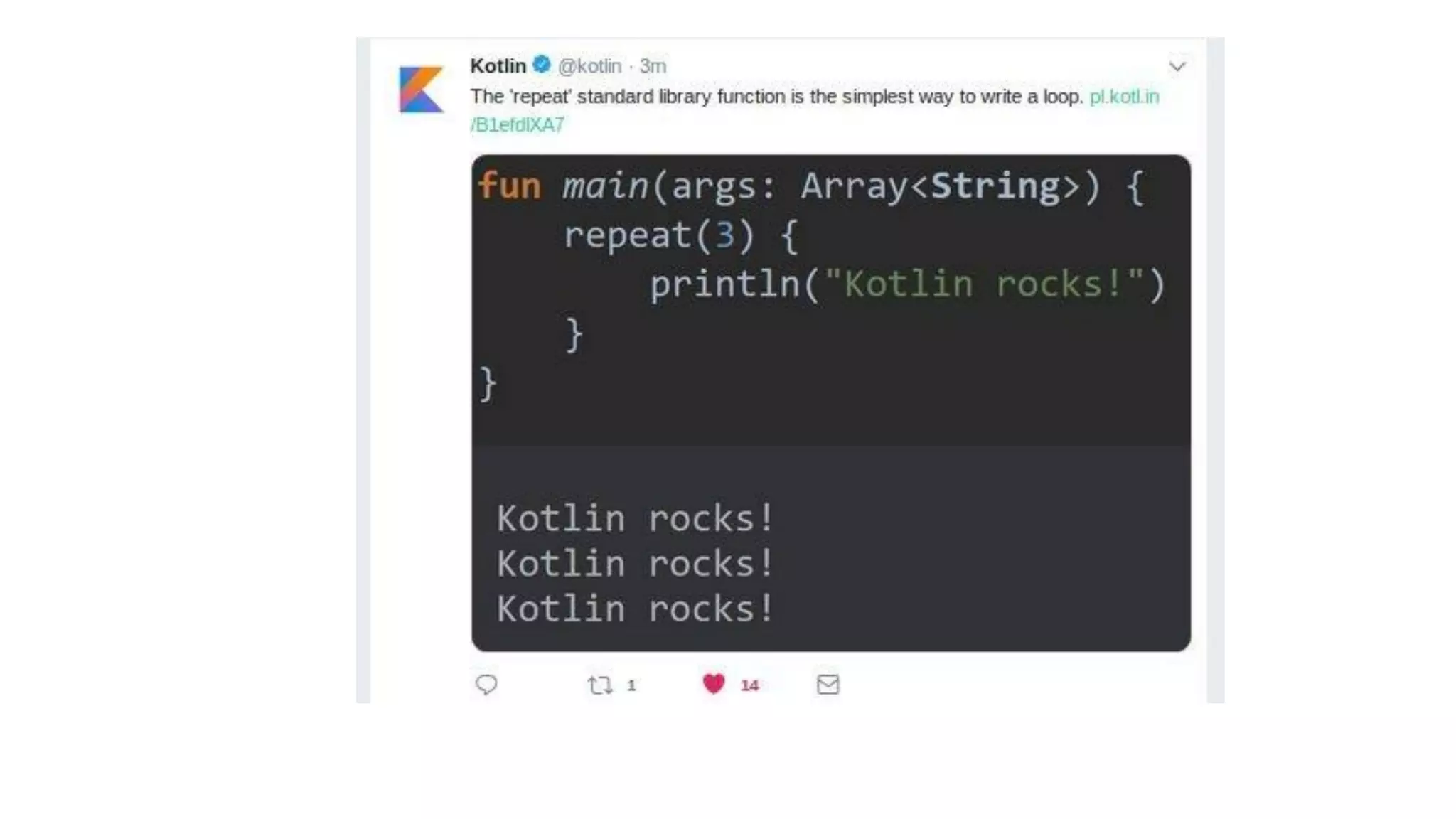
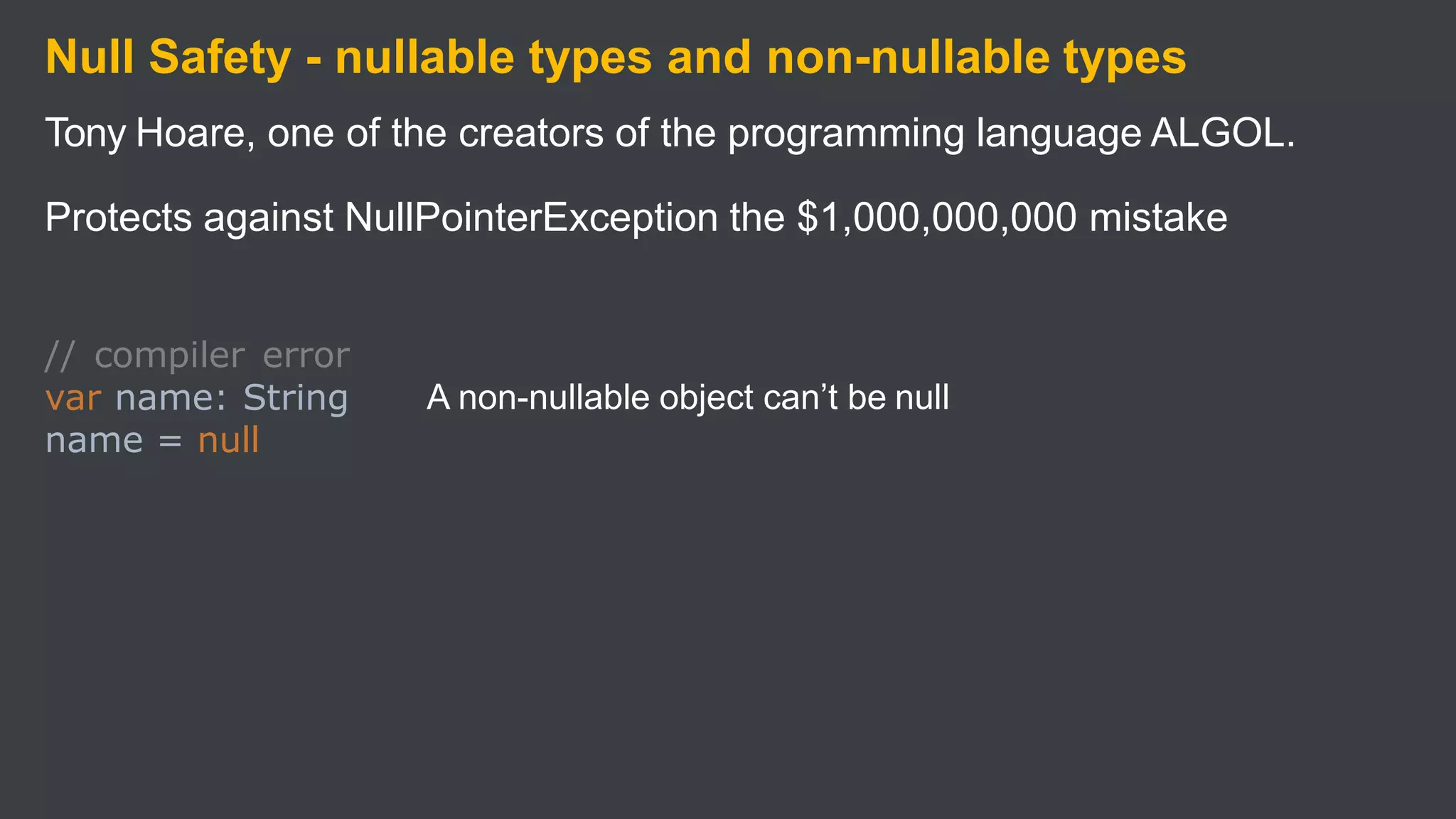
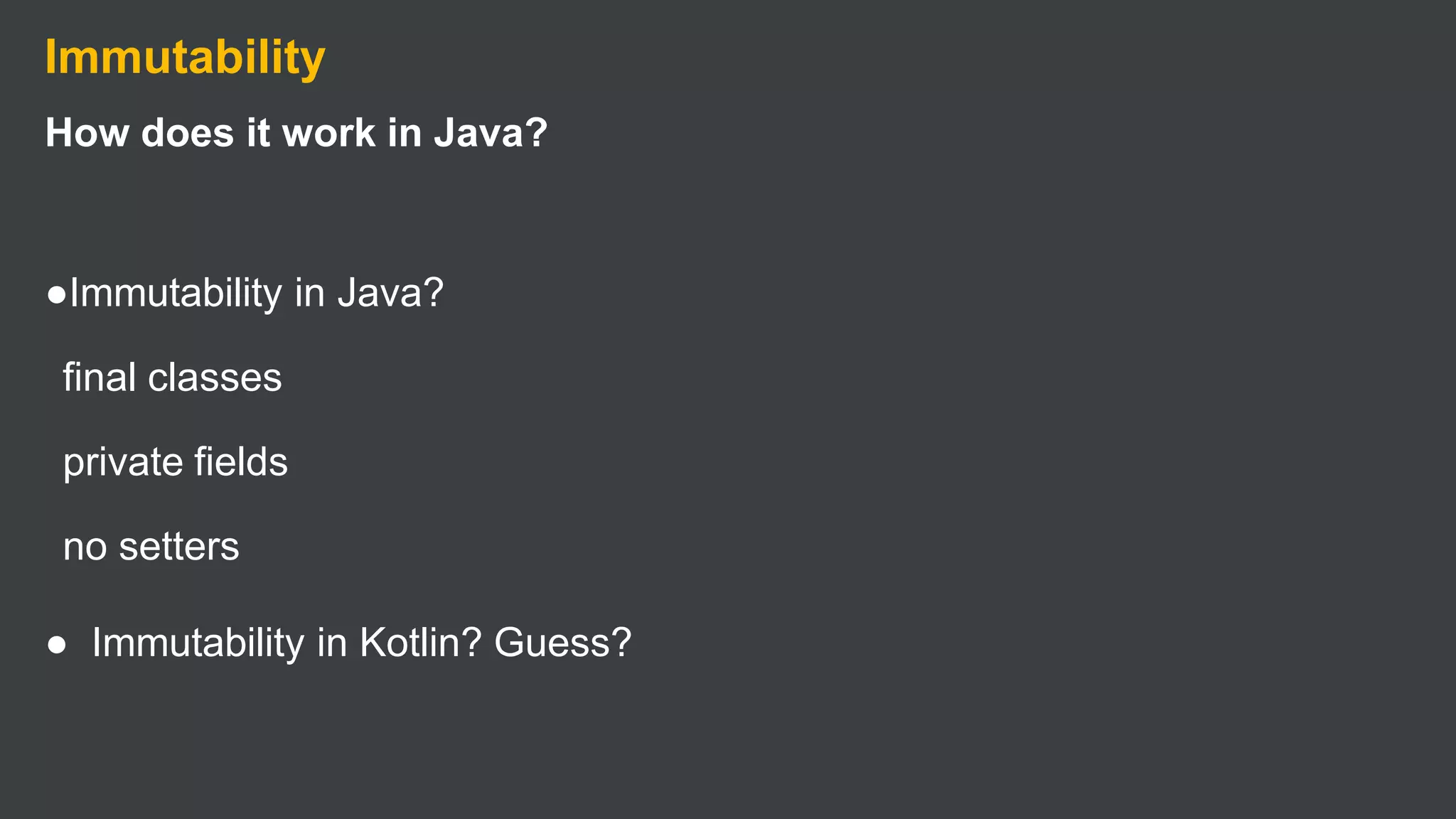
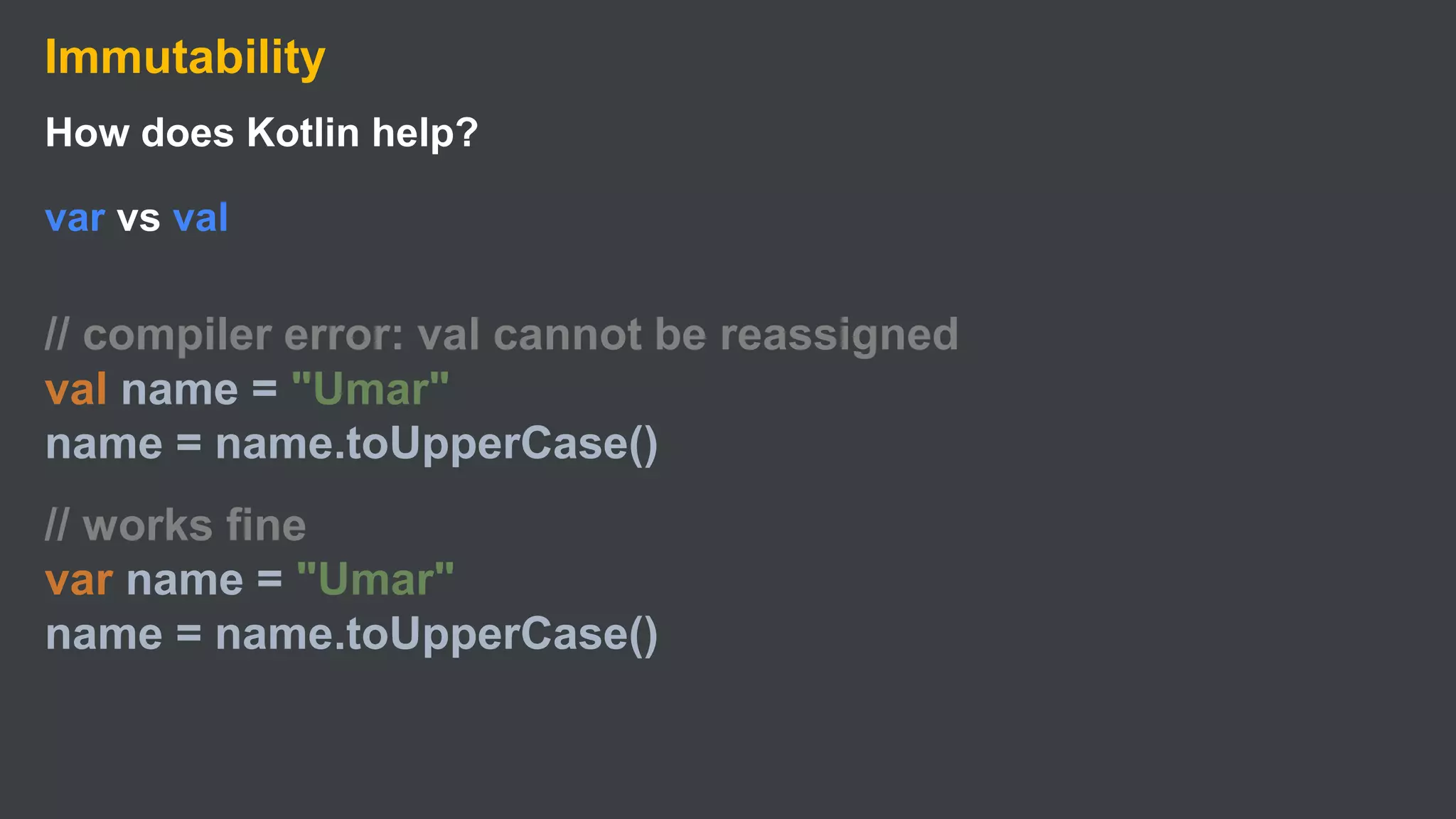
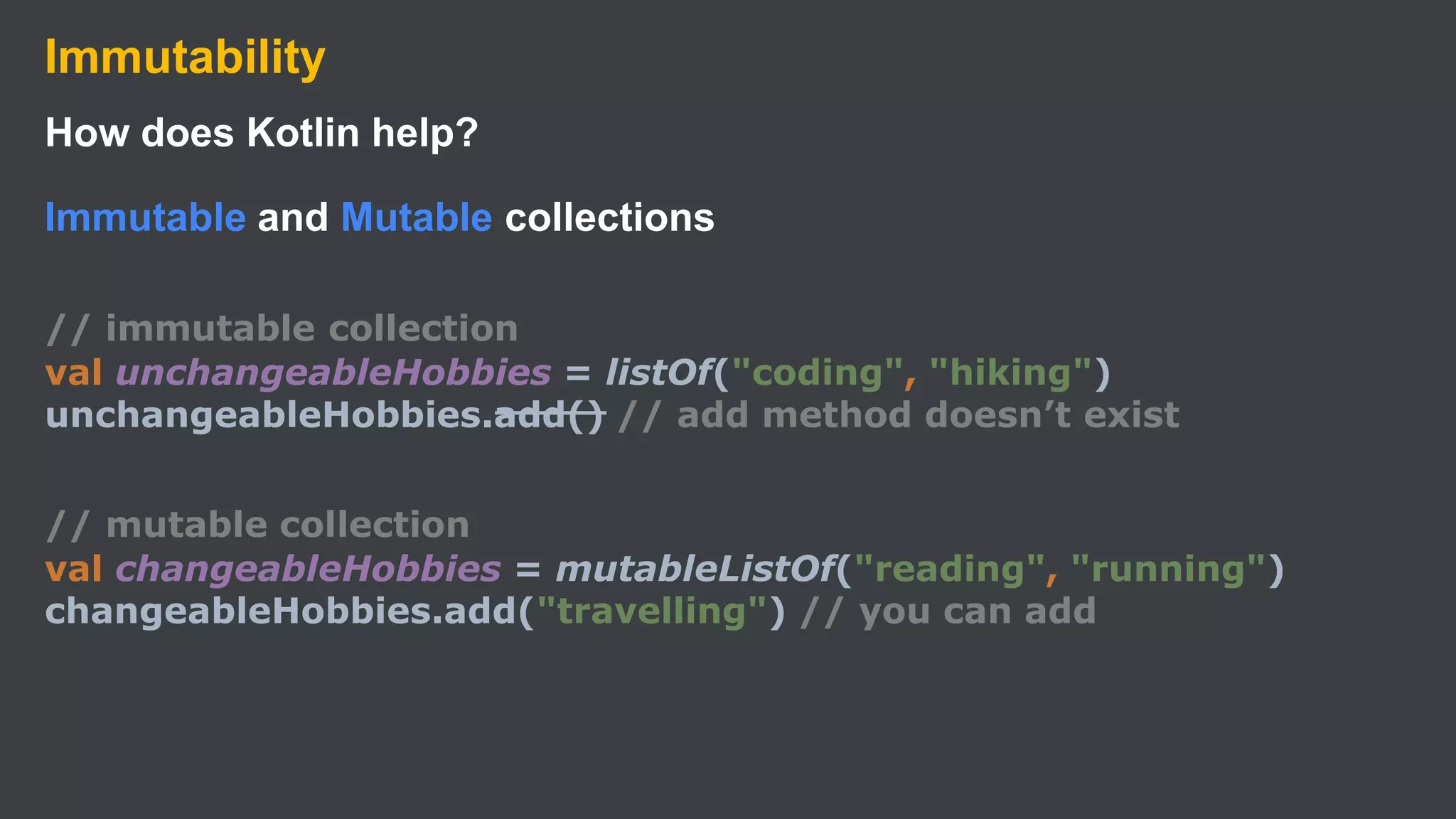
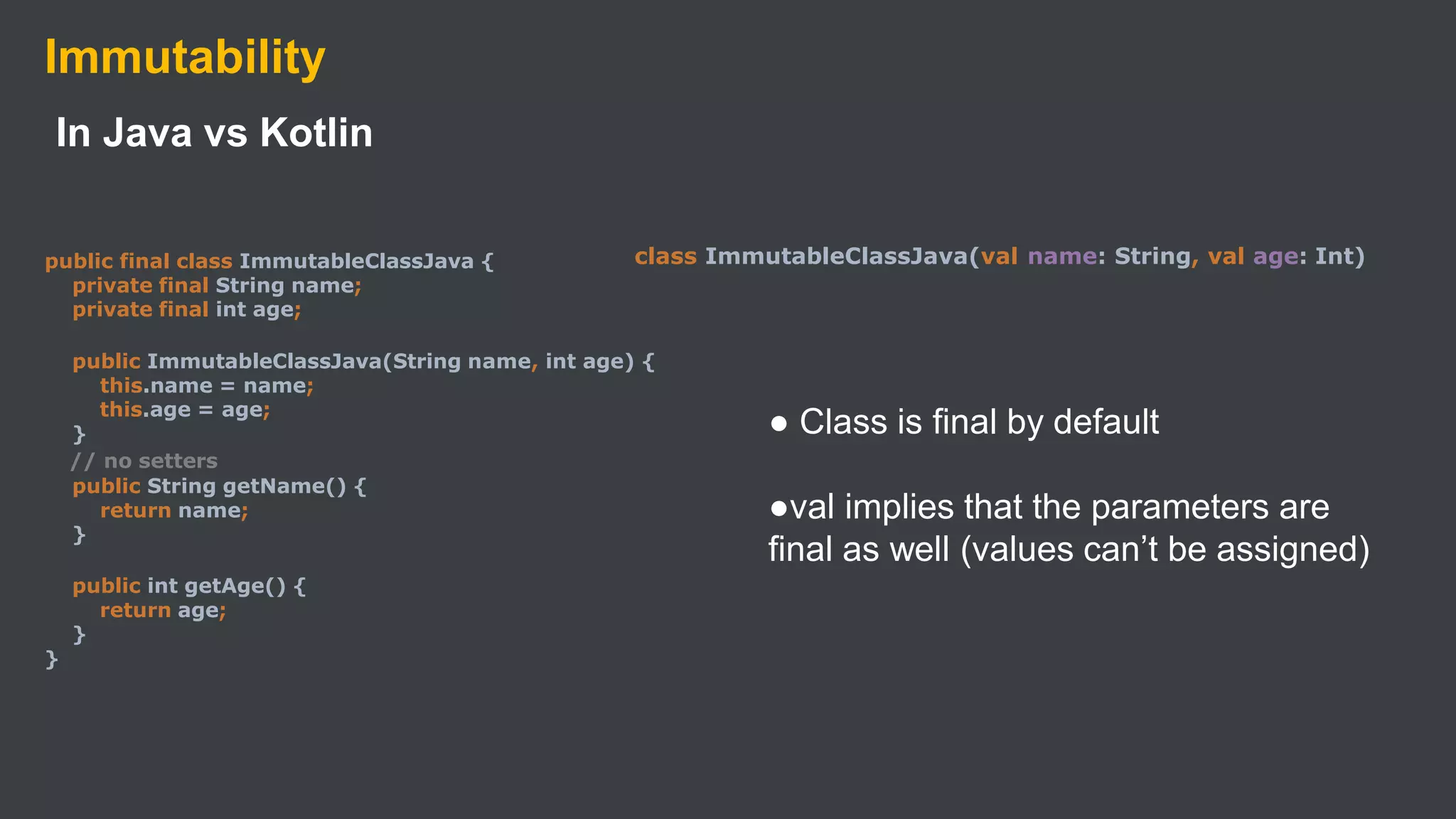
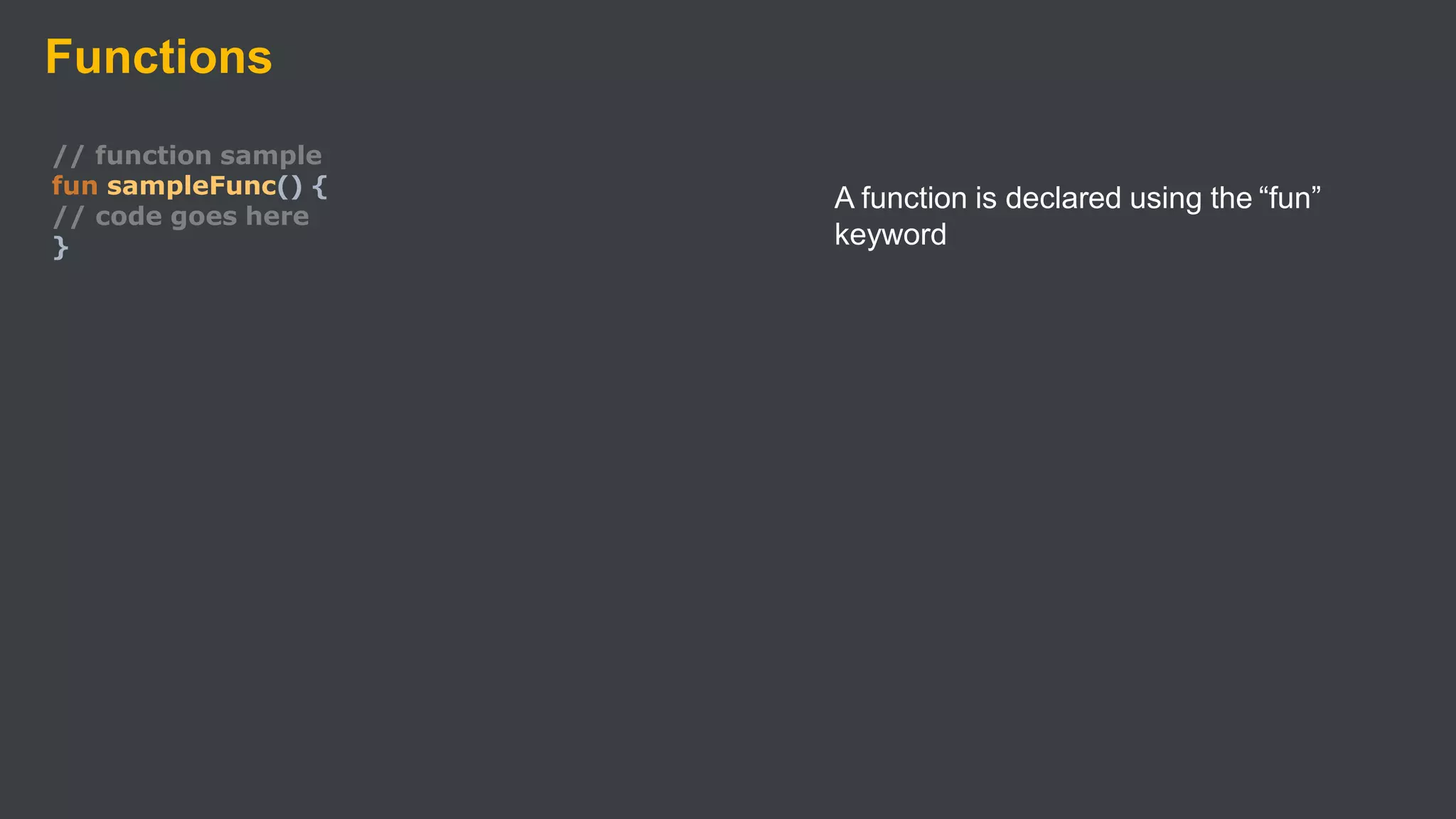
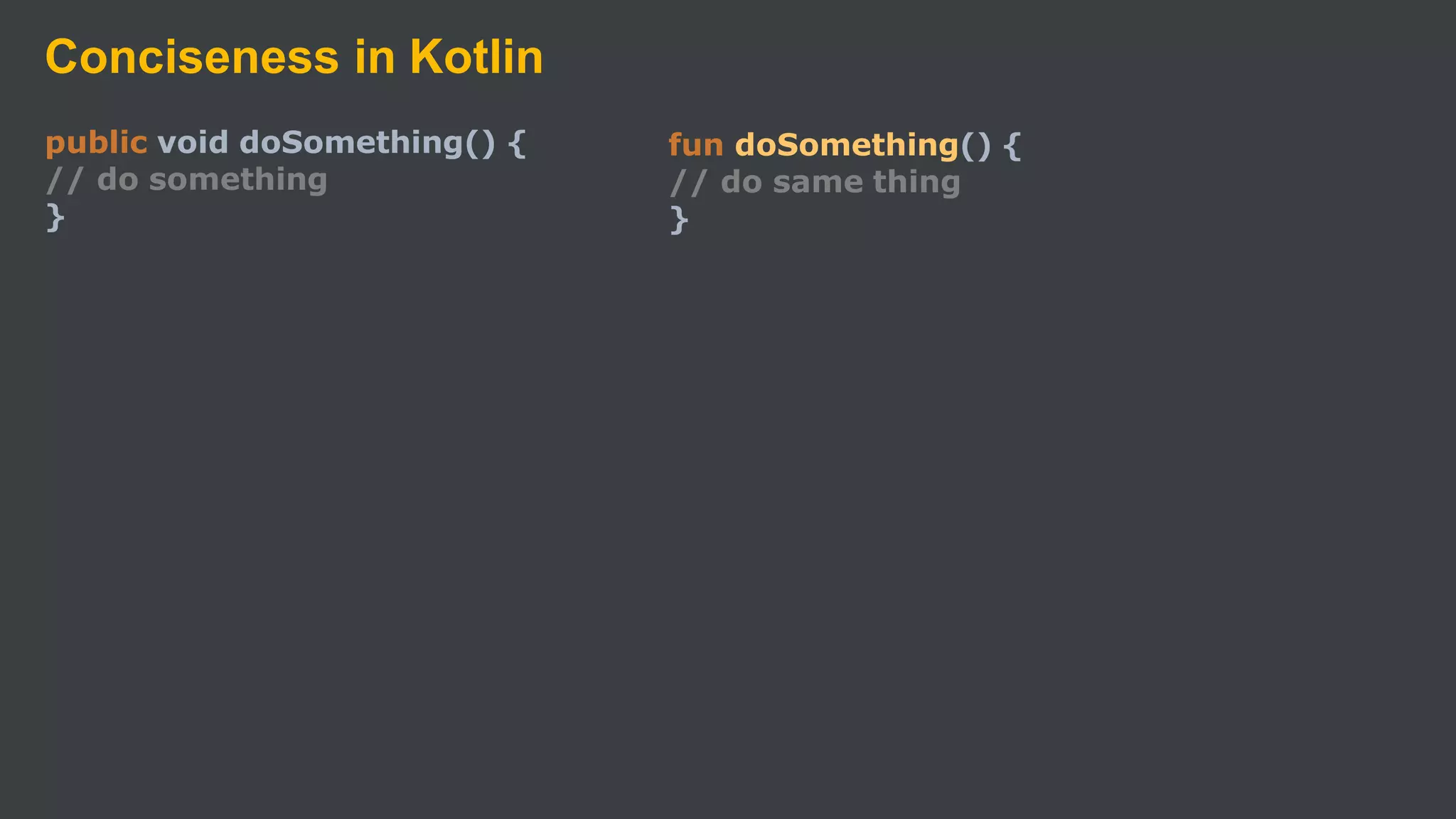
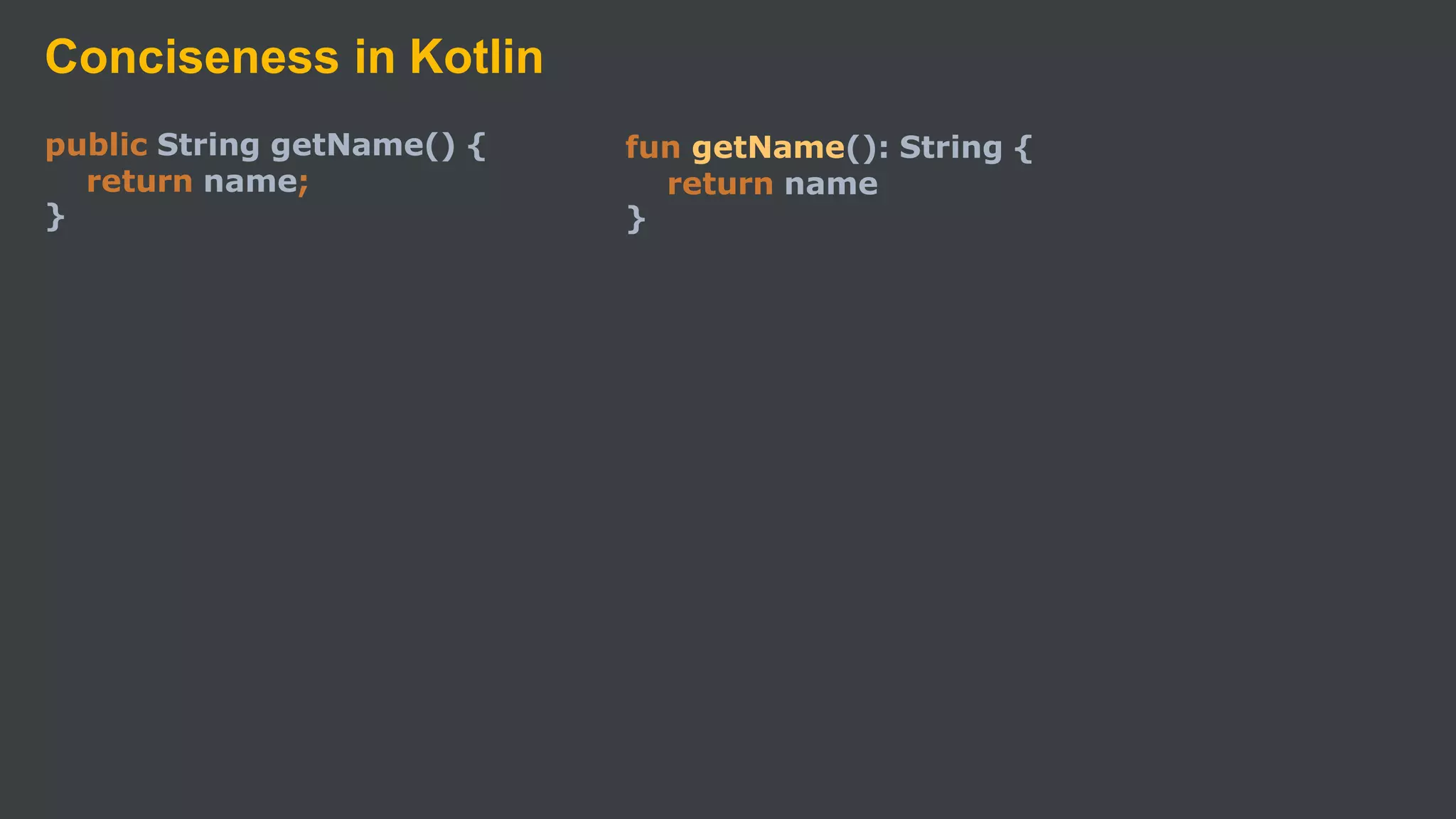
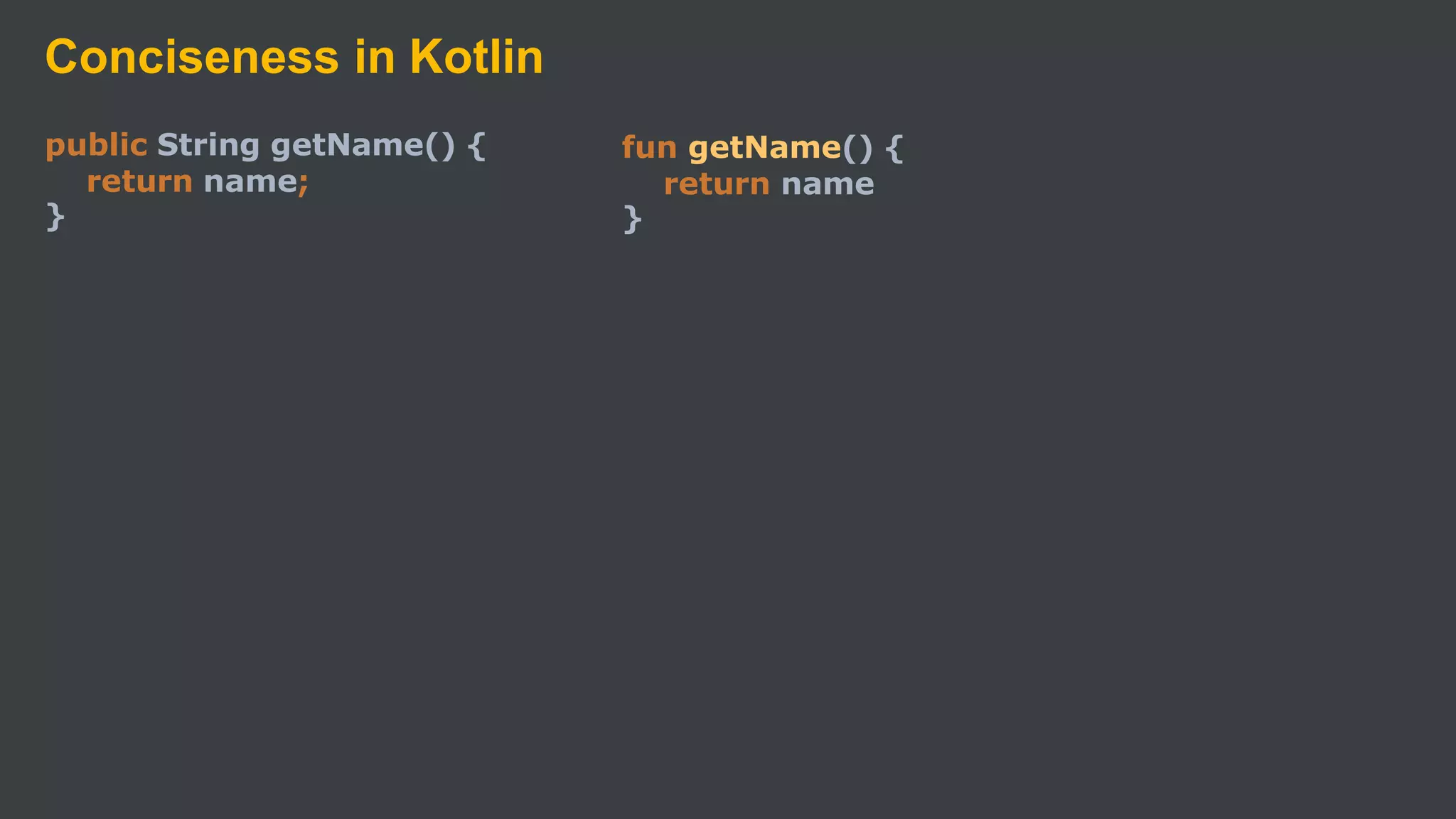
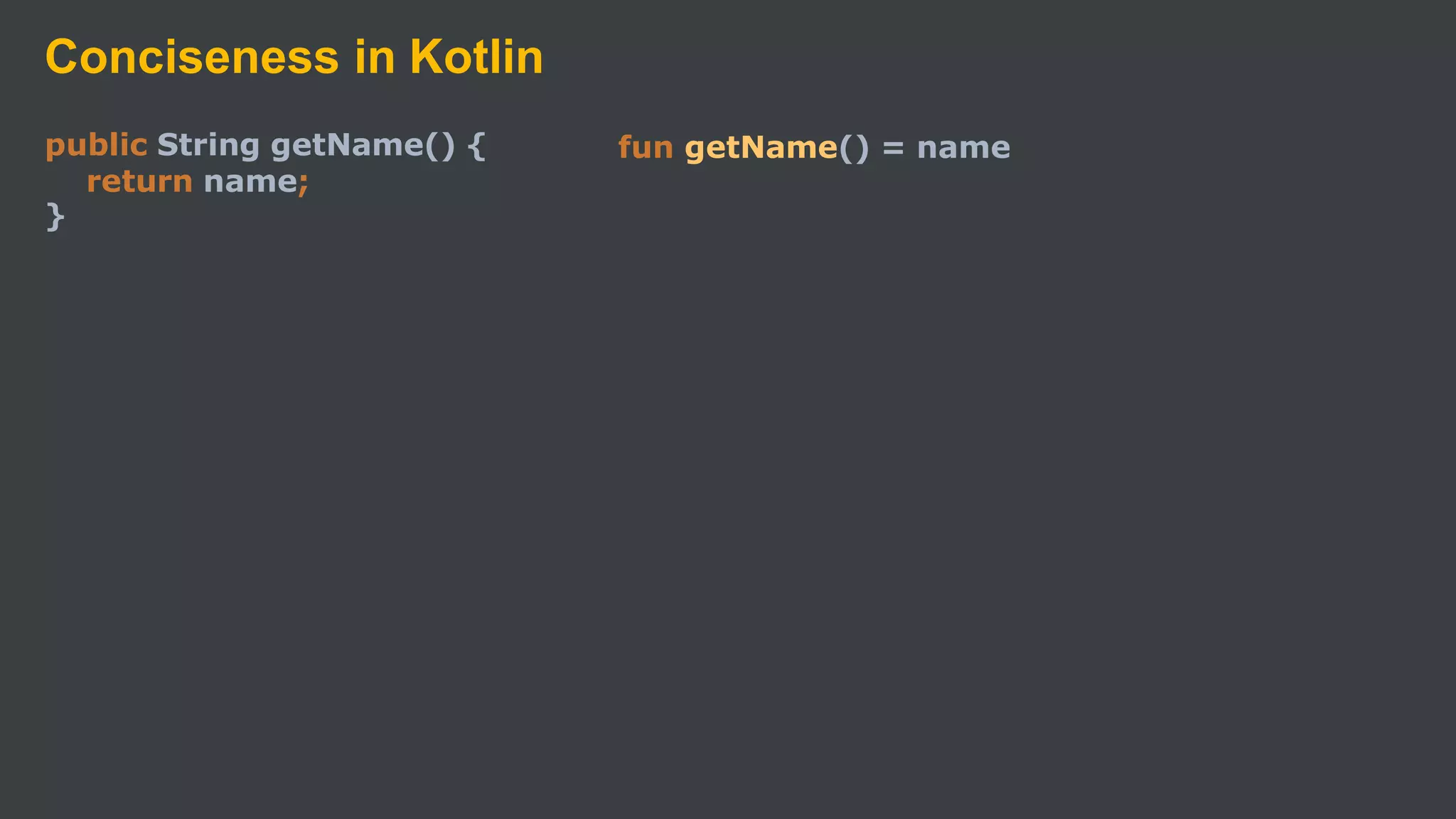
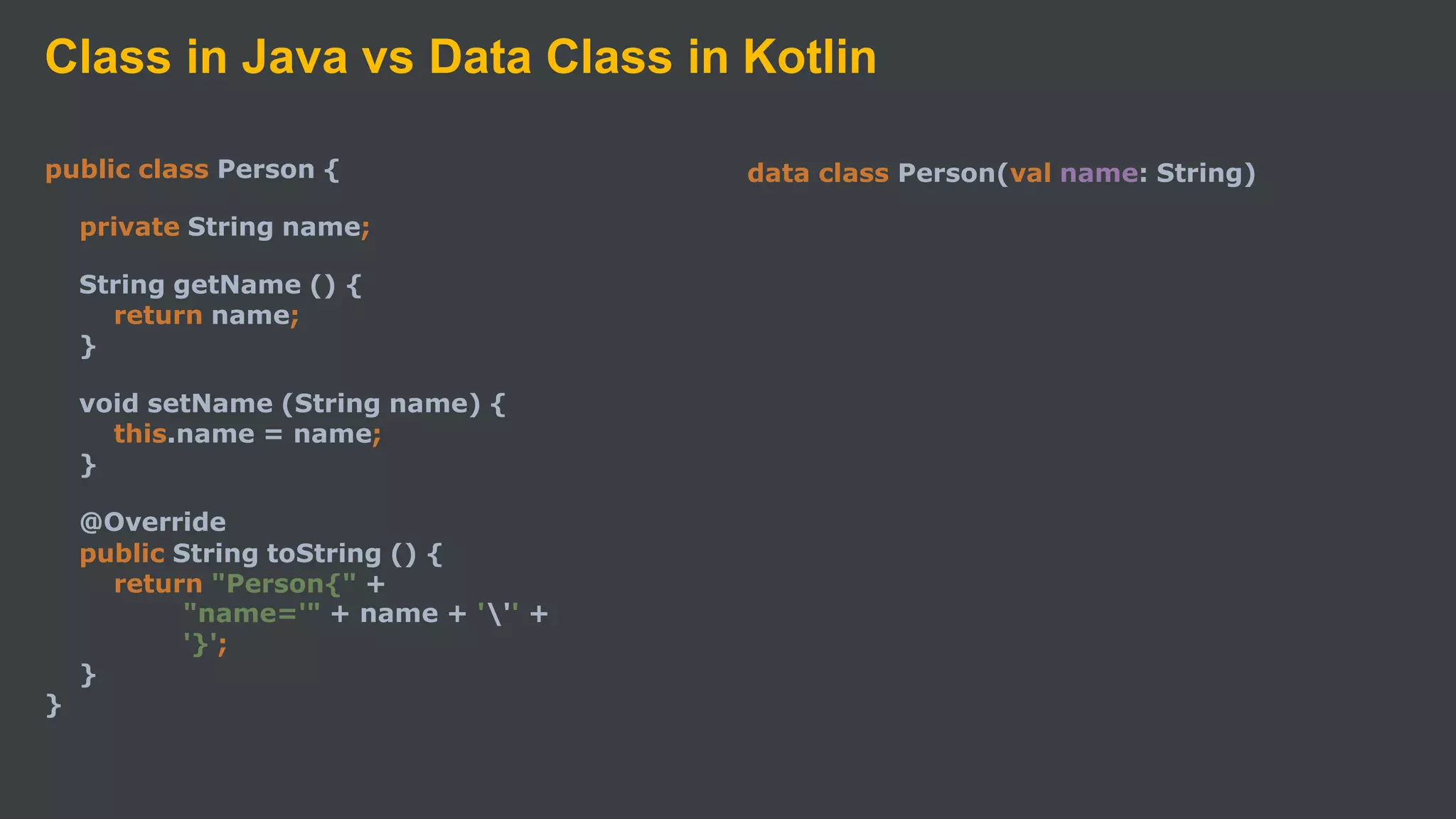
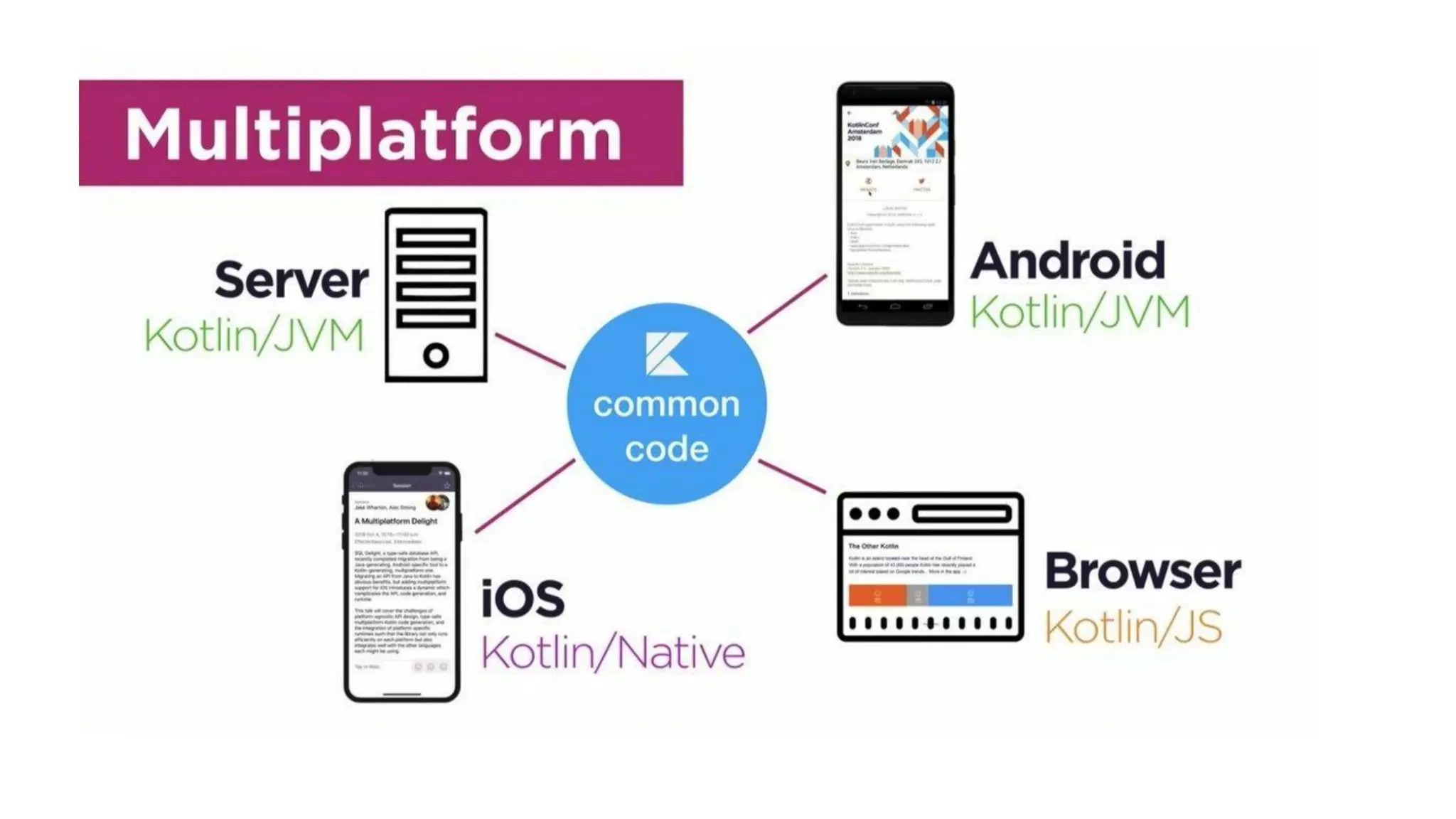
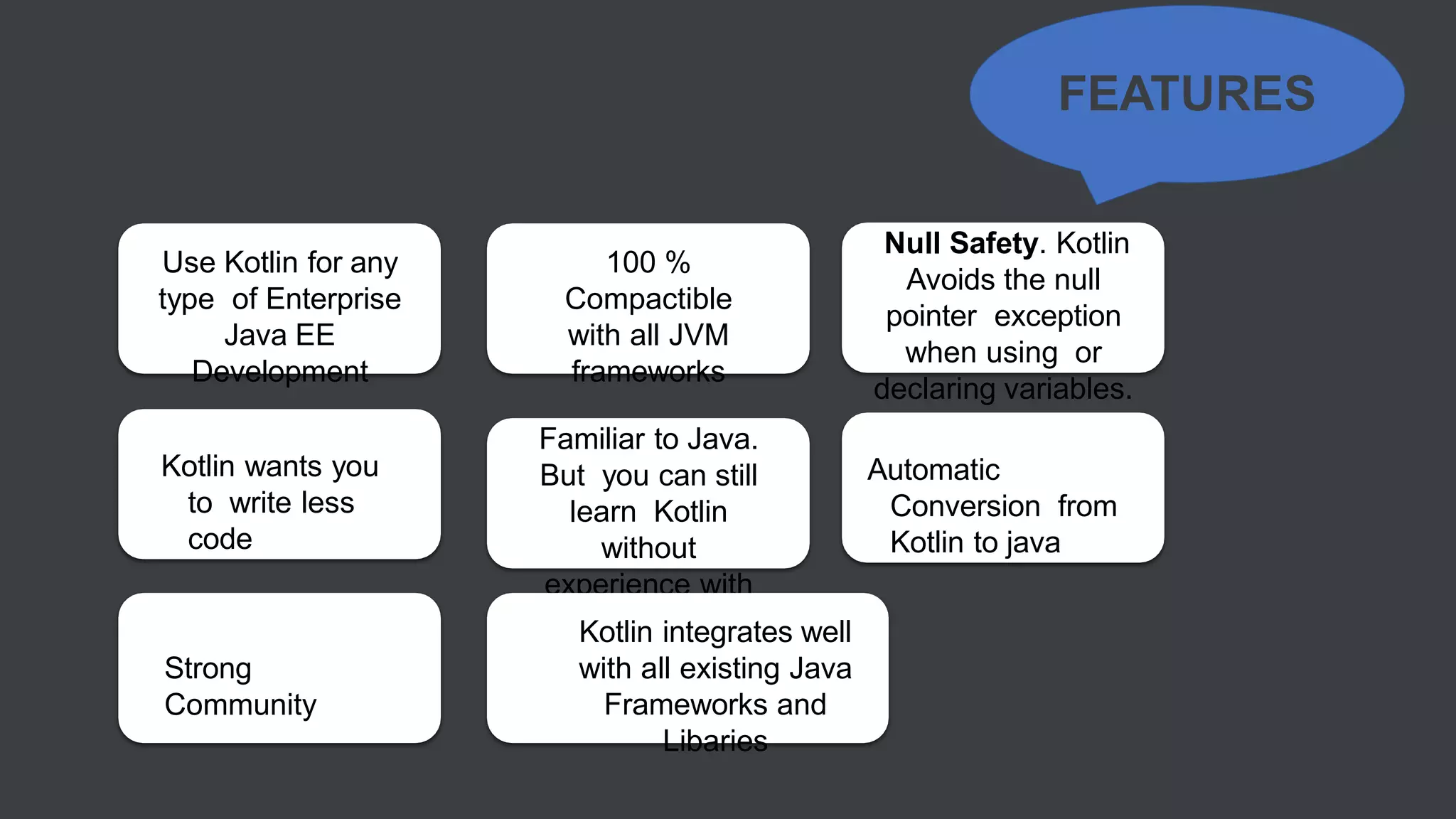
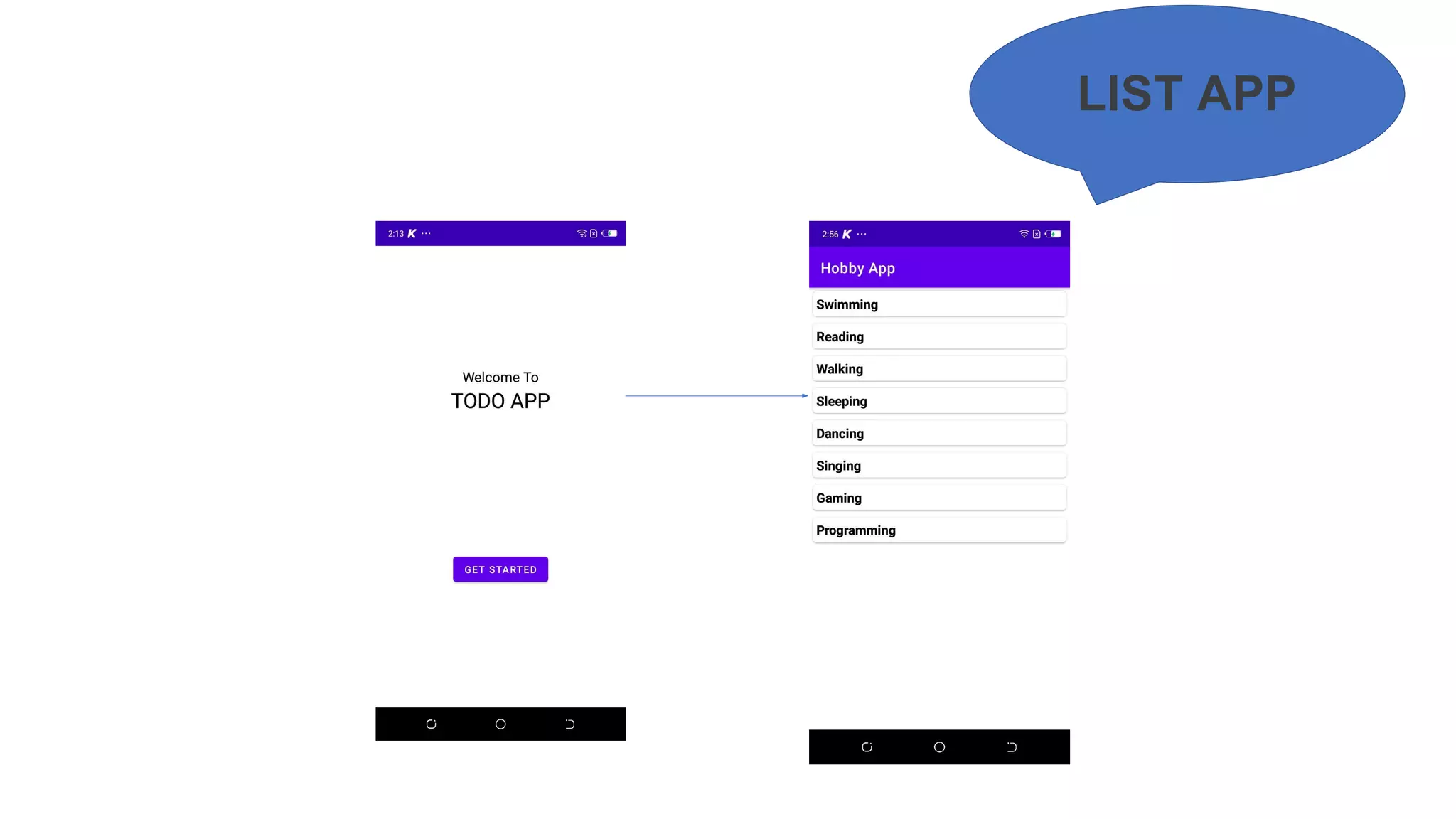
Kotlin is a cross-platform, statically typed programming language that runs on the JVM and JavaScript. It was developed by JetBrains as a pragmatic language for building production-grade applications. Kotlin is fully interoperable with Java and has many features that improve code safety, brevity, and readability compared to Java, like null safety, data classes, string templates, and extension functions. Popular companies like Google, Pinterest, and Square use Kotlin for Android development due to its interoperability with Java and improvements over Java.