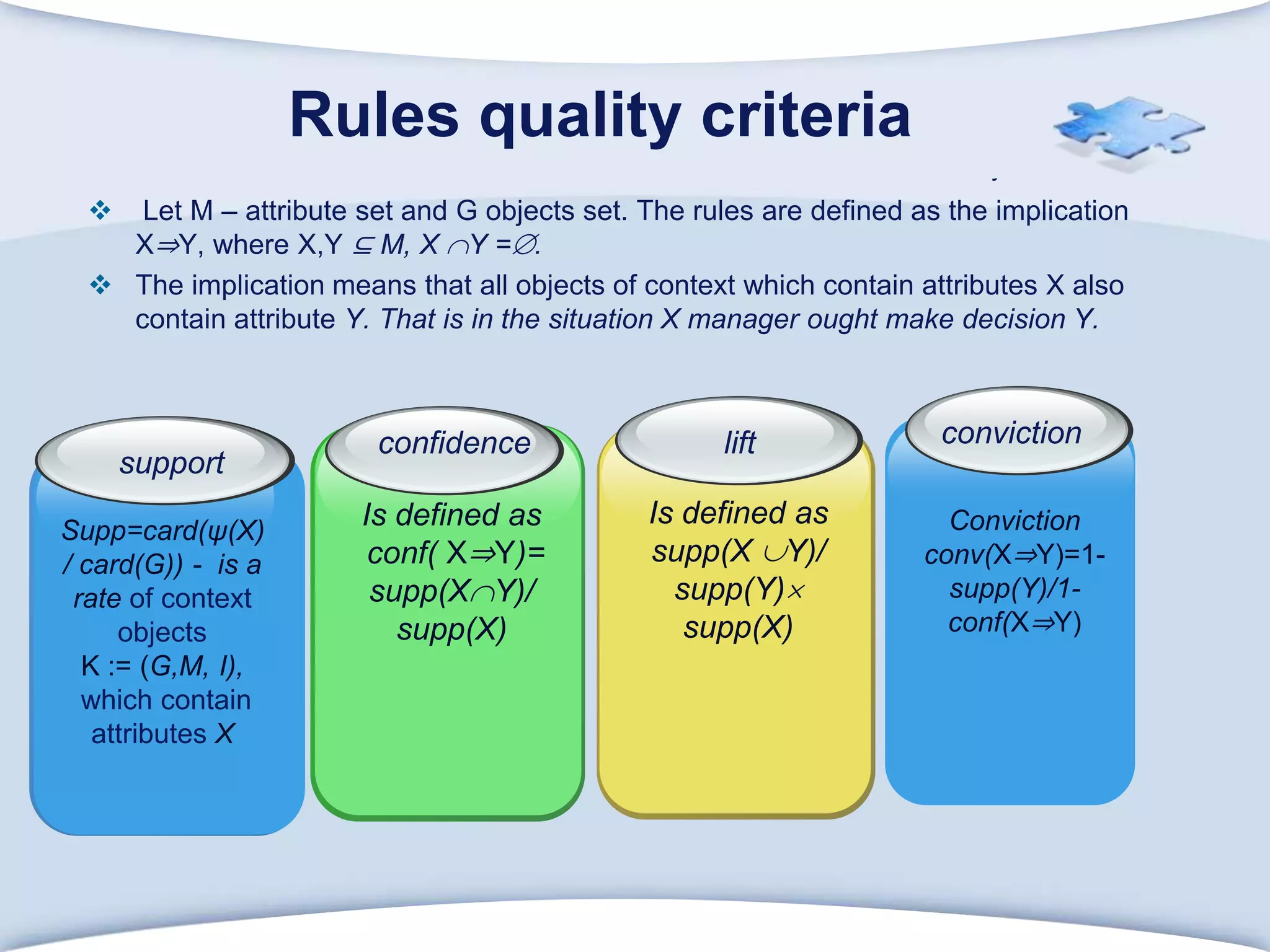
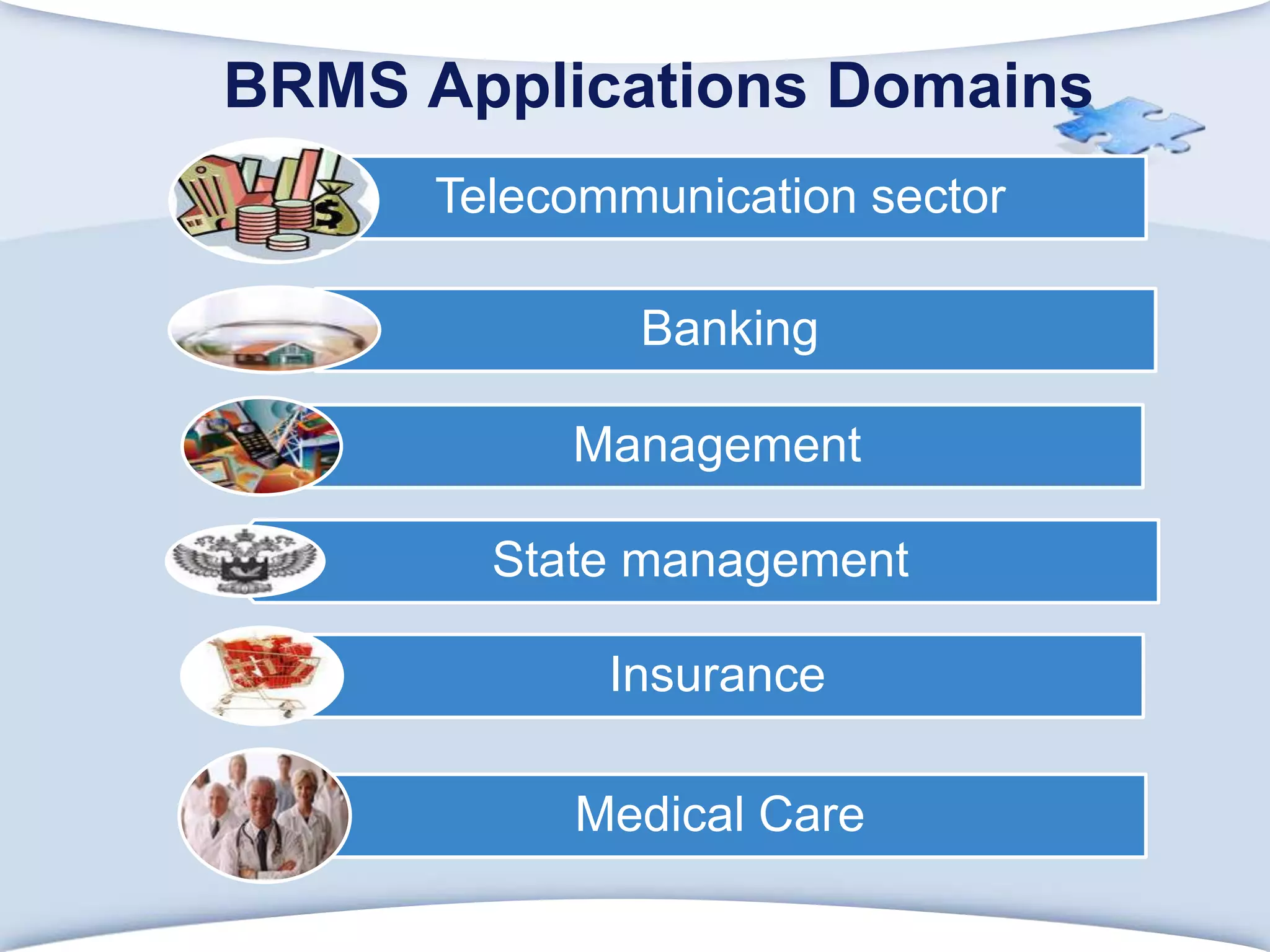
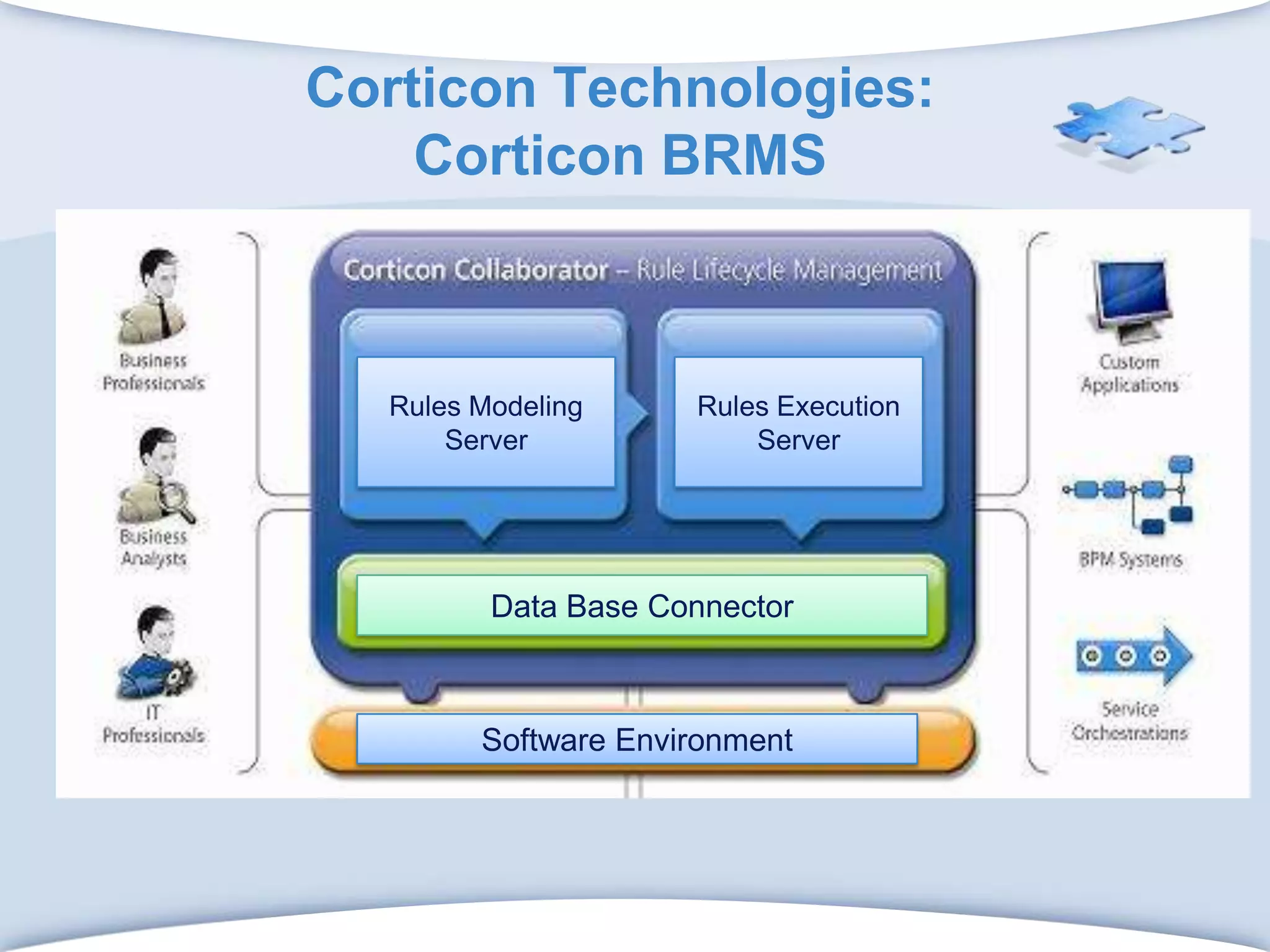
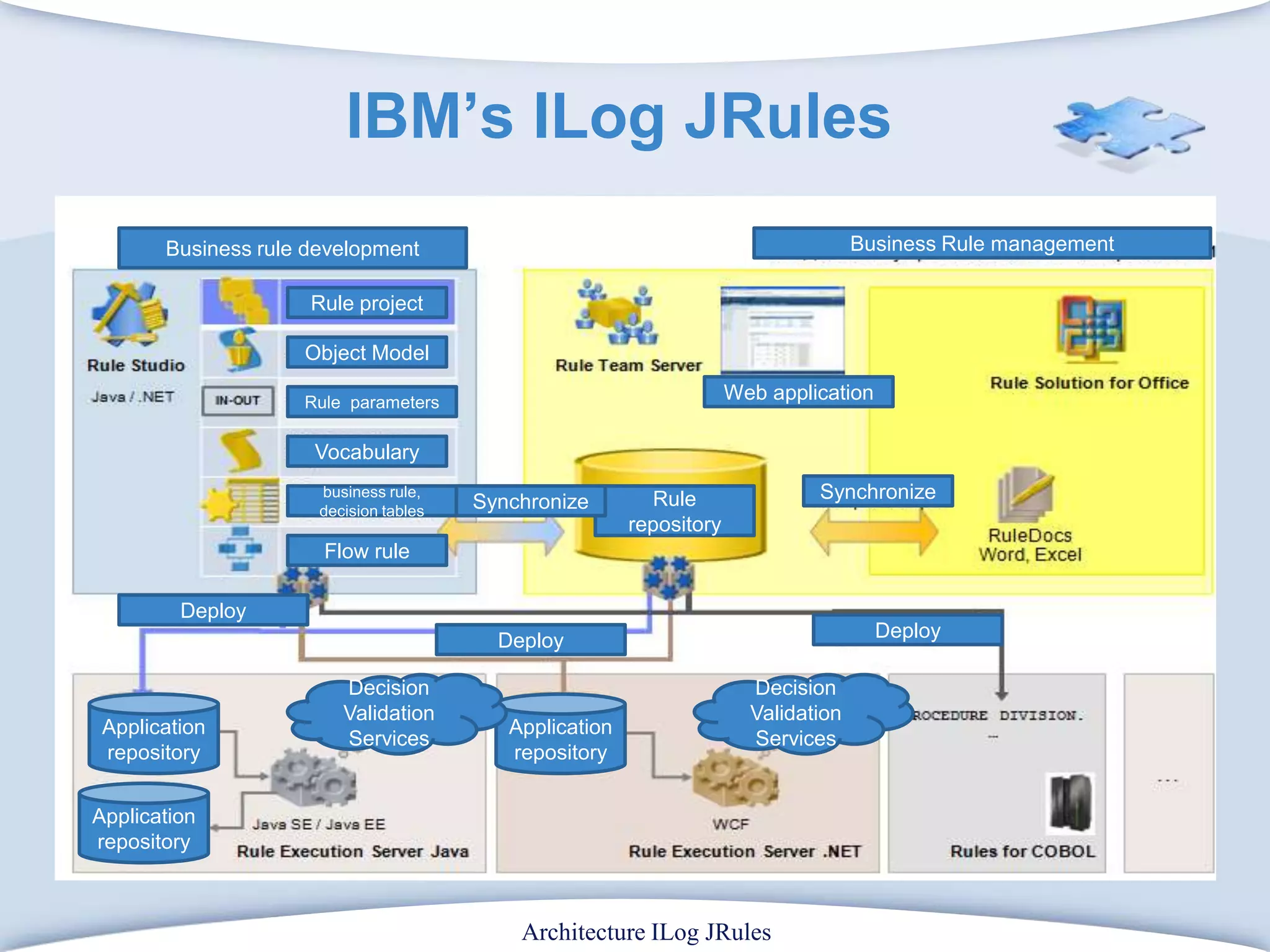
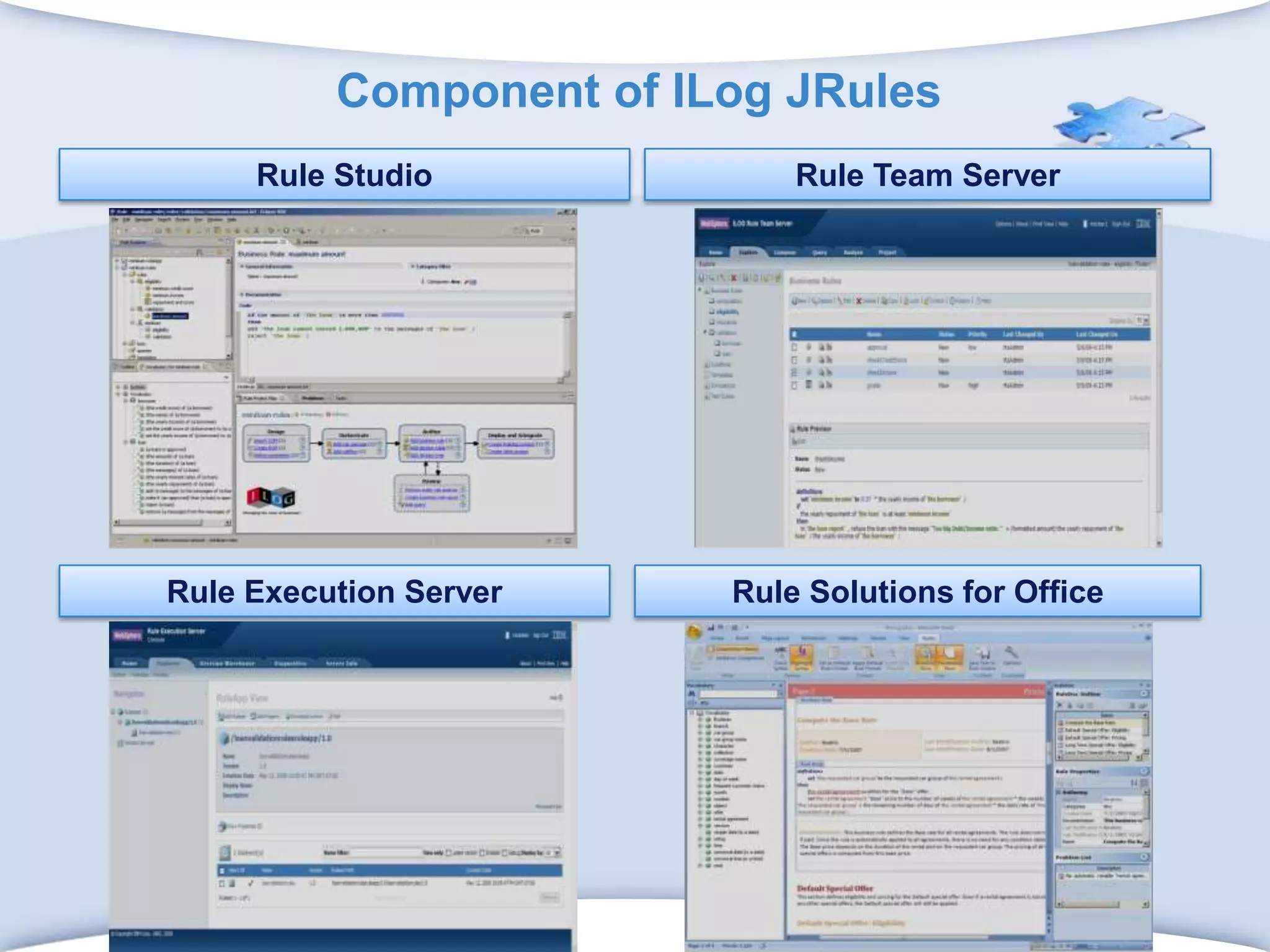
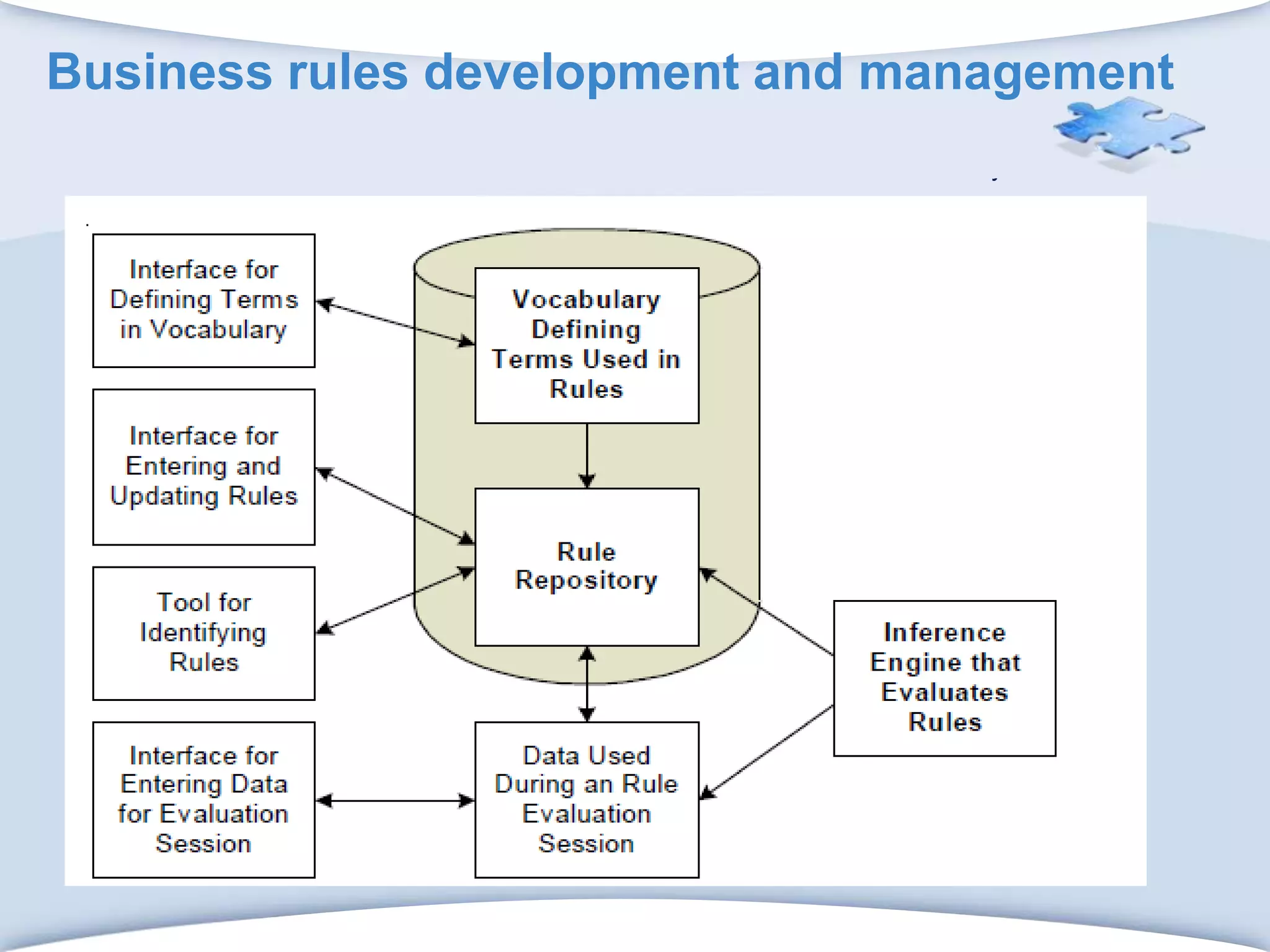
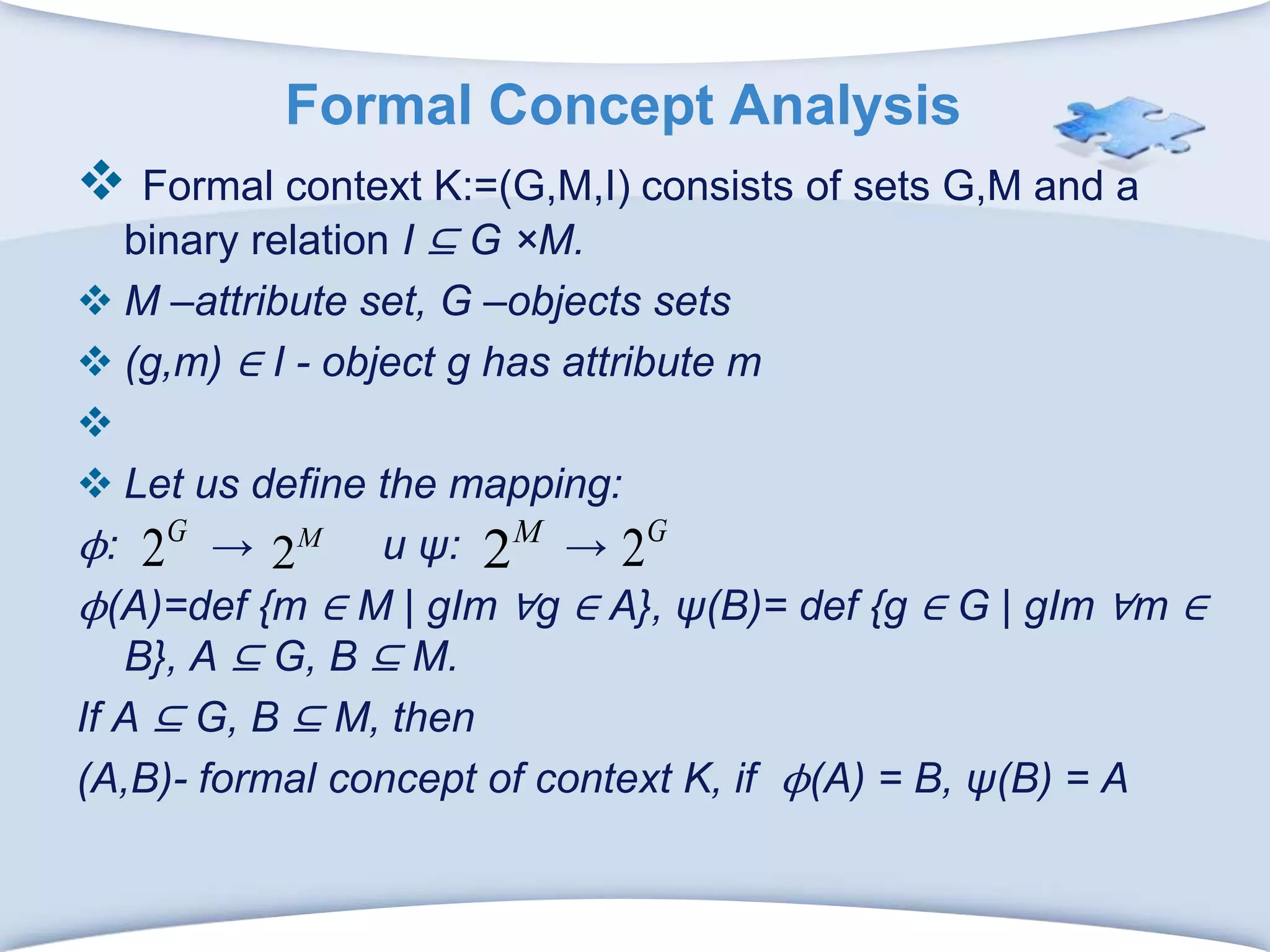
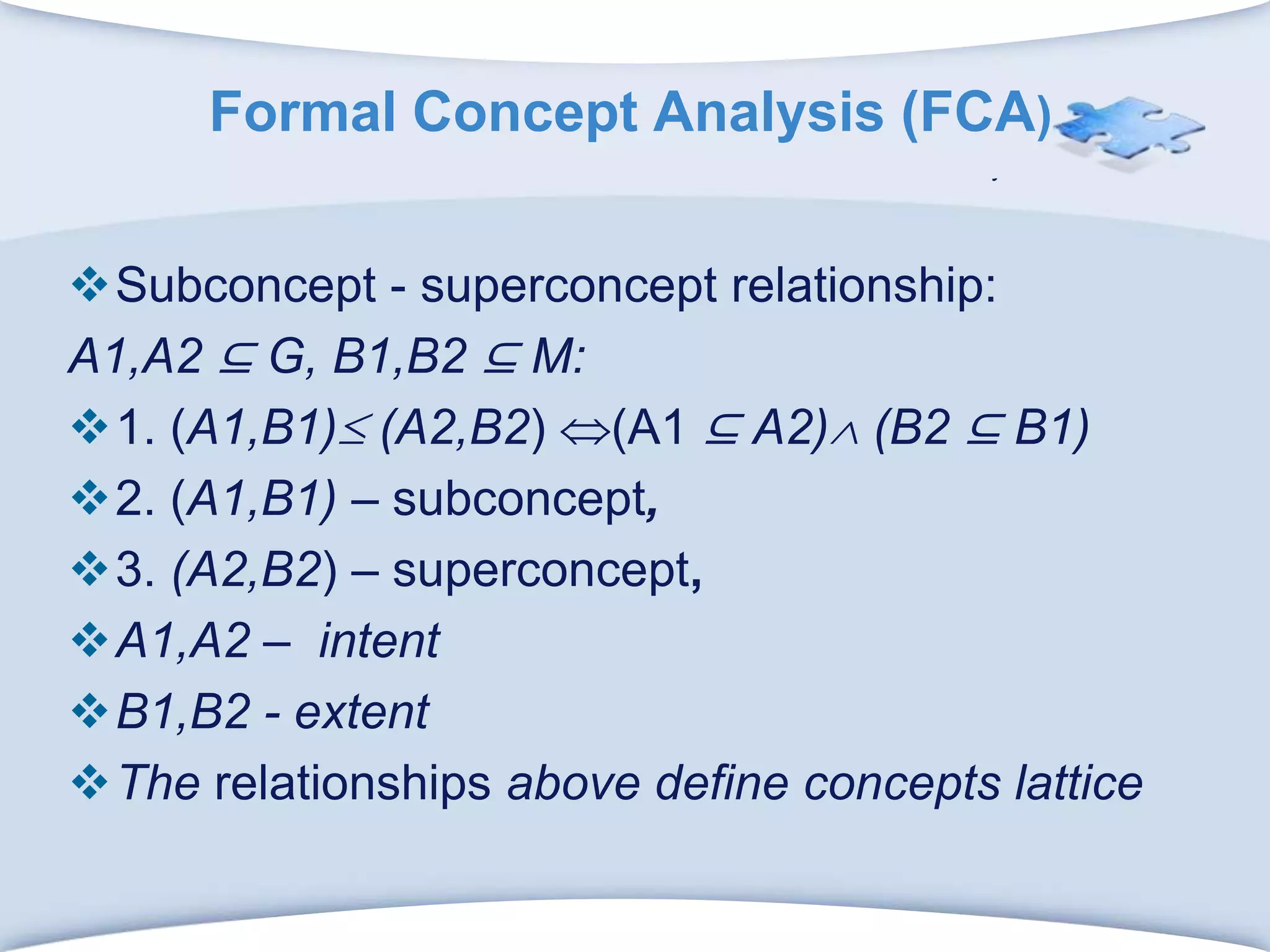
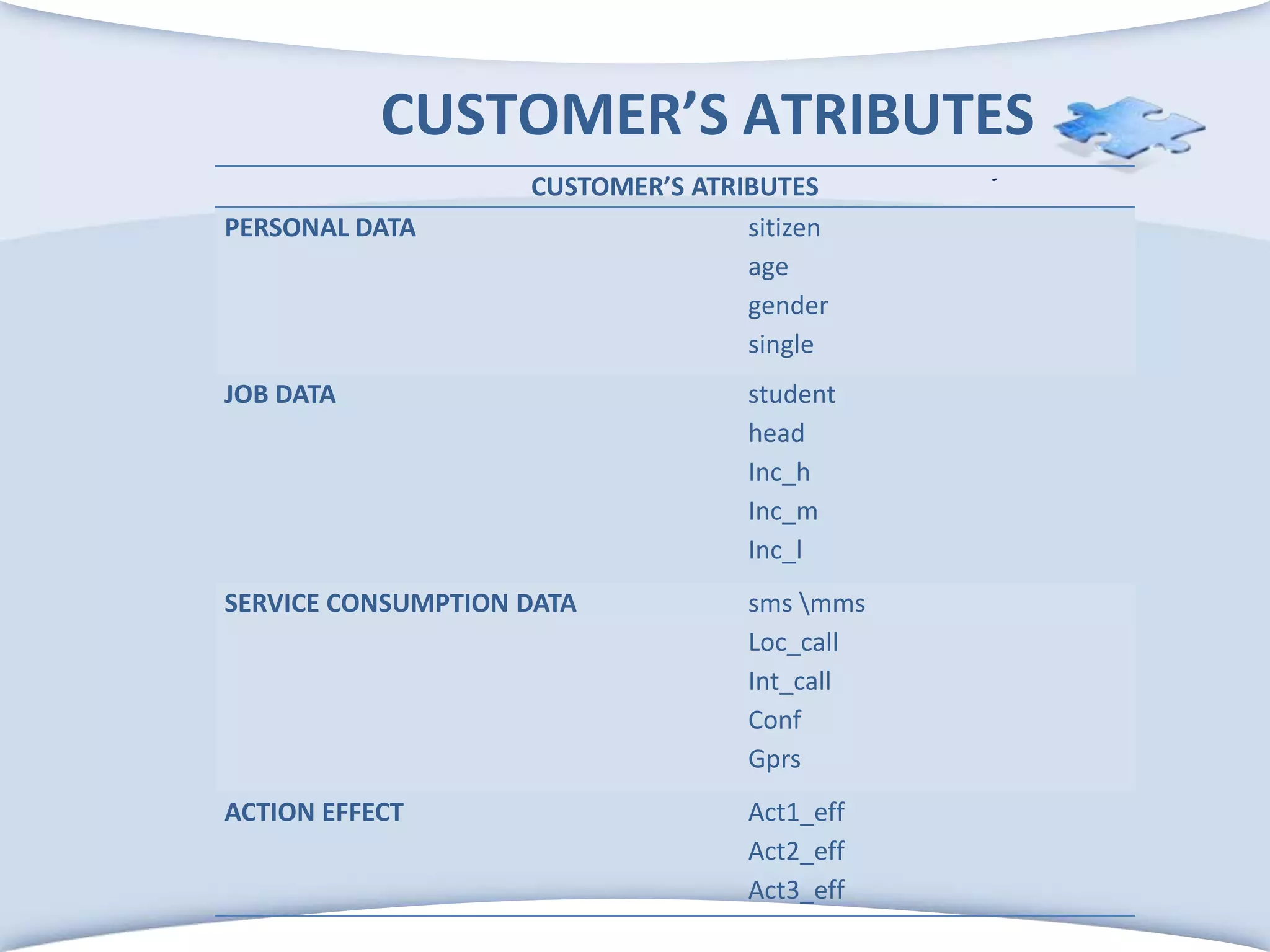
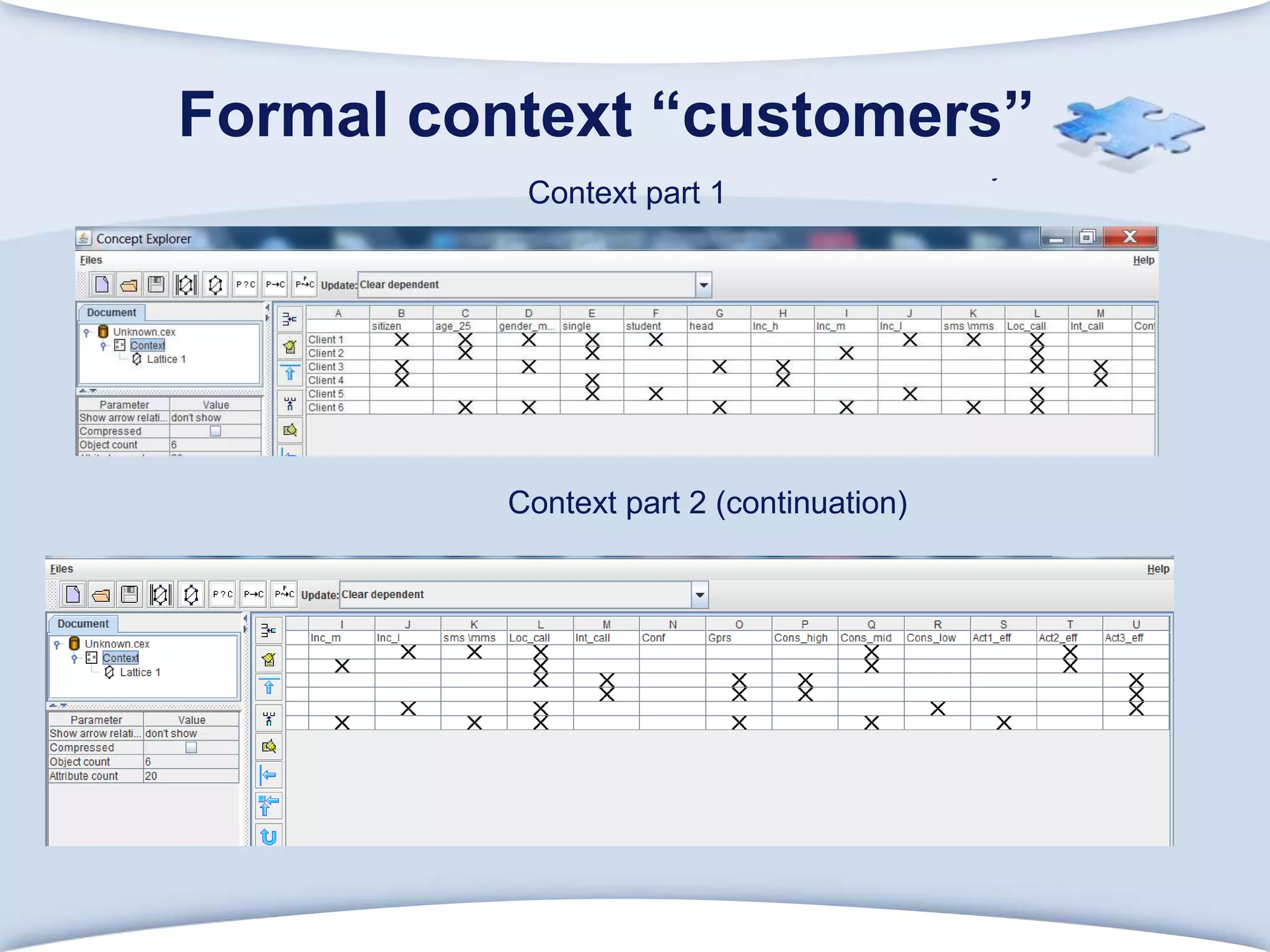
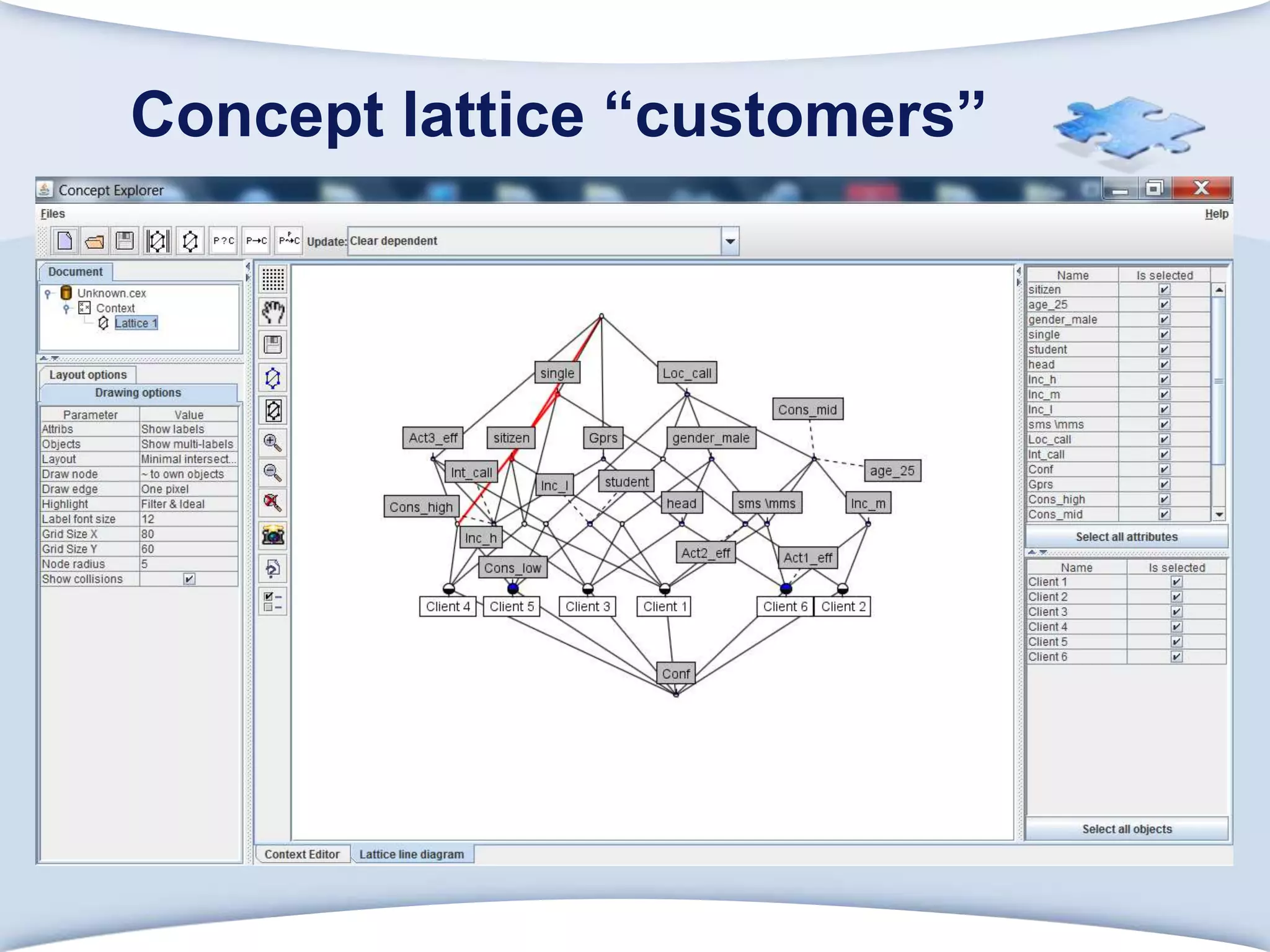
The document discusses using formal concept analysis (FCA) and business rules to develop a customer relationship simulation model for a telecommunications company. It provides background on business rule management systems (BRMS) and reviews some common BRMS vendors. The document then explains how FCA can be used to analyze customer attribute data, extract customer groups and rules about what marketing actions would be effective for different customer profiles. It provides examples of rules extracted from a formal customer context and discusses criteria for evaluating rule quality like confidence, conviction and lift.




![The rules with confidence <100 %63 < 5 > Cons_mid =[80%]=> < 4 > Act2_eff;66 < 5 > single Loc_call =[80%]=> < 4 > Act2_eff;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boston1603-13077172474968-phpapp01-110610094841-phpapp01/75/Boston-16-03-23-2048.jpg)