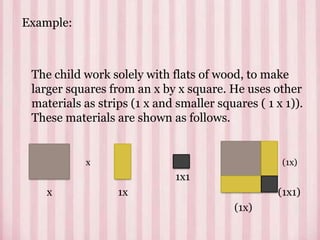
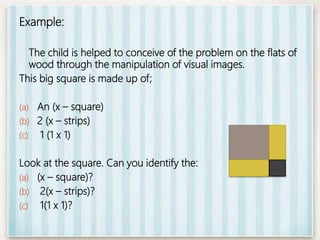
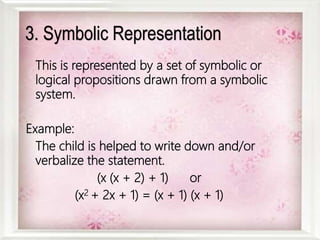
Bruner puts forth the hypothesis that any subject can be effectively taught to children at any stage of development in an intellectually honest form. He argues that basic concepts in science and humanities can be understood by children earlier than previously believed. The best way to stimulate learning is through interesting material rather than external goals or grades. Bruner stresses acquiring learning processes through discovery, which usually begins with a puzzling problem or situation. The levels of representation a child progresses through in learning can be modeled by a cone moving from physical manipulation, to visual representation, to symbolic representation. The major outcomes of discovery learning are increasing intellectual ability, shifting dependence from external to internal rewards, enhancing transfer of skills, and improving memory ability.