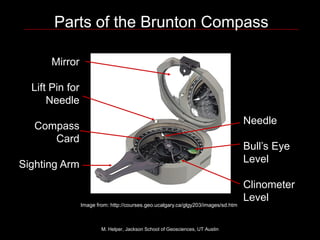
The document introduces the parts and functions of the Brunton compass, which is used to measure orientations in the field. It describes how to measure strike and dip of tilted planes, bearings between locations, and trend and plunge of linear features. Key parts are the needle, clinometer, and sighting arm. Strike is measured by placing the compass flush on the tilted plane. Dip direction is read perpendicular to strike. Trend is measured parallel to the feature using the sighting arm. Plunge uses the clinometer. Examples are given for recording strike/dip, bearings, and trend/plunge.