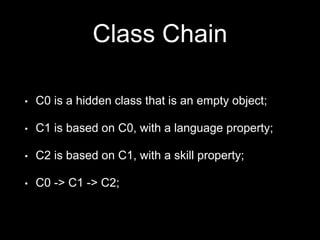
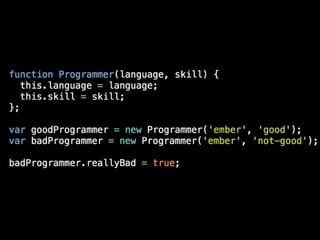
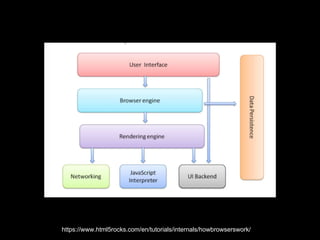
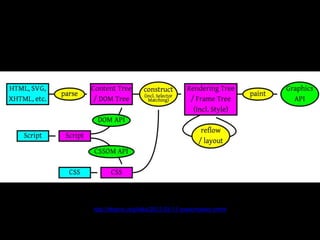
The document discusses browser internals with a focus on JavaScript development, highlighting the roles of various browser components like the DOM tree, render tree, and layout processes. It emphasizes best practices for optimizing performance, managing reflows, and memory usage within JavaScript applications. Additionally, it covers the compilation process of JavaScript within the V8 engine, including optimizations and handling of hidden classes.









































![• In non-strict, V8 preserves the bindings between
arguments[0] & arg0. If you re-assign, V8 says
‘too hard’ and bails out (choses to not optimize);
• It expects arg0 & arguments[0] to have the same
hidden class;
• Using strict does not preserve bindings, meaning
the code can be optimized;
Leaking or re-assigning
arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fitctalk-161004135741/85/Browser-Internals-for-JS-Devs-WebU-Toronto-2016-by-Alex-Blom-50-320.jpg)
![Safe arguments
• arguments[n], where n is defined and not a
param;
• apply(arguments);
• arguments.length;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fitctalk-161004135741/85/Browser-Internals-for-JS-Devs-WebU-Toronto-2016-by-Alex-Blom-51-320.jpg)