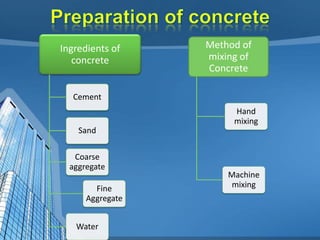
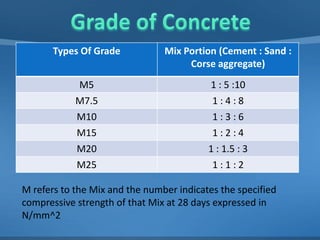
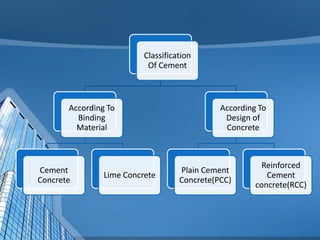
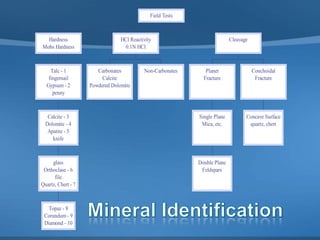
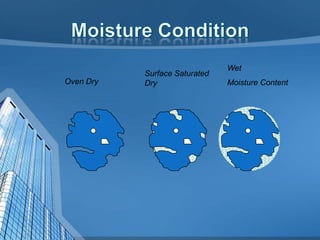
This document provides information on concrete, its ingredients and properties. Concrete is composed of Portland cement, water, aggregates (sand and gravel/crushed stone) and sometimes admixtures. It is mixed either by hand or machine. The cement and water form a paste that binds the aggregates together as it hardens. Concrete has high compressive strength but low tensile strength. Proper curing is required for concrete to attain its full strength. Concrete is a versatile building material with many applications.