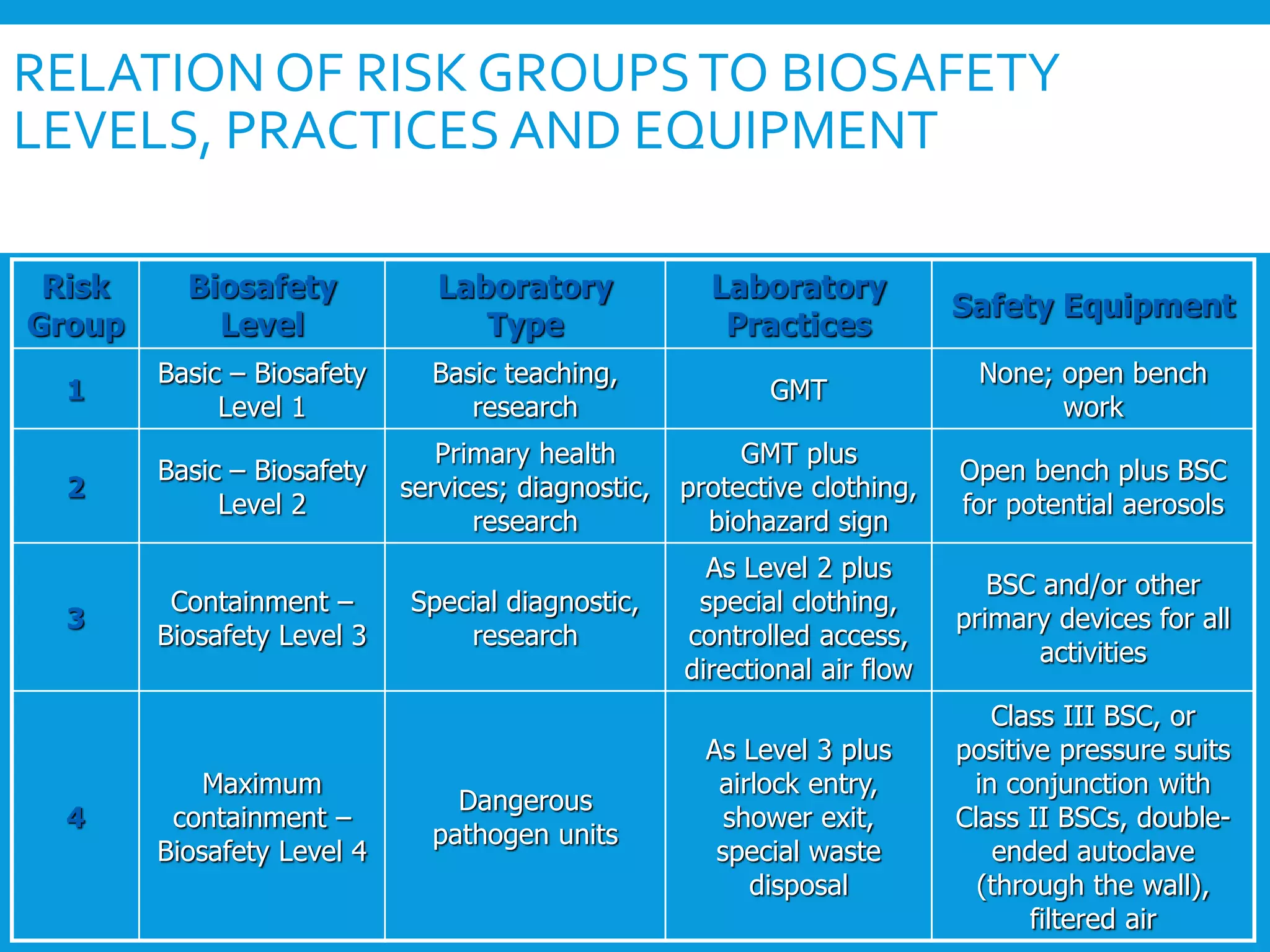
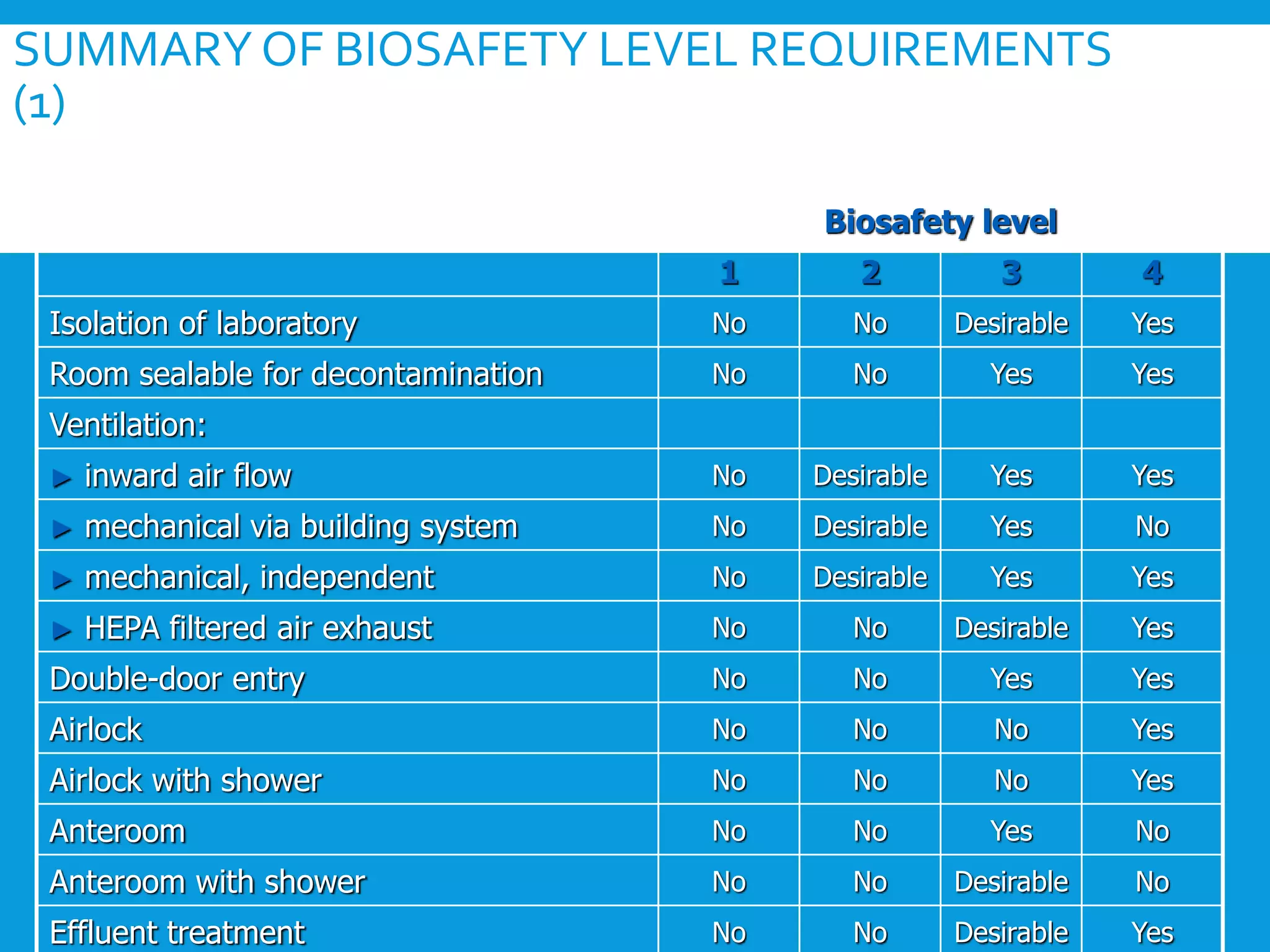
The document discusses general requirements and considerations for BSL-3 and BSL-4 laboratories. It describes four risk groups for infectious microorganisms based on their ability to cause disease and transmissibility. It also outlines relationships between risk groups, biosafety levels, laboratory types, practices, and safety equipment. BSL-4 laboratories require the highest level of containment and have numerous security and safety features both inside and outside the building to restrict access and prevent the release of pathogens.