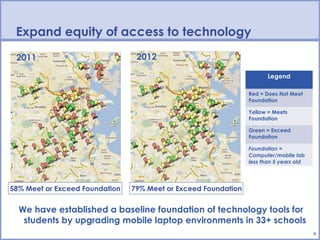
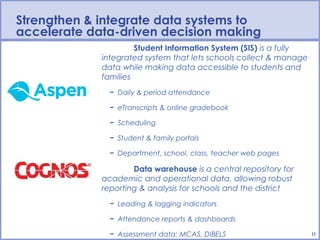
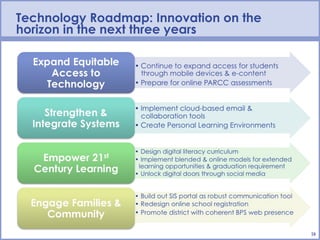
The document outlines the Boston Public Schools' technology vision to prepare students for college and careers through equitable access to technology, data-driven decision making, 21st century skills development, and targeted support for struggling students. The BPS technology efforts focus on expanding access to technology, strengthening integrated data systems, empowering 21st century learning skills, and engaging families and communities with technology. The goal is to foster a personalized learning environment for all students through initiatives like Boston 365.