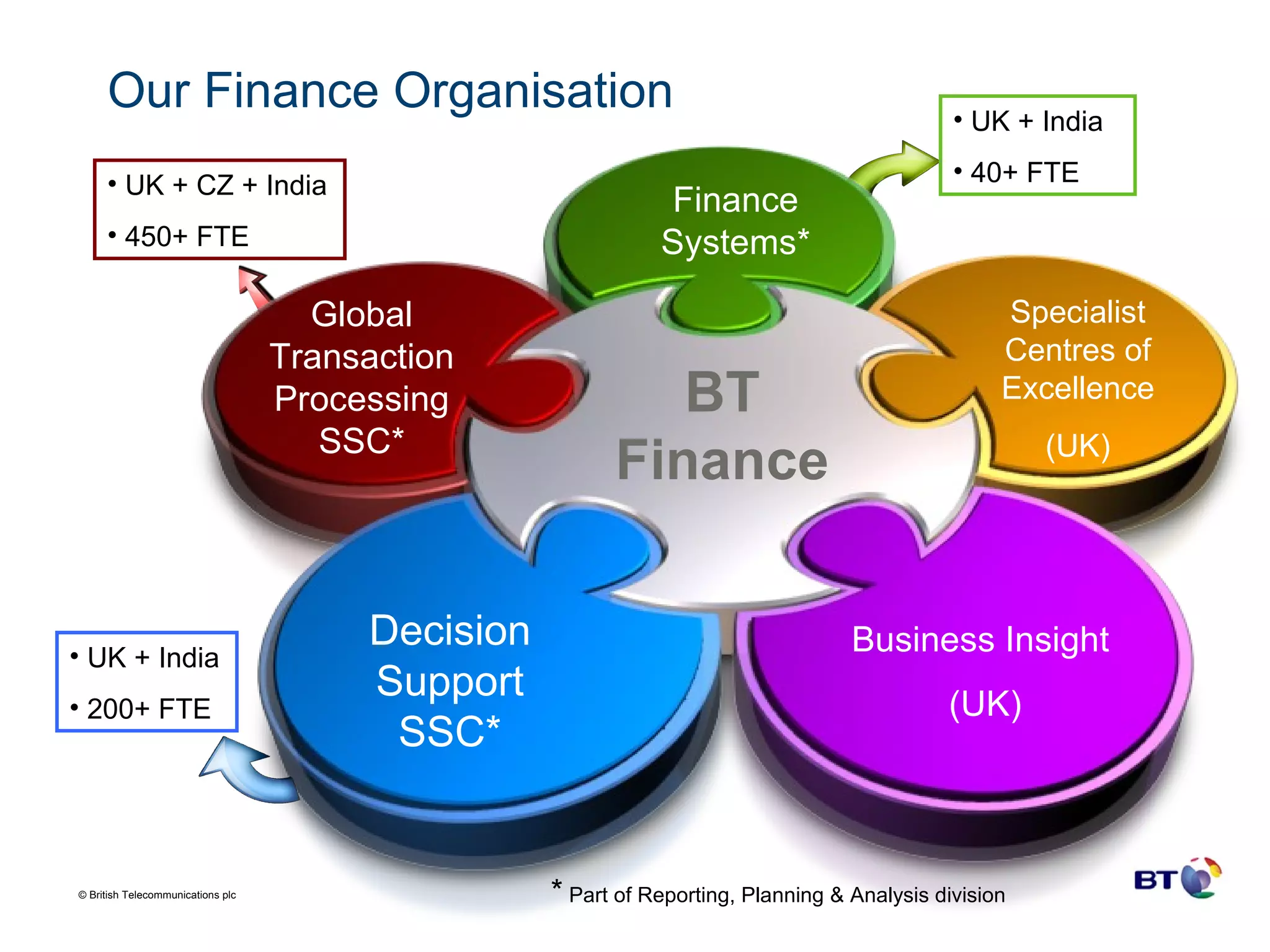
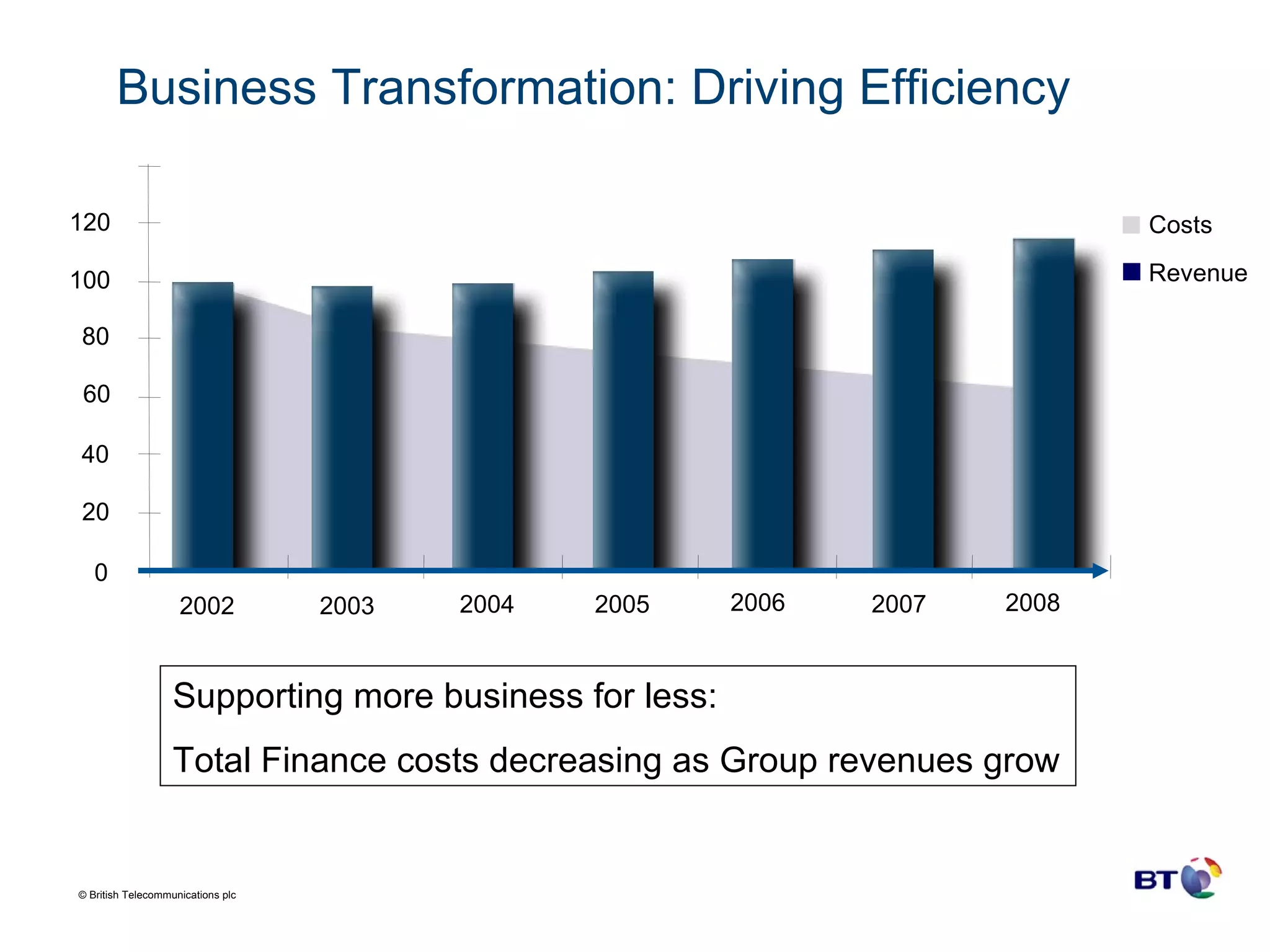
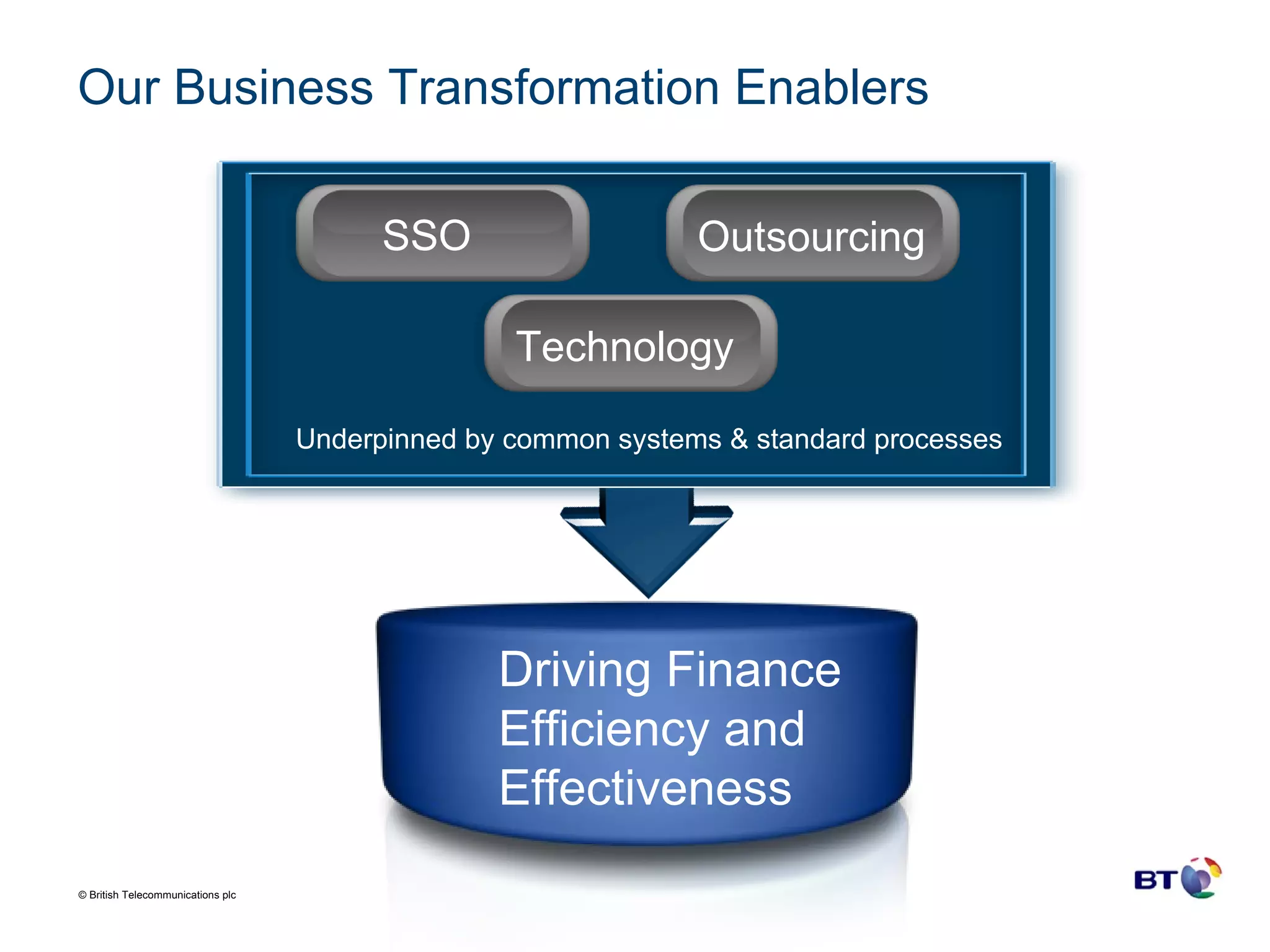
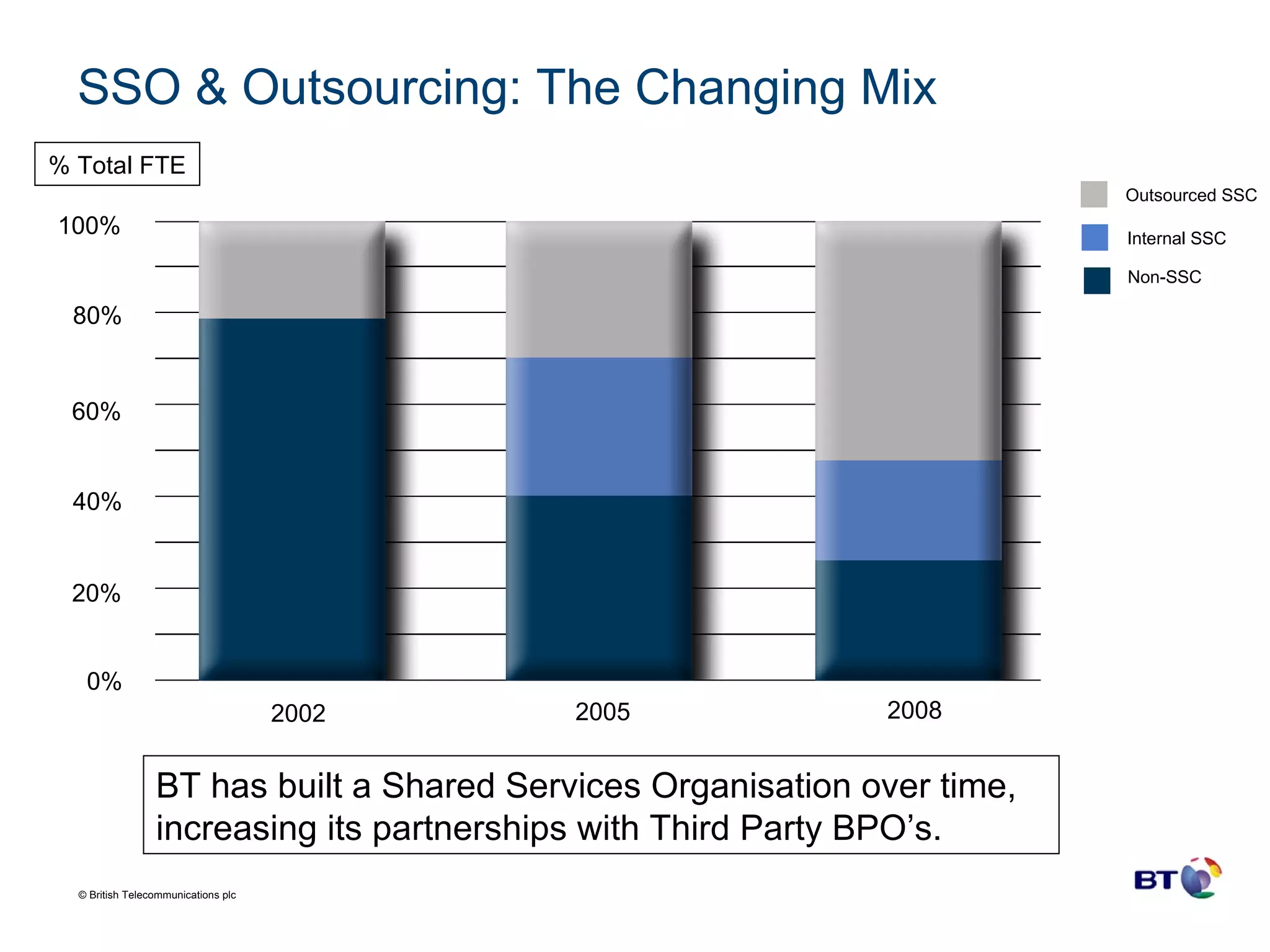
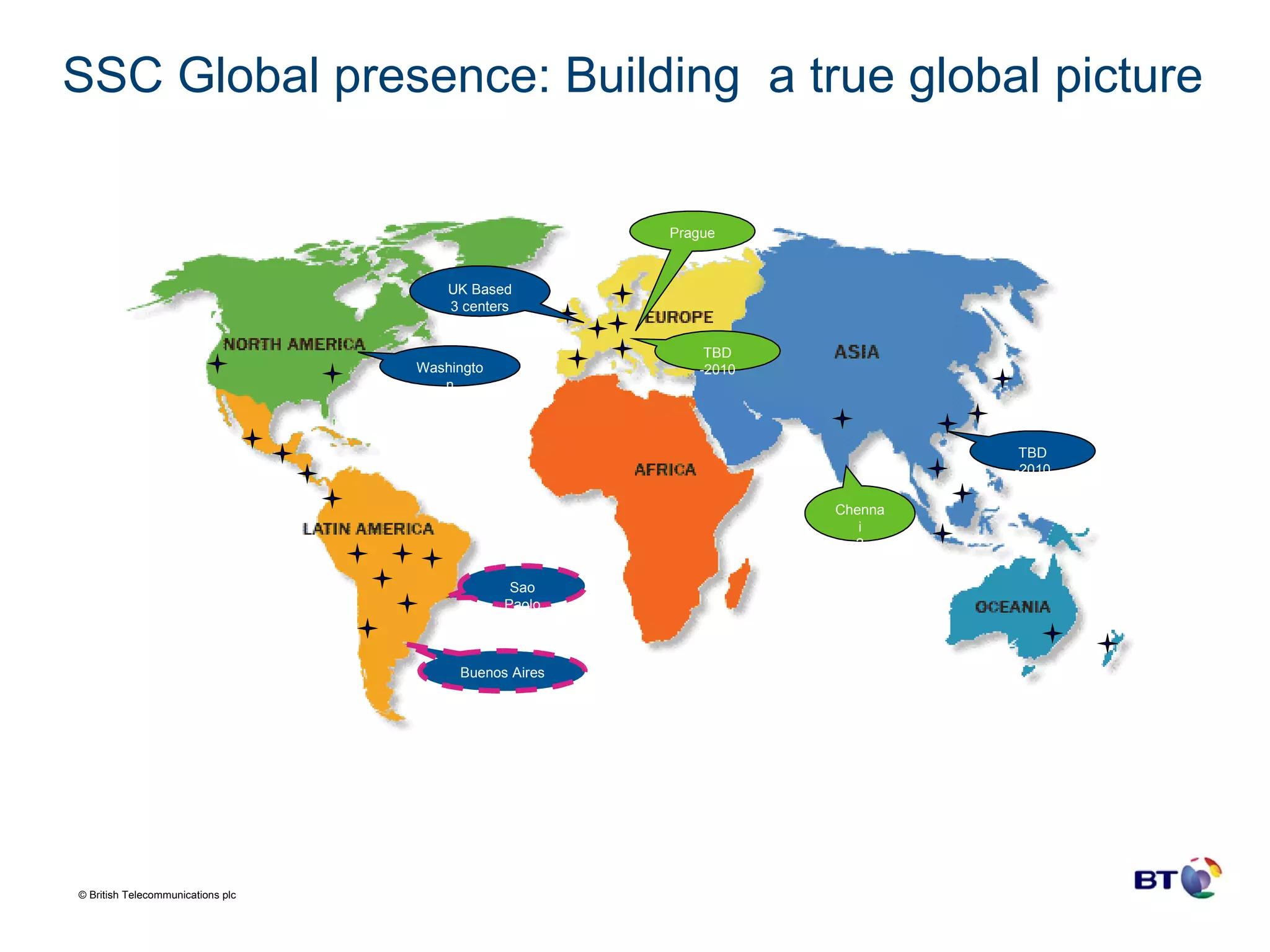
BT Group is a large telecommunications company operating in over 170 countries with over 100,000 employees and $29.4 billion in revenue. Over time, BT Group has transformed its finance organization through the increased use of shared service organizations (SSOs) and outsourcing to drive efficiency. BT Group established its first SSO in the UK in 2001 for transaction processing and IT support and has since expanded its SSOs globally and outsourced more finance functions. Technology has been a key enabler of BT Group's finance transformation, underpinning the organizational changes and alignment of SSOs and outsourcing to reduce costs and drive performance towards best-in-class.