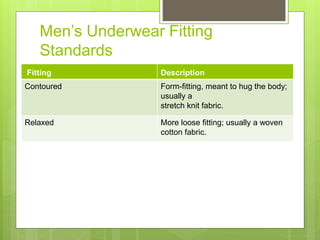
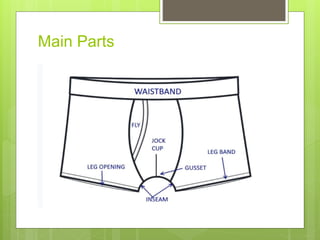
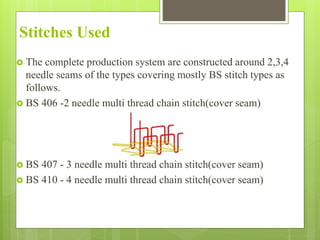
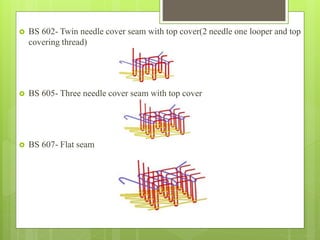
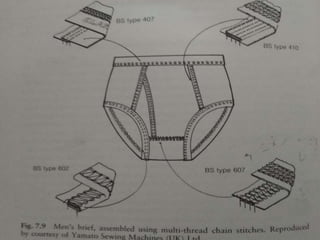
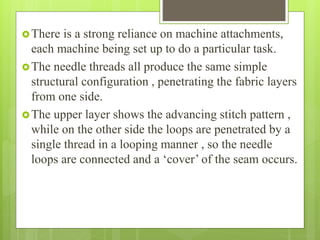
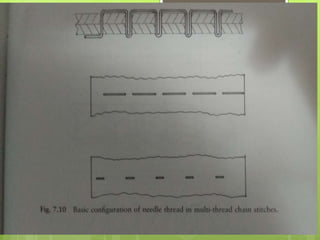
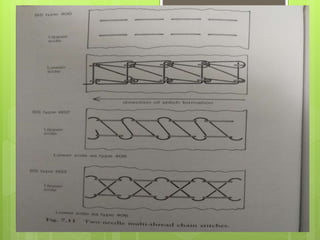
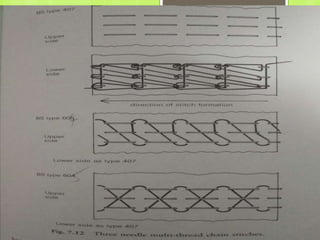
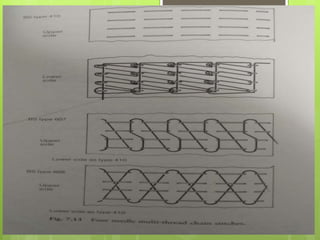
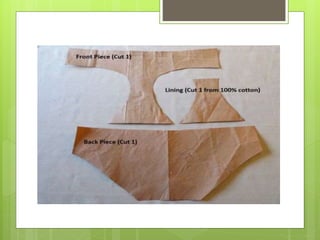
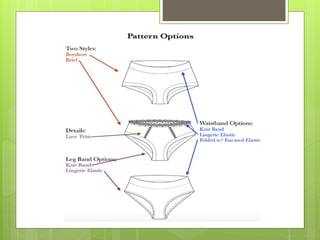
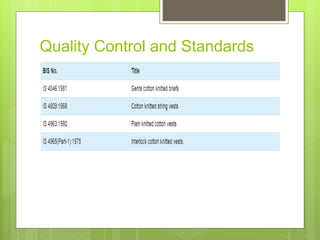
The document discusses the evolution of men's underwear, emphasizing the importance of fabric types such as cotton, microfiber, and their properties, as well as different fitting standards and waistband designs. It details various stitch types and sewing techniques, including traditional methods and innovative sew-free seam technologies that utilize adhesive tapes for construction. Quality control measures and production techniques are also highlighted to ensure the functionality and comfort of men's underwear.