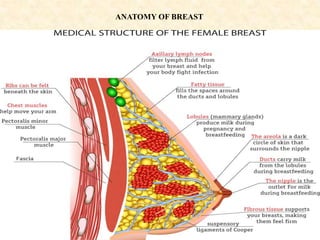
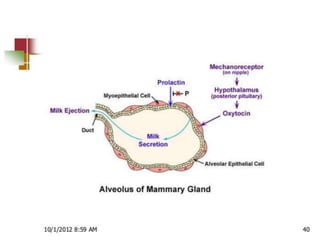
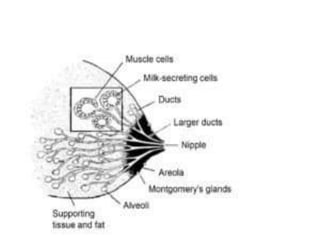
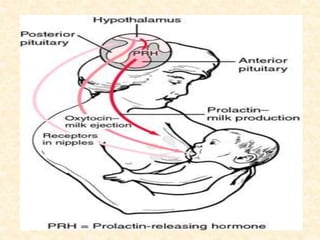
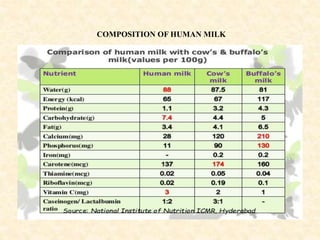
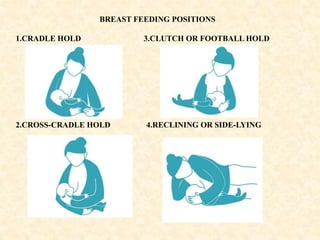
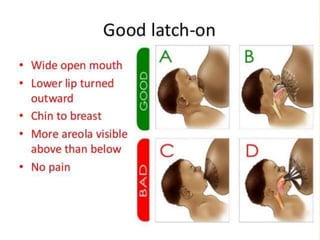
Breastfeeding provides ideal nutrition for infants and has numerous health benefits for both mother and baby. It gives babies antibodies and nutrients tailored for them. The document defines breastfeeding as the normal way to provide young infants with needed nutrients for growth. Breastfeeding is recommended exclusively for six months and continued along with complementary foods up to two years or longer. The anatomy and physiology of lactation are described, including milk production triggered by the baby's sucking. Advantages of breastfeeding include its availability, low cost, protection from infection, and psychological benefits. Contraindications for mothers and infants are outlined.