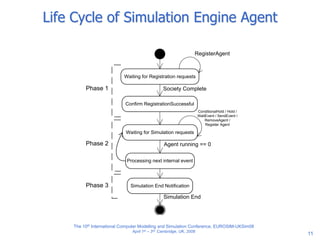
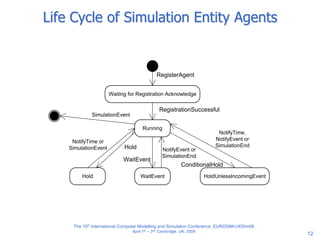
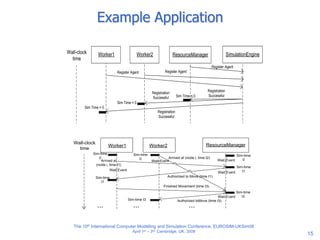
The document discusses an agent-based modeling framework called SimJADE for discrete event simulation. SimJADE models logical processes in discrete event simulation as autonomous agents that interact. It defines concepts like simulation time and services through an ontology and structures the agent society with a simulation engine agent and simulation entity agents. SimJADE allows discrete event simulation concepts to be modeled using a multi-agent approach and integrated with standard agent programming components. An example application of SimJADE for manufacturing simulation is also presented.