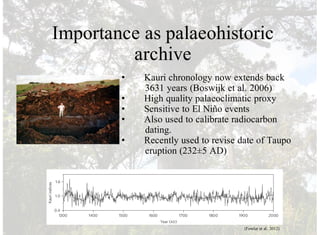
1) Kauri is an ancient conifer species dating back to the time of the dinosaurs that is found primarily in New Zealand.
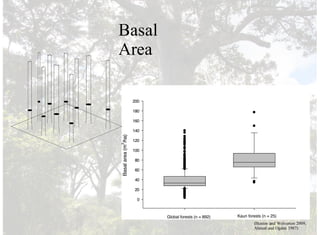
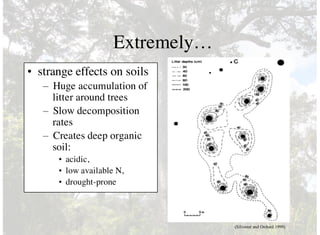
2) Individual kauri trees are extremely large, old, and productive, storing vast amounts of carbon and creating deep, nutrient-poor soils.
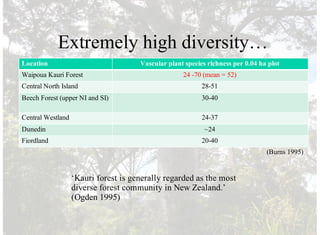
3) Kauri forests have exceptionally high biodiversity and biomass compared to other forest types, making them a foundation species, though the kauri is now threatened by disease.