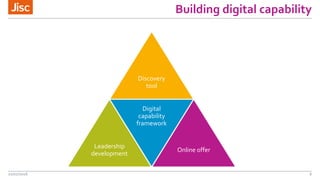
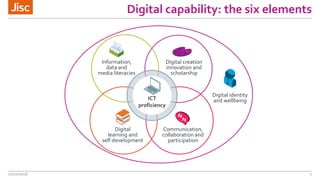
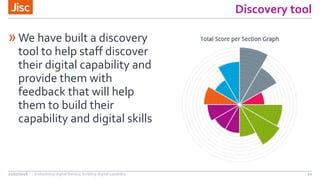
The document outlines a program led by Jisc focused on building digital capability among staff in higher and further education, detailing the agenda for a workshop held on July 21, 2016. It introduces a digital capability framework and discovery tool designed to assess and enhance staff skills, while also discussing service models ranging from basic access to comprehensive institutional support. Key components include leadership development courses and insights into creating a digitally competent organizational infrastructure for improved educational outcomes.